无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 79-86.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250074 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20250074
收稿日期:2025-02-20
修回日期:2025-05-16
出版日期:2026-01-20
网络出版日期:2025-06-10
通讯作者:
李家科, 教授. E-mail: jiakeli.jci@163.com作者简介:王 瑜(1999-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 349035143@qq.com
基金资助:
WANG Yu( ), BASSANYIN Christopher, LIU Xin, WANG Yanxiang, LI Jiake(
), BASSANYIN Christopher, LIU Xin, WANG Yanxiang, LI Jiake( )
)
Received:2025-02-20
Revised:2025-05-16
Published:2026-01-20
Online:2025-06-10
Contact:
LI Jiake, professor. E-mail: jiakeli.jci@163.comAbout author:WANG Yu (1999-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 349035143@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
太阳能收集与存储技术的协同创新为构建新型自供能系统提供了重要方向, 其中光辅助充电超级电容器因其独特的光致电荷存储机制和快速充放电特性成为研究热点, 并且具有高功率密度和快速充放电特性, 为可穿戴电子设备等能源收集与存储提供了一种高效、环保和可持续的新策略。本研究采用水热法合成ZnFe2O4, 将其作为超级电容器光阳极, 以改进Hummers法和水热法合成还原氧化石墨烯水凝胶(Reduced graphene oxide hydrogel, rGH), 将其作为超级电容器的阴极, 以Zn(CF3SO3)2水溶液为电解液构建水系光辅助充电超级电容器。