无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 27-36.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250073 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20250073
张广珩1,2( ), 石金瑜1,2, 沈泓宇1,3, 张洁1(
), 石金瑜1,2, 沈泓宇1,3, 张洁1( ), 王京阳1
), 王京阳1
收稿日期:2025-02-20
修回日期:2025-05-14
出版日期:2026-01-20
网络出版日期:2025-05-22
通讯作者:
张 洁, 研究员. E-mail: jiezhang@imr.ac.cn作者简介:张广珩(1996-), 男, 博士. E-mail: ghzhang@lam.ln.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Guangheng1,2( ), SHI Jinyu1,2, SHEN Hongyu1,3, ZHANG Jie1(
), SHI Jinyu1,2, SHEN Hongyu1,3, ZHANG Jie1( ), WANG Jingyang1
), WANG Jingyang1
Received:2025-02-20
Revised:2025-05-14
Published:2026-01-20
Online:2025-05-22
Contact:
ZHANG Jie, professor. E-mail: jiezhang@imr.ac.cnAbout author:ZHANG Guangheng (1996-), male, PhD. E-mail: ghzhang@lam.ln.cn
Supported by:摘要: 随着航空发动机服役温度的升高, 低熔点钙镁铝硅酸盐(CaO-MgO-AlO1.5-SiO2, CMAS)腐蚀成为导致热结构部件防护涂层失效的重要因素。在典型热障涂层(Thermal barrier coating, TBC)及环境障涂层(Environmental barrier coating, EBC)的CMAS腐蚀过程中, 稀土组分对反应产物的结晶以及CMAS腐蚀渗透过程具有显著影响。本研究聚焦TBC和EBC体系中广泛采用的两种稀土元素——钆和镱, 制备了一系列钆-镱氧化物((GdxYb1-x)2O3, x=0、0.05、0.10、0.20、0.30、0.50和1.00), 系统研究其与CMAS沉积物在1300 ℃下的反应产物, 并探讨这两种稀土元素的协同作用机理。结果表明, 钆离子有效诱导磷灰石结构产物的形成, 但熔体消耗效率较低; 镱离子促进石榴石和磷硅酸钙结构产物的形成, 但其产物结晶动力学迟滞。进一步讨论了钆和镱离子在产物中的配分特征以及残余CMAS熔体成分的变化, 提出在一定比例范围内(钆摩尔分数为5%~20%)两者之间存在协同效应。通过合理设计涂层中钆和镱元素的比例, 可以促进磷灰石结晶, 阻止熔体渗透, 同时改善石榴石和磷硅酸钙迟滞的结晶动力学, 从而加速熔体消耗。探究协同作用为TBC/EBC的抗CMAS腐蚀改性成分设计提供了理论支撑。
中图分类号:
张广珩, 石金瑜, 沈泓宇, 张洁, 王京阳. Gd3+和Yb3+对CMAS腐蚀产物结晶行为的影响及协同作用机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 27-36.
ZHANG Guangheng, SHI Jinyu, SHEN Hongyu, ZHANG Jie, WANG Jingyang. Synergistic Mechanism of Gd3+ and Yb3+ on Crystallization Behavior of CMAS Corrosion Products[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 27-36.
| CMAS | Chemical composition/% (in mole) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | MgO | AlO1.5 | SiO2 | |
| Theoretical value | 33 | 9 | 13 | 45 |
| Measured value | 32.2±2.3 | 9.4±1.0 | 13.2±1.4 | 45.2±0.9 |
表1 CMAS成分的理论值和测量值
Table 1 Theoretical and measured values of CMAS composition
| CMAS | Chemical composition/% (in mole) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | MgO | AlO1.5 | SiO2 | |
| Theoretical value | 33 | 9 | 13 | 45 |
| Measured value | 32.2±2.3 | 9.4±1.0 | 13.2±1.4 | 45.2±0.9 |
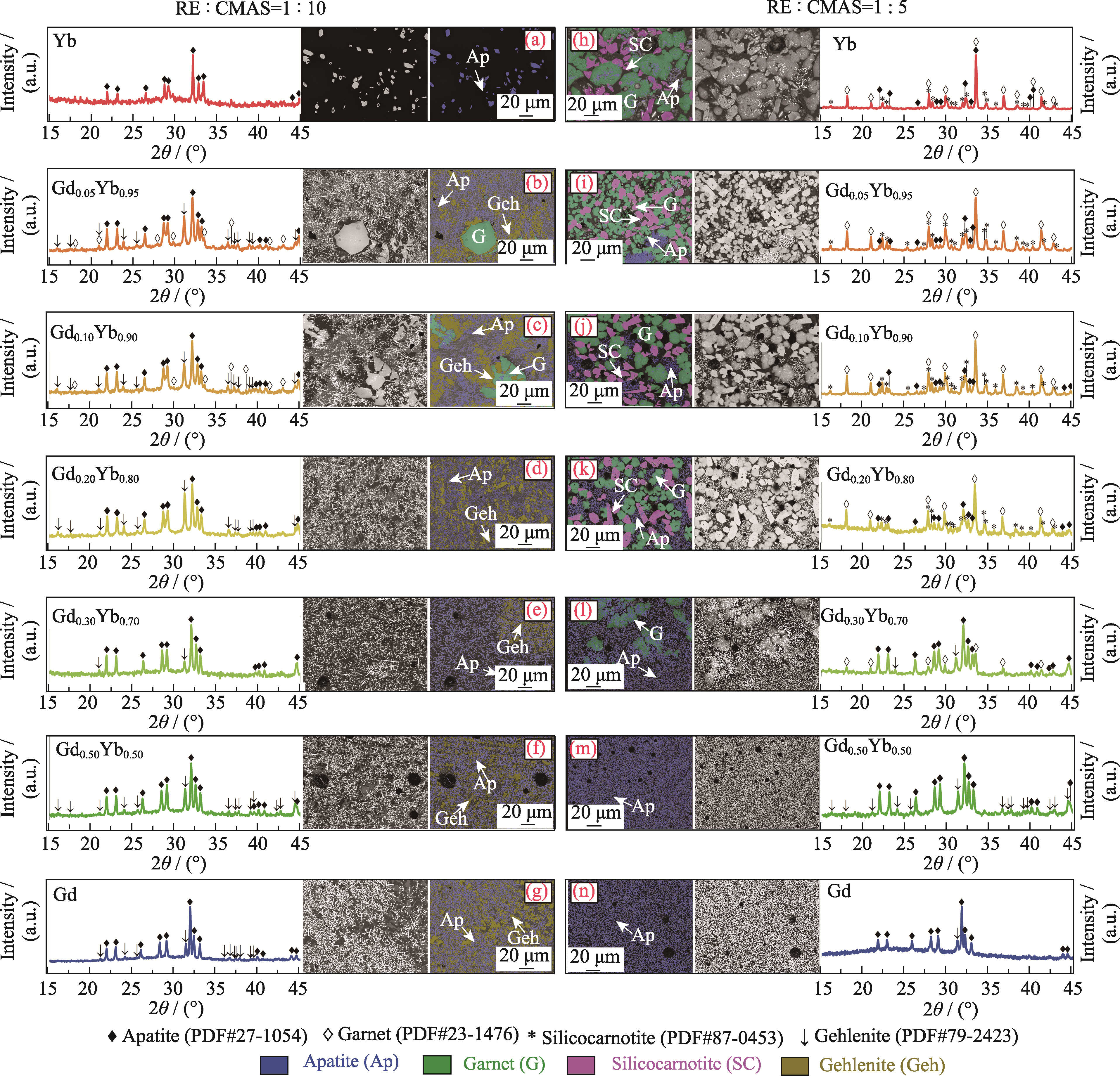
图3 RE : CMAS摩尔比分别为(a~g) 1 : 10和(h~n) 1 : 5的混合粉末经1300 ℃热处理1 h后的XRD图谱和BSE图像
Fig. 3 XRD patterns and BSE images of the mixed powders with RE : CMAS mole ratios of (a-g) 1 : 10 and (h-n) 1 : 5 after heat treatment at 1300 ℃ for 1 h Colorful figures are available on website
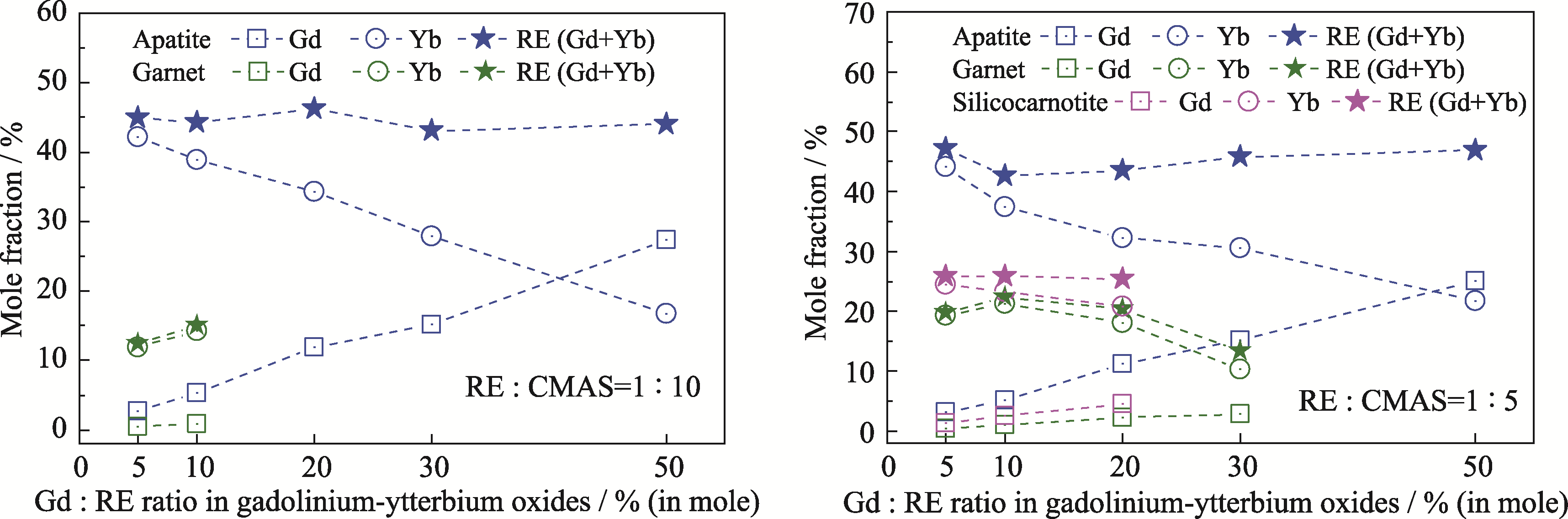
图4 三种反应产物中GdO1.5、YbO1.5以及REO1.5含量的对比
Fig. 4 Comparison of GdO1.5, YbO1.5 and REO1.5 contents in three reaction products Colorful figures are available on website
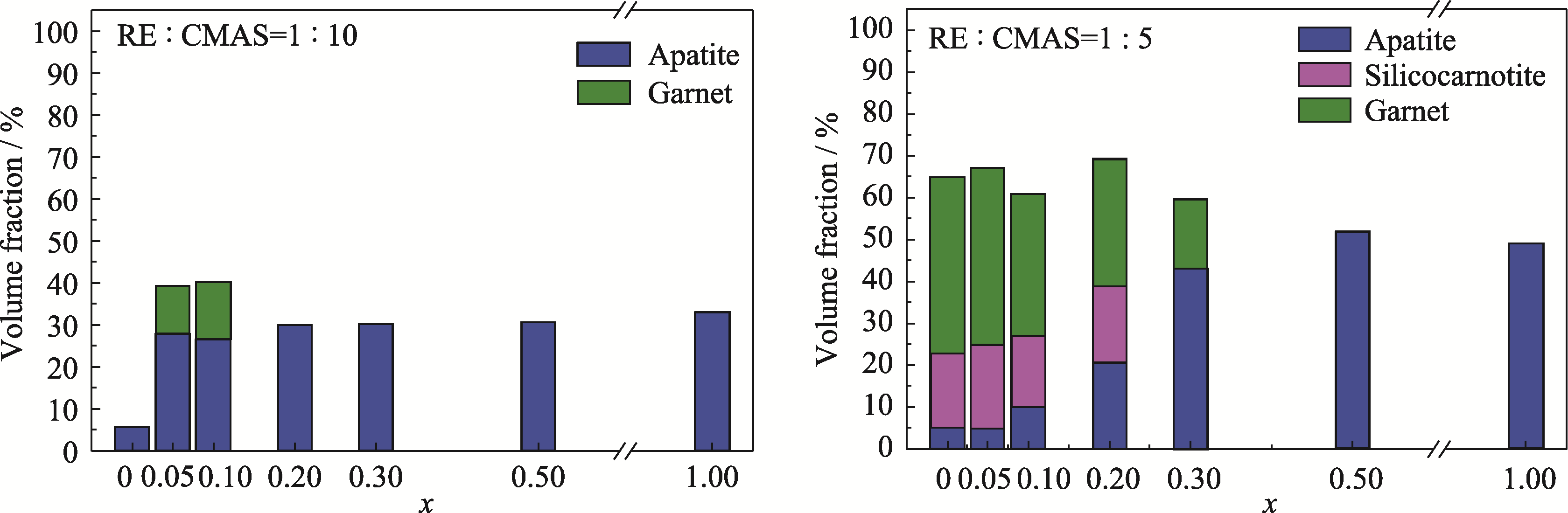
图5 GdxYb1-x-CMAS(x=0、0.05、0.10、0.20、0.30、0.50和1.00)样品中反应产物的体积分数
Fig. 5 Volume fractions of products in GdxYb1-x-CMAS (x=0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.20, 0.30, 0.50 and 1.00) samples Colorful figures are available on website
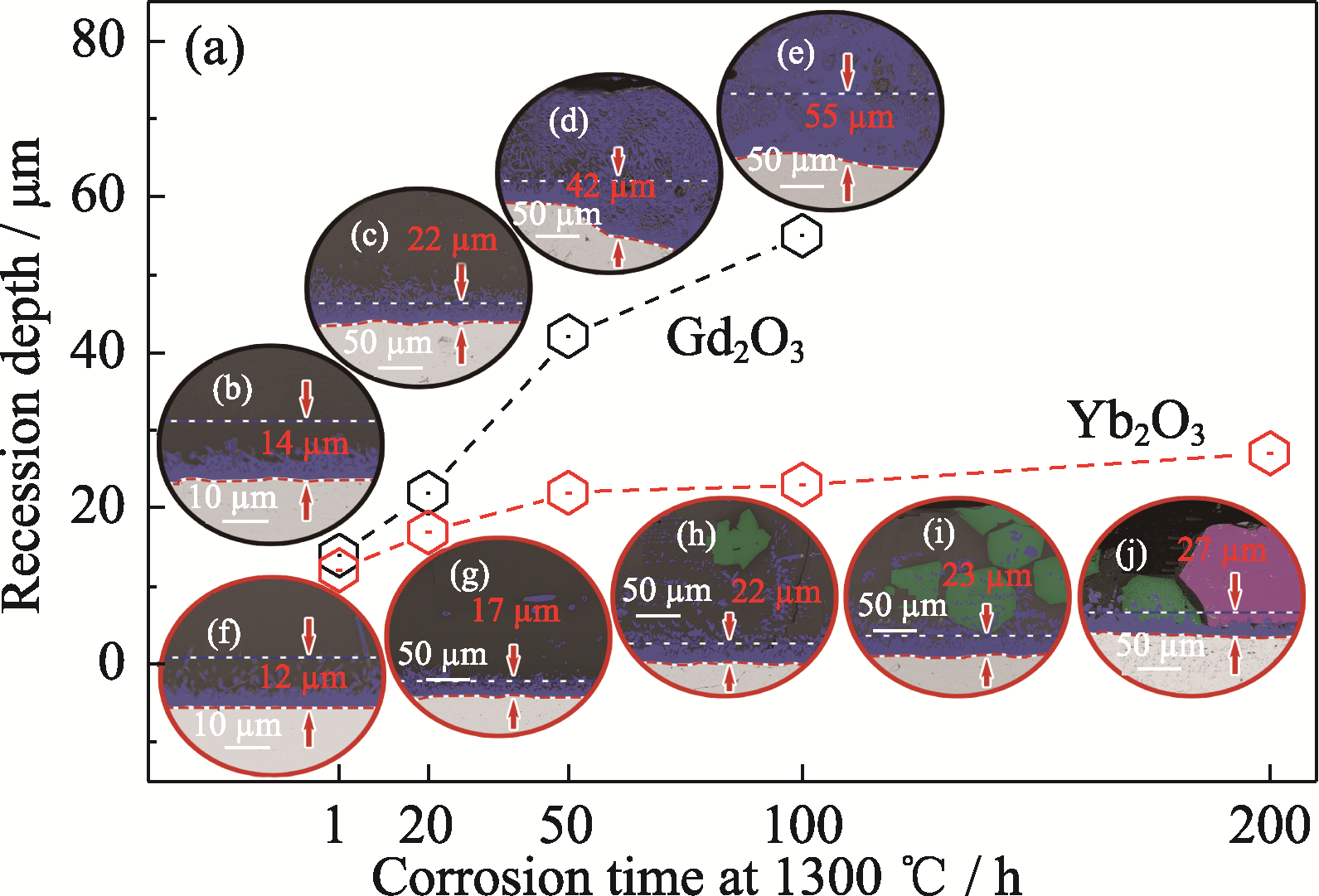
图6 Yb2O3和Gd2O3块体在1300 ℃下CMAS腐蚀不同时间的(a)衰退深度以及(b~j) BSE图像
Fig. 6 (a) Recession depth and (b-j) BSE images of cross sections for Yb2O3 and Gd2O3 pellets after CMAS corrosion at 1300 ℃ for different time Yb2O3: (b) 1 h; (c) 20 h; (d) 50 h; (e) 100 h Gd2O3: (f) 1 h; (g) 20 h; (h) 50 h; (i) 100 h; (j) 200 h
