|
|
Research Progress in Li3V2(PO4)3 as Polyanion-type Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries
QU Chao-Qun, WEI Ying-Jin, JIANG Tao
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 561–567
 Abstract
Abstract(
2719 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(439KB)(
2609
)
The polyanion-type cathode material of Li3V2(PO4)3 is an ideal cathode material for next-generation lithium-ion battery. It has attracted wide attention due to its comprehensive merits in high specific capacity, excellent structural stability, high operating-voltage, and low cost, etc. The structure, electrochemical properties, preparation methods, existing open questions and possible solutions of certain bottleneck issues of Li3V2(PO4)3 were discussed in detail in this paper. The research trends of Li3V2(PO4)3 cathode material was also prospected.
|
|
|
Theoretical and Experimental Investigations of the Effect of Co Addition on the Structural and Properties of AB3.5-type Hydrogen Storage Alloys
YING Yan-Jun, CHENG Li-Fang, ZENG Xiao-Qin, ZOU Jian-Xin, DING Wen-Jiang
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 568–574
 Abstract
Abstract(
1820 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(611KB)(
1295
)
The structures and electronic properties of designed alloys La0.75Mg0.25Ni3.5-xCox (x=0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75) were theoretically investigated by using density functional theory (DFT) of plane wave pseudopotential method. Calculation results showed that, with the increasing Co content, the charge transfer on La atom and the number of states at Fermi level (N(EF)) first increase and then slightly decrease, reaching maximum values at x=0.5. Meanwhile, La0.75Mg0.25Ni3.5-xCox (x=0, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7) alloys were prepared through induced melting method. The effects of substitution Co for Ni on the structure and properties of the alloys were systematically investigated. X-ray diffraction results show that the majority phase in the alloys is Ce2Ni7-type AB3.5 phase. The electrochemical analysis shows that both the discharge capacity and the cycling stability of the alloys reach the maximum values at x=0.5. It is observed from PCT measurements that the alloys can absorb hydrogen under 0.04–0.09 MPa hydrogen pressure at room temperature. Both the lowest absorption pressure of 0.04 MPa and the highest storage capacity of 1.587wt% were obtained with Co content of 0.5. The results clearly show that the property change of AB3.5 alloys with Co content can be predicted by first principle based theoretical calculations.

|
|
|
Microstructures and Microwave Dielectric Properties of (Mg1-xSrx)2Al4Si5O18 Ceramics
SONG Kai-Xin, YANG Yue-Qiang, ZHENG Peng, XU Jun-Ming, QIN Hui-Bin
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 575–579
 Abstract
Abstract(
1863 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(566KB)(
1917
)
(Mg1-xSrx)2Al4Si5O18 ceramics were fabricated by traditional ceramic sintering method. The phase transformation from β-Mg2Al4Si5O18 to α-Mg2Al4Si5O18 was accelerated and the width of sihtering range was boarded due to Sr ions doping. The XRD patterns show that the cordierite solid solution of (Mg,Sr)2Al4Si5O18 are kept in the range of 0≤x<0.2, and the feldspar solid solution of (Sr,Mg)Al2Si2O8 are kept in the range of 0.6<x≤1.0. Meanwhile, the change of feldspar’s crystal cell volumes complies with Vegard’s rules. SEM image show that the porosity and microcracks of cordierite ceramics are well suppressed due to Sr doping. The growth and distribution of feldspar particles are promoted. The dielectric constants of (Mg1-xSrx)2Al4Si5O18 ceramics keep at vicinity of 7.0 in the range of 0≤x≤0.4, then increase to 8.5 at the range of 0.6≤x≤1.0. The quality factors (Qf values) evidently increase from 24100 GHz at x=0 to 38900 GHz at x=0.2, then decrease continually to 14500 GHz at x=1.0.
