
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (10): 1129-1136.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240530
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Lihua( ), WANG Yanshuai, YIN Xinwu, MAO Yeqiong, NIU Dechao(
), WANG Yanshuai, YIN Xinwu, MAO Yeqiong, NIU Dechao( )
)
Received:2024-12-20
Revised:2025-03-15
Published:2025-10-20
Online:2025-04-15
Contact:
NIU Dechao, professor. E-mail: dcniu@ecust.edu.cnAbout author:ZHAO Lihua (1999-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: Lizzzzz233@outlook.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHAO Lihua, WANG Yanshuai, YIN Xinwu, MAO Yeqiong, NIU Dechao. Bismuth Sulfide Nanoclusters-loaded Silica-based Hybrid Micelles: Preparation and Photothermal Antibacterial Property[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1129-1136.
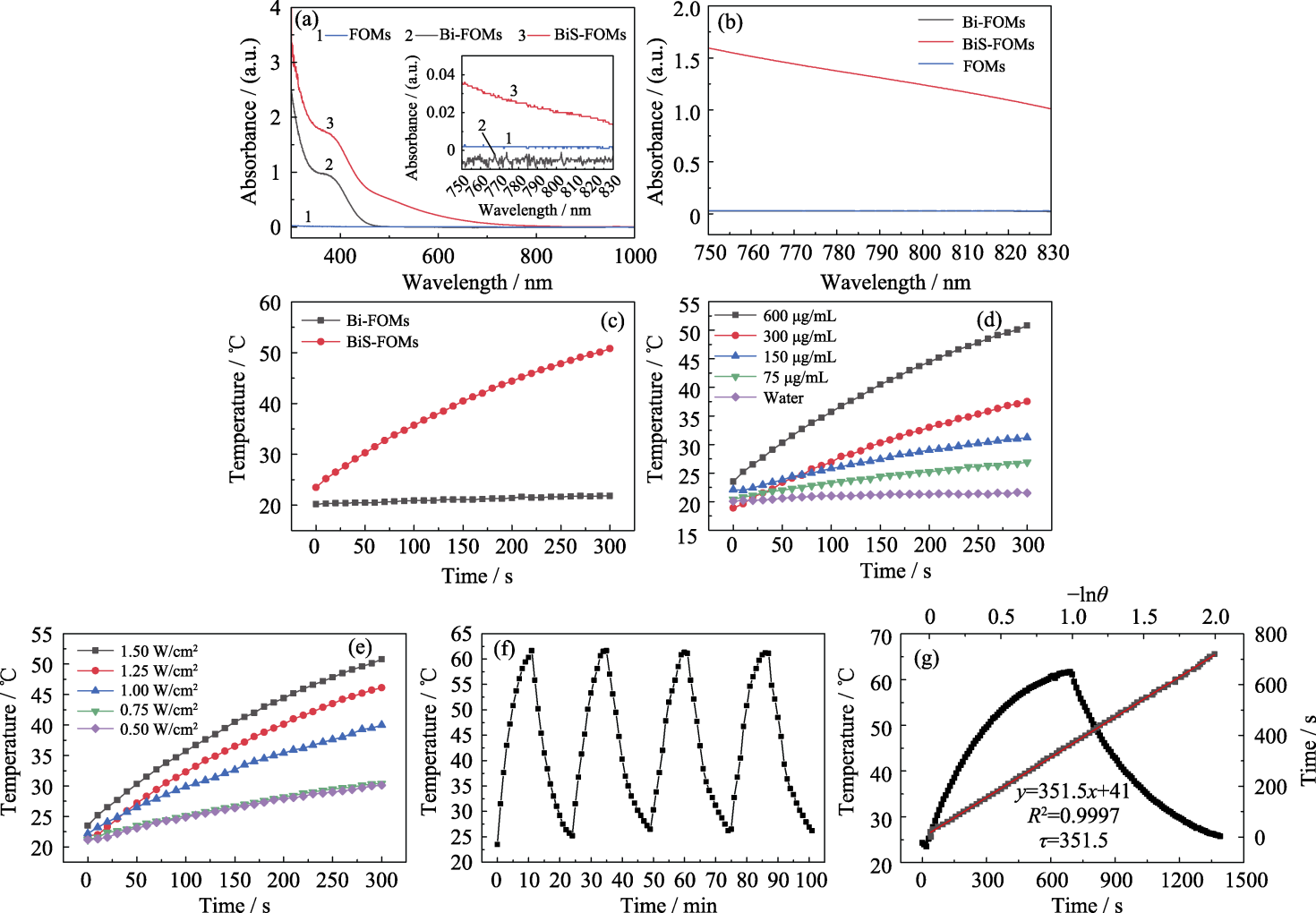
Fig. 7 Photothermal performance of FOMs, Bi-FOMs and BiS-FOMs (a, b) UV-Vis absorption spectra of samples with Bi concentration of 60 (a) and 600 mg/L (b); (c) Temperature-time curves of samples under 808 nm laser radiation for 5 min (power density of 1.5 W/cm2, Bi concentration of 600 mg/L ); (d) Temperature-time relationship of BiS-FOMs with different Bi concentrations under 808 nm laser irradiation for 5 min (power density of 1.5 W/cm2); (e) Temperature-time relationship of BiS-FOMs with Bi concentration at 600 mg/L under 808 nm laser irradiation with different power densities for 5 min; (f) Four ramp-up/down cycle curves of BiS-FOMs with or without laser radiation (1.5 W/cm2, 808 nm, 600 mg/L for Bi); (g) Photothermal conversion efficiency of BiS-FOMs (1.5 W/cm2, 808 nm, 600 mg/L for Bi); Colorful figures are available on website
| Material | Photothermal conversion efficiency, η | Concentration/ (mg·L-1) | Power density/ (W·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi2S3 | 33.58% | 100 | 0.75 | [ |
| Bi2S3-Au NRs | 51.06% | 100 | 0.75 | [ |
| Au/Bi2S3NFs | 58.3% | 180 | 2 | [ |
| Fe3O4@PDA@BSA-Bi2S3NPs | 47.6% | 900 | 1 | [ |
| Cu1.94S-Bi2S3@PSIOAm NCs | 31% | 300 | 1 | [ |
| Au-Bi2S3 HNSCs | ~15% | 50 | 1 | [ |
| Au@Bi2S3 | 35.30% | 125 | 2 | [ |
| Bi2S3/Cu2S/Cu3BiS3 | 43.8% | 200 | 0.75 | [ |
| BiS-FOMs | 86.93% | 600 | 1.5 | This work |
Table 1 Photothermal conversion efficiency of reported Bi-based materials under 808 nm wavelength laser irradiation
| Material | Photothermal conversion efficiency, η | Concentration/ (mg·L-1) | Power density/ (W·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi2S3 | 33.58% | 100 | 0.75 | [ |
| Bi2S3-Au NRs | 51.06% | 100 | 0.75 | [ |
| Au/Bi2S3NFs | 58.3% | 180 | 2 | [ |
| Fe3O4@PDA@BSA-Bi2S3NPs | 47.6% | 900 | 1 | [ |
| Cu1.94S-Bi2S3@PSIOAm NCs | 31% | 300 | 1 | [ |