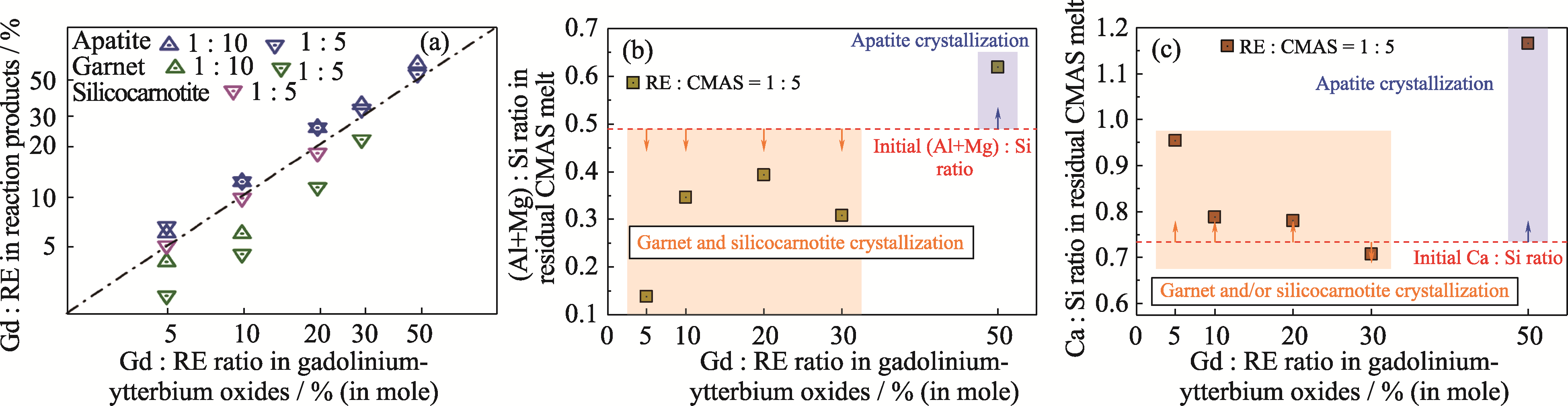
图7 (a)反应产物中Gd : RE以及CMAS熔体中(b) (Mg+Al) : Si和(c) Ca : Si随初始钆-镱氧化物成分的变化
Fig. 7 Variations of (a) Gd : RE ratio in reactive crystallization products as well as (b) (Mg+Al) : Si and (c) Ca : Si ratios in residual CMAS melt with the initial composition of gadolinium-ytterbium oxides
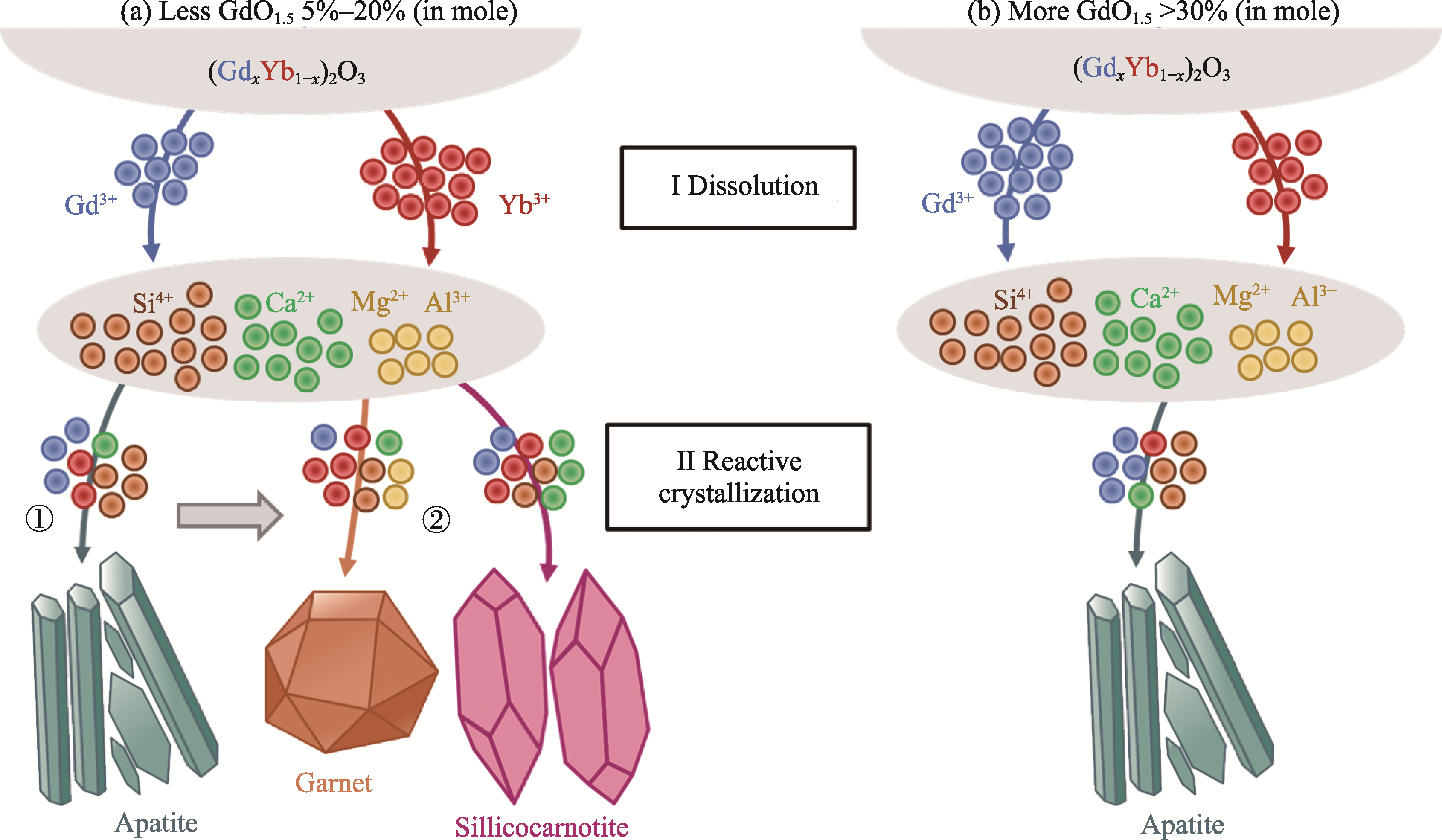
图8 (GdxYb1-x)2O3与CMAS沉积物相互作用过程中不同反应产物消耗钆和镱离子的示意图
Fig. 8 Schematic diagrams of Gd3+ and Yb3+ consumed by different reaction products in the interaction between (GdxYb1-x)2O3 and CMAS deposits (a) Less GdO1.5 (5%-20%, in mole); (b) More GdO1.5 (>30%, in mole)
| 药品名称 | 纯度 | 厂家 | 产地 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 氧化钆(GdO1.5) | 99.99% | 定南大华新材料资源有限公司 | 江西赣州 |
| 氧化镱(YbO1.5) | 99.99% | 定南大华新材料资源有限公司 | 江西赣州 |
| 氧化钙(CaO) | 分析纯AR | 国药集团化学试剂有限公司 | 上海 |
| 氧化镁(MgO) | 分析纯AR | 国药集团化学试剂有限公司 | 上海 |
| 氧化铝(AlO1.5) | 分析纯AR | 国药集团化学试剂有限公司 | 上海 |
| 氧化硅(SiO2) | 分析纯AR | 国药集团化学试剂有限公司 | 上海 |
表S1 几种氧化物原料信息
Table S1 Information of several oxide raw materials
| 药品名称 | 纯度 | 厂家 | 产地 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 氧化钆(GdO1.5) | 99.99% | 定南大华新材料资源有限公司 | 江西赣州 |
| 氧化镱(YbO1.5) | 99.99% | 定南大华新材料资源有限公司 | 江西赣州 |
| 氧化钙(CaO) | 分析纯AR | 国药集团化学试剂有限公司 | 上海 |
| 氧化镁(MgO) | 分析纯AR | 国药集团化学试剂有限公司 | 上海 |
| 氧化铝(AlO1.5) | 分析纯AR | 国药集团化学试剂有限公司 | 上海 |
| 氧化硅(SiO2) | 分析纯AR | 国药集团化学试剂有限公司 | 上海 |
| System | Phase | Chemical composition/% (in mole) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | MgO | AlO1.5 | SiO2 | GdO1.5 | YbO1.5 | ||
| Yb : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 15.5 ± 0.4 | — | — | 37.2 ± 0.2 | — | 47.3 ± 0.2 |
| Melt | 31.7 ± 0.2 | 8.7 ± 0.3 | 12.2 ± 0.5 | 42.0 ± 0.5 | — | 5.5 ± 0.4 | |
| Yb : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 15.9 ± 0.7 | — | — | 38.0 ± 0.6 | — | 46.1 ± 0.8 |
| Garnet | 15.4 ± 0.7 | 15.5 ± 1.4 | 16.4 ± 1.7 | 30.4 ± 2.0 | — | 22.4 ± 2.3 | |
| Silicocarnotite | 35.1 ± 0.1 | — | — | 39.4 ± 0.2 | — | 25.5 ± 0.2 | |
| Melt | 43.6 ± 0.2 | 2.6 ± 0.2 | 3.9 ± 0.1 | 46.0 ± 0.3 | — | 3.9 ± 0.2 | |
| Gd0.05Yb0.95 : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 15.6 ± 0.2 | — | — | 39.4 ± 0.8 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 42.2 ± 0.4 |
| Garnet | 24.8 ± 1.6 | 13.1 ± 1.2 | 12.4 ± 1.2 | 37.3 ± 0.6 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 11.9 ± 1.5 | |
| Gehlenite | 41.1 ± 0.5 | 13.9 ± 0.2 | 7.3 ± 0.3 | 37.7 ± 0.5 | — | — | |
| Melt | 28.4 ± 0.6 | 5.1 ± 1.0 | 15.5 ± 0.2 | 45.6 ± 1.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 5.2 ± 0.6 | |
| Gd0.05Yb0.95 : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 13.9 ± 0.3 | — | — | 38.9 ± 0.5 | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 44.1 ± 0.3 |
| Garnet | 19.2 ± 1.4 | 14.1 ± 0.5 | 13.8 ± 1.3 | 33.0 ± 0.8 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 19.3 ± 1.2 | |
| Silicocarnotite | 36.4 ± 0.2 | — | — | 37.7 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 24.5 ± 0.4 | |
| Melt | 44.1 ± 1.6 | 2.3 ± 0.4 | 4.1 ± 1.6 | 46.2 ± 0.5 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 3.2 ± 0.5 | |
| Gd0.10Yb0.90 : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 15.3 ± 0.2 | — | — | 40.5 ± 0.1 | 5.4 ± 0.2 | 38.9 ± 0.4 |
| Garnet | 22.4 ± 0.6 | 14.7 ± 0.6 | 10.5 ± 0.6 | 37.2 ± 0.6 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 14.2 ± 0.9 | |
