
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 942-948.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170538
Special Issue: 光催化材料与技术; 环境材料优选论文
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHENG Peng, ZHAO Guang-Yao, XU Li, LIU Shuang-Yu, WANG Bo, LIU Hai-Zhen, MA Guang, HAN Yu, CHEN Xin
Received:2017-12-19
Revised:2018-02-02
Published:2018-09-20
Online:2018-08-14
Supported by:CLC Number:
SHENG Peng, ZHAO Guang-Yao, XU Li, LIU Shuang-Yu, WANG Bo, LIU Hai-Zhen, MA Guang, HAN Yu, CHEN Xin. Reductive Preparation of Blue TiO2 via Deposition of Aluminum[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(9): 942-948.
| Samples | Elemental compositions/wt% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XPS | ICP | |||
| Ti | O | Al | Al | |
| TiO2(P25) | 26.4 | 73.6 | — | — |
| TiO2-x | 39.4 | 60.6 | — | — |
| TiO2-Al0.36 | 47.5 | 49.8 | 2.72 | 0.36 |
| TiO2-Al1.37 | 35.8 | 59.0 | 5.19 | 1.37 |
Table 1 Elemental analysis of intrinsic P25 and TiO2-x-Aly
| Samples | Elemental compositions/wt% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XPS | ICP | |||
| Ti | O | Al | Al | |
| TiO2(P25) | 26.4 | 73.6 | — | — |
| TiO2-x | 39.4 | 60.6 | — | — |
| TiO2-Al0.36 | 47.5 | 49.8 | 2.72 | 0.36 |
| TiO2-Al1.37 | 35.8 | 59.0 | 5.19 | 1.37 |

Fig. 6 PL spectra (a), photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange (b) of intrinsic P25 and TiO2-x-Aly and photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange (c) of TiO2-Al0.36
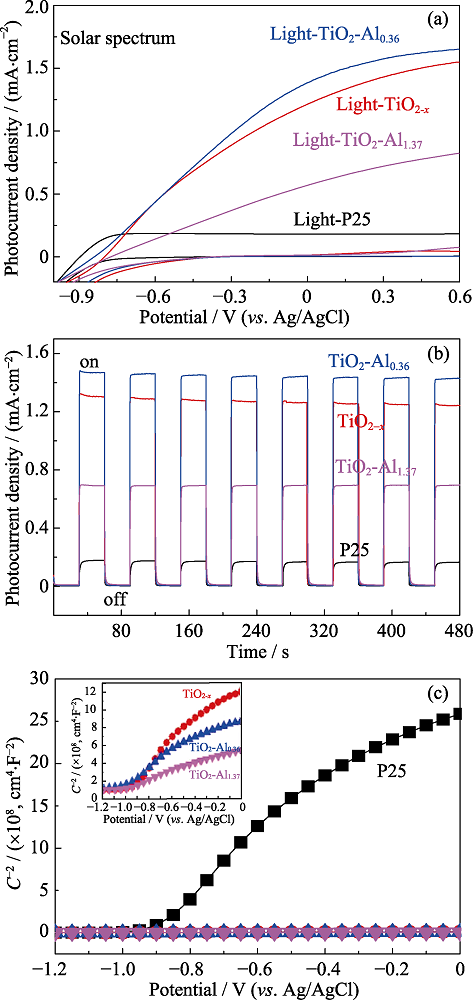
Fig. 7 (a) LSV curves under simulated sunlight irradiation, (b) transient photocurrent curve under full spectra irradiation (0.23 V vs. SCE), and Mott-Schottky curve with no sunlight irradiation at 1 kHz of intrinsic P25 and TiO2-x-Aly
| [1] | GRATZEL M.Photoeletrochemical cells.Nature, 2001, 414(6861): 338-344. |
| [2] | HOFFMANN M R, MARTIN S T, CHOI W Y,et al. Environmental applications of semiconductor photocatalysis. Chemical Reviews, 1995, 95(1): 69-96. |
| [3] | FUJISHIMA A, HONDA K.Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode.Nature, 1972, 238(5358): 37. |
| [4] | CHEN X, MAO S S.Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications.Chemical Reviews, 2007, 107(7): 2891-2959. |
| [5] | LU X J, MOU X L, WU J J,et al. Improved-performance dye-sensitized solar cells using Nb-doped TiO2 electrodes: efficient electron injection and transfer. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 20(3): 509-515. |
| [6] | LU X J, HUANG F Q, MOU X L,et al. A general preparation strategy for hybrid TiO2 hierarchical spheres and their enhanced solar energy utilization efficiency. Advanced Materials, 2010, 22(33): 3719-3722. |
| [7] | SHANKAR K, BASHAM J I, ALLAM N K,et al. Recent advances in the use of TiO2 nanotube and nanowire arrays for oxidative photoelectrochemistry. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113(16): 6327-6359. |
| [8] | HENDERSON M A.A surface science perspective on TiO2 photocatalysis.Surface Science Reports, 2011, 66(6/7): 185-297. |
| [9] | LIU L, CHEN X B.Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: self-structural modifications.Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(19): 9890-9918. |
| [10] | MA Y, WANG X L, JIA Y S,et al. Titanium dioxide-based nanomaterials for photocatalytic fuel generations. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(19): 9987-10043. |