|
|
|
Effect of Mechanical Milling on Structure, Morphology and Electrochemical Performance of Zinc Oxide Powders
LI Jia-Jia, ZHAO Xiang-Yu, MA Li-Qun, DU Wei, DING Yi
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 580–584
 Abstract
Abstract(
1904 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(501KB)(
1737
)
ZnO powders were treated by mechanical milling. The structure and morphology of ZnO powders milled for different periods were characterized by XRD and SEM. The discharge behavior and cycle life of ZnO electrodes in Zn/Ni batteries were studied by galvanostatic charge and discharge tests. The incorporation of cycle voltammetry was adopted to investigate charge and discharge mechanisms of ZnO electrodes. The results showed that the grain size of the powders decreased from 135.6 nm to 17.9 nm while the lattice strain increased from 0.06% to 0.57% during milling, which could be attributed to the formation and movement of dislocations. The electrochemical reaction activity of ZnO powders was improved by mechanical milling, resulting in an increase of discharge capacity. ZnO powders milled for 100 h shows a high discharge capacity of 300.6 mAh/g, which is 50 mAh/g higher than that of the unmilled ZnO powders.
|
|
|
Preparation and Photoelectric Properties of ZnO/TiO2 Nanotubes Film Electrodes
ZHAO Li, FAN Jia-Jie, LI Jing, DAI Guo-Tian, WANG Shi-Min
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 585–590
 Abstract
Abstract(
1855 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(374KB)(
1556
)
ZnO/TiO2 nanotubes were prepared using ZnO nanorods as raw materials, which were synthesized by hydrothermal methods. Then its performance as an electrode of a dye-sensitized solar cell was investigated. The obtained products were characterized by SEM, XRD, EDX and N2 adsorption. Furthermore, the photoelectric properties of ZnO/TiO2 nanotubes film electrodes calcined at different temperatures were investigated by UV-Vis adsorption spectra and electrochemical workstation. It is found that the DSSC based on ZnO/TiO2 nanotubes calcined at 600℃ have optimum photoelectric properties, Jsc=2.28 mA/cm2 and Voc= 0.631 V, yielding the 0.66% maximum conversion efficiency. Additionally, after TiCl4 posttreatment, the performance of DSSC made from ZnO/TiO2 nanotubes are improved obviously and the photoelectric conversion efficiency is up to 1.06%.
|
|
|
Facile Synthesis of Graphene/ZnO Nanocomposites by a Low-temperature Exfoliation Method
YUAN Wen-Hui, GU Ye-Jian, LI Bao-Qing, LI Li
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 591–595
 Abstract
Abstract(
3453 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(468KB)(
1973
)
Graphite oxide/ZnO was prepared at low temperature (80℃) with graphite oxide (GO) and zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO4·7H2O) as initial reactants. The graphene/ZnO (GNS/ZnO) was then prepared by a low-temperature chemical exfoliation method. The as-prepared GNS/ZnO was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscope (FT-IR), thermo-gravimetric analysis (TG), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Raman spectra (RS), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM), respectively. The results indicate that graphite oxide is completely reduced to graphene and the well-dispersed ZnO nanoparticles are successfully deposited on graphene sheets as spacers to keep the neighboring sheets separate. Photoluminescence spectra of ZnO and GNS/ZnO nanocomposites display the ?uorescence quenching property of GNS/ZnO, implying that the GNS/ZnO nanocomposites are expected for practical use in the field of photoelectronics.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Graphene Oxide/β-cyclodextrin Supramolecular Hybrid Material
ZHANG Shu-Peng, SONG Hai-Ou
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 596–602
 Abstract
Abstract(
2770 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(668KB)(
2406
)
A novel hybrid material based on graphene oxide was synthesized by utilizing organic synthesis and supramolecular self-assembly techniques. And the structures of graphene derivatives and product were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Thermogravimetric analysis (TG) shows that introduction of organic groups would significantly enhance the thermal stability of derivatives based on graphene oxide in the range of 50-400℃. The nanomaterial obtained has great potential practical significance and theoretical value to develop organic-inorganic hybrid materials based on graphene with novel features.
