
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2012, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (4): 433-438.DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2012.00433
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Xiao-Rui, WANG Qun, LV Ling-Yuan, LI Yang, YU Xiao, CHEN Gang
Received:2011-04-14
Revised:2011-07-31
Published:2012-04-10
Online:2012-03-12
About author:SHI Xiao-Rui. E-mail: sxrsxy@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
SHI Xiao-Rui, WANG Qun, LV Ling-Yuan, LI Yang, YU Xiao, CHEN Gang. Controllable Synthesis and Electrical Conductivities of Cu7Te4 Nanostructures[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(4): 433-438.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig. 2 (a,b) SEM images of Cu7Te4 nanobelts, (c) TEM images and (d) typical HRTEM image of Cu7Te4 nanobelts using N,N-Dipropylamine as organic solvent the corresponding Cu7Te4 specimen
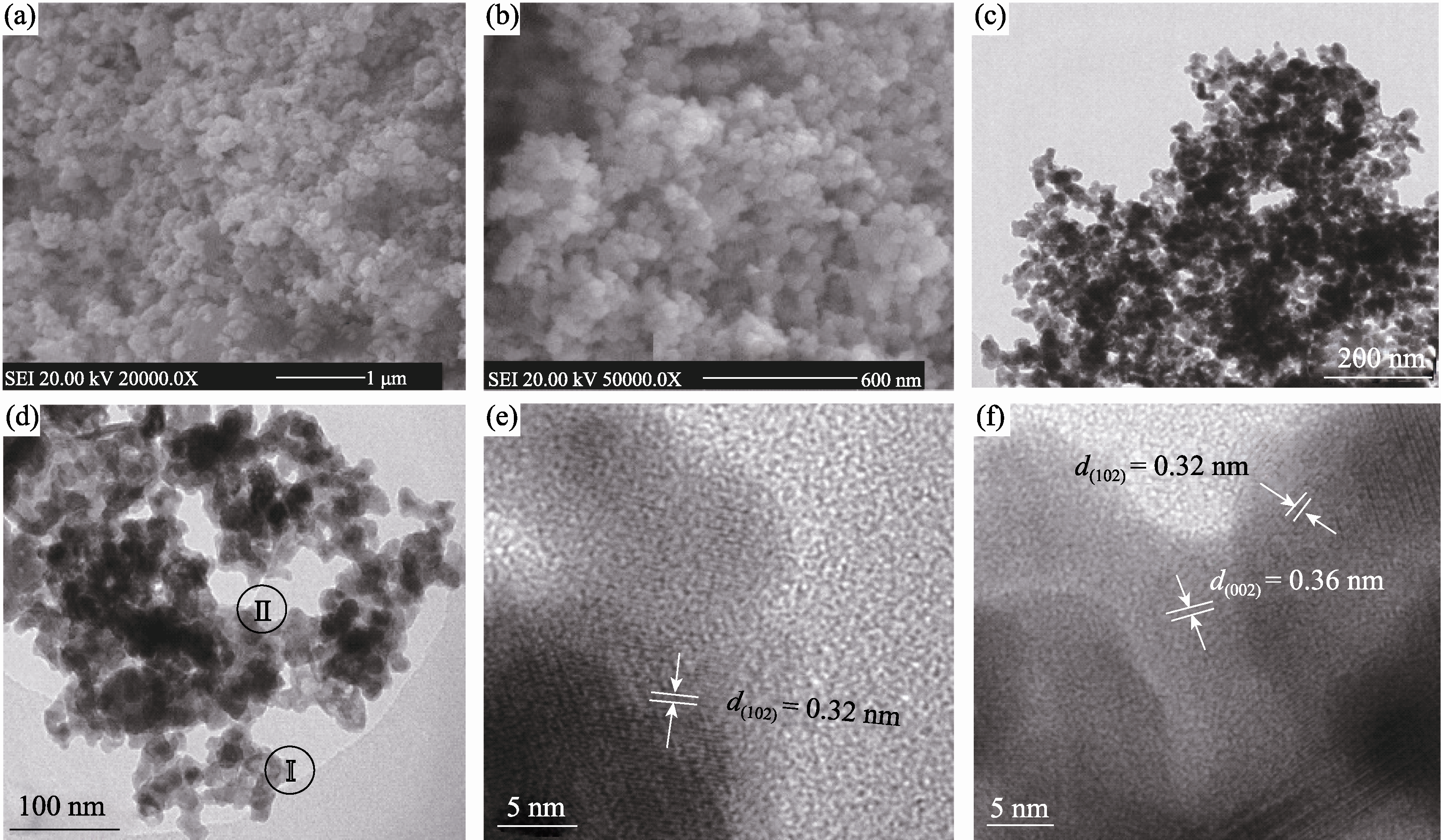
Fig. 3 (a, b) FESEM images, (c, d) TEM images of Cu7Te4 nanoparticles using acetone as organic solvent, and (e, f) typical HRTEM images taken from circle zoneⅠand zoneⅡin Fig. 3(d)

Fig. 4 (a) FESEM image of Cu7Te4 micro-flakes using cyclohexanone as organic solvent, (b) TEM image of an individual Cu7Te4 nanostructure, and (c, d) HRTEM images of the as-synthesized Cu7Te4 micro-flakes
| [1] | CHEN Li-Dong, XIONG Zhen, BAI Sheng-Qiang. Recent progress of thermoelectric nano-composites. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(6): 561-568. |
| [2] | Dresselhaus M S, Chen G, Tang M Y, et al. New directions for low-dimensional thermoelectric materials. Adv. Mater., 2007, 19(8): 1043-1053. |
| [3] | Martin J, Nolas G S, Zhang W, et al. PbTe nanocomposites synthesized from PbTe nanocrystals. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, 90(22): 22211. |
| [4] | Venkatasubramanian R, Siivola E, Colpitts T, et al. Thin-film thermoelectric devices with high room-temperature figures of merit. Nature, 2001, 413(6856): 597-602. |
| [5] | Zhao X B, Ji X H, Zhang Y H, et al. Bismuth telluride nanotubes and the effects on the thermoelectric properties of nanotube-containing nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Lett. , 2005, 86(6): 062111-1-3. |
| [6] | Shi W D, Yu J B, Wang H S, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of single-crystalline antimony telluride nanobelts. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(51): 16490-16491. |
| [7] | XU Xiao-Chuan, WANG Chun-Fen, YAO Qin, et al. Peparation of Bi2Te3-polyaniline heterostructured nanorods by two-step electrochemical depositions. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(6): 1482-1486. |
| [8] | Liufu S C, Chen L D, Yao Q, et al. In situ assembly of CuxS quantum-dots into thin film: a highly conductive p-type transparent film,J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112(32): 12085-12088. |
| [9] | Wang L, Chen G, Wang Q, et al. Shape-controlled synthesis and electrical conductivities of AgPb10SbTe12 materials. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114(13): 5827-5834. |
| [10] | Jin R C, Chen G, Wang Q, et al. PbTe hierarchical nanostructures: solvothermal synthesis, growth mechanism and their electrical conductivities. Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2011, 13(6): 2106-2113. |