| Au-Bi2S3 HNSCs | ~15% | 50 | 1 | [ |
| Au@Bi2S3 | 35.30% | 125 | 2 | [ |
| Bi2S3/Cu2S/Cu3BiS3 | 43.8% | 200 | 0.75 | [ |
| BiS-FOMs | 86.93% | 600 | 1.5 | This work |
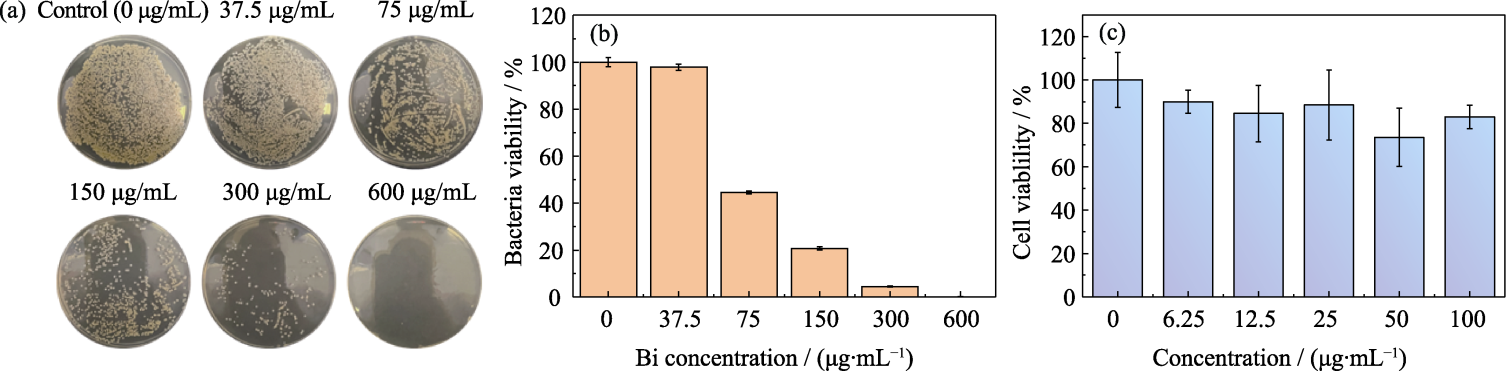
Fig. 8 Antibacterial effect and cytocompatibility of BiS-FOMs (a) Digital photos and (b) quantitetive colonies of Staphylococcus aureus treated with BiS-FOMs at different Bi concentrations under 808 nm laser (1.5 W/cm2) rediation for 10 min; (c) In vitro cell survival rates of HUVECs treated with BiS-FOMs at different Bi concentrations for 48 h
| [1] |
ZHI D F, YANG T, O’HAGAN J, et al. Photothermal therapy. Journal of Controlled Release, 2020, 325: 52.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | LI C W, CHENG Y, LI D W, et al. Antitumor applications of photothermal agents and photothermal synergistic therapies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(14): 7909. |
| [3] | HE Z Y, BU P Z, XU K, et al. Remodeling of the pro-inflammatory microenvironment in osteoarthritis via hydrogel-based photothermal therapy. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2024, 7(2): 36. |
| [4] | LV H W, ZHOU X M, YANG G, et al. Bismuth@bismuth sulfide core@shell structure for near infrared II light triggered photothermal therapy. ChemistrySelect, 2024, 9(12): e202304834. |
| [5] | YE M L, SHI F, SHEN M, et al. Composite soft-template method synthesis and biosensing application of hedgehog-like bismuth sulfide micro-nanostructures. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 613: 126094. |
| [6] | SUN B, FENG T T, DONG J, et al. Green synthesis of bismuth sulfide nanostructures with tunable morphologies and robust photoelectrochemical performance. CrystEngComm, 2019, 21(9): 1474. |
| [7] | ANASANE N, AMETA R. Morphologies of nanostructured bismuth sulphide and Mn (II) doped bismuth sulphide nanoparticles: characterization and application. Materials Science-Poland, 2017, 35(1): 6. |
| [8] | SHAHBAZI M A, FAGHFOURI L, FERREIRA M P A, et al. The versatile biomedical applications of bismuth-based nanoparticles and composites: therapeutic, diagnostic, biosensing, and regenerative properties. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(4): 1253. |
| [9] | NIKODIMOS Y, HUANG C J, TAKLU B W, et al. Chemical stability of sulfide solid-state electrolytes: stability toward humid air and compatibility with solvents and binders. Energy & Environmental Science, 2022, 15(3): 991. |
| [10] | LI Y H, TAN X X, WANG H, et al. Spectral computed tomography-guided photothermal therapy of osteosarcoma by bismuth sulfide nanorods. Nano Research, 2023, 16(7): 9885. |