|
|
|
Effect of N2 Flow on Microstructure and Properties of CrNx Film Prepared by Unbalanced Magnetron Sputtering on the Surface of Depleted Uranium
ZHU Sheng-Fa, WU Yan-Ping, LIU Tian-Wei, YANG Suo-Long, TANG Kai, WEI Qiang
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 603–608
 Abstract
Abstract(
1788 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(437KB)(
1301
)
The chemical nature of depleted uranium is very active and susceptible to oxidation in nature environment. CrNx films were prepared by unbalanced magnetron sputtering ion plating at different N2 flow on the surface of depleted uranium to improve its corrosion resistance. The surface morphology, phase structure, chemical state and corrosion behavior of CrNx films were characterized by SEM, XRD, XPS, and polarization curves (E/I). The results show that, phase structure of CrNx film prepared at 10 sccm N2 flow is composed primarily of the bcc α-Cr. With the increasing of N2 flow, the phase structures transform to HCP-Cr2N and fcc CrN, which preferred orientation transforms from Cr(110) to Cr2N(111) and CrN(200). When N2 flow increases from 10 sccm to 50 sccm, the Cr2p3/2 XPS peaks move toward high binding energy side, the content of metal Cr decreases and the content of nitride chromium increases. When N2 flow increases to 30 sccm, CrNx film has fine grain and better density, its corrosion potential increases to 550 mV and corrosion current density decreases two orders of magnitude. After deposited CrNx film by unbalanced magnetron sputtering, the corrosion resistance of depleted uranium is effectively improved.

|
|
|
Characterization of Polytype Distributions in Nitrogen-doped 6H-SiC Single Crystal by Raman Mapping
GUO Xiao, LIU Xue-Chao, XIN Jun, YANG Jian-Hua, SHI Er-Wei
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 609–614
 Abstract
Abstract(
1948 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(497KB)(
1788
)
Nitrogen-doped 6H-SiC crystal with the diameter of 2-inch was grown along [0001] direction by physical vapor transport method. The spatial distribution of different polytypes such as 6H-SiC, 4H-SiC and 15R-SiC was characterized by mapping Raman spectra. The formation and evolution of different polytypes were investigated during the growth progress. 15R-SiC and 4H-SiC were observed in the as-grown 6H-SiC single crystal. Two different polytype regions are observed from the spatial distribution of different polytypes. One region originates from the growth interface of different polytypes. This region has higher nitrogen doping level and carrier concentration, and the area will become large during the growth process. The other region is dominated by 15R-SiC which appears in the main 6H-SiC due to the perturbation in growth temperature, pressure, etc. This region has less effect on the crystal quality, which could be inhibited by increasing the growth temperature.
|
|
|
Abnormal Relationship between Optical Basicity and Infrared Luminescence Properties of Bismuth-doped Aluminophosphate Glass
SONG Zhi-Guo, LI Chen,YANG Zheng-Wen, YIN Zhao-Yi, ZHOU Da-Cheng, SHANG Ji-Hua, YU Xue, QIU Jian-Bei
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 615–619
 Abstract
Abstract(
1896 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(341KB)(
1127
)
The effect of optical basicity on near infrared (NIR) luminescence properties of bismuth-doped aluminophosphate glasses was investigated. The result show that with increase in the radius of alkali metal ions in glass host, the intensity of NIR emission band at about 1300 nm from Bi ions increases, while the intensity of NIR emission band at 1100 nm decreases. The dependence of intensity of NIR emission band at 1300 nm on the optical basicity of glass host is found to be opposite to those in previous reports as well as to that of NIR emission band at 1100 nm. The infrared emissions peaked at 1100 and 1300 nm may originate from different valent Bi ion, and the relationship between optical basicity and infrared luminescence of bismuth-doped aluminophosphate glasses can be due to the reduction effect of glass matrix.