合成产物的物相组成、微观形貌、化学结构、光吸收性能和超级电容器的光电化学性能的研究结果表明, 在光电协同充电条件(0.2 A·g-1电流密度、95 mW·m-2光照强度)下, 超级电容器的比容量可达148 F·g-1, 比电充比容量提高17%。此外, 该超级电容器在循环10000次条件下, 电充和光电协同充电的容量保持率分别为80%和90%。所构建的水系光辅助充电超级电容器具有较高的比容量和良好的循环稳定性, 在可穿戴电子产品等领域具有潜在应用前景。
中图分类号:
王瑜, 刘欣, 王艳香, 李家科. ZnFe2O4//rGH水系光辅助充电超级电容器的构建与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 79-86.
WANG Yu, BASSANYIN Christopher, LIU Xin, WANG Yanxiang, LI Jiake. Construction and Performance of ZnFe2O4//rGH Aqueous Photo-assisted Charging Supercapacitor[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 79-86.
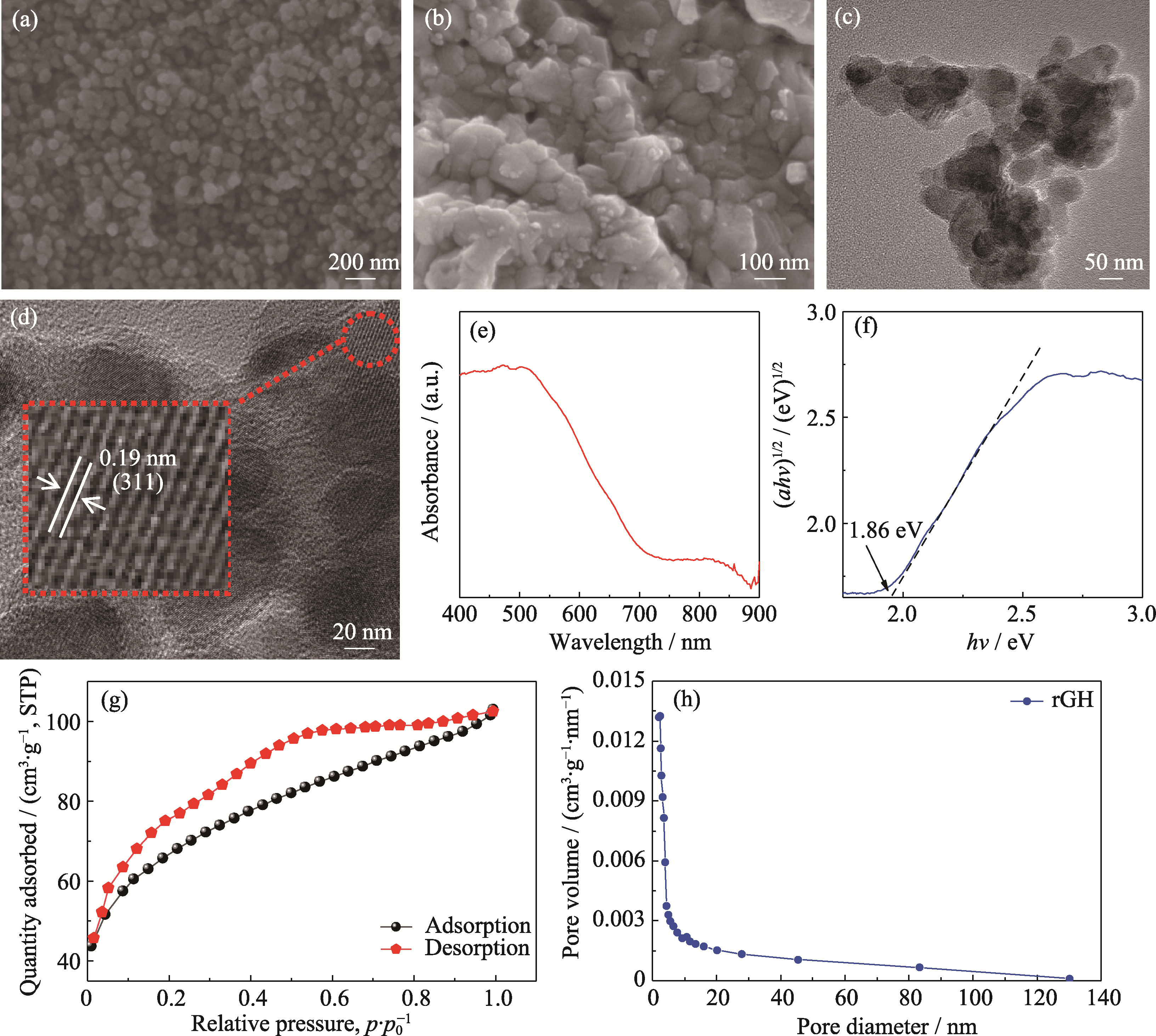
图2 ZnFe2O4的(a, b) SEM照片、(c, d) HRTEM照片、(e) UV-Vis漫反射光谱和(f) (ahv)1/2-hv曲线; rGH的(g) N2吸附-解吸等温线及其(h)孔径分布[18]
Fig. 2 (a, b) SEM images, (c, d) HRTEM images, (e) UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectrum and (f) (ahv) 1/2-hv curve of ZnFe2O4; (g) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and (h) PSD of rGH[18]
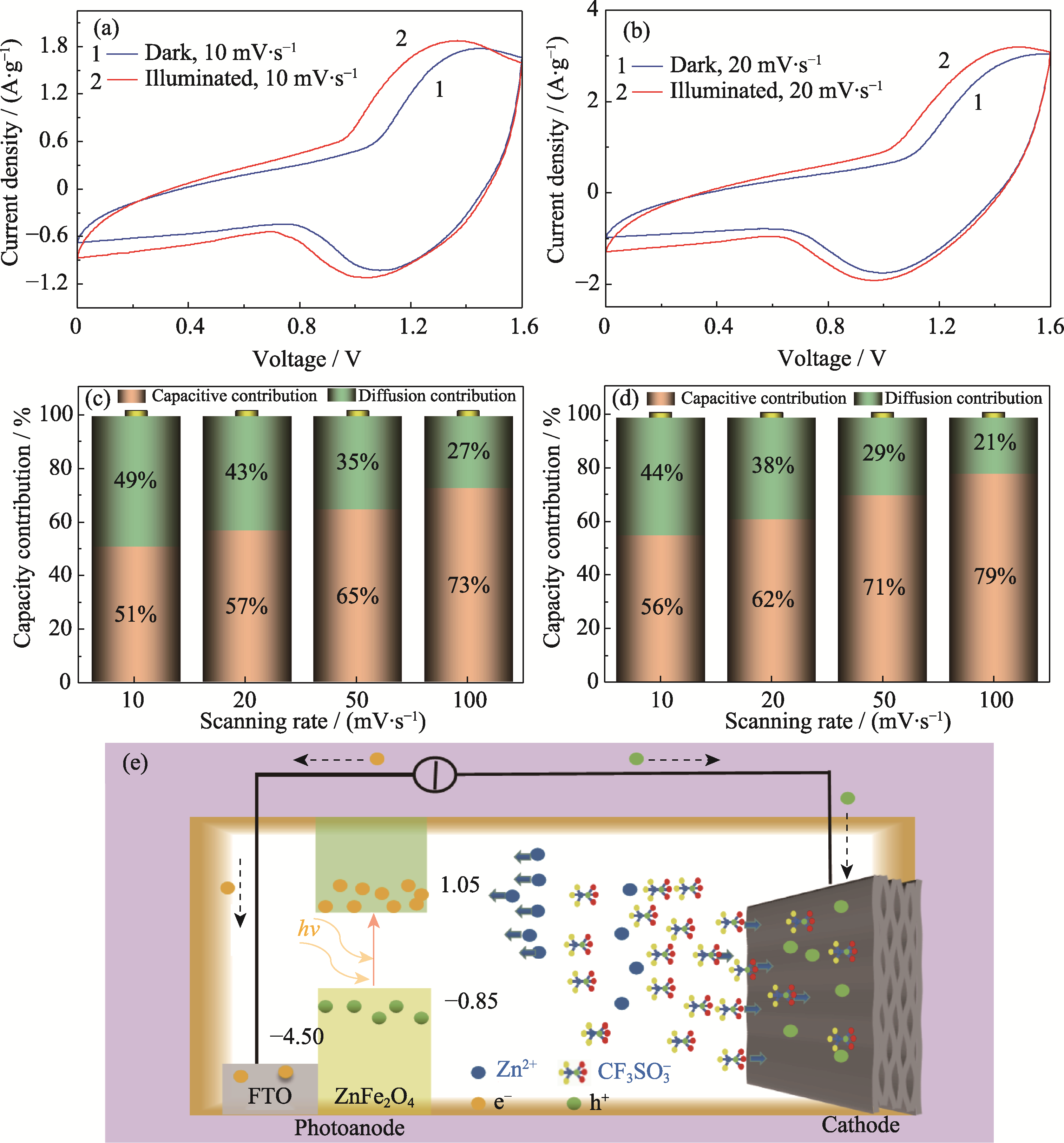
图3 ZnFe2O4//rGH超级电容器(a, b)在不同扫描速率下CV曲线、(c)电充和(d)光电协同充电的电容贡献率、(e)工作原理示意图
