
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 582-586.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170283
Special Issue: 光催化材料与技术
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles
ZHANG Zhi-Jie1, XU Jia-Yue1, ZENG Hai-Bo1,2, ZHANG Na1
Received:2017-06-06
Revised:2017-08-21
Published:2018-05-20
Online:2018-04-26
About author:Zhang Zhi-Jie (1984), PhD. E-mail: zjzhang@sit.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHANG Zhi-Jie, XU Jia-Yue, ZENG Hai-Bo, ZHANG Na. Carbon Quantum Dots/BiPO4 Nanocomposites with Enhanced Visible-light Absorption and Charge Separation[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(5): 582-586.
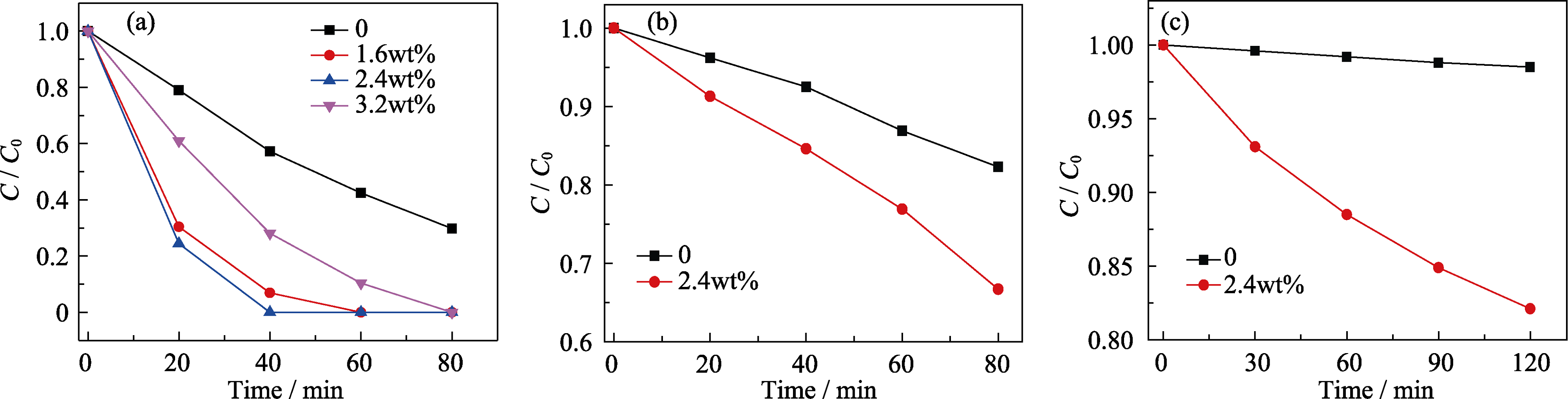
Fig. 4 (a) Degradation efficiency of RhB as a function of time by pure BiPO4 and CQDs/BiPO4 composites with different amounts of CQDs under simulated solar light irradiation; degradation efficiency of RhB (b) and phenol (c) as a function of time by pure BiPO4 and CQDs/BiPO4 composites (2.4wt%) under visible light irradiation (λ>420 nm)
| [1] | RAY S C, SAHA A, JANA N R,et al. Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and bioimaging application. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113(43): 18546-18551. |
| [2] | TANG L B, JI R B, CAO X K,et al. Deep ultraviolet photoluminescence of water-soluble self-passivated graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(6): 5102-5110. |
| [3] | LI H T, HE X D, LIU Y,et al. One-step ultrasonic synthesis of water- soluble carbon nanoparticles with excellent photoluminescent properties. Carbon, 2011, 49(2): 605-609. |
| [4] | YANG S T, CAO L, LUO P G,et al. Carbon dots for optical imaging in vivo. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(32): 11308-11309. |
| [5] | CAO L, SAHU S, ANILKUMAR P,et al. Carbon nanoparticles as visible-light photocatalysts for efficient CO2 conversion and beyond. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(13): 4754-4757. |
| [6] | SHI W, LI X H, MA H M.A tunable ratiometric pH sensor based on carbon nanodots for the quantitative measurement of the intracellular pH of whole cells.Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(26): 6432-6435. |
| [7] | CAO L, WANG X, MEZIANI M J,et al. Carbon dots for multiphoton bioimaging. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(37): 11318-11319. |
| [8] | SHEN J, ZHU Y, CHEN C,et al. Facile preparation and upconversion luminescence of graphene quantum dots. Chemical Communications, 2011, 47: 2580-2582. |
| [9] | LI H T, LIU R H, LIAN S Y,et al. Near-infrared light controlled photocatalytic activity of carbon quantum dots for highly selective oxidation reaction. Nanoscale, 2013, 5: 3289-3297. |
| [10] | MING H, MA Z, LIU Y,et al. Large scale electrochemical synthesis of high quality carbon nanodots and their photocatalytic property. Dalton Transactions, 2012, 41: 9526-9531. |
| [11] | YU X J, LIU J J, YU Y C,et al. Preparation and visible light photocatalytic activity of carbon quantum dots/TiO2 nanosheet composites. Carbon, 2014, 68: 718-724. |
| [12] | PAN J Q, SHENG Y Z, ZHANG J X,et al. Preparation of carbon quantum dots/TiO2 nanotubes composites and their visible light catalytic applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2: 18082-18086. |
| [13] | YU H, ZHANG H C, HUANG H,et al. ZnO/carbon quantum dots nanocomposites: one-step fabrication and superior photocatalytic ability for toxic gas degradation under visible light at room temperature. New Journal of Chemistry, 2012, 36: 1031-1035. |
| [14] | LI H T, LIU R H, LIU Y,et al. Carbon quantum dots/Cu2O composites with protruding nanostructures and their highly efficient (near) infrared photocatalytic behavior. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22: 17470-17475. |