| Gehlenite | 42.2 ± 0.2 | 13.2 ± 0.3 | 8.4 ± 0.1 | 36.1 ± 0.5 | — | — | |
| Melt | 27.9 ± 1.4 | 5.2 ± 0.2 | 16.9 ± 1.3 | 44.6 ± 0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 5.1 ± 0.5 | |
| Gd0.10Yb0.90 : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 16.8 ± 0.6 | — | — | 40.5 ± 0.9 | 5.2 ± 0.1 | 37.4 ± 0.4 |
| Garnet | 17.0 ± 1.5 | 14.1 ± 0.1 | 15.5 ± 1.2 | 31.0 ± 0.4 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 21.3 ± 0.9 | |
| Silicocarnotite | 35.9 ± 0.2 | — | — | 38.3 ± 0.2 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 23.3 ± 0.2 | |
| Melt | 35.9 ± 0.9 | 2.2 ± 0.4 | 13.6 ± 0.5 | 45.5 ± 0.3 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 2.3 ± 0.2 | |
| Gd0.20Yb0.80 : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 14.0 ± 0.4 | — | — | 39.8 ± 0.8 | 11.9 ± 0.6 | 34.3 ± 1.2 |
| Gehlenite | 41.1 ± 0.2 | 13.0 ± 0.2 | 8.3 ± 0.2 | 37.5 ± 0.6 | — | — | |
| Melt | 27.7 ± 0.5 | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 16.9 ± 0.5 | 44.5 ± 0.3 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 4.6 ± 0.5 | |
| Gd0.20Yb0.80 : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 15.4 ± 0.6 | — | — | 41.0 ± 0.7 | 11.2 ± 0.7 | 32.3 ± 0.9 |
| Garnet | 18.4 ± 0.6 | 14.2 ± 0.3 | 13.7 ± 1.1 | 33.2 ± 1.6 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 18.1 ± 1.4 | |
| Silicocarnotite | 36.7 ± 0.3 | — | — | 37.8 ± 0.3 | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 20.8 ± 0.7 | |
| Melt | 34.8 ± 0.8 | 3.1 ± 1.2 | 14.4 ± 1.4 | 44.6 ± 0.9 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | |
| Gd0.30Yb0.70 : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 17.0 ± 0.9 | — | — | 39.8 ± 0.5 | 15.2 ± 0.8 | 27.9 ± 1.0 |
| Gehlenite | 39.8 ± 0.9 | 11.3 ± 0.3 | 11.3 ± 0.6 | 37.6 ± 0.7 | — | — | |
| Melt | 31.6 ± 0.5 | 9.4 ± 0.3 | 13.1 ± 0.3 | 41.6 ± 0.5 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 3.4 ± 0.2 | |
| Gd0.30Yb0.70 : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 15.7 ± 0.1 | — | — | 38.5 ± 0.4 | 15.2 ± 0.4 | 30.6 ± 0.8 |
| Garnet | 22.8 ± 0.7 | 13.3 ± 0.5 | 13.5 ± 0.9 | 37.0 ± 0.6 | 2.9 ± 0.2 | 10.4 ± 0.4 | |
| Melt | 33.8 ± 0.2 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 12.6 ± 0.5 | 47.8 ± 0.7 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | |
| Gd0.50Yb0.50 : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 18.4 ± 0.2 | — | — | 37.6 ± 1.3 | 27.3 ± 1.1 | 16.7 ± 0.8 |
| Gehlenite | 40.3 ± 0.4 | 11.8 ± 0.1 | 9.5 ± 0.4 | 38.4 ± 0.1 | — | — | |
| Melt | 27.0 ± 0.2 | 5.3 ± 0.1 | 18.2 ± 0.1 | 45.1 ± 0.2 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 2.8 ± 0.2 | |
| Gd0.50Yb0.50 : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 15.1 ± 0.3 | — | — | 38.0 ± 0.6 | 25.1 ± 0.7 | 21.7 ± 0.9 |
| Melt | 39.9 ± 0.6 | 11.3 ± 0.2 | 9.9 ± 0.2 | 34.3 ± 0.3 | 2.5 ± 0.6 | 2.1 ± 0.4 | |
| Gd : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 20.7 ± 1.0 | — | — | 38.6 ± 0.1 | 40.7 ± 1.0 | — |
| Gehlenite | 39.9 ± 0.9 | 13.7 ± 0.8 | 9.2 ± 0.4 | 37.2 ± 1.3 | — | — | |
| Melt | 25.7 ± 0.1 | 5.4 ± 0.5 | 20.6 ± 0.7 | 45.6 ± 0.7 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | — | |
| Gd : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 19.9 ± 0.7 | — | — | 39.9 ± 0.8 | 40.2 ± 1.5 | — |
| Melt | 39.7 ± 0.7 | 12.8 ± 0.4 | 9.9 ± 0.6 | 34.9 ± 0.7 | 2.7 ± 1.6 | — | |