Fig. 3 (a, b) CV curves at different scanning rates, (c, d) capacitance contribution rates at different scanning rates under (c) electric charging and (d) photoelectric synergistic charging, and (e) schematic diagram of working principle for ZnFe2O4//rGH supercapacitor
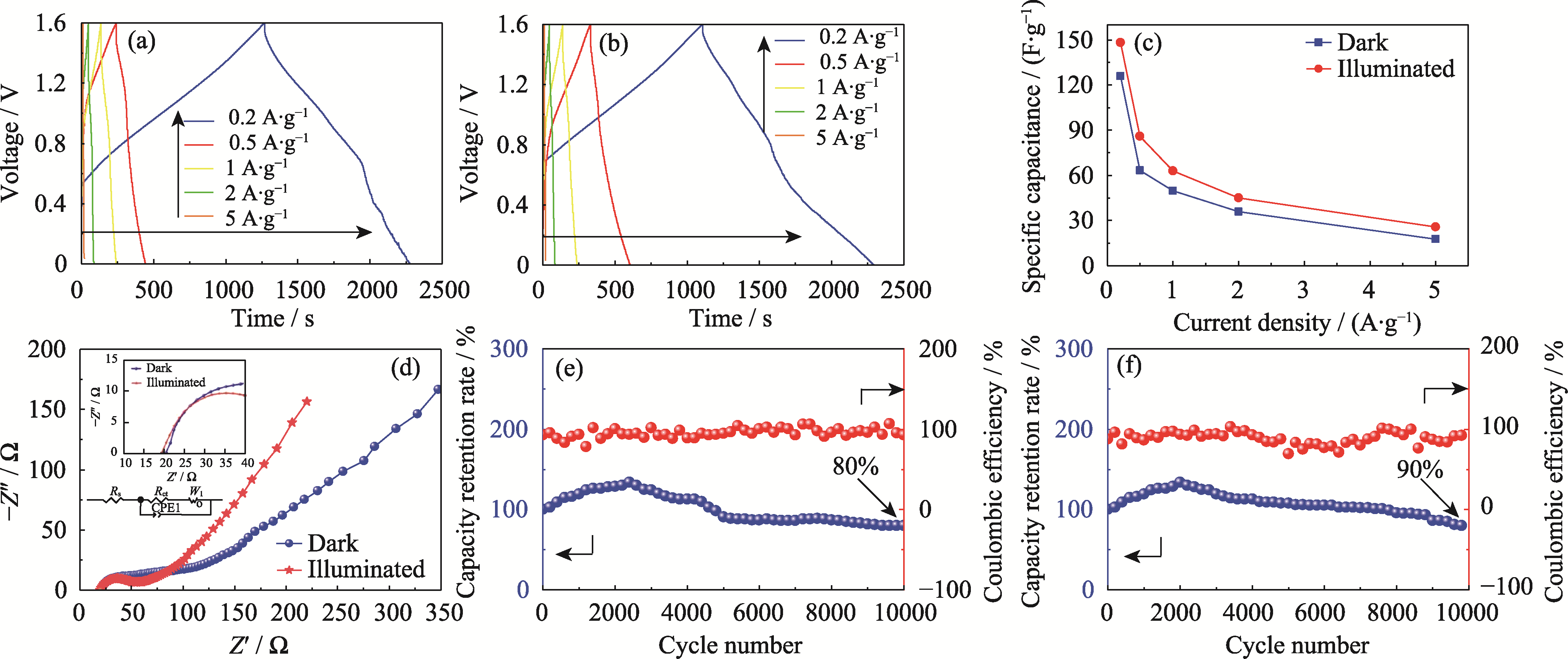
图4 ZnFe2O4//rGH超级电容器(a, e)仅电充和(b, f)光电协同充电条件下的(a, b) GCD曲线、(c)比容量、(d) EIS谱图、(e, f)库仑效率和容量保持率
Fig. 4 (a, b) GCD curves, (c) specific capacitance, (d) EIS spectra, (e, f) Coulombic efficiency and capacity retention rate of ZnFe2O4//rGH supercapacitor with (a, e) only electric charging and (b, f) photoelectric synergistic charging
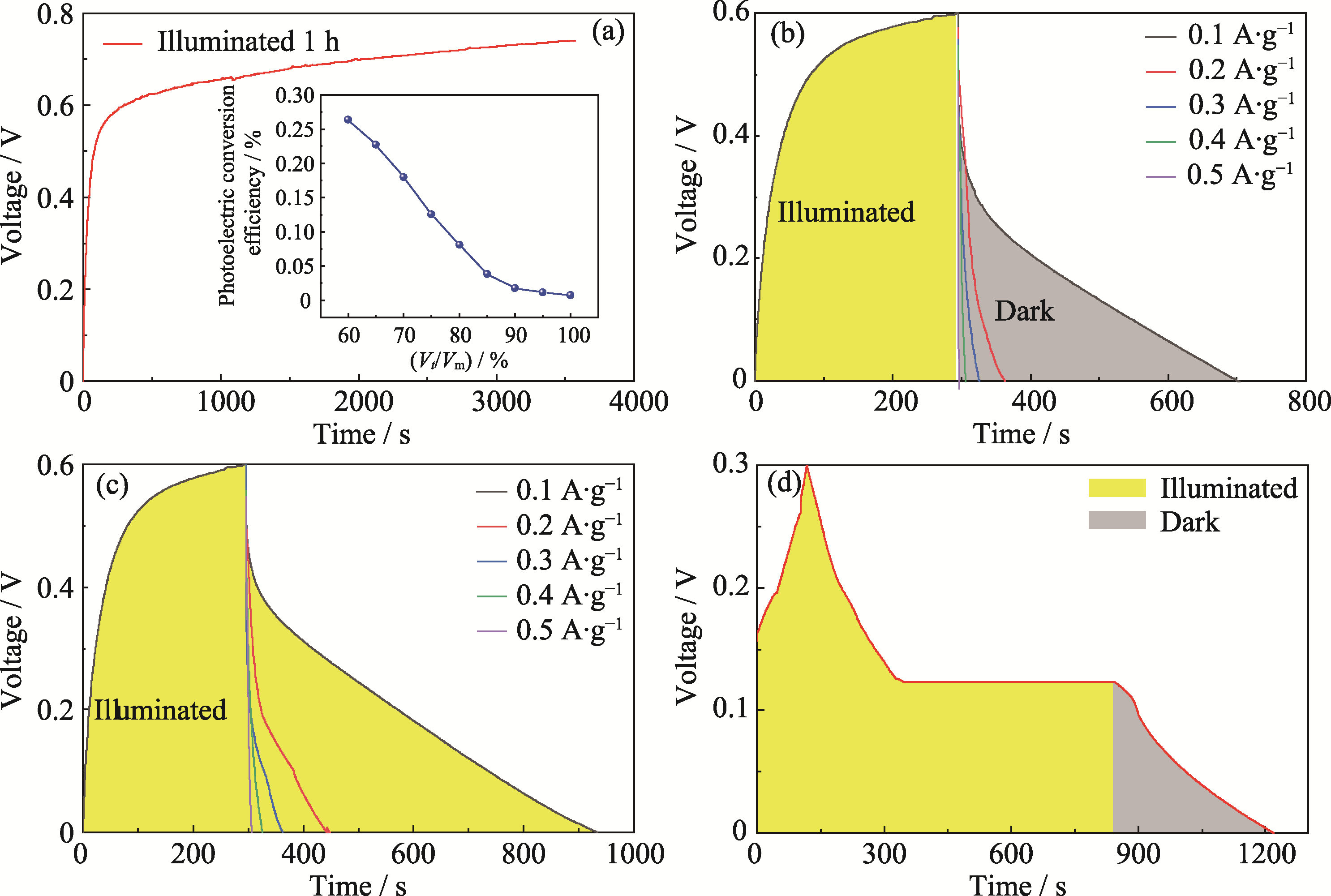
图5 超级电容器光充电时间与光电压之间的关系和光充电后在不同条件下放电的电化学性能
Fig. 5 Relationship between photocharging time and photovoltage of the supercapacitor, and electrochemical performance of discharging under different conditions after photocharging (a) Relationship between photocharging time and photovoltage with inset showing PCE vs. Vt/Vm, where Vt represents voltage at photocharging time t, Vm represents maximum