
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6): 659-666.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170376
Special Issue: 光催化材料与技术
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Dan-Jun, WANG Chan, ZHAO Qiang, GUO Li, YANG Xiao, WU Jiao, FU Feng
Received:2017-08-07
Revised:2017-10-29
Published:2018-06-20
Online:2018-05-24
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Dan-Jun, WANG Chan, ZHAO Qiang, GUO Li, YANG Xiao, WU Jiao, FU Feng. Au Nanoparticles (NPs) Surface Plasmon Resonance Enhanced Photocatalytic Activities of Au/Bi2WO6 Heterogeneous Nanostructures[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(6): 659-666.
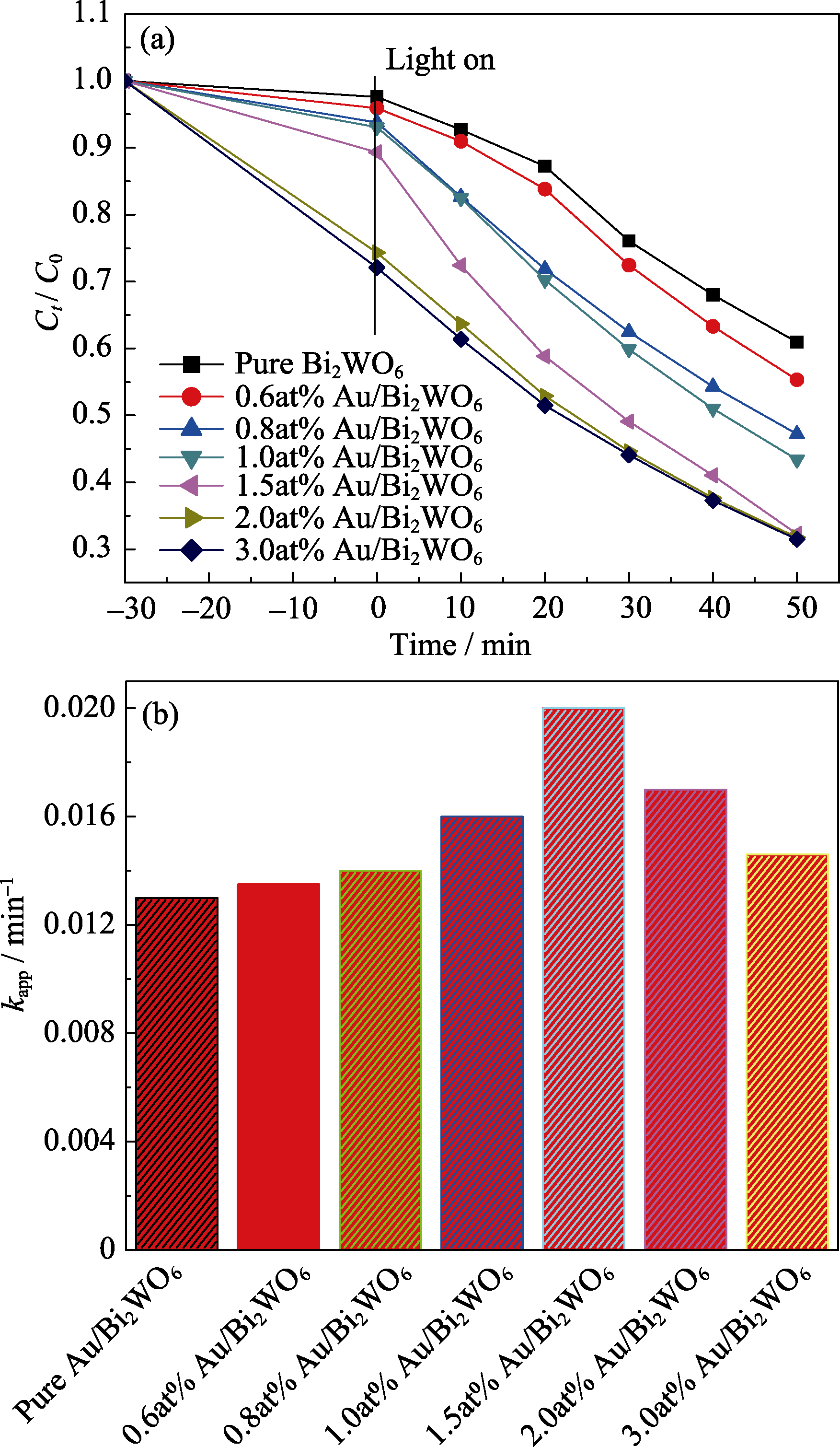
Fig. 6 (a) Photocatalytic degradation acitvities and (b) apparent rate constant (kapp) for the degradation of different Au/Bi2WO6 photocatalysts on RhB
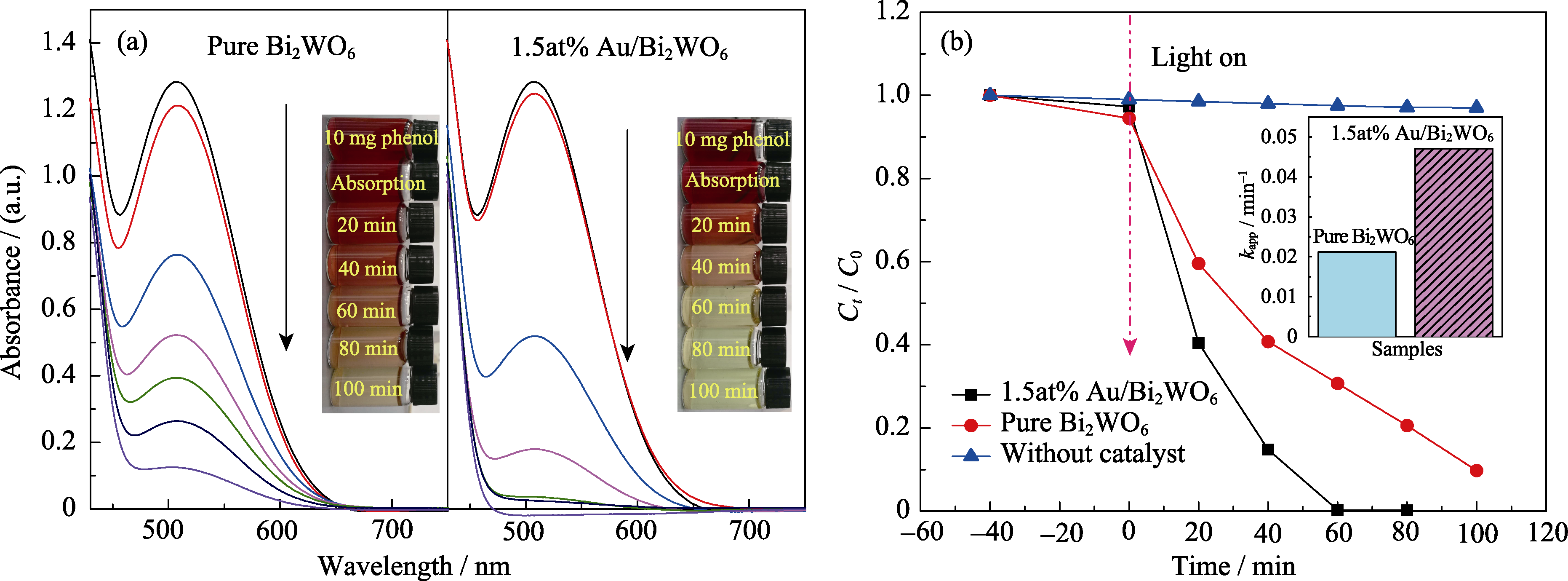
Fig. 7 (a) Photocatalytic acitvities of Bi2WO6 and 1.5at% Au/Bi2WO6 photocatalysts and (b) apparent rate constant (kapp) for the degradation over Bi2WO6 and 1.5at%Au/Bi2WO6 against phenol
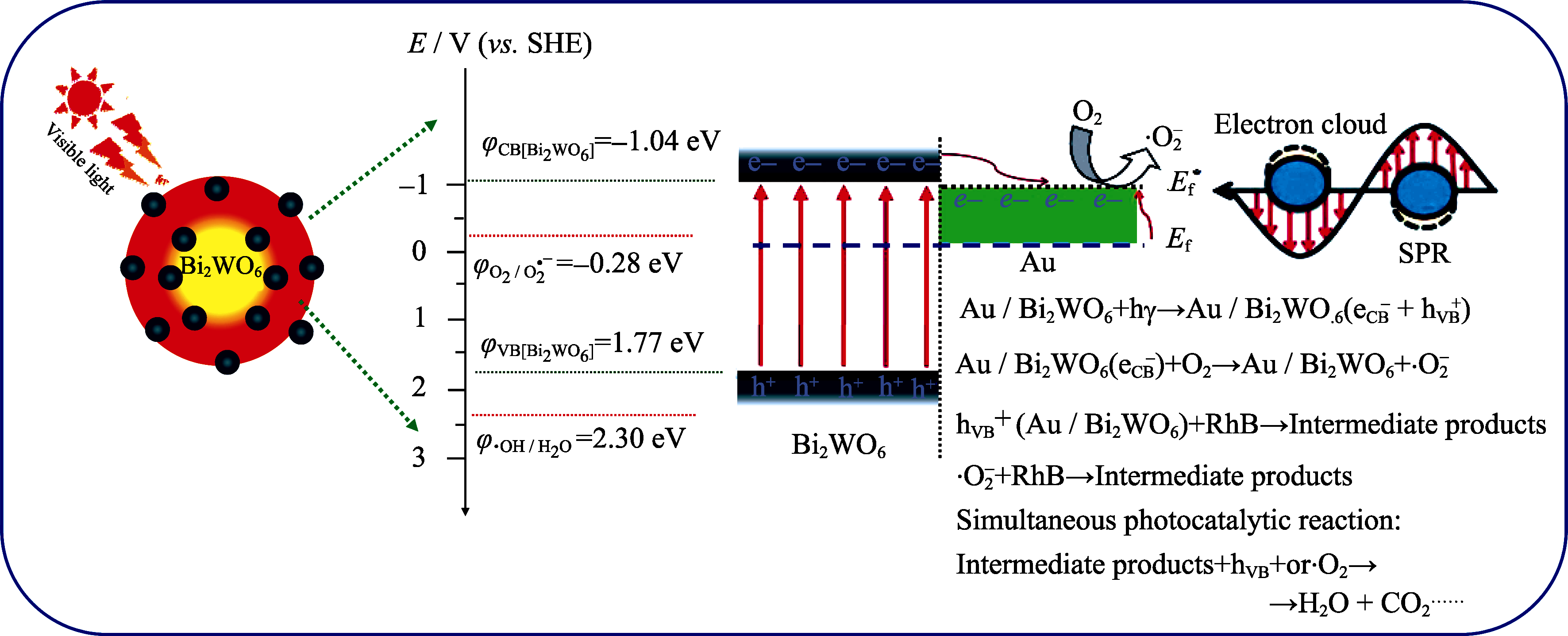
Fig. 9 Schematic illustration of the detailed energy alignment in the Au/Bi2WO6 hegerogeneous nanostructure and the proposed mechanism of photocatalytic degradation of RhB by Au/Bi2WO6 under visible light irradiation
| [1] | KONG X Y, CHOO Y Y, CHAI S P,et al. Oxygen vacancy induced Bi2WO6 for the realization of photocatalytic CO2 reduction over the full solar spectrum: from the UV to the NIR region. Chem. Commun., 2016, 52(99): 14242-14245. |
| [2] | LI M, ZHANG L, FAN X,et al. Highly selective CO2 photoreduction to CO over g-C3N4/Bi2WO6 composites under visible light. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(9): 5189-5196. |
| [3] | ZHANG N, CIRIMINNA R, PAGLIARO M,et al. Nanochemistry- derived Bi2WO6 nanostructures: towards production of sustainable chemicals and fuels induced by visible light. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43(15): 5276-5287. |
| [4] | LI X, YU J, JARONIEC M.Hierarchical photocatalysts.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(9): 2603-2636. |
| [5] | XU Y, SONG J, CHEN F,et al. Amorphous Ti(IV)-modified Bi2WO6 with enhanced photocatalytic performance. RSC Adv., 2016, 6(70): 65902-65910. |