| [11] | CHEN C C, MA W H, ZHAO J C.Semiconductor-mediated photodegradation of pollutants under visible-light irradiation.Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(11): 4206-4219. |
| [12] | CHEN X B, LIU L, HUANG F Q.Black titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanomaterials.Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(7): 1861-1885. |
| [13] | DE ANGELIS F, DI VALENTIN C, FANTACCI S,et al. Theoretical studies on anatase and less common TiO2 phases: bulk, surfaces, and nanomaterials. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(19): 9708-9753. |
| [14] | DAHL M, LIU Y D, YIN Y D.Composite titanium dioxide nanomaterials.Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(19): 9853-9889. |
| [15] | LIU G, YANG H G, PAN J,et al. Titanium dioxide crystals with tailored facets. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(19): 9559-9612. |
| [16] | PAN X Y, YANG M Q, FU X Z,et al. Defective TiO2 with oxygen vacancies: synthesis, properties and photocatalytic applications. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(9): 3601-3614. |
| [17] | REICHE H, BARD A J.Heterogeneous photosynthetic production of amino-acids from methane-ammonia-water at Pt-TiO2. implications in chemical evolution.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1979, 101(11): 3127-3128. |
| [18] | LINSEBIGLER A L, LU G Q, YATES J T.Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: principles, mechanisms, and selected results.Chemical Reviews, 1995, 95(3): 735-758. |
| [19] | CHEN X B, SHEN S H, GUO L J,et al. Semiconductor-based photocatalytic hydrogen generation. Chemical Reviews, 2010, 110(11): 6503-6570. |
| [20] | SCHNEIDER J, MATSUOKA M, TAKEUCHI M,et al. Understanding TiO2 photocatalysis: mechanisms and materials. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(19): 9919-9986. |
| [21] | TSAI C Y, HIS H C, BAI H, et al. Single-step synthesis of Al-doped TiO2 nanoparticles using non-transferred thermal plasma torch. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 51(1): 01AL01. |
| [22] | LEE J E, OH S M, PARK D W.Synthesis of nano-sized Al doped TiO2 powders using thermal plasma.Thin Solid Films, 2004, 457(1): 230-234. |
| [23] | LIU S Y, LIU G C, FENG Q G.Al-doped TiO2 mesoporous materials: synthesis and photodegradation properties.Journal of Porous Materials, 2010, 17(2): 197-206. |
| [24] | KIM S K, CHOI G J, LEE S Y,et al. Al-doped TiO2 films with ultralow leakage currents for next generation dram capacitors. Advanced Materials, 2008, 20(8): 1429-1435. |
| [25] | WANG Z, YANG C Y, LIN T Q,et al. Visible-light photocatalytic, solar thermal and photoelectrochemical properties of aluminium- reduced black titania. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(10): 3007-3014. |
| [26] | WANG M Q, GONG B, YAO X,et al. Preparation and microstructure properties of Al-doped TiO2-SiO2 gel-glass film. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 515(4): 2055-2058. |
| [27] | LI C Z, SHI L Y, XIE D M,et al. Morphology and crystal structure of Al-doped TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by vapor phase oxidation of titanium tetrachloride. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2006, 352(38/39): 4128-4135. |
| [28] | TAYLOR M L, MORRIS G E, SMART R S.Influence of aluminum doping on titania pigment structural and dispersion properties.Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2003, 262(1): 81-88. |