photocharging voltage; (b, c) GCD curves of the supercapacitor photocharged followed by discharging (b) without and (c) with illumination; (d) GCD curve of the supercapacitor photocharged up to 0.3 V followed by discharging at 14 mA·g-1. Colorful figures are available on website
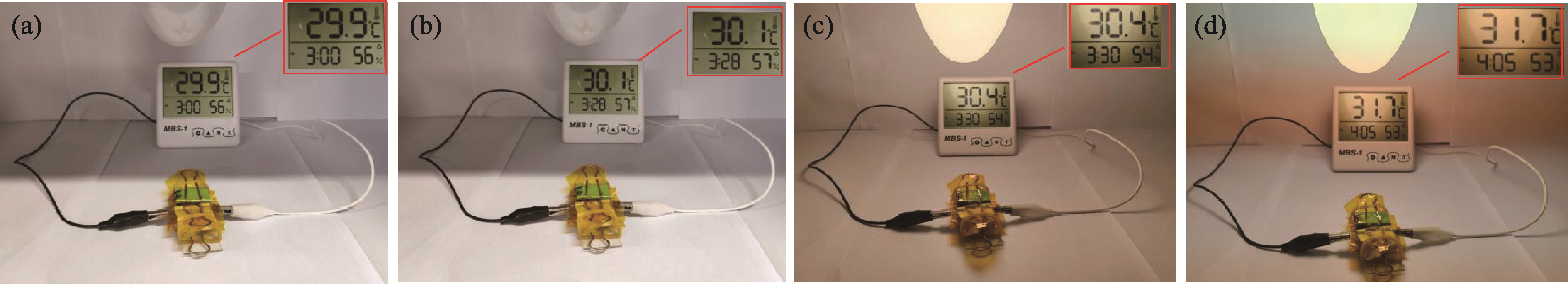
图6 ZnFe2O4//rGH超级电容器在(a, b)无光照和(c, d)光照条件下驱动电子器件(a, c)起始和(b, d)结束的照片
Fig. 6 (a, c) Initial and (b, d) final photographs of electronic hygrometer driven by ZnFe2O4//rGH supercapacitors (a, b) without and (c, d) with illumination
| [1] |
BORUAH B D. Recent advances in off-grid electrochemical capacitors. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 34: 53.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
MANOPRIYA S, HAREESH K. The prospects and challenges of solar electrochemical capacitors. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 35: 102294.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ZHENG X, SUN Y H, QIN H Y, et al. Solar-charged pseudocapacitors: simultaneous conversion and storage of solar energy in ZnO@NiO nanorod arrays. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 781: 351.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
XU X B, LI S H, ZHANG H, et al. A power pack based on organometallic perovskite solar cell and supercapacitors. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(2): 1782.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
LEE J Y, KANG S, LEE D, et al. Boosting the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance via an atomically thin 2D heterojunction visualized by scanning photoelectrochemical microscopy. Nano Energy, 2019, 65: 104053.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
BORUAH B D, MATHIESON A, WEN B, et al. Photo- rechargeable zinc-ion capacitor using 2D graphitic carbon nitrides. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(8): 5967.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
PARK H W, ROH K C. Recent advances in and perspectives on pseudocapacitive materials for supercapacitors-a reviews. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 557: 232558.