表S2 (GdxYb1-x)O1.5-CMAS样品中反应产物的成分
Table S2 Compositions of reaction products and residual CMAS melt in (GdxYb1-x)O1.5-CMAS samples
| System | Phase | Chemical composition/% (in mole) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | MgO | AlO1.5 | SiO2 | GdO1.5 | YbO1.5 | ||
| Yb : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 15.5 ± 0.4 | — | — | 37.2 ± 0.2 | — | 47.3 ± 0.2 |
| Melt | 31.7 ± 0.2 | 8.7 ± 0.3 | 12.2 ± 0.5 | 42.0 ± 0.5 | — | 5.5 ± 0.4 | |
| Yb : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 15.9 ± 0.7 | — | — | 38.0 ± 0.6 | — | 46.1 ± 0.8 |
| Garnet | 15.4 ± 0.7 | 15.5 ± 1.4 | 16.4 ± 1.7 | 30.4 ± 2.0 | — | 22.4 ± 2.3 | |
| Silicocarnotite | 35.1 ± 0.1 | — | — | 39.4 ± 0.2 | — | 25.5 ± 0.2 | |
| Melt | 43.6 ± 0.2 | 2.6 ± 0.2 | 3.9 ± 0.1 | 46.0 ± 0.3 | — | 3.9 ± 0.2 | |
| Gd0.05Yb0.95 : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 15.6 ± 0.2 | — | — | 39.4 ± 0.8 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 42.2 ± 0.4 |
| Garnet | 24.8 ± 1.6 | 13.1 ± 1.2 | 12.4 ± 1.2 | 37.3 ± 0.6 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 11.9 ± 1.5 | |
| Gehlenite | 41.1 ± 0.5 | 13.9 ± 0.2 | 7.3 ± 0.3 | 37.7 ± 0.5 | — | — | |
| Melt | 28.4 ± 0.6 | 5.1 ± 1.0 | 15.5 ± 0.2 | 45.6 ± 1.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 5.2 ± 0.6 | |
| Gd0.05Yb0.95 : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 13.9 ± 0.3 | — | — | 38.9 ± 0.5 | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 44.1 ± 0.3 |
| Garnet | 19.2 ± 1.4 | 14.1 ± 0.5 | 13.8 ± 1.3 | 33.0 ± 0.8 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 19.3 ± 1.2 | |
| Silicocarnotite | 36.4 ± 0.2 | — | — | 37.7 ± 0.2 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 24.5 ± 0.4 | |
| Melt | 44.1 ± 1.6 | 2.3 ± 0.4 | 4.1 ± 1.6 | 46.2 ± 0.5 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 3.2 ± 0.5 | |
| Gd0.10Yb0.90 : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 15.3 ± 0.2 | — | — | 40.5 ± 0.1 | 5.4 ± 0.2 | 38.9 ± 0.4 |
| Garnet | 22.4 ± 0.6 | 14.7 ± 0.6 | 10.5 ± 0.6 | 37.2 ± 0.6 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 14.2 ± 0.9 | |
| Gehlenite | 42.2 ± 0.2 | 13.2 ± 0.3 | 8.4 ± 0.1 | 36.1 ± 0.5 | — | — | |
| Melt | 27.9 ± 1.4 | 5.2 ± 0.2 | 16.9 ± 1.3 | 44.6 ± 0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 5.1 ± 0.5 | |
| Gd0.10Yb0.90 : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 16.8 ± 0.6 | — | — | 40.5 ± 0.9 | 5.2 ± 0.1 | 37.4 ± 0.4 |
| Garnet | 17.0 ± 1.5 | 14.1 ± 0.1 | 15.5 ± 1.2 | 31.0 ± 0.4 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 21.3 ± 0.9 | |
| Silicocarnotite | 35.9 ± 0.2 | — | — | 38.3 ± 0.2 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 23.3 ± 0.2 | |
| Melt | 35.9 ± 0.9 | 2.2 ± 0.4 | 13.6 ± 0.5 | 45.5 ± 0.3 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 2.3 ± 0.2 | |
| Gd0.20Yb0.80 : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 14.0 ± 0.4 | — | — | 39.8 ± 0.8 | 11.9 ± 0.6 | 34.3 ± 1.2 |
| Gehlenite | 41.1 ± 0.2 | 13.0 ± 0.2 | 8.3 ± 0.2 | 37.5 ± 0.6 | — | — | |
| Melt | 27.7 ± 0.5 | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 16.9 ± 0.5 | 44.5 ± 0.3 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 4.6 ± 0.5 | |
| Gd0.20Yb0.80 : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 15.4 ± 0.6 | — | — | 41.0 ± 0.7 | 11.2 ± 0.7 | 32.3 ± 0.9 |