| [6] | SUN S, WANG W, ZHANG L.Bi2WO6 Quantum dots decorated reduced graphene oxide: improved charge separation and enhanced photoconversion efficiency.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(18): 9113-9120. |
| [7] | LIU S J, HOU Y F, ZHENG S L,et al. One-dimensional hierarchical Bi2WO6 hollow tubes with porous walls: synthesis and photocatalytic property. CrystEngComm., 2013, 15(20): 4124-4130. |
| [8] | ZHOU Y, ZHANG Y, LIN M,et al. Monolayered Bi2WO6 nanosheets mimicking heterojunction interface with open surfaces for photocatalysis. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6: 8340. |
| [9] | ZHANG L, BAHNEMANN D.Synthesis of nanovoid Bi2WO6 2D ordered arrays as photoanodes for photoelectrochemical water splitting.ChemSusChem, 2013, 6(2): 283-290. |
| [10] | ZHOU Y X, TONG L, ZENG X H,et al. Green synthesis of flower-like Bi2WO6 microspheres as a visible-light-driven photocatalyst. New J. Chem., 2014, 38(5): 1973-1979. |
| [11] | SUN S, WANG W, ZHANG L.Facile preparation of three- dimensionally ordered macroporous Bi2WO6 with high photocatalytic activity.J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(36): 19244-29249. |
| [12] | WANG F, CAO K, WU Y,et al. Interfacial properties of the enhanced visible-light plasmonic Ag/Bi2WO6(001) nanocomposite. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, 360: 1075-1079. |
| [13] | MOHAMED R M, AAZAM E S.Enhancement of photocatalytic properties of Bi2WO6 nanoparticles by Pt deposition. Mater. Res. Bull., 2013, 48(9): 3572-3578. |
| [14] | MA D, WU J, GAO M,et al. Fabrication of Z-scheme g-C3N4/RGO/Bi2WO6 photocatalyst with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. Chem. Eng. J., 2016, 290: 136-146. |
| [15] | XIAO X, WEI J, YANG Y,et al. Photoreactivity and mechanism of g-C3N4 and Ag co-modified Bi2WO6 microsphere under visible light irradiation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2016, 4(6): 3017-3023. |
| [16] | JO W K, LEE J Y, NATARAJAN T S.Fabrication of hierarchically structured novel redox-mediator-free ZnIn2S4 marigold flower/Bi2WO6 flower-like direct Z-scheme nanocomposite photocatalysts with superior visible light photocatalytic efficiency.Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18(2): 1000-1016. |