DOI URL |
| [8] | SHI Z T, SUN G, YUAN R W, et al. Scalable fabrication of NiCo2O4/reduced graphene oxide composites by ultrasonic spray as binder-free electrodes for supercapacitors with ultralong lifetimes. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 99: 260. |
| [9] |
HUSSAIN S, MAKTEDAR S S. Structural, functional and mechanical performance of advanced graphene-based composite hydrogels. Results in Chemistry, 2023, 6: 101029.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
MA W H, WANG J K, WU T, et al. Three-dimensional nitrogen- doped graphene quantum dots/reduced graphene oxide composite hydrogels as binder-free electrodes for symmetric supercapacitors. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2023, 310: 128365.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ZHANG Y H, LI M J, WANG H J, et al. Supersensitive photoelectrochemical aptasensor based on Br, N-codoped TiO2 sensitized by quantum dots. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(16): 10864.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
RAJAPANDI P, VIRUTHAGIRI G, VIDHYA M, et al. Effect of molar concentration on optoelectronic properties of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles for n-α-Fe2O3/p-Si junction diode application. Solid State Communications, 2025, 399: 115873.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
YU L, GONG W, ZHAO X, et al. Layered BiVO4 photoanodes modified by microwave hydrothermal ZnCo2O4 to alleviate sluggish water oxidation kinetics for water splitting. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2025, 127: 793.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
RENANI A S, HOSSEINI Z, EBERHART D, et al. Photo-assisted symmetric and asymmetric supercapacitors based on molybdenum cobalt coated bismuth vanadate photoelectrodes: all-in-one energy harvesting and storage devices. Journal of Power Sources, 2025, 640: 236687.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
MAJUMDER S, QUANG N D, HIEN T T, et al. Effect of SILAR-anchored ZnFe2O4 on the BiVO4nanostructure: an attempt towards enhancing photoelectrochemical water splitting. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 546: 149033.
DOI URL |
| [16] | SEONG J G, KO T H, LEI D, et al. Engineered NiCo-LDH nanosheets- and ZnFe2O4 nanocubes-decorated carbon nanofiber bonded mats for high-rate asymmetric supercapacitors. Green Energy & Environment, 2022, 7(6): 1228. |
| [17] |
ASKARI M B, SALARIZADEH P, SEIFI M, et al. ZnFe2O4 nanorods on reduced graphene oxide as advanced supercapacitor electrodes. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 860: 158497.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WU L X, LI J K, JIANG H D, et al. Preparation of an aqueous zinc ion rGH/V2O5 photorechargeable supercapacitor. Dalton Transactions, 2024, 53(25): 10626.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
TEJASHWINI D M, NAGASWARUPA H P, NAIK R, et al. Synthesis, characterization, wastewater treatment & plant growth application of ZnFe2O4/Bi2O3 nanocomposite. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2024, 320: 100681.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SHKIR M, CHANDEKAR K V, AL SDRAN N. Influence of Mo dopant on the structural, vibrational, dielectric, and magnetic properties of combustion synthesized ZnFe2O4 nanostructures for optoelectronic and spintronic applications. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2025, 197: 112417.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
REN X C, CHEN R H, DING S Y, et al. Preparation and photocatalytic performance of a magnetically recyclable ZnFe2O4@TiO2@Ag2O p-n/Z-type tandem heterojunction photocatalyst: degradation pathway and mechanism. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 658: 130604.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
GORSI A T, MANSOOR S, JAVED M, et al. Sunlight-active, S-g-C3N4 boosts Ni-doped ZnFe2O4 photocatalysts for efficient organic pollutants degradation. Optical Materials, 2024, 150: 115181.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
PANDA S S S, GANDI S, PARNE S R, et al. Facile hydrothermal synthesis of bio-inspired ZnO/Fe2O3/ZnFe2O4 heterostructure: effect of microwave absorption properties. Surfaces and Interfaces, 2023, 42: 103490.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
YANG E D, LI B L, ZHANG K, et al. ZnCo2O4-ZnO@C@CoS core-shell composite: preparation and application in supercapacitors. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 485.
