
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (10): 1097-1110.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250025
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
YUAN Long1( ), JIA Ru1, YUAN Meng1,2, ZHANG Jian2, DUAN Yu2, MENG Xiangdong1(
), JIA Ru1, YUAN Meng1,2, ZHANG Jian2, DUAN Yu2, MENG Xiangdong1( )
)
Received:2025-01-16
Revised:2025-02-18
Published:2025-10-20
Online:2025-05-09
Contact:
MENG Xiangdong, professor. E-mail: xdmeng@jlnu.edu.cnAbout author:YUAN Long (1988-), male, associate professor. E-mail: yuanlong@jlnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
YUAN Long, JIA Ru, YUAN Meng, ZHANG Jian, DUAN Yu, MENG Xiangdong. Mechanism and Application of X-ray Induced Photochromic Materials: A Review[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1097-1110.
Fig. 1 Electromagnetic spectrum with the red box indicating the wavelength range corresponding to X-rays, and the curve above representing the electromagnetic wave energy
| Material system | Advantage | Disadvantage | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic XP material (Iodine modified isomers based on 9,9'-(6-iodophenoxy- 1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diylbis (9h carbazole)[ compounds[ | Easy to regulate optical properties; Flexible, tunable photosensitive band and reaction rate through chemical modification; Lightweight, easy to shape, and suitable for various carriers | Poor stability and susceptibility to environmental factors such as humidity and oxygen; Low thermal stability | Reversible photoisomeri- zation or open-closed-loop reaction of organic molecules under X-ray excitation to achieve color change by adjusting the electronic transition energy level of the molecule |
