
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 1171-1176.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160083
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
CONG Ri-Dong1,2, CUI Hang1, ZHANG Jian1, CUI Qi-Liang1
Received:2016-02-02
Revised:2016-04-11
Published:2016-11-10
Online:2016-10-25
About author:CONG Ri-Dong. E-mail: congrd@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
CONG Ri-Dong, CUI Hang, ZHANG Jian, CUI Qi-Liang. Synthesis and Characterization of Rare Earth Nitride ScN and YN Microcrystalline[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(11): 1171-1176.
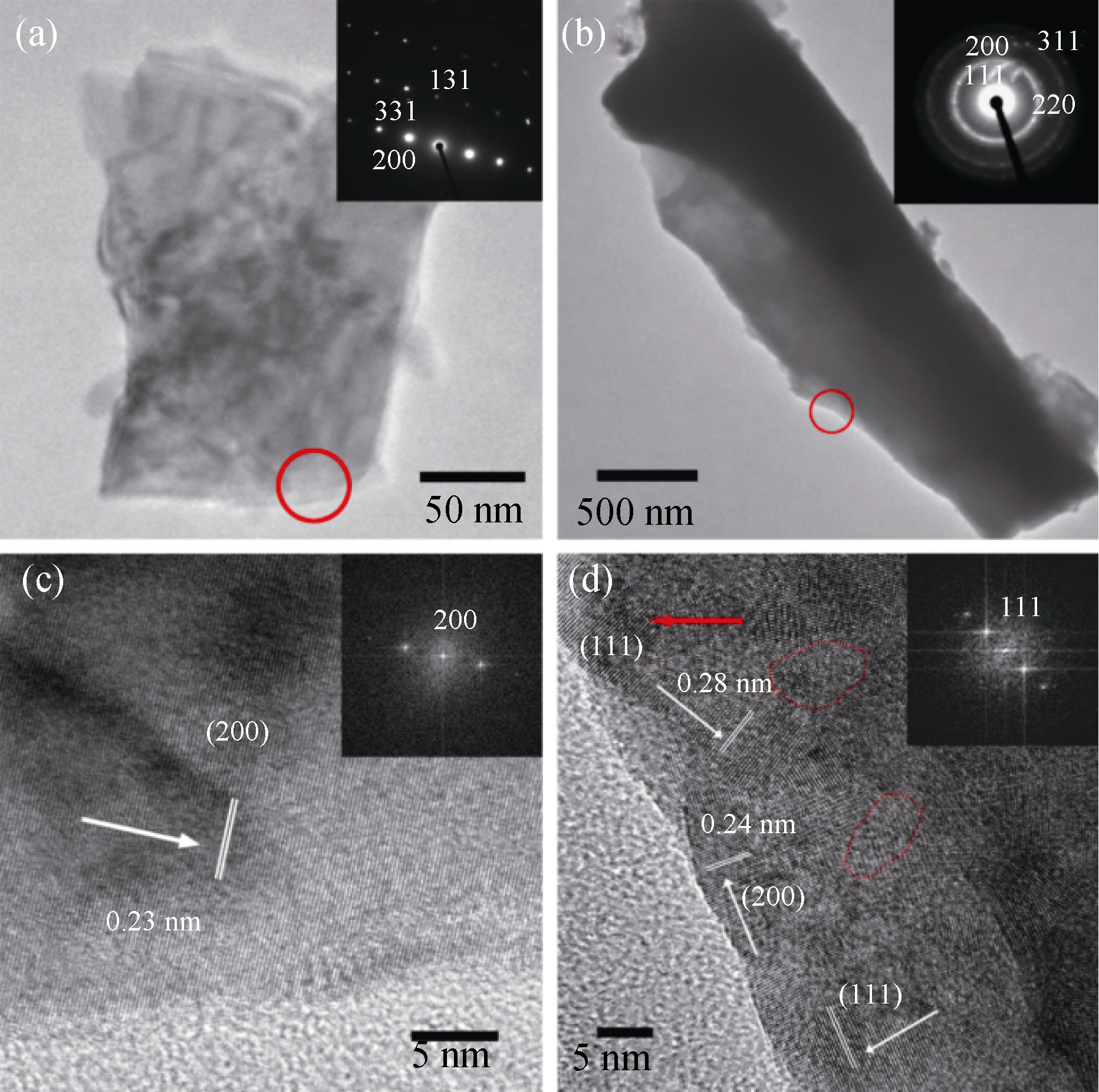
Fig. 3 Typical TEM analysis images of the finely ground ScN and YN (a, b) The insets are the corresponding SAED patterns of the regions marked in red circles. The circle marked regions are also correspondingly to for HRTEM characterization (c, d) showing ScN single crystalline structure corresponding to the (200) base plane, and YN polycrystalline structure composed of small single crystals with random crystallographic orientations
| [1] | BURMISTROVA P V, MAASSEN J, FAVALORO T, et al. Thermoelectric properties of epitaxial ScN films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering onto MgO(001) substrates. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 113(15): 153704-1-8. |
| [2] | TAKEUCHI N. First-principles calculations of the ground-state properties and stability of ScN. Physical Review B, 2002, 65(4): 045204-1-5. |
| [3] | GREGOIRE J M, KIRBY S D, SCOPELIANOS G E, et al. High mobility single crystalline ScN and single-orientation epitaxial YN on sapphire via magnetron sputtering. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 104(7): 074913-1-8. |
| [4] | HOLEC D, FRIAK M, NEUGEBAUER J, et al. Trends in the elastic response of binary early transition metal nitrides. Physical Review B, 2012, 85(6): 064101-1-10. |
| [5] | AL-BRITHEN H A, SMITH A R, GALL D. Surface and bulk electronic structure of ScN(001) investigated by scanning tunneling microscopy/spectroscopy and optical absorption spectroscopy. Physical Review B, 2004,70(4): 045303-1-9. |
| [6] | STAMPFL C, MANNSTADT W, ASAHI R, et al. Electronic structure and physical properties of early transition metal mononitrides: Density-functional theory LDA, GGA, and screened-exchange LDA FLAPW calculations,Physical Review B 2001, 63(15): 155106-1-12. |
| [7] | SMITH A R, AL-BRITHEN H A H, INGRAM D C, et al. Molecular beam epitaxy control of the structural, optical, and electronic properties of ScN(001).Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 90(4): 1809-1816. |
| [8] | LITTLE M E, KORDESCH M E.Band-gap engineering in sputter-deposited ScxGa1-xN.Applied Physics Letters, 2001, 78(19): 2891-2892. |
| [9] | PERJERU F, BAI X, ORTIZ-LIBREROS M I, et al. ScN/GaN heterojunctions: fabrication and characterization.Applied Surface Science, 2001, 175(1): 490-494. |
