
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (12): 1327-1331.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170061
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Yang-Bo, SANG Li-Xia
Received:2017-02-26
Revised:2017-03-27
Published:2017-12-20
Online:2017-11-21
CLC Number:
ZHAO Yang-Bo, SANG Li-Xia. TiO2 Nanoring/Nanotube Hierarchical Structure Growth Mechanism and Optical Absorption Property[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(12): 1327-1331.
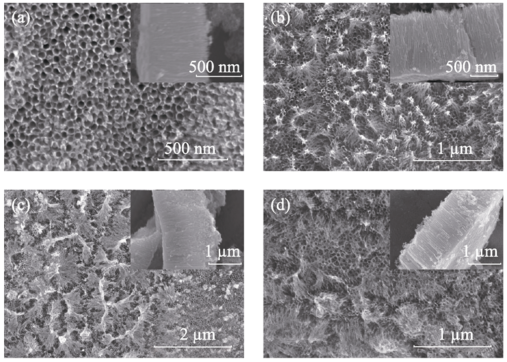
Fig. 1 Top and cross-sectional (insert) morphologies of TiO2 nanotube arrays grown for different oxidation time(a) 20 V-20 min; (b) 20 V-30 min; (c) 20 V-60 min; (d) 20 V-100 min

Fig. 4 Top and cross-sectional (insert) morphologies of TiO2 nanoring/nanotube hierarchical structure grown at different oxidation time in the second step anodization(a) 60 V-1 h/20 V-20 min; (b) 60 V-1 h/20 V-30 min; (c) 60 V-1 h/20 V-60 min; (d) 60 V-1 h/20 V-100 min
| [1] | SANG L X, ZHAO Y X, BURDA C.TiO2 nanoparticles as functional building blocks.Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(19): 9283-9318. |
| [2] | SHANKAR K, MOR G K, FITZGERALD A,et al. Cation effect on the electrochemical formation of very high aspect ratio TiO2 nanotube arrays in formamide-water mixtures. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2007, 111(1): 21-26. |
| [3] | KIM D, GHICOV A, SCHMUKI P.TiO2 Nanotube arrays: elimination of disordered top layers (“nanograss”) for improved photoconversion efficiency in dye-sensitized solar cells.Electrochemistry Communications, 2008, 10(12): 1835-1838. |
| [4] | MENG X, LEE T Y, CHEN H,et al Fabrication of free standing anodic titanium oxide membranes with clean surface using recycling process.Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2010, 10(7): 4259-4265. |
| [5] | SONG Y Y, LYNCH R, KIM D,et al. TiO2 nanotubes: efficient suppression of top etching during anodic growth key to improved high aspect ratio geometries. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2009, 12(7): C17-C20. |
| [6] | ZHANG Z, HOSSAIN M F, TAKAHASHI T.Photoelectrochemical water splitting on highly smooth and ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays for hydrogen generation.International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(16): 8528-8535. |
| [7] | WANG F, LIU Y, DONG W,et al. Tuning TiO2 photoelectrochemical properties by nanoring/nanotube combined structure. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(30): 14635-14640. |
| [8] | ANITHA V C, BANERJEE A N, JOO S W,et al Fabrication of hierarchical porous anodized titania nano-network with enhanced active surface area: ruthenium-based dye adsorption studies for dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) application.Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2015, 29: 227-237. |
| [9] | ZHANG Z, ZHANG L, HEDHILI M N,et al. Plasmonic gold nanocrystals coupled with photonic crystal seamlessly on TiO2 nanotube photoelectrodes for efficient visible light photoelectrochemical water splitting. Nano Letters, 2012, 13(1): 14-20. |
| [10] | ROY P, BERGER S, SCHMUKI P.TiO2 nanotubes: synthesis and applications.Angewandte Chemie, 2011, 50(13): 2904-2939. |
| [11] | BERGER S, KUNZE J, SCHMUKI P,et al. Influence of water content on the growth of anodic TiO2 nanotubes in fluoride- containing ethylene glycol electrolytes. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157(1): C18-C23. |
| [12] | WANG X, ZHANG S, SUN L.A two-step anodization to grow high-aspect-ratio TiO2 nanotubes.Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519(15): 4694-4698. |
| [13] | MOR G K, VARGHESE O K, PAULOSE M,et al. A review on highly ordered, vertically oriented TiO2 nanotube arrays: fabrication, material properties, and solar energy applications. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2006, 90(14): 2011-2075. |
| [14] | MACAK J M, TSUCHIYA H, GHICOV A,et al. TiO2 nanotubes: self-organized electrochemical formation, properties and applications. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 2007, 11(1): 3-18. |
| [15] | ZHAO Z, ZHANG X, ZHANG G,et al. Effect of defects on photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2 nanorods. Nano Research, 2015, 8(12): 4061-4071. |
| [16] | ZUO F, WANG L, WU T,et al. Self-doped Ti3+ enhanced photocatalyst for hydrogen production under visible light. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(34): 11856-11857. |
