
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (11): 1139-1144.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140085
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Qi-Hao, XU Lei-Lei, WANG Lian-Jun, JIANG Wan
Received:2014-02-27
Revised:2014-04-08
Published:2014-11-20
Online:2014-10-24
About author:张骐昊. E-mail: zqh378@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHANG Qi-Hao, XU Lei-Lei, WANG Lian-Jun, JIANG Wan. Effects of Different Amount of Se-doping on Microstructures and Thermoelectric Properties of n-type Bi2Te3-xSex[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(11): 1139-1144.
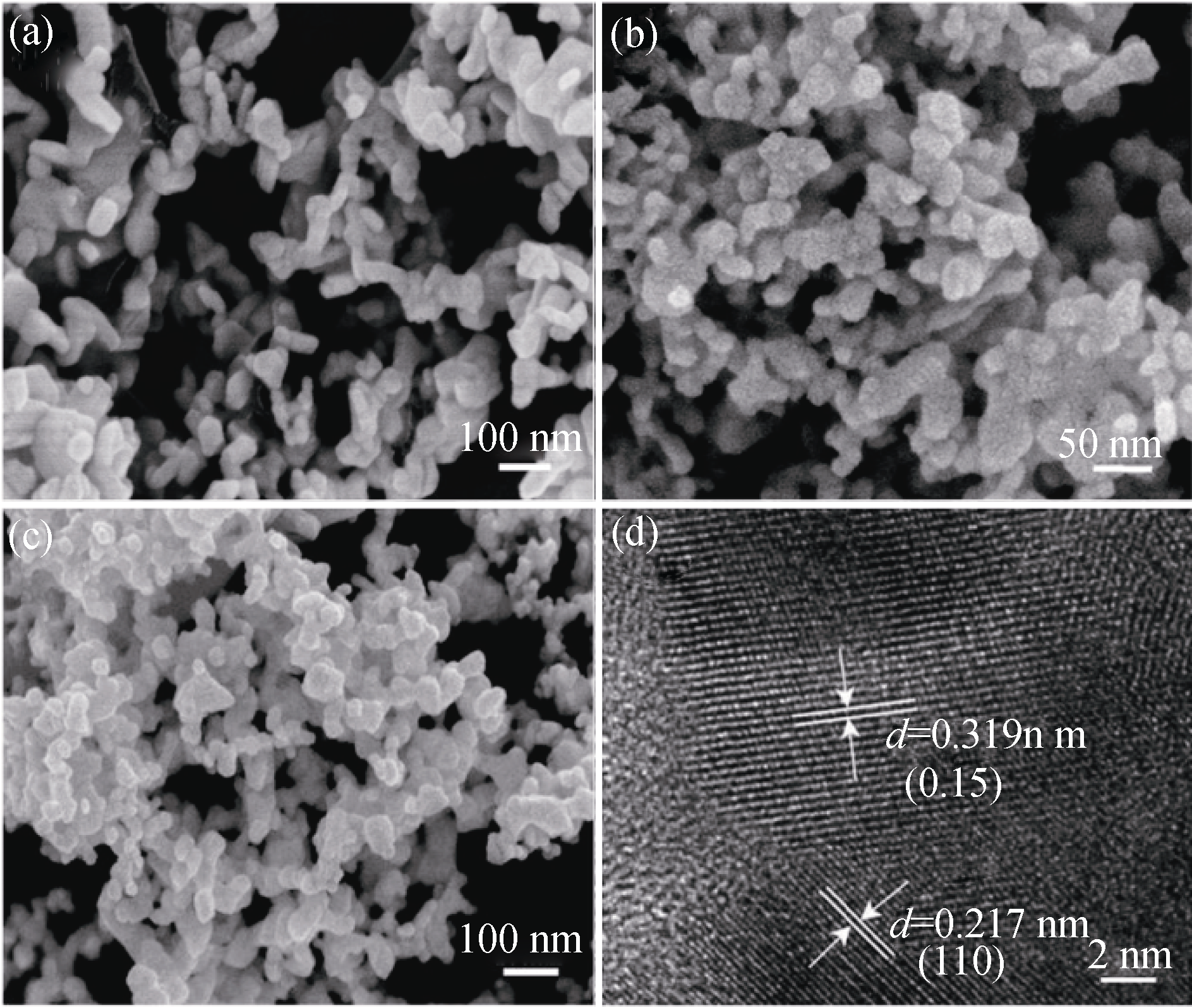
Fig. 2 FE-SEM and HRTEM images of Bi2Te3-xSex nano-powder being doped with different Se contents SEM images of (a) Bi2Te2.9Se0.1, (b) Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 and (c) Bi2Te2.55Se0.45, HRTEM image of (d) Bi2Te2.55Se0.45 nanopowder
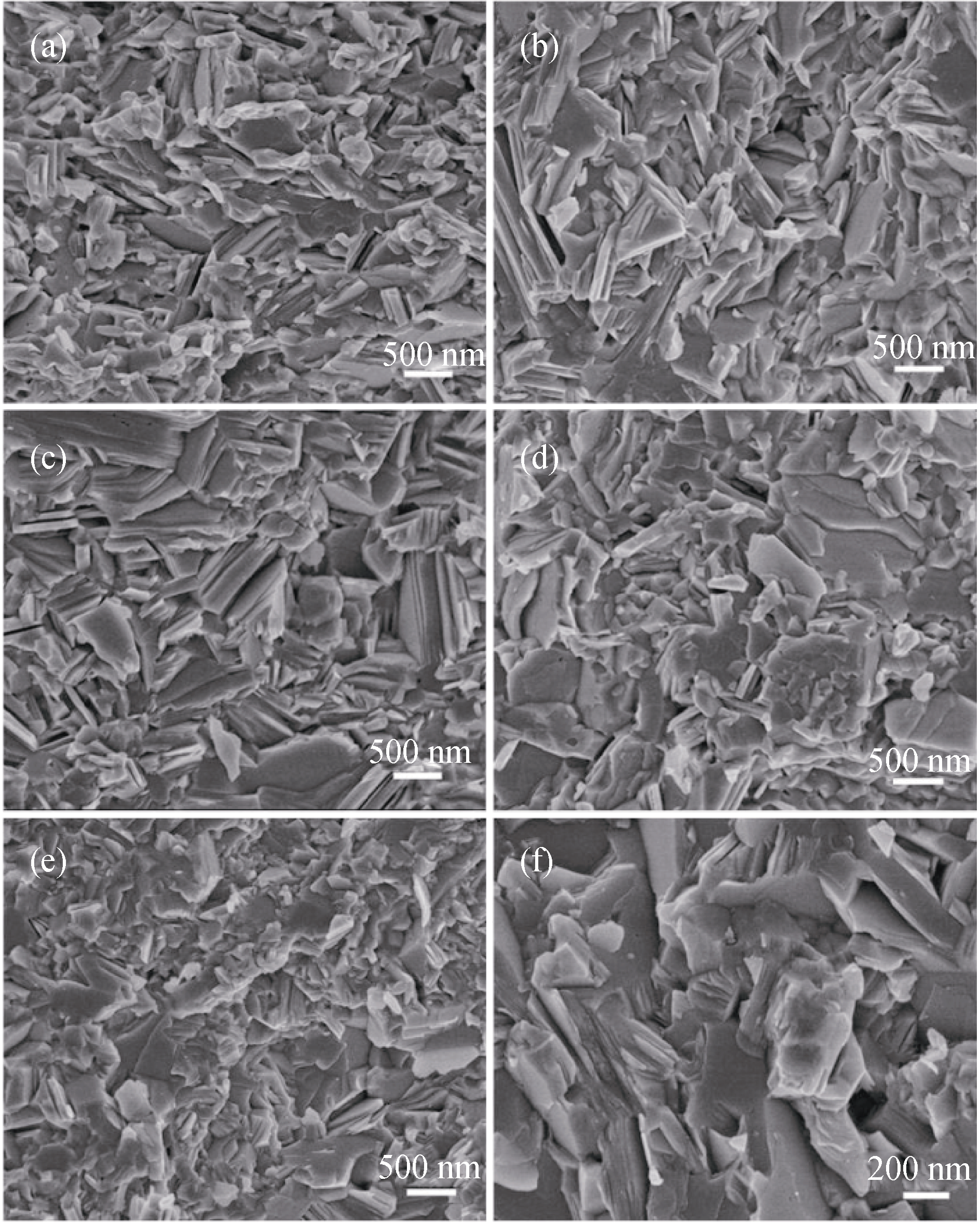
Fig. 3 Fractured surfaces′ morphologies of bulk Bi2Te3-xSex being doped with different Se contents (a) Bi2Te3; (b) Bi2Te2.9Se0.1; (c) Bi2Te2.85Se0.15; (d) Bi2Te2.7Se0.3; (e) and (f) Bi2Te2.55Se0.45
| Sample | Bi2Te3 | Bi2Te2.9Se0.1 | Bi2Te2.85Se0.15 | Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 | Bi2Te2.55Se0.45 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density/(g·cm-3) | 7.820 | 7.755 | 7.760 | 7.753 | 7.759 |
| Relative density | 99.52% | 98.92% | 98.98% | 99.02% | 99.16% |
Tables 1 Densities and relative densities of Bi2Te3-xSex bulk samples being doped with different Se contents
| Sample | Bi2Te3 | Bi2Te2.9Se0.1 | Bi2Te2.85Se0.15 | Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 | Bi2Te2.55Se0.45 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density/(g·cm-3) | 7.820 | 7.755 | 7.760 | 7.753 | 7.759 |