| [10] | MOUSTAKAS T D, DISMUKES J P, PEARTON S J.Proceedings of the first symposium on III-V nitride materials and processes.Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1996, 96(11): 111. |
| [11] | SHIMADA K, ZENPUKU A, FUJIWARA K, et al. Spontaneous polarization and band gap bowing in YxAlyGa1-x-yN alloys latice-matched to GaN. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 110(7): 074114-1-6. |
| [12] | GALL D, PETROV I, GREENE J E.Epitaxial Sc1-xTixN(001): Op tical and electronic transport properties.Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89(1): 401-409. |
| [13] | GREGOIRE J M, KIRBY S D, TURK M E, et al.Structural, electronic and optical properties of (Sc,Y)N solid solutions.Thin Solid Films, 2009, 517(5): 1607-1609. |
| [14] | SAHA B, ACHARYA J, SANDS T D, et al. Electronic structure, phonons,thermal properties of ScN, ZrN,HfN: A first-principles study. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 107(3): 033715-1-9. |
| [15] | SAHA B, SANDS T D, WAGHMARE U V.Thermoelectric properties of HfN/ScN metal/semiconductor superlattices: a first-principles study.Journal of Physics-Condensed Matter, 2012, 24(41): 2733-2737. |
| [16] | JIA X T, YANG W, QIN M H. Magnetism in Mn doped yttrium nitride: First-principles calculations, Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93(22): 222501-1-4. |
| [17] | HERWADKAR A, LAMBRECHT W R L. Mn-doped ScN: a dilute ferromagnetic semiconductor with local exchange coupling. Physical Review B, 2005, 72(23): 235207-1-6. |
| [18] | GALL D, PETROV I, HELLGREN N, et al.Growth of poly- and single-crystal ScN on MgO(001): role of low-energy N2+ irradiation in determining texture, microstructure evolution, and mechanical properties.Journal of Applied Physics, 1999, 84(11): 6034-6041. |
| [19] | PERJERU F, BAI X, ORTIZ-LIBREROS M I, et al. ScN/GaN heterojunctions: fabrication and characterization. Applied Surface Science, 2001, 175-176: 490-494. |
| [20] | MORAM M A, NOVIKOV S V, KENT A J, et al.Growth of epitaxial thin films of scandium nitride on 100-oriented silicon.Journal of Crystal Growth, 2008, 310(11): 2746-2750. |
| [21] | LENGAUER W.The temperature gradient diffusion couple technique: an application of solid-solid phase reactions for phase diagram imaging.Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1991, 91(2): 279-285. |
| [22] | CHARLES P K, KRIKORIAN N H, JOSEPH C M.The crystal structure of yttrium nitride.Journal of Chemical Physics, 1957, 61(1): 1237-1238. |
| [23] | LYUTAYA M D, GONCHARUK A B.Conditions of formation of lanthanum and samarium nitrides.Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics, 1979, 18(8): 569-574. |
| [24] | LYUTAYA M D, GONCHARUK A B, TIMOFEEVA I I.Scandium nitride.Zhurnal Prikladnoi Khimii, 1975, 48(4): 721-724. |
| [25] | SAMSONOV G V, LYUTAYA M D.Preparaion of cerium nitrides.Zhurnal Prikladnoi Khimii, 1962, 35: 2359. |
