
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 415-424.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240378
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
YUAN Liping1( ), WU Yuanbo1, YU Jiajing1, ZHANG Shiyan1, SUN Yi1, HU Yunchu1, FAN Youhua2(
), WU Yuanbo1, YU Jiajing1, ZHANG Shiyan1, SUN Yi1, HU Yunchu1, FAN Youhua2( )
)
Received:2024-08-15
Revised:2024-12-16
Published:2025-04-20
Online:2024-12-27
Contact:
FAN Youhua, professor. E-mail: yh_fan@163.comAbout author:YUAN Liping (1975-), female, associate professor. E-mail: tiansiyuan@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
YUAN Liping, WU Yuanbo, YU Jiajing, ZHANG Shiyan, SUN Yi, HU Yunchu, FAN Youhua. CNFs Aerogel Composite with Phosphomolybdic Acid Intercalated Hydrotalcite: Preparation and Thermal Insulation Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 415-424.
| No. | Sample | CNFs/mL | NO3-LDHs/g | PMo-LDHs/g | BA/g | ρ/(kg·m-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CNFs | 10.0 | — | — | — | 10.01 |
| 2 | NO3-LDHs/CNFs | 10.0 | 0.0375 | — | — | 14.12 |
| 3 | PMo-LDHs/CNFs | 10.0 | — | 0.0375 | — | 14.23 |
| 4 | NO3-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 10.0 | 0.0375 | — | 0.0020 | 14.67 |
| 5 | PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 10.0 | — | 0.0375 | 0.0020 | 14.95 |
| 6 | 50.0PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 10.0 | — | 0.0500 | 0.0020 | 15.72 |
| 7 | 62.5PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 10.0 | — | 0.0625 | 0.0020 | 16.28 |
Table 1 Composition formula and density of LDHs/CNFs aerogel
| No. | Sample | CNFs/mL | NO3-LDHs/g | PMo-LDHs/g | BA/g | ρ/(kg·m-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CNFs | 10.0 | — | — | — | 10.01 |
| 2 | NO3-LDHs/CNFs | 10.0 | 0.0375 | — | — | 14.12 |
| 3 | PMo-LDHs/CNFs | 10.0 | — | 0.0375 | — | 14.23 |
| 4 | NO3-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 10.0 | 0.0375 | — | 0.0020 | 14.67 |
| 5 | PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 10.0 | — | 0.0375 | 0.0020 | 14.95 |
| 6 | 50.0PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 10.0 | — | 0.0500 | 0.0020 | 15.72 |
| 7 | 62.5PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 10.0 | — | 0.0625 | 0.0020 | 16.28 |
| Sample | d(003)/nm | d(006)/nm | d(009)/nm | d(110)/nm | 2θ(003)/(o) | a/nm | c/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO3-LDHs | 0.888 | 0.445 | 0.265 | 0.153 | 9.94 | 0.307 | 2.67 |
| PMo-LDHs | 0.975 | 0.488 | 0.267 | 0.153 | 9.06 | 0.306 | 2.92 |
Table 2 Interplanar spacing and lattice parameters of NO3-LDHs and PMo-LDHs
| Sample | d(003)/nm | d(006)/nm | d(009)/nm | d(110)/nm | 2θ(003)/(o) | a/nm | c/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO3-LDHs | 0.888 | 0.445 | 0.265 | 0.153 | 9.94 | 0.307 | 2.67 |
| PMo-LDHs | 0.975 | 0.488 | 0.267 | 0.153 | 9.06 | 0.306 | 2.92 |
| Sample | T1/℃ | R1/(%·℃-1) | T2/℃ | R2/(%·℃-1) | T50/℃ | M800/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNFs | 56.7 | 0.186 | 257.3 | 0.569 | 297.1 | 20.8 |
| NO3-LDHs/CNFs | 58.1 | 0.160 | 304.5 | 0.595 | 322.7 | 23.6 |
| PMo-LDHs/CNFs | 55.7 | 0.172 | 286.8 | 0.418 | 360.1 | 27.3 |
| NO3-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 48.2 | 0.157 | 305.6 | 0.587 | 348.7 | 27.2 |
| PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 53.5 | 0.169 | 295.8 | 0.401 | 381.2 | 27.6 |
| 50.0PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 51.8 | 0.154 | 294.1 | 0.352 | 423.4 | 31.9 |
| 62.5PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 50.7 | 0.127 | 282.2 | 0.306 | 620.2 | 38.9 |
Table 3 TG/DTG parameters of LDHs/CNFs aerogels
| Sample | T1/℃ | R1/(%·℃-1) | T2/℃ | R2/(%·℃-1) | T50/℃ | M800/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNFs | 56.7 | 0.186 | 257.3 | 0.569 | 297.1 | 20.8 |
| NO3-LDHs/CNFs | 58.1 | 0.160 | 304.5 | 0.595 | 322.7 | 23.6 |
| PMo-LDHs/CNFs | 55.7 | 0.172 | 286.8 | 0.418 | 360.1 | 27.3 |
| NO3-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 48.2 | 0.157 | 305.6 | 0.587 | 348.7 | 27.2 |
| PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 53.5 | 0.169 | 295.8 | 0.401 | 381.2 | 27.6 |
| 50.0PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 51.8 | 0.154 | 294.1 | 0.352 | 423.4 | 31.9 |
| 62.5PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 50.7 | 0.127 | 282.2 | 0.306 | 620.2 | 38.9 |
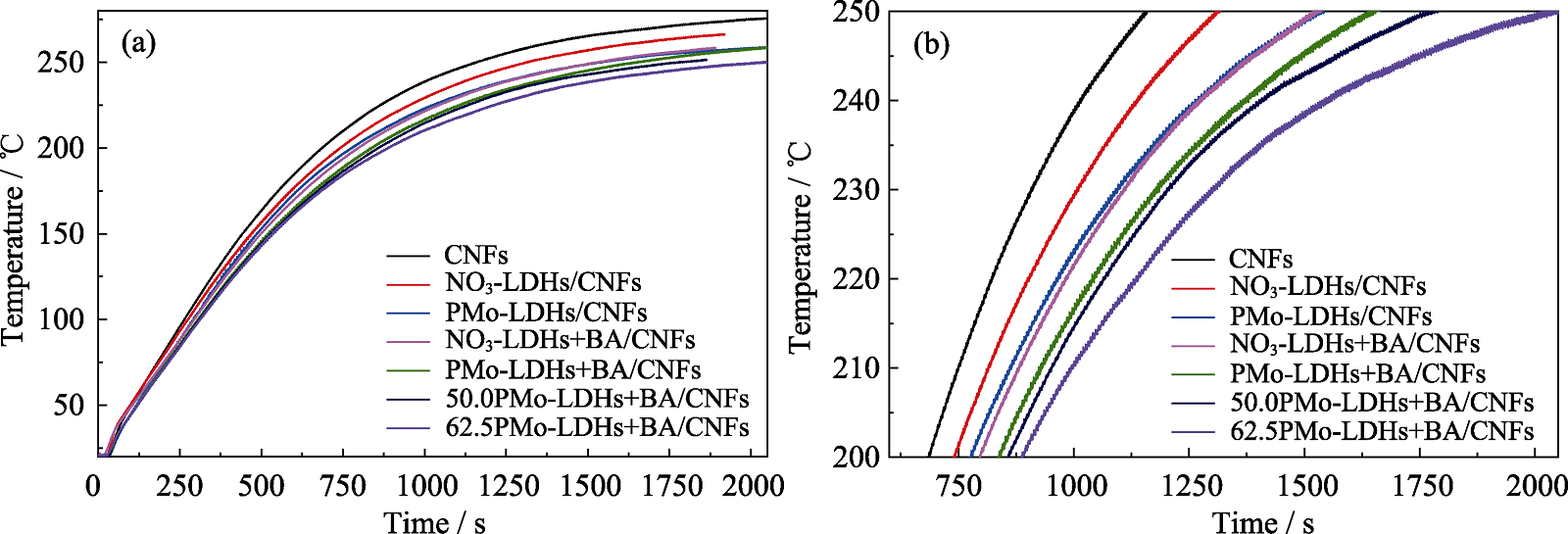
Fig. 8 Thermal insulation back-fire temperature curves (a) and magnified curves of thermal insulation back-fire temperature curves after 750 s (b) of LDHs/CNFs aerogels Colorful figures are available on website
| Sample | t200/s | t250/s | R200/(℃·s-1) | R250/(℃·s-1) | λ/(W·m-1·K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNFs | 685.4 | 1155.0 | 0.292 | 0.216 | 0.045 |
| NO3-LDHs/CNFs | 739.4 | 1306.6 | 0.270 | 0.191 | — |
| PMo-LDHs/CNFs | 776.7 | 1527.5 | 0.258 | 0.164 | — |
| NO3-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 793.5 | 1524.4 | 0.252 | 0.164 | 0.047 |
| PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 837.6 | 1642.6 | 0.239 | 0.152 | — |
| 50.0PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 857.6 | 1771.2 | 0.233 | 0.141 | — |
| 62.5PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 886.5 | 2022.8 | 0.226 | 0.124 | 0.044 |
Table 4 Thermal insulation back-fire temperature test parameters and thermal conductivity of LDHs/CNFs aerogels
| Sample | t200/s | t250/s | R200/(℃·s-1) | R250/(℃·s-1) | λ/(W·m-1·K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNFs | 685.4 | 1155.0 | 0.292 | 0.216 | 0.045 |
| NO3-LDHs/CNFs | 739.4 | 1306.6 | 0.270 | 0.191 | — |
| PMo-LDHs/CNFs | 776.7 | 1527.5 | 0.258 | 0.164 | — |
| NO3-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 793.5 | 1524.4 | 0.252 | 0.164 | 0.047 |
| PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 837.6 | 1642.6 | 0.239 | 0.152 | — |
| 50.0PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 857.6 | 1771.2 | 0.233 | 0.141 | — |
| 62.5PMo-LDHs+BA/CNFs | 886.5 | 2022.8 | 0.226 | 0.124 | 0.044 |
| [1] | LI Y G, LIU X F, DONG L H, et al. Preparation and high- temperature service performance of hierarchically pore-structured BN fiber aerogels. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(24):36287. |
| [2] | JIN R Z, ZHOU Z H, LIU J, et al. Aerogels for thermal protection and their application in aerospace. Gels, 2023, 9(8):606. |
| [3] | GUO P F, SU L, PENG K, et al. Additive manufacturing of resilient SiC nanowire aerogels. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(4):6625. |
| [4] | LIAO Y R, ZHANG S Z, YANG Z Y, et al. Ambient drying to fabricate polybenzoxazine aerogels for thermal insulation in aerospace. Materials Today Nano, 2024, 28: 100517. |