| [15] | ZHANG H C, MING H, LIAN S Y,et al. Fe2O3/carbon quantum dots complex photocatalysts and their enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light. Dalton Transactions, 2011, 40: 10822-10825. |
| [16] | ZHANG H, HUANG H, MING H,et al. Carbon quantum dots/ Ag3PO4 complex photocatalysts with enhanced photocatalytic activity and stability under visible light. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22: 10501-10506. |
| [17] | LIU J, LIU Y, LIU N Y,et al. Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible water splitting via a two-electron pathway. Science, 2015, 347(6225): 970-974. |
| [18] | PAN C, ZHU Y.New type of BiPO4 oxy-acid salt photocatalyst with high photocatalytic activity on degradation of dye.Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(14): 5570-5574. |
| [19] | PAN C, ZHU Y.Size-controlled synthesis of BiPO4 nanocrystals for enhanced photocatalytic performance.Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21: 4235-4241. |
| [20] | PAN C, XU J, WANG Y,et al. Dramatic activity of C3N4/BiPO4 photocatalyst with core/shell structure formed by self-assembly. Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22(7): 1518-1524. |
| [21] | LU B, MA X, PAN C, et al. Photocatalytic. Photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical properties of in situ carbon hybridized BiPO4 films. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2012, 435-436: 93-98. |
| [22] | PAN C, XU J, CHEN Y, ,et al. Influence of OH-related defects on the performances of BiPO4 photocatalyst for the degradation of rhodamine B. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2012, 115-116: 314-319. |
| [23] | LV T, PAN L, LIU X,et al. Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by BiPO4-CdS composites synthesized using a microwave-assisted method. RSC Advances, 2012, 2: 12706-12709. |
| [24] | XU H, XU Y, LI H,et al. Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic property of AgBr/BiPO4 heterojunction photocatalyst. Dalton Transactions, 2012, 41: 3387-3394. |
| [25] | LIN H, YE H, XU B,et al. Ag3PO4 quantum dot sensitized BiPO4: a novel p-n junction Ag3PO4/BiPO4 with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. Catalysis Communications, 2013, 37: 55-59. |
| [26] | LIN H, YE H, CHEN S,et al. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of BiPO4/BiVO4 with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activities for methylene blue degradation. RSC Advances, 2014, 4: 10968-10974. |
| [27] | LV Y, ZHU Y, ZHU Y.Enhanced photocatalytic performance for the BiPO4-x nanorod induced by surface oxygen vacancy. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(36): 18520-18528. |
| [28] | LV Y, LIU Y, ZHU Y,et al. Surface oxygen vacancy induced photocatalytic performance enhancement of a BiPO4 nanorod. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2: 1174-1182. |
| [29] | LIU Y, LV Y, ZHU Y,et al. Fluorine mediated photocatalytic activity of BiPO4 . Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2014, 147: 851-857. |
| [30] | ZHANG Y, FAN H, LI M,et al. Ag/BiPO4 heterostructures: synthesis, characterization and their enhanced photocatalytic properties. Dalton Transactions, 2013, 42: 13172-13178. |
| [31] | FULEKAR M H, SINGH A, DUTTA D P,et al. Ag incorporated nano BiPO4: sonochemical synthesis, characterization and improved visible light photocatalytic properties. RSC Advances, 2014, 4: 10097-10107. |
| [32] | MARTINDALE B C M, HUTTON G A M, CAPUTO C A,et al. Solar hydrogen production using carbon quantum dots and a molecular nickel catalyst. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(18): 6018-6025. |