| [17] | WANG D J, ZHEN Y Z, XUE G L, et al. AgBr quantum dots decorated mesoporous Bi2WO6 architectures with enhanced photocatalytic activities for methylene blue. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2: 11716-11727. |
| [18] | LIU S, XU Y J. Photo-induced transformation process at gold clusters- semiconductor interface: implications for the complexity of gold clusters-based photocatalysis. Sci. Rep., 2016, 6: 22742-1-13. |
| [19] | MA X C, DAI Y, YU L, et al. Energy transfer in plasmonic photocatalytic composites. Light Sci. Appl., 2016, 5: e6017-1-13. |
| [20] | ZHANG G, ZHAO Z, TAN H,et al. Hierarchical TiO2 spheres decorated with Au nanoparticles for visible light hydrogen production. RSC Adv., 2015, 5(27): 21237-21241. |
| [21] | WANG H, YOU T, SHI W,et al. Au/TiO2/Au as a plasmonic coupling photocatalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116(10): 6490-6494. |
| [22] | LI P, WEI Z, WU T,et al. Au-ZnO hybrid nanopyramids and their photocatalytic properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(15): 5660-5663. |
| [23] | BHATTACHARJEE U, MEN L, ROSALES B A,et al. Using ATTO dyes to probe the photocatalytic activity of Au-CdS nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121(1): 676-683. |
| [24] | CAO S W, YIN Z, BARBER J,et al. Preparation of Au-BiVO4 heterogeneous nanostructures as highly efficient visible-light photocatalysts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2012, 4(1): 418-423. |
| [25] | SHANG M, HOU H, GAO F,et al. Mesoporous Ag@TiO2 nanofibers and their photocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution. RSC Adv., 2017, 7(48): 30051-30059. |
| [26] | WANG D J, XUE G L, ZHEN Y Z,et al. Monodispersed Ag nanoparticles loaded on the surface of spherical Bi2WO6 nanoarchitectures with enhanced photocatalytic activities. J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(11): 4751-4758. |
| [27] | QAMAR M, ELSAYED R B, ALHOOSHANI K R,et al. Highly efficient and selective oxidation of aromatic alcohols photocatalyzed by nanoporous hierarchical Pt/Bi2WO6 in organic solvent- free environment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7(2): 1257-1269. |
| [28] | ISMAIL A A, BAHNEMANN D W.Mesostructured Pt/TiO2 nanocomposites as highly active photocatalysts for the photooxidation of dichloroacetic acid.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(13): 5784-5791. |