| [5] |
杨冬晖, 李猛, 尚坤. 航天服隔热材料技术研究进展. 航空材料学报, 2016, 36(2):87.
DOI |
| [6] |
CHHOWALLA M, JARIWALA D. Hyperbolic 3D architectures with 2D ceramics. Science, 2019, 363(6428):694.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | LI M M, XU Q Y, JIANG W, et al. Preparation and investigation of Fe3O4@rGO/CNF foams for electromagnetic interference shielding. Fibers and Polymers, 2023, 24: 771. |
| [8] | ZHOU X J, LI B, XU Y, et al. Tannin-furanic resin foam reinforced with cellulose nanofibers (CNF). Industrial Crops & Products, 2019, 134: 107. |
| [9] | SONG Y P, XUE C H, GUO W C, et al. Foamed geopolymer insulation materials: research progress on insulation performance and durability. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 444: 140991. |
| [10] | ZHAO J J, LI S, TANG Y M. Preparation of building insulation foam materials by recycling industrial and agroforestry wastes. Journal of Building Engineering, 2023, 68: 105988. |
| [11] | BURATTI C, BELLONI E, LASCARO E, et al. Rice husk panels for building applications: thermal, acoustic and environmental characterization and comparison with other innovative recycled waste materials. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 171: 338. |
| [12] | MUTHURAJ R, LACOSTE C, LACROIX P, et al. Sustainable thermal insulation biocomposites from rice husk, wheat husk, wood fibers and textile waste fibers: elaboration and performances evaluation. Industrial Crops and Products, 2019, 135: 238. |
| [13] | ALI M, ALABDULKAREM A, NUHAIT A, et al. Thermal and acoustic characteristics of novel thermal insulating materials made of eucalyptus globulus leaves and wheat straw fibers. Journal of Building Engineering, 2020, 32: 101. |
| [14] | LIU L, LI H Q, LAZZARETTO A, et al. The development history and prospects of biomass-based insulation materials for buildings. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 69: 912. |
| [15] | KUMAR D, ALAM M, ZOU P X W, et al. Comparative analysis of building insulation material properties and performance. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 131: 110. |
| [16] | WANG D, FENG X M, ZHANG L P, et al. Cyclotriphosphazene- bridged periodic mesoporous organosilica-integrated cellulose nanofiber aniso-tropic foam with highly flame-retardant and thermally insulating properties. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 375: 121933. |
| [17] | CHRISTINE T G, VANESSA P, CLAUDE F, et al. Tailoring hybrid layered double hydroxides for the development of innovative applications. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 28(27):1702868. |
| [18] |
GUO Y X, WANG J, LI D Q, et al. Micrometer-sized dihydrogenphosphate-intercalated layered double hydroxides: synthesis, selective infrared absorption properties, and applications as agricultural films. Dalton Trans, 2018, 47(9):3144.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | HUANG F L, TIAN S Q, QI Y, et al. Synthesis of FePcS-PMA-LDH cointercalation composite with enhanced visible light photo-fenton catalytic activity for BPA degradation at circumneutral pH. Materials, 2020, 13(8): 1951. |