|
|
|
Thermal Etching Characteristics of AgInSbTe Phase Change Film
LI Hao, GENG Yong-You, WU Yi-Qun
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 620–626
 Abstract
Abstract(
1734 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(444KB)(
1344
)
The etching characteristics of the AgInSbTe phase change film as a new thermal lithography material were studied. The amorphous AgInSbTe film was deposited by using radio frequency magnetron sputtering method at room temperature, and then crystallized by vacuum-annealing. Using sodium hydroxide aqueous solution as etchant, influences of annealing temperature, etchant concentration and etching time on etching properties of the amorphous and crystalline AgInSbTe films were investigated. Experimental results indicate that the etching rate of the amorphous AgInSbTe film is lower than 0.04 nm/s in 0.001 mol/L sodium hydroxide solution. After vacuum-annealing, the etching rate of the film increases markedly and the etching selectivity between the crystalline and amorphous films increases with the increase of the annealing temperature. At the etching time of 20 min, the etching rate of the crystalline AgInSbTe film annealed at 300℃ is 45 times higher than that of the amorphous film. The surface quality of the AgInSbTe film after etching is good, and the surface roughness is less than 1nm in the area of 10 μm×10 μm. The wet-etching mechanism of the AgInSbTe film in sodium hydroxide solution is discussed.

|
|
|
Effect of Both Acid and Base Etching on Phosphate Laser Glass Surfaces
ZHANG Lei, HUANG Li, DING Jia, CHEN Hui-Yu, CHEN Wei, HU Li-Li
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 627–632
 Abstract
Abstract(
2042 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(491KB)(
1809
)
The effect of chemical etching processes on phosphate laser glass surfaces was investigated. Under different process conditions (e.g. sonication and agitation), conventionally polished and subsequently washed phosphate glass plates were treated by submerging in both HCl and KOH solution either with or without BaCl2. Subsequently, Raman spectra and X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS) of the treated surfaces were measured. The precipitation of metal cations and depolymerization of the glass network structure are the two main chemical reactions in both solutions: One refers to the substitution of P-O-H for P-O-M, the other is that the Q2 tetrahedra, the basic structural unit of the original metaphosphate glass, has gradually been replaced by the Q1 or Q0 tetrahedra. Finally, the reaction models of phosphate laser glasses dissolved in both HCl and KOH solution are proposed.
|
|
|
Impact of Thickness of Columnar Crystal TiO2 Film on Photocatalytic Activity of FTO/TiO2 Coated Glass
TENG Fan, LIU Yong, GE Yan-Kai, ZHANG Rui-Shuo, SONG Chen-Lu, HAN Gao-Rong
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 633–637
 Abstract
Abstract(
2081 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(464KB)(
1414
)
Columnar crystal structured TiO2 thin films were prepared on the FTO (SnO2: F) low-emissivity coated glass substrates, obtaining double-layer structure FTO/TiO2 coated glass samples. The effect of TiO2 film thickness on the photocatalytic activity, the low-emissivity performance and light transmission properties of the FTO/TiO2 coated glass samples was investigated. The results showed that the photocatalytic activity of the samples increased firstly and then decrease with the increase of the film thickness. The best catalytic activity was observed for the sample coated with 300 nm TiO2 film. The low-emissivity properties of the samples declined as the TiO2 film thickness increased. The sample still have some low-emissivity performance when the TiO2 film thickness is 300 nm, while the light transmittance of the samples have little relations with the TiO2 films thickness. The visible light transmittances of the samples remain at about 72% with a smooth surface. The average surface roughness of the sample is about 1 nm. The FTO/TiO2 coated glass has photocatalytic self-cleaning properties with excellent low emissive performance and light transmittance property, thus guaranteeing good application prospects.