| [29] | XIAO F X.Metal-cluster-decorated TiO2 nanotube arrays: a composite heterostructure toward versatile photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical applications. Small, 2015, 11(S): 554-567. |
| [30] | CHEN Y S, KAMAT P V.Glutathione-capped gold nanoclusters as photosensitizers. visible light-induced hydrogen generation in neutral water.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(16): 6075-6082. |
| [31] | SUBRAMANIAN V, WOLF E E, KAMAT P V.Catalysis with TiO2/gold nanocomposites. effect of metal particle size on the fermi level equilibration.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(15): 4943-4950. |
| [32] | WANG Z H, ZHAO S P, ZHU S Y,et al. Photocatalytic synthesis of M/Cu2O (M=Ag,Au) heterogeneous nanocrystals and their photocatalytic properties. CrystEngComm., 2011, 13(7): 2262-2267. |
| [1] | CAI Miao, CHEN Zihang, ZENG Shi, DU Jianghui, XIONG Juan. CuS Nanosheet Decorated Bi5O7I Composite for the Enhanced Photocatalytic Reduction Activity of Aqueous Cr(VI) [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 665-672. |
| [2] | LIU Cai, LIU Fang, HUANG Fang, WANG Xiaojuan. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Alga-based CDs-Cu-TiO2 Composite Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1154-1162. |
| [3] | XU Shichao,ZHU Tianzhe,QIAO Yang,BAI Xuejian,TANG Nan,ZHENG Chunming. Fabrication of Z-scheme BiVO4/GO/g-C3N4 Photocatalyst with Efficient Visble-light Photocatalytic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 839-846. |
| [4] | ZHU Enquan,MA Yuhua,AINIWA· Munire,SU Zhi. Adsorption-enrichment and Localized-photodegradation of Bentonite-supported Red Phosphorus Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 803-808. |
| [5] | LI Jian, ZHANG Gang-Hua, FAN Li-Kun, HUANG Guo-Quan, GAO Zhi-Peng, ZENG Tao. Enhanced Visible-light-driven Photocatalytic Activity of Multiferroic KBiFe2O5 by Adjusting pH Value [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(7): 805-810. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zhi-Jie, XU Jia-Yue, ZENG Hai-Bo, ZHANG Na. Carbon Quantum Dots/BiPO4 Nanocomposites with Enhanced Visible-light Absorption and Charge Separation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(5): 582-586. |