| Relative density | 99.52% | 98.92% | 98.98% | 99.02% | 99.16% |
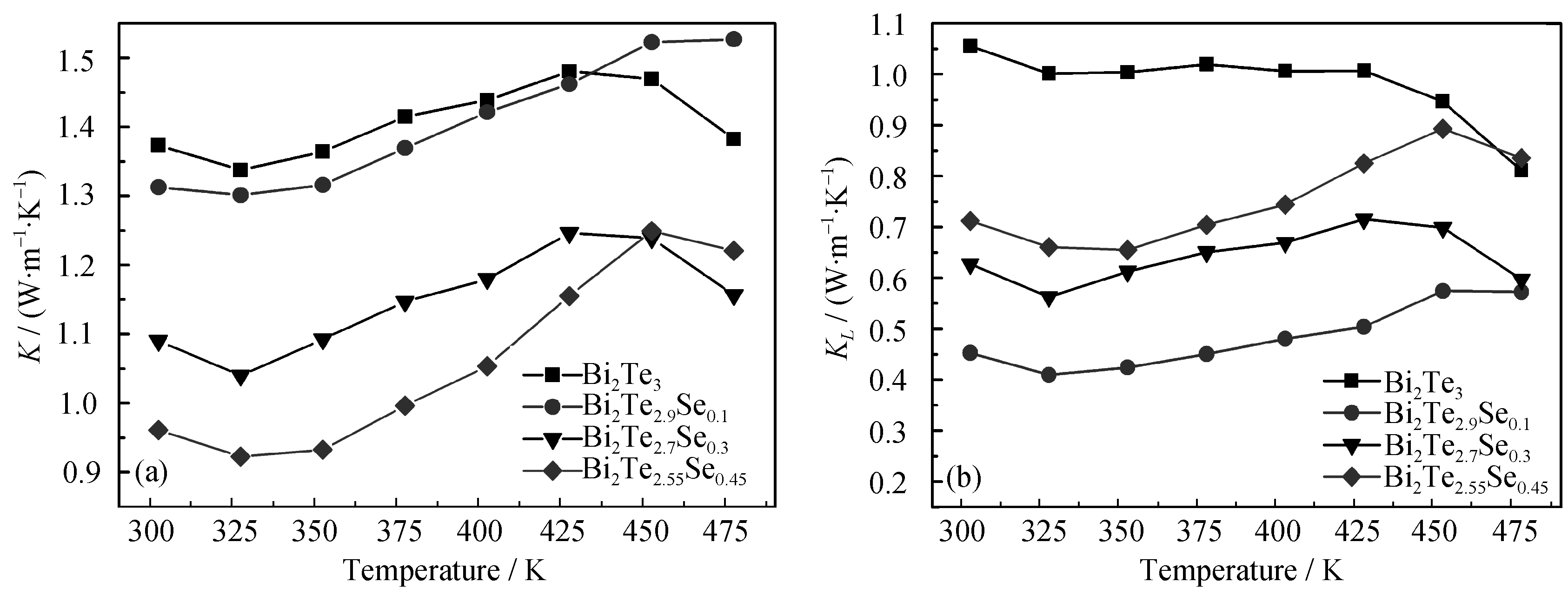
Fig. 6 Temperature dependence of (a) thermal conductivity and (b) lattice thermal conductivity for Bi2Te3-xSex bulk samples being doped with different Se contents
| [1] | NOLAS G S, SHARP J, GOLDSMID H J. Thermoelectrics: Basic Principles and New Materials Developments. Springer: New York, 2001: 17-29. |
| [2] | POUDEL B, HAO Q, MA Y, et al. High-thermoelectric performance of nanostructured bismuth antimony telluride bulk alloys. Science, 2008, 320: 634-638. |
| [3] | HOU XIAN-HUA, HU SHE-JUN, RU QIANG, et al. Current status and development of Bi2Te3-based thermoelectric materials. Materials Review, 2007, 21(7): 111-118. |
| [4] | CHEN G, DRESSELHAUS M S, FLEURIAL J P, et al. Recent developments in thermoelectric materials. International Material Reviews, 2003, 48(1): 45-66. |
| [5] | MINNICH A J, DRESSELHAUS M S, REN Z F, et al. Bulk nanostructured thermoelectric materials: current research and future prospects. Energy Environ Sci, 2009, 2: 466-479. |
| [6] | SOOTSMAN J R, CHUNG D Y, KANATZIDIS M G. New and old concepts in thermoelectric materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, 2009, 48: 8616-8639. |
| [7] | XIAO Y, POUDEL B, MA Y, et al. Experimental studies on anisotropic thermoelectric properties and structures of n-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3. Nano Letters, 2010, 10(9): 3373-3378. |
| [8] | ZHANG Y C, WANG H, KRAEMER S, et al. Surfactant-free synthesis of Bi2Te3-Te micro-nano heterostructure with enhanced thermoelectric figure of merit. ACS Nano, 2011, 4: 3158-3165. |