| [20] | PENG Y, WANG W, CAO J Z, et al. Synthesis of 5-sulfosalicylic acid-intercalated layered double hydroxide and its effects on wood flour/polypropylene composites during accelerated UV weathering. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2017, 134(11):44597. |
| [21] | LI L, MA R Z, EBINA Y, et al. Positively charged nanosheets derived via total delamination of layyered doubled hydroxides. Chemistry of Materials, 2005, 17: 4386. |
| [22] | ZHANG L L, CHEN K L, HE L. Super-reinforced photothermal stability of cellulose nanofibrils films by armour-type ordered doping Mg-Al layered double hydroxides. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2019, 212: 229. |
| [23] | ZHANG Z, SONG F F, ZHANG M, et al. Cellulose nanopaper with controllable optical haze and high efficiency ultraviolet blocking for flexible optoelectronics. Cellulose, 2019, 26(4): 2201. |
| [24] | DENG Y, GUAN Q Q, HE L, et al. The photothermal stability of CNFs/ ZnAl-LDHs composited films: influence of the crystal morphology of ZnAl-LDHs. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2021, 263: 117981. |
| [25] | KAUL P K, SAMSON J A, SELVAN T G, et al. Synergistic effect of LDH in the presence of organophosphate on thermal and flammable properties of an epoxy nanocomposite. Applied Clay Science, 2017, 135: 234. |
| [26] | CHEN C, TAO L, DU S Q, et al. Advanced exfoliation strategies for layered double hydroxides and applications in energy conversion and storage. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(14):1909832. |
| [27] | CHEN X, WAG B Y, HAO Z F, et al. Synergistic effect of multifunctional layered double hydroxide based hybrids and modified phosphagen with an active amino group for enhancing the smoke suppression and flame retardancy of epoxy. ACS Omega, 2022, 7(25):21714. |
| [28] | ZHANG S, YAN Y X, WANG W J, et al. Intercalation of phosphotungstic acid into layered double hydroxides by reconstruction method and its application in intumescent flame retardant poly (lactic acid) composites. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2018, 147: 142. |
| [29] | XU Y, HUANG W J, CHEN X Y, et al. Self-assembled ZnAl-LDH/PMo12 nano-hybrids as effective catalysts on the degradation of methyl orange under room temperature and ambient pressure. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2018, 550: 206. |
| [30] | MENG R R, HE X M, CHEN J J, et al. Silver and sodium fluorescein co-doped phosphomolybdate microspindle: synthesis and spectroscopic properties. Journal of Cluster Science, 2019, 30: 141. |
| [31] | LI C, WU S P, CHEN Z W, et al. Synthesis of Fe3O4-decorated Mg-Al layered double hydroxides magnetic nanosheets to improve anti-ultraviolet aging and microwave absorption properties used in asphalt materials. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 30(220):320. |
| [32] | LI W, ZHU J N, SHEN N N, et al. Assembling [M(P4Mo6)2] (M = Na, Mn, Na/Cu) dimeric clusters via transition metal/sodium ions into 0D to 3D phosphomolybdates. CrystEngComm, 2019, 21: 971. |
| [33] | HONG N N, SONG L, WANG B B, et al. Co-precipitation synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/NiAl-layered double hydroxide hybrid and its application in flame retarding poly (methyl methacrylate). Materials Research Bulletin, 2014, 49: 657. |