| [33] | LIU Y F, YAO W Q, LIU D,et al. Enhancement of visible light mineralization ability and photocatalytic activity of BiPO4/BiOI. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 163: 547-553. |
| [34] | YUE D, CHEN D M, WANG Z H,et al. Enhancement of visible photocatalytic performances of a Bi2MoO6-BiOCl nanocomposite with plate-on-plate heterojunction structure. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16: 26314-26321. |
| [1] | FAN Xiaoxuan, ZHENG Yonggui, XU Lirong, YAO Zimin, CAO Shuo, WANG Kexin, WANG Jiwei. Organic Pollutant Fenton Degradation Driven by Self-activated Afterglow from Oxygen-vacancy-rich LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ Long Afterglow Phosphor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 481-488. |
| [2] | JIA Xianghua, ZHANG Huixia, LIU Yanfeng, ZUO Guihong. Cu2O/Cu Hollow Spherical Heterojunction Photocatalysts Prepared by Wet Chemical Approach [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 397-404. |
| [3] | MA Binbin, ZHONG Wanling, HAN Jian, CHEN Liangyu, SUN Jingjing, LEI Caixia. ZIF-8/TiO2 Composite Mesocrystals: Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 937-944. |
| [4] | CAO Qingqing, CHEN Xiangyu, WU Jianhao, WANG Xiaozhuo, WANG Yixuan, WANG Yuhan, LI Chunyan, RU Fei, LI Lan, CHEN Zhi. Visible-light Photodegradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride on Self-sensitive Carbon-nitride Microspheres Enhanced by SiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 787-792. |
| [5] | WANG Zhaoyang, QIN Peng, JIANG Yin, FENG Xiaobo, YANG Peizhi, HUANG Fuqiang. Sandwich Structured Ru@TiO2 Composite for Efficient Photocatalytic Tetracycline Degradation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 383-389. |
| [6] | WU Lin, HU Minglei, WANG Liping, HUANG Shaomeng, ZHOU Xiangyuan. Preparation of TiHAP@g-C3N4 Heterojunction and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [7] | LING Jie, ZHOU Anning, WANG Wenzhen, JIA Xinyu, MA Mengdan. Effect of Cu/Mg Ratio on CO2 Adsorption Performance of Cu/Mg-MOF-74 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1379-1386. |
| [8] | SUN Chen, ZHAO Kunfeng, YI Zhiguo. Research Progress in Catalytic Total Oxidation of Methane [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1245-1256. |
| [9] | MA Xinquan, LI Xibao, CHEN Zhi, FENG Zhijun, HUANG Juntong. BiOBr/ZnMoO4 Step-scheme Heterojunction: Construction and Photocatalytic Degradation Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [10] | CHEN Hanxiang, ZHOU Min, MO Zhao, YI Jianjian, LI Huaming, XU Hui. 0D/2D CoN/g-C3N4 Composites: Structure and Photocatalytic Performance for Hydrogen Production [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [11] | XUE Hongyun, WANG Congyu, MAHMOOD Asad, YU Jiajun, WANG Yan, XIE Xiaofeng, SUN Jing. Two-dimensional g-C3N4 Compositing with Ag-TiO2 as Deactivation Resistant Photocatalyst for Degradation of Gaseous Acetaldehyde [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [12] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [13] | WANG Xiaojun, XU Wen, LIU Runlu, PAN Hui, ZHU Shenmin. Preparation and Properties of Ag@C3N4 Photocatalyst Supported by Hydrogel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [14] | LIU Xuechen, ZENG Di, ZHOU Yuanyi, WANG Haipeng, ZHANG Ling, WANG Wenzhong. Selective Oxidation of Biomass over Modified Carbon Nitride Photocatalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 38-44. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xian, ZHANG Ce, JIANG Wenjun, FENG Deqiang, YAO Wei. Synthesis, Electronic Structure and Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance of Quaternary BiMnVO5 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||