| [9] | 樊希安. (Bi, Sb)2(Te, Se)3系热电材料的制备及性能优化研究. 武汉: 华中科技大学博士学位论文, 2007. |
| [10] | LI D, QIN X Y, LIU Y F, et al. Improved thermoelectric properties for solution grown Bi2Te3-xSex nanoplatelet composites. RSC Adv., 2013, 3: 2632-2638. |
| [11] | MA Y, CHEN G, REN Z F, et al. Enhanced thermoelectric figure-of-merit in p-Type nanostructured bismuth antimony tellurium alloys made from elemental chunks. Nano Lett., 2008, 8: 2580-2584. |
| [12] | CAO Y Q, ZHAO X B, ZHANG X B, et al. Syntheses and thermoelectric properties of Bi2Te3/Sb2Te3 bulk nanocomposites with laminated nanostructure. Appl. Phys. Lett. , 2008, 92: 143106-1-3. |
| [13] | XIE W, TANG X, TRITT T M, et al. High thermoelectric performance BiSbTe alloy with unique low-dimensional structure. J. Appl. Phys., 2009, 105: 113713-113718. |
| [14] | NI HUA-LIANG, ZHU TIE-JUN, ZHAO XIN-BING. Thermoelectric properties of hydrothermal synthesized Bi-Te-Se alloys. Journal of Functional Materials, 2006, 10(37): 1561-1563. |
| [15] | LV QIANG, CHENG YING, WANG JING-JU, et al. Preparation of Bi2Te3-based p-type pseudoternary thermoelectric materials by the hot-press method and their properties. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2008, 36(5): 683-688. |
| [16] | LI D, QIN X Y, DOU Y C, et al. Thermoelectric properties of hydrothermally synthesized Bi2Te3-xSex nanocrystals. Scripta Materialia, 2012, 67: 161-164. |
| [17] | JIANG J, CHEN L D, BAI S Q, et al. Fabrication and thermoelectric performance of textured n-type Bi2(Te, Se)3 by spark plasma sintering. Material Science Engineering B, 2005, 117(3): 334-338. |