| Organic inorganic hybrid XP material (Zn(II)-viologen coordination polymers[ | Combining flexibility of organic materials with stability of inorganic materials; Multifunctional and adjustable based on the ratio of organic and inorganic parts; Wide radiation response range tunable optical properties through material design | Complex synthesis, stability of interface bonding needs to be further improved; Complexity of material composites resulting in difficulty in mass production and repeatability control | Based on the interfacial charge transfer or energy transfer between organic and inorganic components, the synergistic initiation of structural reorganization or redox reaction leads to color change |
| Inorganic XP material (NaLuF4:Ho3+[ BaMgSiO4[ | High stability, high temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance; Strong responsiveness to high- energy radiation such as X-rays; Good thermal, light, and chemical stability, excellent long-term performance | Usually, less obvious color change than that of organic materials, difficult in controlling reversibility; Poor flexibility, difficult in processing into complex structures | X-rays induce lattice defects or metal ion valence state changes, changing the band structure of the material or forming a color center, and finally achieving color change |
Table 1 Advantages and disadvantages of XP materials[14-21]
| Material system | Advantage | Disadvantage | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic XP material (Iodine modified isomers based on 9,9'-(6-iodophenoxy- 1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diylbis (9h carbazole)[ compounds[ | Easy to regulate optical properties; Flexible, tunable photosensitive band and reaction rate through chemical modification; Lightweight, easy to shape, and suitable for various carriers | Poor stability and