| Garnet | 18.4 ± 0.6 | 14.2 ± 0.3 | 13.7 ± 1.1 | 33.2 ± 1.6 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 18.1 ± 1.4 | |
| Silicocarnotite | 36.7 ± 0.3 | — | — | 37.8 ± 0.3 | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 20.8 ± 0.7 | |
| Melt | 34.8 ± 0.8 | 3.1 ± 1.2 | 14.4 ± 1.4 | 44.6 ± 0.9 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | |
| Gd0.30Yb0.70 : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 17.0 ± 0.9 | — | — | 39.8 ± 0.5 | 15.2 ± 0.8 | 27.9 ± 1.0 |
| Gehlenite | 39.8 ± 0.9 | 11.3 ± 0.3 | 11.3 ± 0.6 | 37.6 ± 0.7 | — | — | |
| Melt | 31.6 ± 0.5 | 9.4 ± 0.3 | 13.1 ± 0.3 | 41.6 ± 0.5 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 3.4 ± 0.2 | |
| Gd0.30Yb0.70 : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 15.7 ± 0.1 | — | — | 38.5 ± 0.4 | 15.2 ± 0.4 | 30.6 ± 0.8 |
| Garnet | 22.8 ± 0.7 | 13.3 ± 0.5 | 13.5 ± 0.9 | 37.0 ± 0.6 | 2.9 ± 0.2 | 10.4 ± 0.4 | |
| Melt | 33.8 ± 0.2 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 12.6 ± 0.5 | 47.8 ± 0.7 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | |
| Gd0.50Yb0.50 : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 18.4 ± 0.2 | — | — | 37.6 ± 1.3 | 27.3 ± 1.1 | 16.7 ± 0.8 |
| Gehlenite | 40.3 ± 0.4 | 11.8 ± 0.1 | 9.5 ± 0.4 | 38.4 ± 0.1 | — | — | |
| Melt | 27.0 ± 0.2 | 5.3 ± 0.1 | 18.2 ± 0.1 | 45.1 ± 0.2 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 2.8 ± 0.2 | |
| Gd0.50Yb0.50 : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 15.1 ± 0.3 | — | — | 38.0 ± 0.6 | 25.1 ± 0.7 | 21.7 ± 0.9 |
| Melt | 39.9 ± 0.6 | 11.3 ± 0.2 | 9.9 ± 0.2 | 34.3 ± 0.3 | 2.5 ± 0.6 | 2.1 ± 0.4 | |
| Gd : CMAS = 1 : 10 | Apatite | 20.7 ± 1.0 | — | — | 38.6 ± 0.1 | 40.7 ± 1.0 | — |
| Gehlenite | 39.9 ± 0.9 | 13.7 ± 0.8 | 9.2 ± 0.4 | 37.2 ± 1.3 | — | — | |
| Melt | 25.7 ± 0.1 | 5.4 ± 0.5 | 20.6 ± 0.7 | 45.6 ± 0.7 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | — | |
| Gd : CMAS = 1 : 5 | Apatite | 19.9 ± 0.7 | — | — | 39.9 ± 0.8 | 40.2 ± 1.5 | — |
| Melt | 39.7 ± 0.7 | 12.8 ± 0.4 | 9.9 ± 0.6 | 34.9 ± 0.7 | 2.7 ± 1.6 | — | |
| System | Phase | Chemical composition/% (in mole) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | MgO | AlO1.5 | SiO2 | GdO1.5 | ||
| 1300 ℃, 1 h | Apatite | 14.1 ± 0.5 | — | — | 36.5 ± 0.5 | 49.4 ± 1.0 |
| 1300 ℃, 20 h | Apatite | 13.7 ± 0.7 | — | — | 35.9 ± 0.5 | 50.3 ± 0.9 |
| 1300 ℃, 50 h | Apatite | 13.6 ± 0.1 | — | — | 35.4 ± 0.4 | 51.0 ± 0.4 |
| 1300 ℃,100 h | Apatite | 14.1 ± 0.2 | — | — | 35.8 ± 0.6 | 50.0 ± 0.7 |
表S3 Gd2O3块体样品中反应产物的成分
Table S3 Compositions of reaction products in Gd2O3 pellets
| System | Phase | Chemical composition/% (in mole) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | MgO | AlO1.5 | SiO2 | GdO1.5 | ||
| 1300 ℃, 1 h | Apatite | 14.1 ± 0.5 | — | — | 36.5 ± 0.5 | 49.4 ± 1.0 |
| 1300 ℃, 20 h | Apatite | 13.7 ± 0.7 | — | — | 35.9 ± 0.5 | 50.3 ± 0.9 |
| 1300 ℃, 50 h | Apatite | 13.6 ± 0.1 | — | — | 35.4 ± 0.4 | 51.0 ± 0.4 |
| 1300 ℃,100 h | Apatite | 14.1 ± 0.2 | — | — | 35.8 ± 0.6 | 50.0 ± 0.7 |
| System | Phase | Chemical composition/% (in mole) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | MgO | AlO1.5 | SiO2 | YbO1.5 | ||
| 1300 ℃, 1 h | Apatite | 13.4 ± 0.4 | — | — | 49.6 ± 0.4 | 37.0 ± 0.5 |
| 1300 ℃, 20 h | Apatite | 12.7 ± 0.4 | — | — | 49.8 ± 0.4 | 37.5 ± 0.4 |
| 1300 ℃, 50 h | Apatite | 12.7 ± 0.4 | — | — | 49.0 ± 0.6 | 38.3 ± 0.5 |
| Garnet | 24.2 ± 1.0 | 13.6 ± 0.5 | 12.2 ± 0.6 | 37.4 ± 0.2 | 12.5 ± 1.0 | |