| [11] | FANG Q L, XU Y, LUO L J, et al. Controllable synthesis of layered black bismuth oxidechloride nanosheets and their applications in internal tumor ablation. Regenerative Biomaterials, 2022, 9: rbac036. |
| [12] | SONG S L, LIAO L, LEI H, et al. Purification of iodine from high-temperature argon environment by bismuth sulfide-modified zeolite. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2025, 59(1): 57. |
| [13] | DING F C, WANG Q J, ZHOU S F, et al. Synthesis of Bi2S3 thin films based on pulse-plating bismuth nanocrystallines and its photoelectrochemical properties. Royal Society Open Science, 2020, 7(8): 200479. |
| [14] | CHENG J H, FENG W L, YANG X Z, et al. High-performance Bi2S3 photodetector based on oxygen-mediated defect engineering and its wafer-scale fast fabrication. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2025, 679: 373. |
| [15] | ZHAO Z W, CHI Z R, SUN Q Q, et al. Preparation and performance of palladium clusters-loaded silica-based hybrid micelles. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology, 2023, 49(4): 498. |
| [16] |
ZHANG X, QIAO X F, SHI W, et al. Phonon and Raman scattering of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides from monolayer, multilayer to bulk material. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(9): 2757.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | YU N, LIU X L, LU Z W, et al. Polymorph control, phase transitions and photocatalytic activity of bismuth oxide with emphasis on sodium-impurity effects. Ceramics International, 2025, 51(18): 24960. |
| [18] | CHENG D Y, CHANG Y, FENG Y L, et al. Deep-level defect enhanced photothermal performance of bismuth sulfide-gold heterojunction nanorods for photothermal therapy of cancer guided by computed tomography imaging. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(1): 246. |
| [19] | ZHAO X S, LI S W, HUANG T D, et al. Synthesis of Au/Bi2S3 nanoflowers for efficient photothermal therapy. New Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 44(43): 18724. |
| [20] | LUO K Y, ZHAO J L, JIA C Z, et al. Integration of Fe3O4 with Bi2S3 for multi-modality tumor theranostics. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(20): 22650. |
| [21] | LU X, LI Y, BAI X, et al. Multifunctional Cu1.94S-Bi2S3@polymer nanocomposites for computed tomography imaging guided photothermal ablation. Science China Materials, 2017, 60(8): 777. |
| [22] | WANG X, ZHANG C Y, DU J F, et al. Enhanced generation of non-oxygen dependent free radicals by Schottky-type heterostructures of Au-Bi2S3 nanoparticles via X-ray-induced catalytic reaction for radiosensitization. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(5): 5947. |