| [7] | TONG Qin, DONG Ya-Mei, YAN Liang, HE Dan-Nong. High-efficient Synthesis and Photocatalytic Properties of Ag/AgBr/TiO2 Monolithic Photocatalysts Using Sodium Alginate as Substrate [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(6): 637-642. |
| [8] | YANG Min, JIA Xiao-Peng, LI Bing-Ke, DENG Guo-Wei, WANG Qi-Hui, LIU Xiao-Yang. One-pot Synthesis and Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Properties of Zn2GeO4 Microspheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(2): 141-147. |
| [9] | JIANG Wen-Long, ZHOU Wei, YING Ji-Fei, YANG Tie-Ying, GAO Yan-Min. Thermal Stable Perovskite Solar Cells Improved by ZnO/Graphene Oxide as Electron Transfer Layers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 96-100. |
| [10] | SUN Tong, CHEN Yang, MA Xiao-Qing, LI Zhong, LI Hui, CUI Xiao-Li. Facile Synthesis of Visible Light Activated Carbon-incorporated Mn Doped TiO2 Microspheres via Flame Thermal Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(9): 1002-1008. |
| [11] | QU Ting, HUANG Qiang, ZHAO Zhen-Bo. Preparation and Visible Light Responsive Photocatalytic Activity of Bi2MoO6/Ni-Fe LDH Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(8): 825-832. |
| [12] | ZHOU Yu, ZHANG Zhi-Jie, XU Jia-Yue, CHU Yao-Qing, YOU Ming-Jiang. Synthesis and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Er3+-doped ZnWO4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(5): 549-554. |
| [13] | LIU Shi-Xin, LI Xiao-Song, DENG Xiao-Qing, SUN Zhi-Guang, ZHU Ai-Min. Influence of Calcination Temperature on Nano-TiO2 Photocatalyst Synthesized by Gliding Arc Plasma [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(2): 189-194. |
| [14] | ZENG Tao, BAI Yang, LI Hao, MAO Chao-Liang, DONG Xian-Lin, GUI Shu-Xiang. Fabrication of Barium Strontium Titanate Nanophotocatalysts with Gridding Structures and Their Photocatalytic Activities [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(12): 1334-1338. |
| [15] | HAN Cheng, LEI Yong-Peng, WANG Ying-De. Recent Progress on Nano-heterostructure Photocatalysts for Solar Fuels Generation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(11): 1121-1130. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||