| [1] | LI Fuping, CHU Jiabao, QIU Haibo, DANG Wei, LI Chenxi, ZHAO Kang, TANG Yufei. Compressive Resilience Mechanism of SiO2 Nanofibre Aerogels [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 981-988. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xiangsong, LIU Yetong, WANG Yongying, WU Zirui, LIU Zhenzhong, LI Yi, YANG Juan. Self-assembled Platinum-iridium Alloy Aerogels and Their Efficient Electrocatalytic Ammonia Oxidation Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 511-520. |
| [3] | LUO Yi, XIA Shuhai, NIU Bo, ZHANG Yayun, LONG Donghui. Preparation and High Temperature Inorganic Transformation of Flexible Silicone Aerogels [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1281-1288. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xiaoshan, WANG Bing, WU Nan, HAN Cheng, LIU Haiyan, WANG Yingde. Infrared Radiation Shielded SiZrOC Nanofiber Membranes: Preparation and High-temperature Thermal Insulation Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 93-100. |
| [5] | PENG Fei, JIANG Yonggang, FENG Jian, CAI Huafei, FENG Junzong, LI Liangjun. Research Progress on Alumina Aerogel Composites for High-temperature Thermal Insulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 673-684. |
| [6] | ZHANG Xiaoshan, WANG Bing, WU Nan, HAN Cheng, WU Chunzhi, WANG Yingde. Micro-nano Ceramic Fibers for High Temperature Thermal Insulation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 245-256. |
| [7] | PAN Bichen,REN Penghe,ZHOU Tejun,CAI Zhenyang,ZHAO Xiaojun,ZHOU Hongming,XIAO Lairong. Microstructure and Property of Thermal Insulation Coating on the Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Resin Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 947-952. |
| [8] | ZHANG Ze,WANG Xiaodong,SHEN Jun. Effect of Organic-inorganic Crosslinking Degree on the Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Aerogels [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 454-460. |
| [9] | LUO Yi,FENG Junzong,FENG Jian,JIANG Yonggang,LI Liangjun. Research Progress on Advanced Carbon Materials as Pt Support for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(4): 407-415. |
| [10] | LIU Fengqi, FENG Jian, JIANG Yonggang, LI Liangjun. Preparation and Application of Boron Nitride Aerogels [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1193-1202. |
| [11] | DING Zhuofeng, YANG Yongqiang, LI Zaijun. Synthesis and Supercapacitor Performance of Histidine-functionalized Carbon Dots/Graphene Aerogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1130-1136. |
| [12] | LYU Ziye, TANG Yiping, CAO Huazhen, ZHENG Guoqu, HOU Guangya. Effect of V Doping on Electrocatalytic Performance of Ni-Co-S on Bacterial Cellulose-derived Carbon Aerogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1142-1148. |
| [13] | ZHU Zhao-Xian,WANG Fei,YAO Hong-Jun,DONG Jin-Xin,LONG Dong-Hui. High-temperature Insulation Property of Opacifier-doped Al2O3-SiO2 Aerogel/Mullite Fiber Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(9): 969-975. |
| [14] | WANG Yong, YU Yun, FENG Ai-Hu, JIANG Feng, HU Xue-Bing, SONG Li-Xin. Nafion Modified Graphene Aerogel with Hierarchical Porous Structures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(4): 469-474. |
| [15] | YANG Jing-Feng, WANG Qi-Hua, WANG Ting-Mei. Synthesis and Property of Alumina Aerogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(3): 259-265. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||