| [29] | ISLAM M M, BREDOW T, GERSON A. Electronic properties of oxygen-deficient and aluminum-doped rutile TiO2 from first principles. Physical Review B, 2007, 76(4): 045217-1-9. |
| [30] | CHOI Y J, SEELEY Z, BANDYOPADHYAY A,et al. Aluminum- doped TiO2 nano-powders for gas sensors. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2007, 124(1): 111-117. |
| [31] | WANG Z, YANG C Y, LIN T Q,et al. H-doped black titania with very high solar absorption and excellent photocatalysis enhanced by localized surface plasmon resonance. Advanced Functional Materials, 2013, 23(43): 5444-5450. |
| [32] | CHEN X B, LIU L, YU P Y,et al. Increasing solar absorption for photocatalysis with black hydrogenated titanium dioxide nanocrystals. Science, 2011, 331(6018): 746-750. |
| [33] | LI L D, YAN J Q, WANG T,et al. Sub-10 nm rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles for efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen production. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 5881. |
| [34] | LEI F C, SUN Y F, LIU KT,et al. Oxygen vacancies confined in ultrathin indium oxide porous sheets for promoted visible-light water splitting. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(19): 6826-6829. |
| [35] | TSAI C Y, KUO T H, HIS H C.Fabrication of Al-doped TiO2 visible- light photocatalyst for low-concentration mercury removal.International Journal of Photoenergy, 2012(2): 483-490. |
| [36] | PARKER J C, SIEGEL R W.Raman microprobe study of nanophase TiO2 and oxidation-induced spectral changes.Journal of Materials Research, 1990, 5(6): 1246-1252. |
| [37] | LI BASSI A, CATTANEO D, RUSSO V, ,et al. Raman spectroscopy characterization of titania nanoparticles produced by flame pyrolysis: the influence of size. Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 98(7): 074305-1-9. |
| [38] | CORONADO J M, MAIRA A J, CONESA J C,et al. EPR study of the surface characteristics of nanostructured TiO2 under UV irradiation. Langmuir, 2001, 17(17): 5368-5374. |
| [39] | XIONG L B, LI J L, YANG B, ,et al. Ti3+ in the surface of titanium dioxide: generation, properties and photocatalytic application. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2012: 831524-1-13. |
| [40] | CUI H, ZHAO W, YANG C Y,et al. Black TiO2 nanotube arrays for high-efficiency photoelectrochemical water-splitting. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(23): 8612-8616. |
| [41] | YIN H, LIN T Q, YANG C Y,et al. Gray TiO2 nanowires synthesized by aluminum-mediated reduction and their excellent photocatalytic activity for water cleaning. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2013, 19(40): 13313-13316. |
| [42] | ZHU G L, LIN T Q, LU X J,et al. Black brookite titania with high solar absorption and excellent photocatalytic performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(34): 9650-9653. |
| [43] | BERTOTI I, MOHAI M, SULLIVAN J L,et al. Surface characterization of plasma-nitrided titanium: an XPS study. Applied Surface Science, 1995, 84(4): 357-371. |
| [44] | RAHMAN M M, KRISHNA K M, SOGA T,et al. Optical properties and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study of pure and Pb-doped TiO2 thin films. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1999, 60(2): 201-210. |
| [45] | GESENHUES U.Al-doped TiO2 pigments: influence of doping on the photocatalytic degradation of alkyd resins.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A-Chemistry, 2001, 139(2/3): 243-251. |