|
|
|
Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2 Thin Films on Al Alloys
CAI Qian, WANG Jin-Shu, LI Hong-Yi, LIU Shao-Lin, LI Yu-Mei
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 638–642
 Abstract
Abstract(
1810 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(441KB)(
1064
)
Using anodized 6061 aluminum alloy and pure aluminum as the templates, TiO2 thin films were prepared through a liquid deposition method. The TiO2 thin film fabricated on the 6061 aluminum alloy substrates appears as bamboo-like structures with holes, whereas that prepared on anodized pure aluminum substrate has one-dimensional tubular structures. The main reason is that magnesium in aluminum alloy is oxidized to form magnesium oxide which has a lower volume than that of Al2O3. The photocatalytic ability of the TiO2 films prepared on the aluminum alloy is superior to that of the films fabricated on the pure aluminum. TiO2 prepared on aluminum alloy has higher specific surface area due to its bamboo-like structures with holes, leading to better performance in the degradation of methylene blue. The photocatalytic performance of the TiO2 by the degradation of aqueous methylene blue is in accordance with the first kinetic equation. TiO2 films deposited in 0.1 mol/L (NH4) TiF6 solution obtain the best photocatalytic performance at apparent reaction rate of 0.00444/min.

|
|
|
Preparation and Visible Light Responsive Photocatalytic Activity of Nitrogen-doped Bi2O3 Photocatalyst
LU Yuan-Gang, YANG Ying-Chun, YE Zhi-Xiang, LIU Sheng-Yu
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 643–648
 Abstract
Abstract(
2282 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(543KB)(
2374
)
Bi2O3 photocatalysts doped with different amounts of nitrogen were synthesized by a precipitation method using bismuth nitrate and hexamethylenetetramine as precursors. The as-synthesized samples were characterized and analyzed by XRD, FT-IR, XPS, UV-Vis and PL. The results indicate that the undoped Bi2O3 displays a single monoclinic phase. While the N-doped Bi2O3 samples are mixed crystals, which were composed of tetragonal β-Bi2O3 and Bi5O7NO3 phases. The oxygen in the lattice of Bi2O3 is partially substituted by nitrogen atom, existed stably in the form of Bi-N bond. Meanwhile, nitrogen dopant promotes the formation of β-Bi2O3 phase. Compared with undoped Bi2O3, the light absorption property of N-doped Bi2O3 has apparently extended into visible light region and the fluorescence intensity decreases evidently. Furthermore, the photodegradation performance of methyl orange shows that N-doped Bi2O3 samples have excellent visible light photocatalytic activity.
|
|
|
Preparation of TiO2 Nano-particles with Controllable Surface Charges for Electrophoretic Display
LIU Zhi-Jie, LI Xiang-Gao, WANG Shi-Rong
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 649–654
 Abstract
Abstract(
1761 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(484KB)(
1446
)
Preparation of TiO2 nano-particles with controllable surface charges for electrophoretic display was investigated in ethylene tetrachloride, Isopar H and dodecylbenzene, in which TiO2 nano-particles were modified by anionic surfactants, cationic surfactants and polymers, respectively. The research results showed that TiO2 nano-particles modified by cationic surfactants had negative charges in ethylene tetrachloride, while it had positive charges in Isopar H and dodecylbenzene, the nano-particles modified by anionic surfactants had the opposite character. The influence of concentration of charge control agents on TiO2 nano-particles surface charges was discussed, in which TiO2 nano-particles were modified by sodium dodecylbenzenesulphonate, hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and styrene/divinylbenzene, respectively. It was shown that ξ potential of TiO2 nano-particles had a minimum value near the critical micelle concentrations of the charge control agents, and a regular change with the increasing concentration, while the property of ξ potential was still maintained. So, preparation of controllable surface charges of TiO2 nano-particles can be achieved.v

|
|
|
Preparation of Cefradine/ Montmorillonite Intercalation Compound
ZHAO Yan-Zhao, GUO Wen-Ji, WANG Lan
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 655–659
 Abstract
Abstract(
1702 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(473KB)(
1202
)
The cefradine/montmorillonite compounds were prepared by pharmaceutical montmorillonite (MMT) and sodium-montmorillonite (Na-MMT) by the method of solution intercalation. The drug load was quantitatively measured by UV spectrophotometry. The structures of compounds were determined by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transformed infrared (FT-IR) spectroscope. The results show that cefradine can be intercalated into MMT mainly due to ion exchange, which cannot intercalate into MMT by mechanically mixing. Pharmaceutical MMT shows better ion exchange property after sodium modification, which is easily intercalated. The basal spacing of pharmaceutical MMT changes little after intercalation in water, however, the basal spacing of Na-MMT and pharmaceutical MMT after sodium modification increase.