| [1] | FENG Guanzheng, YANG Jian, ZHOU Du, CHEN Qiming, XU Wentao, ZHOU Youfu. Mechanism for Hydrothermal-carbothermal Synthesis of AlN Nanopowders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 104-110. |
| [2] | LI Junsheng, ZENG Liang, LIU Rongjun, WANG Yanfei, WAN Fan, LI Duan. Functional Strontium Tantalum Oxynitride Ceramics: Efficient Synthesis, Densification and Dielectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 885-892. |
| [3] | WANG Xu, GU Ming, LIAO Jincheng, SONG Qingfeng, SHI Xun, BAI Shengqiang, CHEN Lidong. High Temperature Interfacial Stability of Fe/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 Thermoelectric Elements [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 197-202. |
| [4] | WANG Tingting, SHI Shumei, LIU Chenyuan, ZHU Wancheng, ZHANG Heng. Synthesis of Hierarchical Porous Nickel Phyllosilicate Microspheres as Efficient Adsorbents for Removal of Basic Fuchsin [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1330-1336. |
| [5] | SONG Keke, HUANG Hao, LU Mengjie, YANG Anchun, WENG Jie, DUAN Ke. Hydrothermal Preparation and Characterization of Zn, Si, Mg, Fe Doped Hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1091-1096. |
| [6] | WAN Peng, LI Mian, HUANG Qing. Molten Salt Assisted Synthesis of Dy3Si2C2 Coated SiC Powders and Sintering Behavior of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 49-54. |
| [7] | ZHAO Zhankui, LI Tao, LU Shuhan, WANG Minggang, ZHANG Jingjing, CHENG Daowen, WU Chen, CHI Yue, WANG Hongli. Magnetic Properties and Resistivity of Soft Magnetic Composites Regulated by SPS Enhanced Interface Reaction Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1223-1226. |
| [8] | HUANG Zhi-Cheng, YAO Yao, PEI Jun, DONG Jin-Feng, ZHANG Bo-Ping, LI Jing-Feng, SHANG Peng-Peng. Preparation and Thermoelectric Property of n-type SnS [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 321-327. |