susceptibility to environmental factors such as humidity and oxygen; Low thermal stability | Reversible photoisomeri- zation or open-closed-loop reaction of organic molecules under X-ray excitation to achieve color change by adjusting the electronic transition energy level of the molecule |
| Organic inorganic hybrid XP material (Zn(II)-viologen coordination polymers[ | Combining flexibility of organic materials with stability of inorganic materials; Multifunctional and adjustable based on the ratio of organic and inorganic parts; Wide radiation response range tunable optical properties through material design | Complex synthesis, stability of interface bonding needs to be further improved; Complexity of material composites resulting in difficulty in mass production and repeatability control | Based on the interfacial charge transfer or energy transfer between organic and inorganic components, the synergistic initiation of structural reorganization or redox reaction leads to color change |
| Inorganic XP material (NaLuF4:Ho3+[ BaMgSiO4[ | High stability, high temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance; Strong responsiveness to high- energy radiation such as X-rays; Good thermal, light, and chemical stability, excellent long-term performance | Usually, less obvious color change than that of organic materials, difficult in controlling reversibility; Poor flexibility, difficult in processing into complex structures | X-rays induce lattice defects or metal ion valence state changes, changing the band structure of the material or forming a color center, and finally achieving color change |
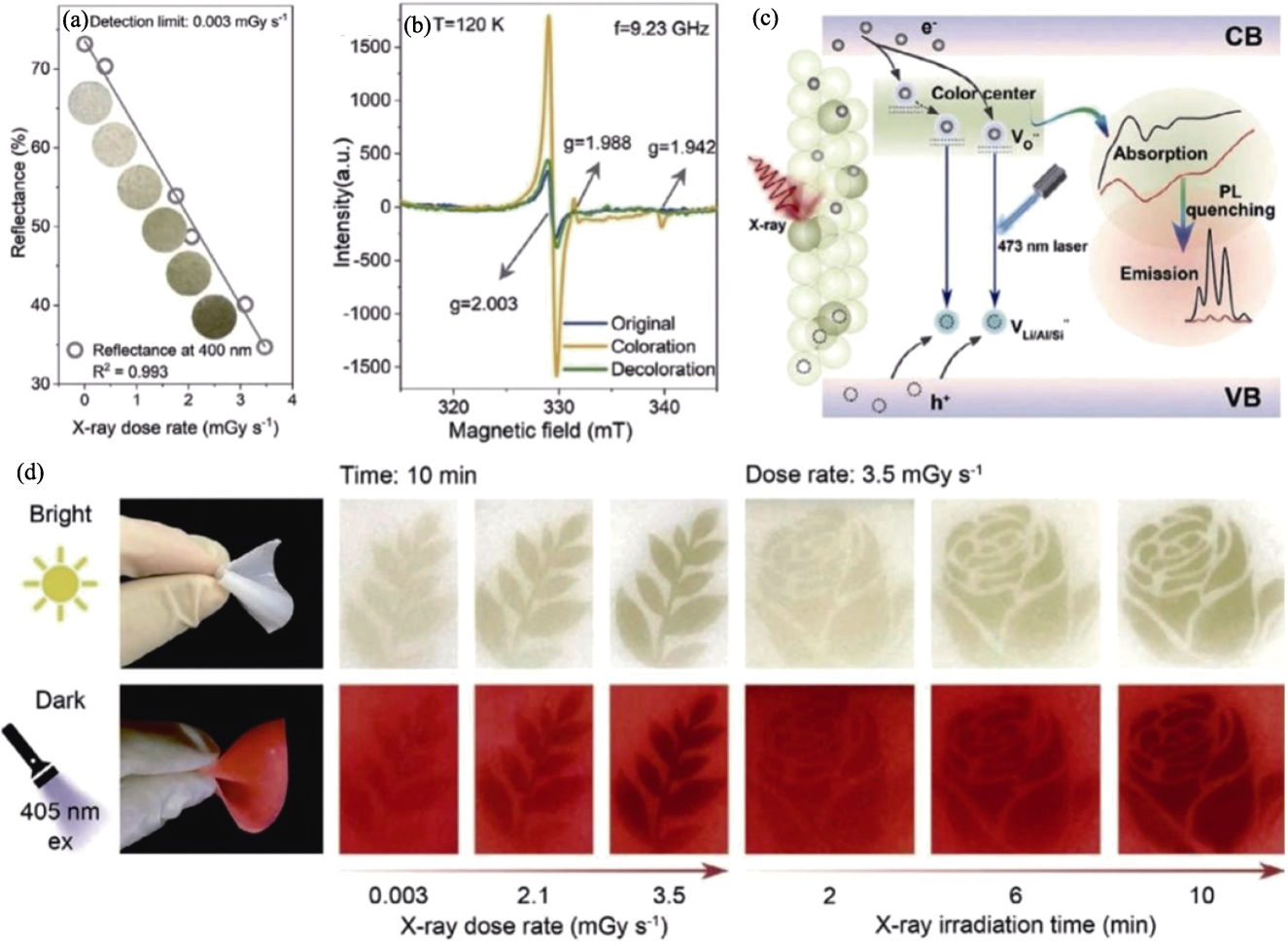