|
|
|
Equilibrium and Kinetic Adsorption Study of the Removal of Orange-G Dye Using Carbon Mesoporous Material
KAVEH Arzani, BEHDAD Ghaderi Ashtiani, AMIRHOSSEIN Haji Aboutorab Kashi
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 660–666
 Abstract
Abstract(
5860 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(317KB)(
2004
)
Mesoporous carbon CMK-3 was synthesized by using SBA-15 silica mesoporous as hard template and characterized through nitrogen adsorption/desorption and low angle X-ray diffraction. As-prepared material with large pores and high surface area was used to remove Orange G dye from aqueous solution. Adsorption experiments were carried out as batch studies at variety of contact times, pH, initial dye concentrations, temperatures and salt concentrations. Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models were employed to simulate the equilibrium data of anionic dye. It was found that the equilibrium data were well represented by the Langmuir isotherm, yielding maximum monolayer adsorption capacity of 189 mg/g. Experimental data were analyzed using pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order kinetic models and obtained results indicated that kinetics followed a pseudo-second order equation.
|
|
|
A Microwave Approach to the Preparation of Sb-doped SnO2 Electrode
XU Hao, TANG Cheng-Li, ZHANG Qian, YAN Wei
2012 Vol. 27 (6): 667–672
 Abstract
Abstract(
5321 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(367KB)(
2032
)
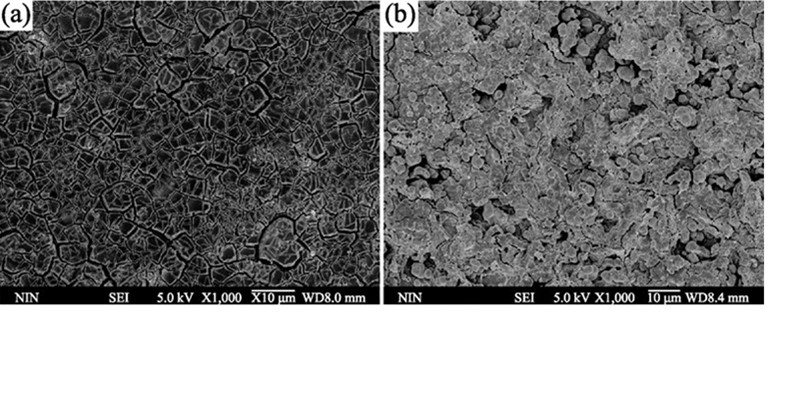
A novel method of microwave irradiation assisted thermal decomposition to prepare metal oxide electrodes was proposed in this paper. The electrodes were prepared by the microwave irradiation and the dip-coating method, respectively. The as-prepared electrodes were characterized with scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), linear sweep voltammetry and accelerated life test to find out the difference between the novel method and the traditional one. Wastewater degradation experiment was also carried out using the electrodes prepared with the above mentioned approaches, with Acid Red G as target pollutant. In comparison with the traditional dip-coating thermal decomposition method, the microwave irradiation method takes less time (2 h) and less complicated operation procedure. The results demonstrate that the electrode prepared by the novel microwave method is better in surface morphology, crystalline, stability and electro-catalytic property, comparing with that prepared by traditional method.
|
|