| [11] | Sridhar K, Chattopadhyay K. Synthesis by mechanical alloying and thermoelectric properties of Cu2Te. J. Alloys Compd., 1998, 264(1/2): 293-298. |
| [12] | Wu X, Zhou J, Duda A. Phase control of CuxTe film and its effects on CdS/CdTe solar cell. Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515(15): 5798-5803. |
| [13] | Zhou J, Wu X, Duda A, et al. The formation of different phases of CuxTe and their effects on CdTe/CdS solar cells. Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515(18): 7364-7369. |
| [14] | Li B, Xie Y, Huang J X, et al. Sonochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline copper tellurides Cu7Te4 and Cu4Te3 at room temperature. Chem. Mater., 2000, 12(9): 2614-2616. |
| [15] | Jiang L, Zhu Y J, Cui J B. Nanostructures of metal tellurides (PbTe, CdTe, CoTe2, Bi2Te3, and Cu7Te4) with various morphologies: a general solvothermal synthesis and optical properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. , 2010, 2010(19): 3005-3011. |
| [16] | Wang Q, Li G D, Liu Y L, et al. Fabrication and growth mechanism of selenium and tellurium nanobelts through a vacuum vapor deposition route. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(35): 12926-12932. |
| [17] | Zhang Q, Liu S J, Yu S H. Recent advances in oriented attachment growth and synthesis of functional materials: concept, evidence, mechanism, and future. J. Mater. Chem., 2009, 19(2): 191-207. |
| [18] | Seoudi R, Shabaka A A, Elokr M M, et al. Optical properties and electrical conductivity studies of copper selenide nanoparticle. Mater. Lett., 2007, 61(16): 3451-3455. |
| [19] | Martin J, Nolas G S, Zhang W, et al. PbTe nanocomposites synthesized from PbTe nanocrystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. , 2007, 90(22): 222112-1-3. |
| [20] | Shi W D, Zhou L, Song S Y, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis and thermoelectric transport properties of impurity-free antimony telluride hexagonal nanoplates. Adv. Mater., 2008, 20(10): 1892-1897. |
| [21] | Xiao F, Chen G, Wang Q, et al. Simple synthesis of ultra-long Ag2Te nanowires through solvothermal co-reduction method. J. Solid State Chem., 2010, 183(10): 2382-2388. |
| [22] | 黄永明, 水合肼提纯的机理分析. 天然气化工2008, 33(6): 47-49. |
| [23] | Xu J, Xue D. Fabrication of copper hydroxyphosphate with complex architectures. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(15): 7750-7756. |
| [24] | Zhong Z Y, Lin M, Ng V, et al. A versatile wet-chemical method for synthesis of one-dimensional ferric and other transition metal oxides. Chem. Mater., 2006, 18(25): 6031-6036. |
| [25] | Zhong Z Y, Ng V, Luo J Z, et al. Manipulating the self-assembling process to obtain control over the morphologies of copper oxide in hydrothermal synthesis and creating pores in the oxide architecture. Langmuir, 2007, 23(11): 5971-5977. |
| [1] | ZHANG Ruiyang, WANG Yi, OU Bowen, ZHOU Ying. α-Ni(OH)2 Surface Hydroxyls Synergize Ni3+ Sites for Catalytic Formaldehyde Oxidation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1216-1222. |
| [2] | GAO Wa, XIONG Yujie, WU Congping, ZHOU Yong, ZOU Zhigang. Recent Progress on Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction with Ultrathin Nanostructures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 3-14. |