| [26] | NIEWA R, ZHEREBTSOV D A, KIRCHNER M, et al.New ways to high-quality bulk scandium nitride.Chemistry of Materials, 2004, 16(25): 5445-5451. |
| [27] | GU Z, EDGAR J H, POMEROY J, et al.Crystal growth and properties of scandium nitride.Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics. 2004, 15(8): 555-559. |
| [28] | DU L, EDGAR J H, PEASCOE-MEISNER R A, et al. Sublimation crystal growth of yttrium nitride.Journal of Crystal Growth, 2010, 312(20): 2896-2903. |
| [29] | LEI W W, LIU D, MA Y M, et al.Scandium-doped AlN 1D hexagonal nanoprisms: a class of room-temperature ferromagnetic materials.Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2010, 49(1): 173-176. |
| [30] | LIU C, HU Z, WU Q, et al.Vapor-solid growth and characterization of aluminum nitride nanocones.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127(4): 1318-1322. |
| [31] | HE J H, YANG R S, CHUEH Y L, et al.Aligned AlN nanorods with multi-tipped surfaces-growth, field-emission, and cathodoluminescence properties.Advanced Materials, 2006, 18(5): 650-654. |
| [32] | SUNDGREN J E, JOHANSSON B O, ROCKETT A, et al.TiNx (0.6<x<1.2): atomic arrangements, electronic structure and recent results on crystal growth and physical properties of epitaxial layers.AIP Conference Proceedings, 1986, 149: 95-115. |
| [33] | PORTE L.Stoichiometric ScN and nitrogen deficient scandium nitride layers studied by photoelectron spectroscopy.Journal of Physical Chemistry: Solid State Physics, 1985, 18(36): 6701-6709. |
| [34] | HUISMAN L M, CARLSSON A E, GELATT C D, et al.Mechanisms for energetic-vacancy stabilization: TiO and TiC.Physical Review B, 1980, 22(2): 991-1006. |
| [35] | GALL D, PETROV I, MADSEN L D, et al.Microstructure and electronic properties of the refractory semiconductor ScN grown on MgO(001) by ultra-high-vacuum reactive magnetron sputter deposition.Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A, 1998, 16(4): 2411-2417. |
| [36] | SAHA B, SANDS T D, WAGHMARE U V. Electronic structure, vibrational spectrum,thermal properties of yttrium nitride: a first-principles study. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 109(7): 073720-1-7. |
| [37] | SCHIMKA L, GAUDOIN R, KLIMES J, et al. Lattice constants and cohesive energies of alkali, alkaline-earth,transition metals: Random phase approximation and density functional theory results. Physical Review B, 2013, 87(21): 214102-1-9. |
| [38] | JANTHON P, KOZLOV S M, VINES F, et al.Establishing the accuracy of broadly used density functionals in describing bulk properties of transition metals.Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2013, 9(3): 1631-1640. |
| [39] | YOUNG D A.Phase Diagrams of the Elements. University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, 1991. |
| [40] | HSU K C, ETEMADI K, PFENDER E.Study of the free-burning high-intensity argon arc.Journal of Applied Physics, 1983, 54(3): 1293-1301. |