| 1300 ℃, 100 h | Apatite | 14.1 ± 0.2 | — | — | 35.8 ± 0.6 | 50.0 ± 0.7 |
| Garnet | 24.8 ± 1.3 | 12.5 ± 1.1 | 12.8 ± 1.1 | 36.8 ± 0.4 | 13.1 ± 0.2 | |
| 1300 ℃, 200 h | Apatite | 12.7 ± 0.1 | — | — | 47.8 ± 0.6 | 39.6 ± 0.7 |
| Garnet | 18.2 ± 0.2 | 15.1 ± 0.4 | 10.9 ± 0.2 | 38.6 ± 0.8 | 17.2 ± 0.9 | |
| Silicocarnotite | 33.8 ± 0.4 | — | — | 41.5 ± 0.5 | 24.7 ± 0.5 | |
表S4 Yb2O3块体样品中反应产物的成分
Table S4 Compositions of reaction products in Yb2O3 pellets
| System | Phase | Chemical composition/% (in mole) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | MgO | AlO1.5 | SiO2 | YbO1.5 | ||
| 1300 ℃, 1 h | Apatite | 13.4 ± 0.4 | — | — | 49.6 ± 0.4 | 37.0 ± 0.5 |
| 1300 ℃, 20 h | Apatite | 12.7 ± 0.4 | — | — | 49.8 ± 0.4 | 37.5 ± 0.4 |
| 1300 ℃, 50 h | Apatite | 12.7 ± 0.4 | — | — | 49.0 ± 0.6 | 38.3 ± 0.5 |
| Garnet | 24.2 ± 1.0 | 13.6 ± 0.5 | 12.2 ± 0.6 | 37.4 ± 0.2 | 12.5 ± 1.0 | |
| 1300 ℃, 100 h | Apatite | 14.1 ± 0.2 | — | — | 35.8 ± 0.6 | 50.0 ± 0.7 |
| Garnet | 24.8 ± 1.3 | 12.5 ± 1.1 | 12.8 ± 1.1 | 36.8 ± 0.4 | 13.1 ± 0.2 | |
| 1300 ℃, 200 h | Apatite | 12.7 ± 0.1 | — | — | 47.8 ± 0.6 | 39.6 ± 0.7 |
| Garnet | 18.2 ± 0.2 | 15.1 ± 0.4 | 10.9 ± 0.2 | 38.6 ± 0.8 | 17.2 ± 0.9 | |
| Silicocarnotite | 33.8 ± 0.4 | — | — | 41.5 ± 0.5 | 24.7 ± 0.5 | |
| [1] |
WEI Z, MENG G, CHEN L, et al. Progress in ceramic materials and structure design toward advanced thermal barrier coatings. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11(7): 985.
DOI |
| [2] |
TEJERO M D, BENNETT C, HUSSAIN T. A review on environmental barrier coatings: history, current state of the art and future developments. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(3): 1747.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
POERSCHKE D L, JACKSON R W, LEVI C G. Silicate deposit degradation of engineered coatings in gas turbines: progress toward models and materials solutions. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2017, 47(1): 297.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
NIETO A, AGRAWAL R, BRAVO L, et al. Calcia-magnesia- alumina-silicate (CMAS) attack mechanisms and roadmap towards Sandphobic thermal and environmental barrier coatings. International Materials Reviews, 2020, 66(7): 451.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
MERCER C, FAULHABER S, EVANS A G, et al. A delamination mechanism for thermal barrier coatings subject to calcium-magnesium-alumino-silicate (CMAS) infiltration. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53(4): 1029.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
POERSCHKE D L, SHAW J H, VERMA N, et al. Interaction of yttrium disilicate environmental barrier coatings with calcium- magnesium-iron alumino-silicate melts. Acta Materialia, 2018, 145: 451.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
SUMMERS W D, POERSCHKE D L, TAYLOR A A, et al. Reactions of molten silicate deposits with yttrium monosilicate. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(4): 2919.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
MOTOC A M, VALSAN S, SLOBOZEANU A E, et al. Design, fabrication, and characterization of new materials based on zirconia doped with mixed rare earth oxides: review and first experimental results. Metals, 2020, 10(6): 746.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHANG Z, PENG F, HUANG Y, et al. CMAS corrosion resistance of rare-earth cerates at higher temperature. Ceramics International, 2025, 51(6): 7906.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