| [3] | ZHENG Yanning, JI Junrong, LIANG Xueling, LAI Zhengjie, CHENG Qifan, LIAO Dankui. Performance of Nitrogen-doped Hollow Carbon Spheres as Oxidase Mimic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 527-534. |
| [4] | XU Yun-Qing,WANG Hai-Zeng. Sodium Magnesium Fluoride Particles of Different Morphologies: Prepared by EDTA-assisted Hydrothermal Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 933-937. |
| [5] | WANG Dan-Jun, WANG Chan, ZHAO Qiang, GUO Li, YANG Xiao, WU Jiao, FU Feng. Au Nanoparticles (NPs) Surface Plasmon Resonance Enhanced Photocatalytic Activities of Au/Bi2WO6 Heterogeneous Nanostructures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(6): 659-666. |
| [6] | LIU Xue-Jiao, HE Zhen-Yu, WU Hao, LUO Ting, MENG Xie, CHEN Chu-Sheng, ZHAN Zhong-Liang. Influence of Impregnated Nano-scale LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3-δ Particles on the Oxygen Permeation Performance of Zr0.84Y0.16O2-δ-La0.8Sr0.2Cr0.5Fe0.5O3-δ Composite Membranes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(1): 14-18. |
| [7] | TAN Man-Lin, MA Dong-Cao, FU Dong-Ju, MA Qing, LI Dong-Shuang, WANG Xiao-Wei, ZHANG Wei-Li, CHEN Jian-Jun, ZHANG Hua-Yu. Properties of Silver Nanostructures Incorporated Perovskite Based Thin Films for Solar Cell Applications [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(9): 908-914. |
| [8] | YU Yin-Hu, WANG Tao, LIAO Qiu-Ping, MIAO Run-Jie, PAN Jian-Feng, ZHANG Du-Bao. Low-temperature Solid-state Synthesis of Nanometer TiB2-TiC Composite Powder [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(3): 324-328. |
| [9] | WANG Ya-Peng, LIU Jia-Jia, LIU Chun-Xiao, CHEN Wei-Wei, LI Ting-Ting, GUO Hong. Morphology-controlled Synthesis of Hollow Core-shell Structural α-MoO3-SnO2 with Superior Lithium Storage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(9): 919-924. |
| [10] | YU Yin-Hu, WANG Tao, ZHANG Hong-Min, ZHANG Du-Bao, PAN Jian-Feng. Low Temperature Combustion Synthesis of TiC Powder Induced by PTFE [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 272-276. |
| [11] | DOU Zhi-He, ZHANG Ting-An, WEN Ming, SHI Guan-Yong, HE Ji-Cheng. Preparation of Ultra-fine NdB6 Powders by Combustion Synthesis and Its Reaction Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(7): 711-716. |
| [12] | GUO Xiang-Xin, HUANG Shi-Ting, ZHAO Ning, CUI Zhong-Hui, FAN Wu-Gang, LI Chi-Lin, LI Hong. Rapid Development and Critical Issues of Secondary Lithium-air Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(2): 113-123. |
| [13] | MU Yun-Chao, LIANG Bao-Yan, GUO Ji-Feng. Reaction Mechanism of Ti3SiC2 Formed on the Diamond [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(10): 1099-1104. |
| [14] | ZHANG Wen, HE Yong-Ning, ZHOU Cheng-Bo, CUI Wu-Yuan. Controlled Growth of Zinc Oxide Nano Structures by Electrochemical Synthesis and Their Photoluminescence Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(6): 602-606. |
| [15] | XU Xiu-Hua,XIAO Han-Ning,GUO Wen-Ming,GAO Peng-Zhao,PENG Su-Hua. Preparation and Reaction Mechanism of LaB6 Powder by Solid-state Reaction at Atmospheric Pressure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(4): 417-421. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||