| [23] | WANG W N, PEI P, CHU Z Y, et al. Bi2S3 coated Au nanorods for enhanced photodynamic and photothermal antibacterial activities under NIR light. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 397: 125488. |
| [24] | YU G D, LIU A L, JIN H L, et al. Urchin-shaped Bi2S3/Cu2S/Cu3BiS3 composites with enhanced photothermal and CT imaging performance. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(7): 3794. |
| [1] | CHI Zheren, ZHANG Liao, GUO Zhiqian, LI Yongsheng, NIU Dechao. Flav7-loaded Silica-based Hybrid Micelles: Synthesis and Photothermal Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1236-1244. |
| [2] | LUO Wei, WEI Jing DENG Yong-Hui, LI Yu-Hui, WANG Lian-Jun, ZHAO Tao, JIANG Wan. Progress on the Fabrication of Ordered Mesoporous Materials with Large Pores by Using Novel Amphiphilic Block Copolymers as Templates [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 1-10. |
| [3] | CHEN Yu, LI Wen-Rui, XU Can, SU Jia-Can, LI Ming, LIU Chang-Sheng. Study on Hemostatic Materials of Mesoporous Silicon Dioxide Doped Ca and Ag with Antibacterial Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(5): 513-518. |
| [4] | SONG Wei-Juan,LIU Hong-Tao,WANG Kun,CAO Jin,XU Chun-Yan,ZHANG Ze-Ting. Preparation of Trimodal Macro-meso-microporous Aluminosilicates by Colloidal Crystal/P123 Dual Templates [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 15(2): 163-167. |
| [5] | DAI Jin-Ming,HOU Wen-Sheng,WEI Li-Qiao,JIA Hu-Sheng,LIU Xu-Guang,XU Bing-She. Study on the Color Change Resistant Property of Silver and Zinc-loading Zeolite 4A Antibacterial Agent [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(5): 1011-1015. |
| [6] | HOU Wen-Sheng,WEI Li-Qiao,DAI Jin-Ming,JIA Hu-Sheng,XU Bing-She. Preparation and Antibacterial Performance of Zeolite Loaded Silver Antibacterial Agent [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2005, 20(4): 907-913. |
| [7] | ZHOU Yan-Fei,WANG Jin-Chang,TANG Lian-An,CHEN Nuo-Fu,CHEN Wan-Chun. Growth of CeO2:Bi12SiO20 Crystals in Multi-Position Furnace(Ⅱ)- Space Growth Experiment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2004, 19(2): 283-288. |
| [8] | ZHU Rong,CHEN Hang-Hong,SHI Jian-Lin,VAN Dong-Sheng. Synthesis and Characterization of SBA-15 and SBA-16 Templated by Block Copolymers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2003, 18(4): 855-860. |
| [9] | ZHOU Yan-Fei,TANG Lian-An,AI Fei,ZHU Jun-Xiong. Crystal Growth of Bismuth Silicon Oxide(BSO) in Space [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2003, 18(1): 211-214. |
| [10] | ZHOU Yan-Fei,TANG Lian-An,ZHU Jun-Xiong. Growth of CeO2:Bi12SiO20 Crystals in the Multi-Position Furnace [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2002, 17(2): 353-356. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||