MOURET T, MAILLÉ L, DANET J, et al. Thermochemical interaction of pure rare earth silicates (Y and Yb) with CMAS: role and stability of the corrosion products. Corrosion Science, 2025, 250: 112864.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
TIAN Z, ZHANG J, ZHENG L, et al. General trend on the phase stability and corrosion resistance of rare earth monosilicates to molten calcium-magnesium-aluminosilicate at 1300 ℃. Corrosion Science, 2019, 148: 281.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
POERSCHKE D L, LEVI C G. Effects of cation substitution and temperature on the interaction between thermal barrier oxides and molten CMAS. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2015, 35(2): 681.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
KRÄMER S, YANG J, LEVI C G. Infiltration-Inhibiting reaction of gadolinium zirconate thermal barrier coatings with CMAS melts. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(2): 576.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZHONG X, WANG Y, NIU Y, et al. Corrosion behaviors and mechanisms of ytterbium silicate environmental barrier coatings by molten calcium-magnesium-alumino-silicate melts. Corrosion Science, 2021, 191: 109718.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
POERSCHKE D L, BARTH T L, LEVI C G. Equilibrium relationships between thermal barrier oxides and silicate melts. Acta Materialia, 2016, 120: 302.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
KIM S H, NAGASHIMA N, MATSUSHITA Y, et al. Interaction of Gd2Si2O7 with CMAS melts for environmental barrier coatings. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(2): 593.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WU N, WANG Y, TONG Y, et al. Interaction of ytterbium monosilicate environmental barrier coating material with molten calcium-magnesium-aluminosilicate (CMAS). Corrosion Science, 2023, 211: 110864.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIU P, ZHONG X, NIU Y, et al. Reaction behaviors and mechanisms of tri-layer Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si environmental barrier coatings with molten calcium-magnesium-alumino-silicate. Corrosion Science, 2022, 197: 110069.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
TURCER L R, PADTURE N P. Towards multifunctional thermal environmental barrier coatings (TEBCs) based on rare-earth pyrosilicate solid-solution ceramics. Scripta Materialia, 2018, 154: 111.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
STEINBERG L, MIKULLA C, NARAPARAJU R, et al. Erosion behavior of CMAS/VA infiltrated EB-PVD Gd2Zr2O7 TBCs: special emphasis on the effect of mechanical properties of the reaction products. Wear, 2022, 506/507: 204450.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
QIAN B, WANG Y, ZU J, et al. A review on multicomponent rare earth silicate environmental barrier coatings. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2024, 29: 1231.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
VAKILIFARD H, SHAHBAZI H, LIBERATI A C, et al. High entropy oxides as promising materials for thermal barrier topcoats: a review. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2024, 33(2/3): 447.