| [46] | LUO Z H, GAO Q H.Decrease in the photoactivity of TiO2 pigment on doping with transition-metals.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A-Chemistry, 1992, 63(3): 367-375. |
| [1] | FAN Xiaoxuan, ZHENG Yonggui, XU Lirong, YAO Zimin, CAO Shuo, WANG Kexin, WANG Jiwei. Organic Pollutant Fenton Degradation Driven by Self-activated Afterglow from Oxygen-vacancy-rich LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ Long Afterglow Phosphor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 481-488. |
| [2] | JIA Xianghua, ZHANG Huixia, LIU Yanfeng, ZUO Guihong. Cu2O/Cu Hollow Spherical Heterojunction Photocatalysts Prepared by Wet Chemical Approach [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 397-404. |
| [3] | MA Binbin, ZHONG Wanling, HAN Jian, CHEN Liangyu, SUN Jingjing, LEI Caixia. ZIF-8/TiO2 Composite Mesocrystals: Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 937-944. |
| [4] | CAO Qingqing, CHEN Xiangyu, WU Jianhao, WANG Xiaozhuo, WANG Yixuan, WANG Yuhan, LI Chunyan, RU Fei, LI Lan, CHEN Zhi. Visible-light Photodegradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride on Self-sensitive Carbon-nitride Microspheres Enhanced by SiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 787-792. |
| [5] | WANG Zhaoyang, QIN Peng, JIANG Yin, FENG Xiaobo, YANG Peizhi, HUANG Fuqiang. Sandwich Structured Ru@TiO2 Composite for Efficient Photocatalytic Tetracycline Degradation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 383-389. |
| [6] | WU Lin, HU Minglei, WANG Liping, HUANG Shaomeng, ZHOU Xiangyuan. Preparation of TiHAP@g-C3N4 Heterojunction and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [7] | LING Jie, ZHOU Anning, WANG Wenzhen, JIA Xinyu, MA Mengdan. Effect of Cu/Mg Ratio on CO2 Adsorption Performance of Cu/Mg-MOF-74 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1379-1386. |
| [8] | SUN Chen, ZHAO Kunfeng, YI Zhiguo. Research Progress in Catalytic Total Oxidation of Methane [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1245-1256. |
| [9] | MA Xinquan, LI Xibao, CHEN Zhi, FENG Zhijun, HUANG Juntong. BiOBr/ZnMoO4 Step-scheme Heterojunction: Construction and Photocatalytic Degradation Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [10] | CHEN Hanxiang, ZHOU Min, MO Zhao, YI Jianjian, LI Huaming, XU Hui. 0D/2D CoN/g-C3N4 Composites: Structure and Photocatalytic Performance for Hydrogen Production [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [11] | XUE Hongyun, WANG Congyu, MAHMOOD Asad, YU Jiajun, WANG Yan, XIE Xiaofeng, SUN Jing. Two-dimensional g-C3N4 Compositing with Ag-TiO2 as Deactivation Resistant Photocatalyst for Degradation of Gaseous Acetaldehyde [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [12] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [13] | WANG Xiaojun, XU Wen, LIU Runlu, PAN Hui, ZHU Shenmin. Preparation and Properties of Ag@C3N4 Photocatalyst Supported by Hydrogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [14] | LIU Xuechen, ZENG Di, ZHOU Yuanyi, WANG Haipeng, ZHANG Ling, WANG Wenzhong. Selective Oxidation of Biomass over Modified Carbon Nitride Photocatalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 38-44. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xian, ZHANG Ce, JIANG Wenjun, FENG Deqiang, YAO Wei. Synthesis, Electronic Structure and Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance of Quaternary BiMnVO5 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||