Fig. 2 Reversible formation mechanism of color center[45] (a) LAS-Sm relationship between diffuse reflectance intensity and X-ray dose rate accompanied by its corresponding photos; (b) EPR spectra of O element in initial state, photochromic state, and decolorized state; (c) Photochromic and luminescent modulation mechanism of LAS-Sm fluorescent powder; (d) Morphology of leaves and roses after irradiation with gradually prolonged time or different dose rates in bright and dark fields
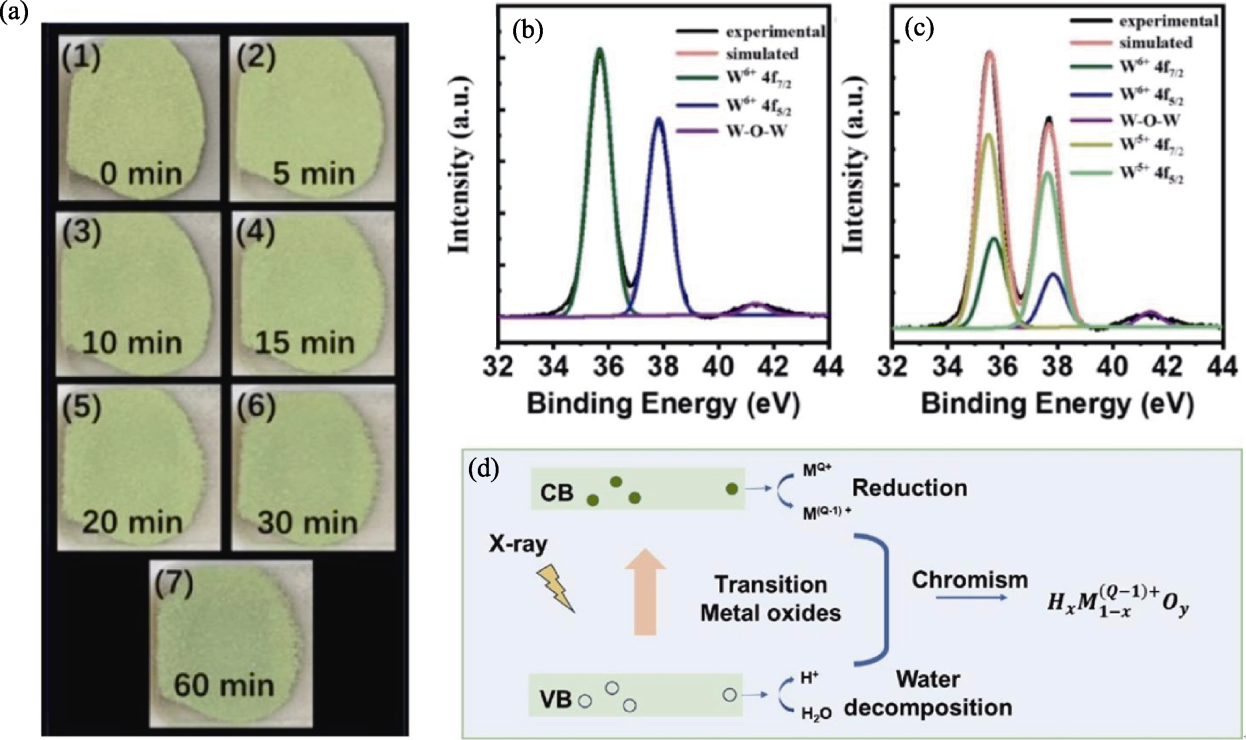
Fig. 3 Redox reaction mechanism[20,25] (a) Digital photos of WO3 powder under different X-ray irradiation times[20]; (b, c) XPS (Al-Kα) nuclear level spectra of WO3 powder before (b) and after (c) X-ray irradiation[20]; (d) General model for X-ray induced photochromism of transition metal oxides[25]
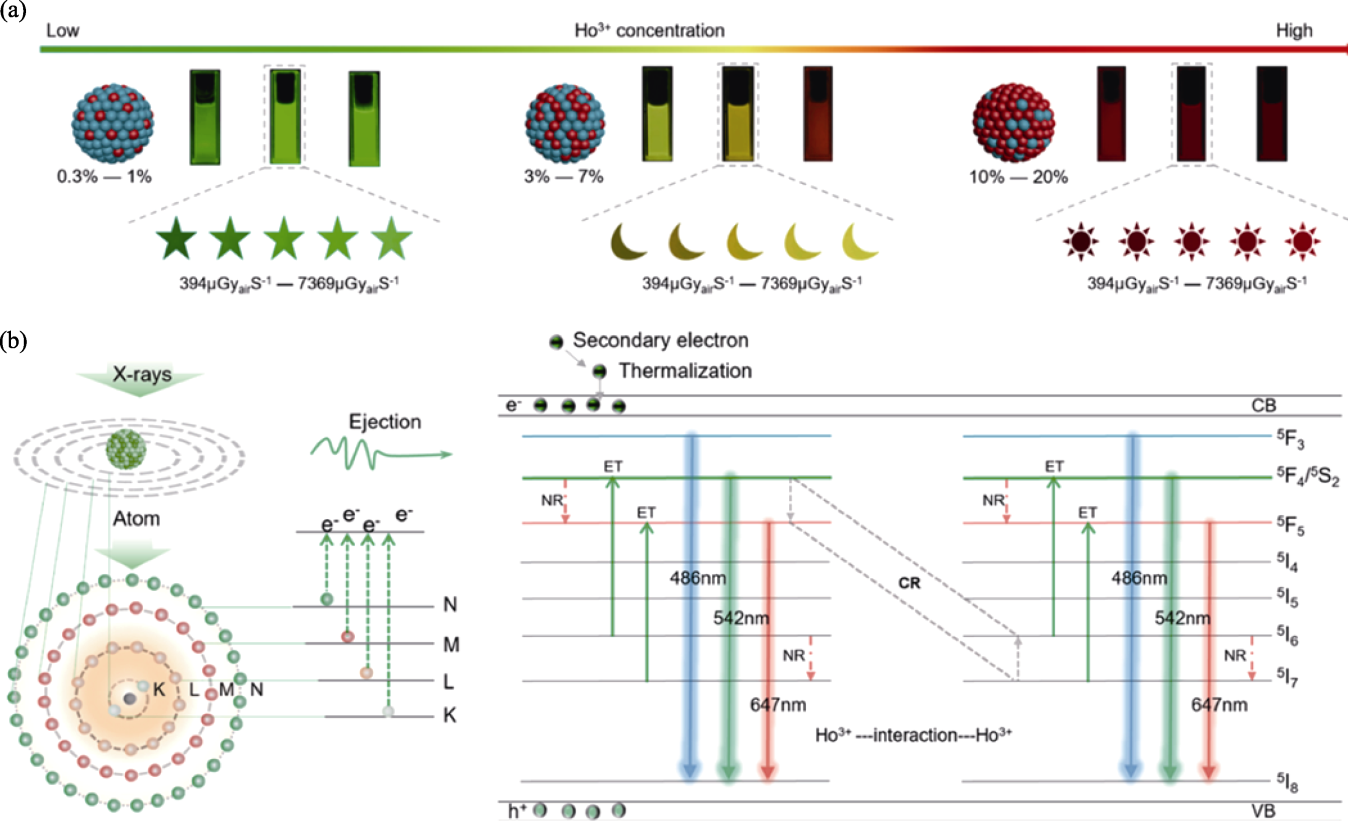
Fig. 4 Photoelectron transfer mechanism of defects associated with cross-relaxation[19] (a) Photos of NaLuF4: Ho3+ NCs doped with different concentrations of Ho3+ ions at different X-ray irradiation doses; (b) Color changing mechanism of NaLuF4: Ho3+ NCs
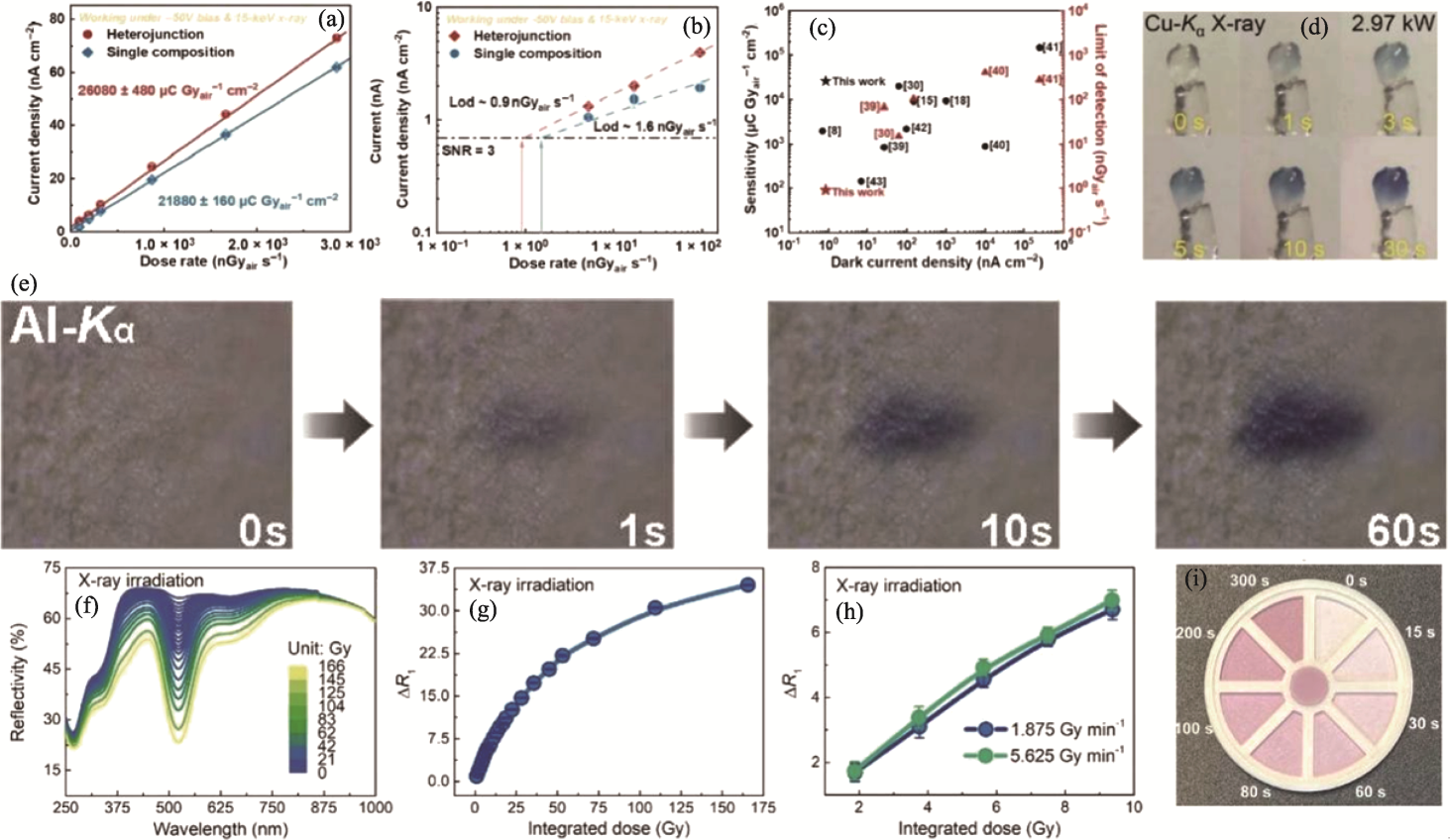
Fig. 5 Application of XP materials in X-ray detectors[18,21,27,57] (a-c) X-ray detection performance of single component and heterojunction detectors under 15 keV X-ray and -50 V bias[57]: (a) Current density of single component and heterojunction as a function of incident dose rate; (b) Dose dependent current density of single component and heterojunction with dashed line representing a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of 3; (c) Comparison of dark current density, sensitivity, and detection limit (LOD) of several advanced polycrystalline perovskite X-ray detectors; (d) Single crystal exposed to Cu-Kα X-ray (λ at 0.154056 nm, generator power at 2.97 kW) discoloration photo[18]; (e) Colour images of Al-Kα X-rays over time after 1 min of