| [17] | WANG H, YOU T, SHI W,et al. Au/TiO2/Au as a plasmonic coupling photocatalyst. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(10): 6490-6494. |
| [18] | CHIARELLO G, TEALDI C, MUSTARELLI P,et al. Fabrication of Pt/Ti/TiO2 photoelectrodes by RF-magnetron sputtering for separate hydrogen and oxygen production. Materials, 2016, 9(4): 279. |
| [19] | MUTITU J G, SHI S, BARNETT A,et al Hybrid dielectric- metallic back reflector for amorphous silicon solar cells.Energies, 2010, 3(12): 1914-1933. |
| [20] | SANG L X, ZHANG Z Y, MA C F.Photoelectrical and charge transfer properties of hydrogen-evolving TiO2 nanotube arrays electrodes annealed in different gases.International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(8): 4732-4738. |
| [21] | TSUI L K, ZANGARI G.Titania nanotubes by electrochemical anodization for solar energy conversion.Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2014, 161(7): D3066-D3077. |
| [1] | YANG Yan, ZHANG Faqiang, MA Mingsheng, WANG Yongzhe, OUYANG Qi, LIU Zhifu. Low Temperature Sintering of ZnAl2O4 Ceramics with CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5 Composite Oxide Sintering Aid [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 711-718. |
| [2] | MA Binbin, ZHONG Wanling, HAN Jian, CHEN Liangyu, SUN Jingjing, LEI Caixia. ZIF-8/TiO2 Composite Mesocrystals: Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 937-944. |
| [3] | REN Guanyuan, LI Yiguan, DING Donghai, LIANG Ruihong, ZHOU Zhiyong. CaBi2Nb2O9 Ferroelectric Thin Films: Modulation of Growth Orientation and Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1228-1234. |
| [4] | CHEN Haiyan, TANG Zhipeng, YIN Liangjun, ZHANG Linbo, XU Xin. Low-frequency Microwave Absorption of CIPs@Mn0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4-CNTs Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 71-80. |
| [5] | TIAN Yubin, TIAN Chaofan, LI Sen, ZHAO Yongxin, XING Tao, LI Zhi, CHEN Xiaoru, XIANG Shuairong, DAI Pengcheng. Biomass-derived High-conductivity Carbon Cloth: Preparation and Application as Gas Diffusion Layers in Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1316-1322. |
| [6] | WANG Mengtao, SUO Jun, FANG Dong, YI Jianhong, LIU Yichun, Olim RUZIMURADOV. Visible-light Catalytic Performance of ITO/TiO2 Nanotube Array Composite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1292-1300. |
| [7] | JIA Xin, LI Jinyu, DING Shihao, SHEN Qianqian, JIA Husheng, XUE Jinbo. Synergy Effect of Pd Nanoparticles and Oxygen Vacancies for Enhancing TiO2 Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1301-1308. |
| [8] | AN Lin, WU Hao, HAN Xin, LI Yaogang, WANG Hongzhi, ZHANG Qinghong. Non-precious Metals Co5.47N/Nitrogen-doped rGO Co-catalyst Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Performance of TiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 534-540. |
| [9] | WU Qiuqin, YAO Fenfa, JIN Chuanhong, ZHENG Yifan. One-dimensional Sub-stoichiometric W3O8 Nanowires Filled Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 413-419. |
| [10] | LÜ Qingyang, ZHANG Yuting, GU Xuehong. Fabrication of Hollow Fiber Supported TiO2 Ultrafiltration Membranes via Ultrasound-assisted Sol-Gel Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1051-1057. |
| [11] | LIU Fangfang, CHUAN Xiuyun, YANG Yang, LI Aijun. Influence of N/S Co-doping on Electrochemical Property of Brucite Template Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 711-717. |
| [12] | XIAO Xiang, GUO Shaoke, DING Cheng, ZHANG Zhijie, HUANG Hairui, XU Jiayue. CsPbBr3@TiO2 Core-shell Structure Nanocomposite as Water Stable and Efficient Visible-light-driven Photocatalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 507-512. |
| [13] | XI Wen, LI Haibo. Preparation of TiO2/Ti3C2Tx Composite for Hybrid Capacitive Deionization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 283-291. |
| [14] | LIU Cai, LIU Fang, HUANG Fang, WANG Xiaojuan. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Alga-based CDs-Cu-TiO2 Composite Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1154-1162. |
| [15] | Li Cuixia, SUN Huizhen, JIN Haize, SHI Xiao, LI Wensheng, KONG Wenhui. Construction and Photocatalytic Performance of 3D Hierarchical Pore rGO/TiO2 Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1039-1046. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||