| [41] | AITHAL S M, SUBRAMANIAM V V, PAGAN J, et al.Numerical model of a transferred plasma arc.Journal of Applied Physics, 1998, 84(7): 3506-3517. |
| [42] | JUN W K, WILLENS R H, DUWEZ P.Non-crystalline structure in solidified gold-silicon alloys.Nature, 1960, 187(4740): 869-870. |
| [43] | LÖFFLER J F. Bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics, 2003, 11(6): 529-540. |
| [44] | WANG W H, DONG C, SHEK C H.Bulk metallic glasses.Materials Science and Engineering R, 2004, 44(2/3): 45-89. |
| [1] | GOU Yanzi, KANG Weifeng, WANG Pengren. Influence of Sintering Conditions on Preparation of Nearly Stoichiometric SiC Fibers with Highly Crystalline Microstructure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 405-414. |
| [2] | HAO Yongxin, SUN Jun, YANG Jinfeng, ZHAO Chencheng, LIU Ziqi, LI Qinglian, XU Jingjun. Twinning Defects in Near-stoichiometric Lithium Niobate Single Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 196-204. |
| [3] | JIN Min, MA Yupeng, WEI Tianran, LIN Siqi, BAI Xudong, SHI Xun, LIU Xuechao. Growth and Characterization of Large-size InSe Crystal from Non-stoichiometric Solution via a Zone Melting Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 554-560. |
| [4] | WU Qiuqin, YAO Fenfa, JIN Chuanhong, ZHENG Yifan. One-dimensional Sub-stoichiometric W3O8 Nanowires Filled Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 413-419. |
| [5] | XU Jiayue, LI Zhichao, PAN Yunfang, ZHOU Ding, WEN Feng, MA Wenjun. Research Progress of Hyperstoichiometric UO2 Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1183-1192. |
| [6] | LEE Sai-Xi, WANG Xue-Yin, GU Qing-Wen, XIA Yong-Gao, LIU Zhao-Ping, HE Jie. Tuning Electrochemical Performance through Non-stoichiometric Compositions in High-voltage Spinel Cathode Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(9): 993-1000. |
| [7] | WANG Huan, ZHANG Hua, JIN Hong-Jian, ZHAO Wen-Wen. Effect of Fuel Amount on Synthesis of Gd0.8Sr0.2CoO3-δ Cathode Material by Glycine-nitrate Process [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(8): 818-824. |
| [8] | FAN Xiu-Jun, WANG Yue. Microstructure, Electrical Properties of Mn-doped Sr2-xCaxNaNb5O15 (x=0.05-0.35) Lead Free Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(9): 933-938. |
| [9] |
ZHUGE Fu-Wei,GAO Xiang-Dong,LI Xiao-Min,GAN Xiao-Yan.
Microstructure and Optical Properties of CuSCN Thin Film Deposited by Successive Ionic Layer Adsorption and Reaction (SILAR) Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(1): 8-12. |
| [10] | LI Song-Li,WANG Shao-Rong,NIE Huai-Wen,WANG Yuan-Song,WEN Ting-Lian. La0.85Sr0.15Cr0.9Ni0.1O3-δCe0.8Sm0.2O1.9as an Anode Material of SOFC [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(5): 1121-1126. |
| [11] | WANG Hai-Li,HANG Yin,ZHANG Lian-Han,ZHU Shi-Ning,XU Jun. Growth of Mg-doped Near Stoichiometric LiNbO3 Crystal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2004, 19(5): 1191-1194. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||