irradiation[27]; (f) Reflectance of BaMgSiO4 after exposure to different doses of X-rays (1.875 Gy·min-1)[21]; (g) Relationship between ΔR1 (coloring) and comprehensive X-ray irradiation dose[21]; (h) Dosimetric behavior of BaMgSiO4 under different X-ray irradiation intensities[21]; (i) Concept validation dosimeter for colorimetric detection of radiation dose[21]
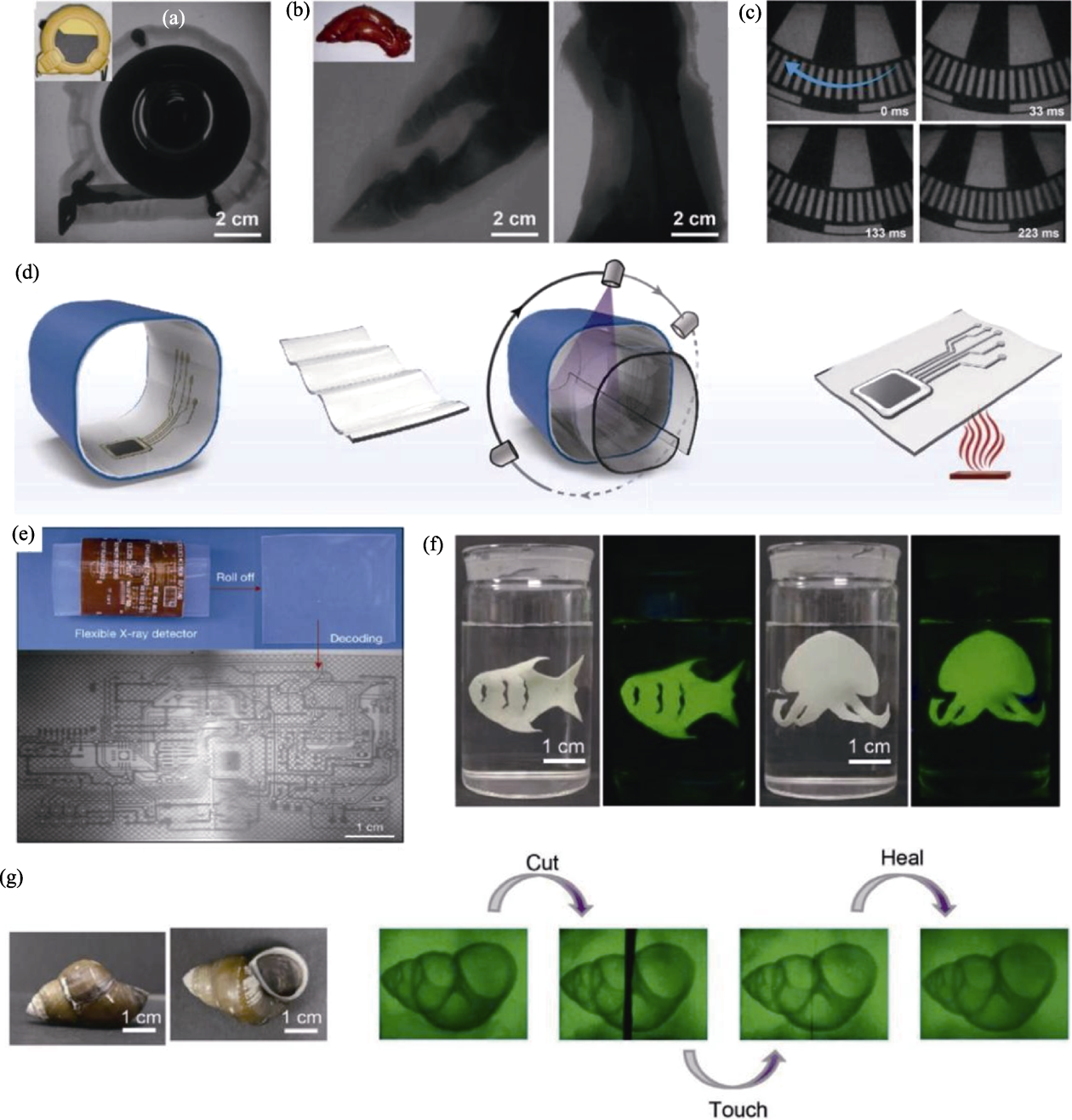
Fig. 6 XP materials for X-ray imaging applications[26,28,36] (a) X-ray image of a tape measure[28]; (b) Pig trotters with a large flashing screen[28]; (c) Dynamic X-ray image of a chopper[28]; (d) High resolution Xr LEI illustrated by schematic diagram of 3D electronic imaging achieved by a flexible detector integrated with nano scintillators (Firstly, insert the detector into the 3D electronic circuit board for conformal coating; Next, the image of the electronic board is projected onto the detector; After stopping the X-ray, the detector is transferred to a hot substrate for thermal stimulation and subsequent luminescence imaging)[36]; (e) Xr LEI (voltage 50 kV) of 3D electronic board using prototype NaLuF4:Tb (15%, in mol) @NaYF4 detector[36]; (f) Photos of organic gel scintillators immersed in water under visible light and 365 nm ultraviolet light[26]; (g) Photos of snails under visible light and organic gel scintillators conducting self-healing X-ray imaging in water[26]
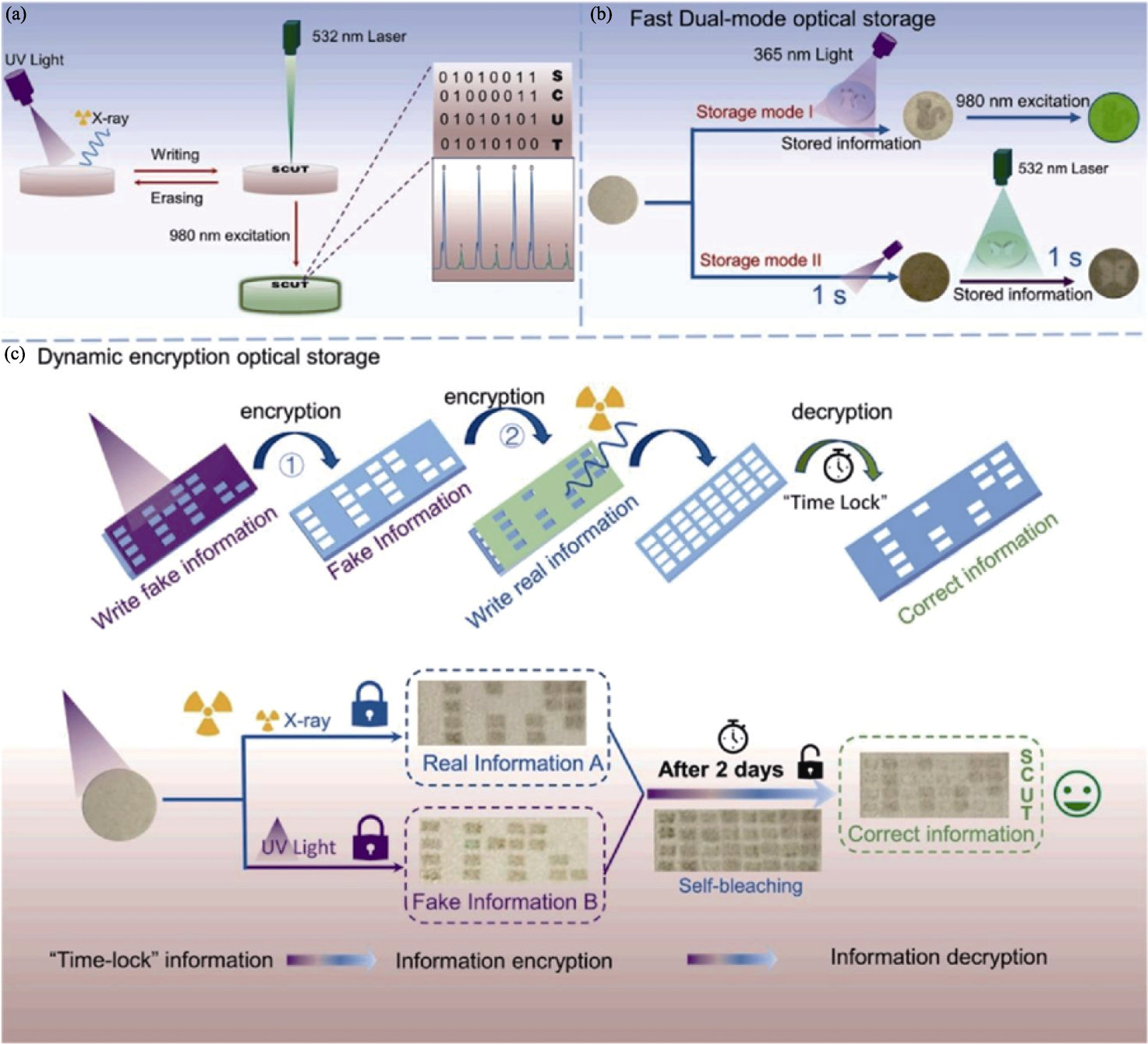
Fig. 7 Application of XP materials in the field of information storage and anti-counterfeiting[35] (a) BNN:Er ceramic for reading, writing, and erasing processes of optical information; (b) Dual mode for fast optical storage; (c) Dynamic encryption for optical storage model
| [1] |
GLASS B. The genetic hazards of nuclear radiations. Science, 1957, 126(3267): 241.