DOI URL |
| [25] | ZHAO C Y, XE X Q, WAN S H, et al. Covalent organic framework modified polyaniline electrospun nanofiber membrane for electrochemical detecting of Pb2+. Journal of Liaocheng University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 36(4): 74. |
| [26] |
LV M S, CHEN G L, WANG T T, et al. Willow catkins-assisted synthesis of ZnFe2O4/ZnO hetero-tubes for chemiresistive dibutylamine sensors operated at 130 ℃. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2024, 417: 136203.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
TU F L, JIA Y K, TAO X C, et al. Improved photocathodic protection and S-scheme mechanism of graphene and ZnFe2O4 decorated TiO2 nanosheets with {001} facet exposed. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2024, 976: 173100.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
JIANG L, WU D, YU F S, et al. Construction of novel dual wave-absorbing ZnFe2O4/CNTs nanoparticles with more hotspots for enhanced microwave-induced catalytic activity: performance and mechanism. Ceramics International, 2024, 50: 52808.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WANG B, QIN Y, TAN W, et al. Smartly designed 3D N-doped mesoporous graphene for high-performance supercapacitor electrodes. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 241: 1.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
FU X, CHANG J, GUO W, et al. Heteroatoms-doped hierarchically porous graphene as electrode material for supercapacitors with ultra-high capacitance. Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 603: 234474.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 杨恩东, 李宝乐, 张珂, 谭鲁, 娄永兵. ZnCo2O4-ZnO@C@CoS核壳复合材料的制备及其在超级电容器中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 485-493. |
| [2] | 费玲, 雷蕾, 汪德高. 二维MXene材料在新型薄膜太阳能电池技术中的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 215-224. |
| [3] | 晁少飞, 薛艳辉, 吴琼, 伍复发, MUHAMMAD Sufyan Javed, 张伟. MXene异质结Ti-O-H-O电子快速通道促进高效率储钾[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1212-1220. |
| [4] | 丁玲, 蒋瑞, 唐子龙, 杨运琼. MXene材料的纳米工程及其作为超级电容器电极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [5] | 孙鹏, 张绍宁, 毕辉, 董武杰, 黄富强. 基于结构调节碳材料的掺氮种类和含量及其超级电容器储能应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 766-772. |
| [6] | 刘芳芳, 传秀云, 杨扬, 李爱军. 氮/硫共掺杂对纤水镁石模板碳纳米管电化学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 711-717. |
| [7] | 李泽晖,谭美娟,郑元昊,骆雨阳,经求是,蒋靖坤,李明杰. 导电金属有机骨架材料在超级电容器中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(7): 769-780. |
| [8] | 陈钧,马培华,张诚,劳伦·鲁尔曼,吕耀康. 新型多功能无机/有机复合薄膜的制备及电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 217-223. |
| [9] | 费明婕, 张任平, 朱归胜, 俞兆喆, 颜东亮. 磷酸根掺杂MnFe2O4及其赝电容特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(10): 1137-1141. |
| [10] | 丁卓峰, 杨永强, 李在均. 组氨酸功能化碳点/石墨烯气凝胶的制备及超级电容器性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(10): 1130-1136. |
| [11] | 马亚楠, 刘宇飞, 余晨旭, 张传坤, 罗时军, 高义华. 不同横向尺寸单层Ti3C2Tx纳米片的制备及其电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(1): 93-98. |
| [12] | 李腾飞, 黄璐君, 闫旭东, 刘庆雷, 顾佳俊. 碳化钛/椴木多孔碳复合材料用于超级电容器性能的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(1): 126-130. |
| [13] | 张天宇, 崔聪, 程仁飞, 胡敏敏, 王晓辉. 同步氨化/碳化法制备MXene/C平面多孔复合电极[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(1): 112-118. |
| [14] | 许伟佳, 邱大平, 刘诗强, 李敏, 杨儒. 用于高性能超级电容器电极的栓皮栎基多孔活性炭的制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 625-632. |
| [15] | 刘伟, 郑凯, 王东红, 雷忆三, 范怀林. Co3O4纳米线阵列@活性炭纤维复合材料的水热合成及电化学应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(5): 487-492. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||