| [9] | WANG Wei, LUO Shi-Jie, XIAN Cong, XIAO Qun, YANG Yang, OU Yun, LIU Yun-Ya, XIE Shu-Hong. Enhanced Thermoelectric Properties of Hydrothermal Synthesized BiCl3/Bi2S3 Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 328-334. |
| [10] | LIU Hong-Xia, LI Wen, ZHANG Xin-Yue, LI Juan, PEI Yan-Zhong. Thermoelectric Properties of (Ag2Se)1-x(Bi2Se3)x [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 341-348. |
| [11] | WANG Shu-Jiang, YANG Yong-Heng, WEN Chun-Yang, ZHANG Guo-Kui, YUAN Chun-Hui. Preparation and Property of Nano-Ag/illite Composite Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(5): 570-576. |
| [12] | JIA Si-Qi, JIANG Zheng, CHI Li-Na, YE Ying, HU Shuang-Shuang. Synthesis and Photoelectrocatalytic Performance of Sb2S3 Nanorods from Natural Stibnite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(11): 1213-1218. |
| [13] | WANG Ming-Hui, ZHONG Hong-Bin, FAN Yu-Chi, CHEN Ting. Spark Plasma Sintering of Bioactive Ca2MgSi2O7 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(8): 825-830. |
| [14] | YANG Kun-Kun, YANG Shao-Hua, ZHAO Ping, ZHAO Yan-Long. Hydrothermal Synthesis of FeS2/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite with Enhanced Discharge Performance for Thermal Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 691-698. |
| [15] | GUO Yu, LI Dong-Xin, WU Hong-Mei, JIN Yu-Jia, ZHOU Li-Dai, CHEN Qiang-Qiang. Preparation, Characterization and Catalytic Performance of Supported Titanium Silicalite-1 Zeolite Membrane Catalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(6): 631-636. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||