PMID |
| [2] | DU M H, WANG J, XU S J, et al. Super-elastic scintillating fibers and fabrics for efficient and visual radiation detection. Advanced Fiber Materials, 2023, 5(4): 1493. |
| [3] | LUO Z C, WU Y Y, WANG Y N, et al. Clinical radiation dose verification by topographic persistent luminescence dosimetry. Nano Today, 2023, 50: 101854. |
| [4] | CAO C T, TONEY M F, SHAM T K, et al. Emerging X-ray imaging technologies for energy materials. Materials Today, 2020, 34: 132. |
| [5] | HAN J S, LEE S H, GO H, et al. High-performance cold cathode X-ray tubes using a carbon nanotube field electron emitter. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(7): 10231. |
| [6] | NAKAJIMA T, MURAYAMA Y, MATSUZAWA T, et al. Development of a new highly sensitive LiF thermoluminescence dosimeter and its applications. Nuclear Instruments and Methods, 1978, 157(1): 155. |
| [7] | ZHANG H, YANG Z, ZHOU M, et al. Reproducible X-ray imaging with a perovskite nanocrystal scintillator embedded in a transparent amorphous network structure. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(40): 2102529. |
| [8] | COLETTE D, MAZON D, BARNSLEY R, et al. Conceptual study of energy resolved X-ray measurement and electron temperature reconstruction on ITER with low voltage ionization chambers. The Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92(8): 083511. |
| [9] | JIANG J, XIONG M, FAN K, et al. Synergistic strain engineering of perovskite single crystals for highly stable and sensitive X-ray detectors with low bias imaging and monitoring. Nature Photonics, 2022, 16: 575. |
| [10] |
THIRIMANNE H M, JAYAWARDENA K I, PARNELL A J, et al. High sensitivity organic inorganic hybrid X-ray detectors with direct transduction and broadband response. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 2926.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | LEISTNER A L, PIANOWSKI Z L. Smart photochromic materials triggered with visible light. European Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 2022(19): e202101271. |
| [12] | BEAUMONT J H, HART M. Multiple Bragg reflection monochromators for synchrotron X radiation. Journal of Physics E: Scientific Instruments, 1974, 7(10): 823. |
| [13] | KAYANI A B, KURIAKOSE S, MONSHIPOURI M, et al. UV photochromism in transition metal oxides and hybrid materials. Small, 2021, 17(32): 2100621. |
| [14] | WANG X, SHI H F, MA H L, et al. Organic phosphors with bright triplet excitons for efficient X-ray-excited luminescence. Nature Photonics, 2021, 15(3): 187. |
| [15] | KAWAMURA I, KAWAMOTO H, FUJIMOTO Y, et al. Isomerization behavior of diarylethene-type photochromic compounds under X-ray irradiation: application to dosimetry. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 59(4): 046004. |
| [16] | YANG D D, ZHENG H W, XUE J H, et al. Effect of lattice water on the photochromic property/photochromism of a Zn(II)-viologen coordination polymers. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2024, 1311: 138340. |
| [17] | WU J B, TAO C Y, LI Y, et al. Methylviologen-templated layered bimetal phosphate: a multifunctional X-ray-induced photochromic material. Chemical Science, 2014, 5(11): 4237. |
| [18] | HAN Y F, XU X M, WANG S H, et al. Reusable radiochromic semiconductive MOF for dual-mode X-ray detection using color change and electric signal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 437: 135468. |
| [19] |
LU L, PENG S C, ZHAO L, et al. Visualized X-ray dosimetry for multienvironment applications. Nano Letters, 2023, 23(18): 8753.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | YUAN M, JIA R, JIANG X, et al. Room-temperature X-ray induced photochromic properties of tungsten oxide. Materials Letters, 2023, 349: 134688. |
| [21] | YANG Z T, HU J Q, VAN DER HEGGEN D, et al. A versatile photochromic dosimeter enabling detection of X-Ray, ultraviolet, and visible photons. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2023, 17(5): 2200809. |
| [22] | LIU J J, LU Y W, LI J, et al. UV and X-ray dual photochromic properties of three CPs based on a new viologen ligand. Dyes and Pigments, 2020, 177: 108276. |
| [23] | LIU J J, LU Y W, LU W B. Sun, UV and X-ray triple photochromic properties of three coordination polymers based on 1, 1′-bis(3-carboxylatobenzyl)-4,4′-bipyridinium ligand. CrystEngComm, 2020, 22(12): 2121. |
| [24] | ASAI K, KOSHIMIZU M, FUJIMOTO Y, et al. Isomerization behavior of spiropyran-based compounds upon X-ray irradiation. Radiation Measurements, 2017, 106: 166. |
| [25] | DU J R, YANG Z T, LIN H W, et al. Inorganic photochromic materials: recent advances, mechanism, and emerging applications. Responsive Materials, 2024, 2(2): e20240004. |
| [26] | LIU L L, HU H J, PAN W T, et al. Robust organogel scintillator for self-healing and ultra-flexible X-ray imaging. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(13): 2311206. |
| [27] | GUO P Y, SUN C, ZHANG N N, et al. An inorganic-organic hybrid photochromic material with fast response to hard and soft X-rays at room temperature. Chemical Communications, 2018, 54(36): 4525. |
| [28] | ZHANG F, ZHOU Y C, CHEN Z P, et al. Large-area X-ray scintillator screen based on cesium hafnium chloride microcrystals films with high sensitivity and stability. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2023, 17(5): 2200848. |