DOI |
| [23] | DENG S, HE G, YANG Z, et al. Calcium-magnesium-alumina-silicate (CMAS) resistant high entropy ceramic (Y0.2Gd0.2Er0.2Yb0.2Lu0.2)2Zr2O7 for thermal barrier coatings. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 107: 259. |
| [24] |
LUO Z, JIANG J, DONG S, et al. (Gd0.2Ho0.2Er0.2Yb0.2Lu0.2)2Si2O7 and (Sc0.2Ho0.2Er0.2Yb0.2Lu0.2)2Si2O7 high-entropy rare-earth disilicates as promising materials for environmental barrier coatings. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(13): 23342.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SUN L, LUO Y, TIAN Z, et al. High temperature corrosion of (Er0.25Tm0.25Yb0.25Lu0.25)2Si2O7 environmental barrier coating material subjected to water vapor and molten calcium-magnesium- aluminosilicate (CMAS). Corrosion Science, 2020, 175: 108881.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
WANG X, MENG M, XU F, et al. (Lu1/7Yb1/7Sc1/7Er1/7Y1/7Ho1/7Dy1/7)2Si2O7 high entropy rare-earth disilicate with low thermal conductivity and excellent resistance to CMAS corrosion. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2024, 13(5): 549.
DOI URL |
| [27] | POERSCHKE D L. Developments in thermodynamic models of deposit-induced corrosion of high-temperature coatings. The Journal of the Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 2021, 74(1): 260. |
| [28] |
POERSCHKE D L, BARTH T L, FABRICHNAYA O, et al. Phase equilibria and crystal chemistry in the calcia-silica-yttria system. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(7): 1743.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
YAMANE H, NAGASAWA T, SHIMADA M, et al. Ca3Y2(SiO4)3. Acta Crystallographica Section C: Crystal Structure Communications, 1997, 53: 1367.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
GODBOLE E, VON DER HANDT A, POERSCHKE D. Apatite and garnet stability in the Al-Ca-Mg-Si-(Gd/Y/Yb)-O systems and implications for T/EBC: CMAS reactions. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2021, 105(2): 1596.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
PICCINELLI F, LAUSI A, SPEGHINI A, et al. Crystal structure study of new lanthanide silicates with silico-carnotite structure. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2012, 194: 233.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ZHANG G, ZHANG J, WANG J. Synthesis and characterization of ytterbium oxide: a novel CMAS-resistant environmental barrier coating material. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 106(1): 621.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
GODBOLE E, KARTHIKEYAN N, POERSCHKE D. Garnet stability in the Al-Ca-Mg-Si-Y-O system with implications for reactions between TBCs, EBCs, and silicate deposits. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(9): 5270.
DOI URL |
| [34] | SHANNON R D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomie distances. Acta Crystallographica Section A: Foundations of Crystallography, 1976, 25: 751. |
| [35] |
ZHANG G, SHI J, ZHANG J, et al. Investigation on crystallization behavior between (ScxYb1-x)O1.5 and CMAS: a new insight in the effect of Sc substitution. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2024, 13(6): 789.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ZHENG X, ZHANG L, LI Q, et al. Corrosion behavior and mechanism of aluminum-rich CMAS on rare-earth silicate environmental barrier coatings. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 544.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 樊文楷, 杨潇, 李宏华, 李永, 李江涛. 无压烧结制备(Y0.2Gd0.2Er0.2Yb0.2Lu0.2)2Zr2O7高熵陶瓷及其高温抗CMAS腐蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 159-167. |
| [2] | 李刘媛, 黄开明, 赵秀艺, 刘会超, 王超. RE-Si-Al-O玻璃相对高熵稀土双硅酸盐微结构及耐CMAS腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 793-802. |
| [3] | 李捷, 罗志新, 崔阳, 张广珩, 孙鲁超, 王京阳. 大气等离子喷涂Y3Al5O12/Al2O3陶瓷涂层的CMAS腐蚀抗力[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 671-680. |
| [4] | 范栋, 钟鑫, 王亚文, 张振忠, 牛亚然, 李其连, 张乐, 郑学斌. 富铝CMAS对稀土硅酸盐环境障涂层的腐蚀行为与机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 544-552. |
| [5] | 王苹,李心宇,时占领,李海涛. Ag与Ag2O协同增强TiO2光催化制氢性能的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(7): 781-788. |
| [6] | 范佳锋,张小锋,周克崧,刘敏,邓畅光,邓春明,牛少鹏,邓子谦. 镀铝改性对PS-PVD 7YSZ热障涂层抗CMAS腐蚀影响机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 938-946. |
| [7] | 张小锋, 周克崧, 宋进兵, 邓春明, 牛少鹏, 邓子谦. 等离子喷涂-物理气相沉积7YSZ热障涂层沉积机理及 其CMAS腐蚀失效机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(3): 287-293. |
| [8] | 赵彩霞,张伟德. 载钛(Ⅳ)锌(Ⅱ)纳米羟基磷灰石的制备及抗菌性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(6): 1243-1248. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||