| [29] | SUN F, XU H, HONG W, et al. 2D CuInP2Se6 in high-sensitivity UV-VIS and X-ray detection. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(22): 2313776. |
| [30] | BYRON H C, SWAIN C, PATURI P, et al. Highly tuneable photochromic sodalites for dosimetry, security marking and imaging. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(42): 2303398. |
| [31] | SAMOILENKO Y, KAGANOVSKII Y, LIPOVSKII A A, et al. CW laser discoloration of X-ray irradiated silver doped silicate glasses. Optical Materials, 2008, 30(11): 1715. |
| [32] | YUAN W N, NIU G D, XIAN Y M, et al. In situ regulating the order-disorder phase transition in Cs2AgBiBr6 single crystal toward the application in an X-ray detector. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(20): 1900234. |
| [33] | TANG H T, LIU S B, FANG Z H, et al. High-resolution X-ray time-lapse imaging from fluoride nanocrystals embedded in glass matrix. Advanced Optical Materials, 2022, 10(12): 2102836. |
| [34] | SONG Y Y, ZHAO H P, ZI Y Z, et al. X-ray-irradiation-induced discoloration and persistent radioluminescence for reversible dual-mode imaging and detection applications. ACS Energy Letters, 2023, 8(5): 2232. |
| [35] | HU Y J, SUN Y S, HOU S R, et al. UV and X-ray induced photochromic material based on defect state exchanges. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 495: 153600. |
| [36] | OU X Y, QIN X, HUANG B L, et al. High-resolution X-ray luminescence extension imaging. Nature, 2021, 590(7846): 410. |
| [37] | ZUO J, KEIL P, GRUNDMEIER G. Synthesis and characterization of photochromic Ag-embedded TiO2 nanocomposite thin films by non-reactive RF-magnetron sputter deposition. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258(18): 7231. |
| [38] | HOLTON W C, BLUM H. Paramagnetic resonance of F centers in alkali halides. Physical Review, 1962, 125(1): 89. |
| [39] | SEITZ F. Color centers in alkali halide crystals. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1946, 18(3): 384. |
| [40] | JOSHI C, ABINANDANAN T A, MUKHERJEE R, et al. Destabilisation of nanoporous membranes through GB grooving and grain growth. Computational Materials Science, 2017, 139: 75. |
| [41] | ZHU Y, SUN H Q, JIA Q N, et al. Site-selective occupancy of Eu2+ toward high luminescence switching contrast in BaMgSiO4-based photochromic materials. Advanced Optical Materials, 2021, 9(6): 2001626. |
| [42] | JIN Y H, HU Y H, YUAN L F, et al. Multifunctional near-infrared emitting Cr3+-doped Mg4Ga8Ge2O20 particles with long persistent and photostimulated persistent luminescence, and photochromic properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(27): 6614. |
| [43] | RABIN H, KLICK C C. Formation of F centers at low and room temperatures. Physical Review, 1960, 117(4): 1005. |
| [44] | ROY R. ChemInform abstract: ceramics by the solution-Sol-Gel route. ChemInform, 1988, 19(18): 1664. |
| [45] | BAI X, XU Z, ZI Y Z, et al. Dual-functional X-ray photochromic phosphor: high-performance detection and 3D imaging. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(37): 2402452. |
| [46] | PATHAK N, GUPTA S K, GHOSH P S, et al. Probing local site environments and distribution of manganese in SrZrO3:Mn; PL and EPR spectroscopy complimented by DFT calculations. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(23): 17501. |
| [47] | ZHANG Y Y, LUO L H, LI K X, et al. Reversible up-conversion luminescence modulation based on UV-VIS light-controlled photochromism in Er3+ doped Sr2SnO4+. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6(48): 13148. |
| [48] | LEE S H, CHEONG H M, LIU P, et al. Raman spectroscopic studies of gasochromic a-WO3 thin films. Electrochimica Acta, 2001, 46(13/14): 1995. |
| [49] | HE Y P, WU Z Y, FU L M, et al. Photochromism and size effect of WO3 and WO3-TiO2 aqueous sol. Chemistry of Materials, 2003, 15(21): 4039. |
| [50] | EGRANOV A V, SIZOVA T Y, SHENDRIK R Y, et al. Instability of some divalent rare earth ions and photochromic effect. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2016, 90: 7. |
| [51] | SCOULER W J, SMAKULA A. Coloration of pure and doped calcium fluoride crystals at 20 ℃ and -190 ℃. Physical Review, 1960, 120(4): 1154. |
| [52] | SUN Y H, LI C L, WANG W F, et al. A photochromic and scintillation Eu-MOF with visual X-ray detection in bright and dark environments. Chemical Communications, 2022, 58(25): 4056. |
| [53] | PAN L, LIU Z, WELTON C, et al. Ultrahigh-flux X-ray detection by a solution-grown perovskite CsPbBr3 single-crystal semiconductor detector. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(25): 2211840. |
| [54] | YANG L L, ZHANG H, ZHOU M, et al. High-stable X-ray imaging from all-inorganic perovskite nanocrystals under a high dose radiation. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2020, 11(21): 9203. |
| [55] | LIU J Y, SHABBIR B, WANG C J, et al. Flexible, printable soft-X-ray detectors based on all-inorganic perovskite quantum dots. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(30): 1901644. |
| [56] |
ZHANG Y H, SUN R J, OU X Y, et al. Metal halide perovskite nanosheet for X-ray high-resolution scintillation imaging screens. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(2): 2520.
DOI PMID |
| [57] | LI L Q, TAO L T, WANG L X, et al. Monolithic integration of perovskite heterojunction on TFT backplanes through vapor deposition for sensitive and stable X-ray imaging. Science Advances, 2024, 10(17): eadj8659. |
| [58] | ZHAO J J, ZHAO L, DENG Y H, et al. Perovskite-filled membranes for flexible and large-area direct-conversion X-ray detector arrays. Nature Photonics, 2020, 14: 612. |
| [59] | LI W, XU Y L, PENG J L, et al. Evaporated perovskite thick junctions for X-ray detection. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(2): 2971. |
| [60] | QIAN W, XU X W, WANG J, et al. An aerosol-liquid-solid process for the general synthesis of halide perovskite thick films for direct-conversion X-ray detectors. Matter, 2021, 4(3): 942. |
| [61] | LIU L L, LI W J, FENG X P, et al. Energy transfer assisted fast X-ray detection in direct/indirect hybrid perovskite wafer. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(15): 2103735. |
| [62] | XIA M L, SONG Z H, WU H D, et al. Compact and large-area perovskite films achieved via soft-pressing and multi-functional polymerizable binder for flat-panel X-ray imager. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(16): 2110729. |
| [63] | DEUMEL S, VAN BREEMEN A, GELINCK G, et al. High- sensitivity high-resolution X-ray imaging with soft-sintered metal halide perovskites. Nature Electronics, 2021, 4: 681. |
| [64] | DU X Y, LIU Y M, PAN W C, et al. Chemical potential diagram guided rational tuning of electrical properties: a case study of CsPbBr3 for X-ray detection. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(17): 2110252. |
| [65] | ZHOU Y, ZHAO L, NI Z Y, et al. Heterojunction structures for reduced noise in large-area and sensitive perovskite X-ray detectors. Science Advances, 2021, 7(36): eabg6716. |
| [66] | CHEN C, SUN J K, ZHANG Y J, et al. Flexible viologen-based porous framework showing X-ray induced photochromism with single-crystal-to-single-crystal transformation. Angewandte International Edition Chemie, 2017, 56(46): 14458. |
| [67] |
LU H J, XIE J, WANG X Y, et al. Visible colorimetric dosimetry of UV and ionizing radiations by a dual-module photochromic nanocluster. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 2798.
DOI PMID |
| [68] |
ABDOLLAHI A, ROGHANI-MAMAQANI H, RAZAVI B, et al. Photoluminescent and chromic nanomaterials for anticounterfeiting technologies: recent advances and future challenges. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(11): 14417.
DOI PMID |
| [69] | BAR N, CHOWDHURY P. A brief review on advances in rhodamine B based chromic materials and their prospects. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2022, 4(8): 3749. |
| [70] |
WUTTIG M, YAMADA N. Phase-change materials for rewriteable data storage. Nature Materials, 2007, 6(11): 824.
PMID |
| [71] | SUN H Q, LI X F, ZHU Y, et al. Achieving multicolor emission readout and tunable photoswitching via multiplexing of dual lanthanides in ferroelectric oxides. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(19): 5782. |
| [72] | YANG Z T, DU J R, MARTIN L I D J, et al. Designing photochromic materials with large luminescence modulation and strong photochromic efficiency for dual-mode rewritable optical storage. Advanced Optical Materials, 2021, 9(20): 2100669. |
| [73] | LI X F, GUAN L L, LI Y, et al. Optical control of Er3+-doped M0.5Bi2.5Nb2O9 (M=Li, Na, K) materials for thermal stability and temperature sensing using photochromic reactions. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2020, 8(44): 15685. |
| [74] | ZHANG H L, ZHANG X, SUN W H, et al. All-solid-state transparent variable infrared emissivity devices for multi-mode smart windows. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(16): 2307356. |
| [75] | CHOI K, CHON J W M, GU M, et al. Low-distortion holographic data storage media using free-radical ring-opening polymerization. Advanced Functional Materials, 2009, 19(22): 3560. |
| [76] | XIAO Y, XIONG P, ZHANG S, et al. Cation-defect-induced self-reduction towards efficient mechanoluminescence in Mn2+- activated perovskites. Materials Horizons, 2023, 10(9): 3476. |
| [1] | YU Shengyang, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, YU Minghui, YAO Jiatong, YANG Peixin. A Review of Pore Defects in Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics by Laser Additive Manufacturing: Formation and Suppression [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [2] | LIU Jiangping, GUAN Xin, TANG Zhenjie, ZHU Wenjie, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Nitrogen-containing Volatile Organic Compounds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [3] | XIAO Xiaolin, WANG Yuxiang, GU Peiyang, ZHU Zhenrong, SUN Yong. Advances in Regulation of Damaged Skin Regeneration by Two-dimensional Inorganic Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [4] | MA Jingge, WU Chengtie. Application of Inorganic Bioceramics in Promoting Hair Follicle Regeneration and Hair Growth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [5] | ZHANG Hongjian, ZHAO Ziyi, WU Chengtie. Inorganic Biomaterials on Regulating Neural Cell Function and Innervated Tissue Regeneration: A Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [6] | AI Minhui, LEI Bo. Micro-nanoscale Bioactive Glass: Functionalized Design and Angiogenic Skin Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [7] | WANG Yutong, CHANG Jiang, XU He, WU Chengtie. Advances in Silicate Bioceramic/Bioglass for Wound Healing: Effects, Mechanisms and Application Ways [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [8] | MA Wenping, HAN Yahui, WU Chengtie, LÜ Hongxu. Application of Inorganic Bioactive Materials in Organoid Research [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [9] | LUO Xiaomin, QIAO Zhilong, LIU Ying, YANG Chen, CHANG Jiang. Inorganic Bioactive Materials Regulating Myocardial Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [10] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [11] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [12] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [13] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [14] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [15] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||