
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 1017-1021.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170603
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
SONG Jian-Min1, 2, DAI Xiu-Hong1, LIANG Jie-Tong1, ZHAO Lei1, ZHOU Yang1, GE Da-Yong1, MENG Xu-Dong3, LIU Bao-Ting1
Received:2017-12-20
Revised:2018-02-11
Published:2018-09-20
Online:2018-08-14
About author:SONG Jian-Min. E-mail: sjm@hebau.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
SONG Jian-Min, DAI Xiu-Hong, LIANG Jie-Tong, ZHAO Lei, ZHOU Yang, GE Da-Yong, MENG Xu-Dong, LIU Bao-Ting. Resistive Switching Effect and Dielectric Property of Epitaxial BiFeO3 Thin Films by Off-axis Magnetron Sputtering[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(9): 1017-1021.
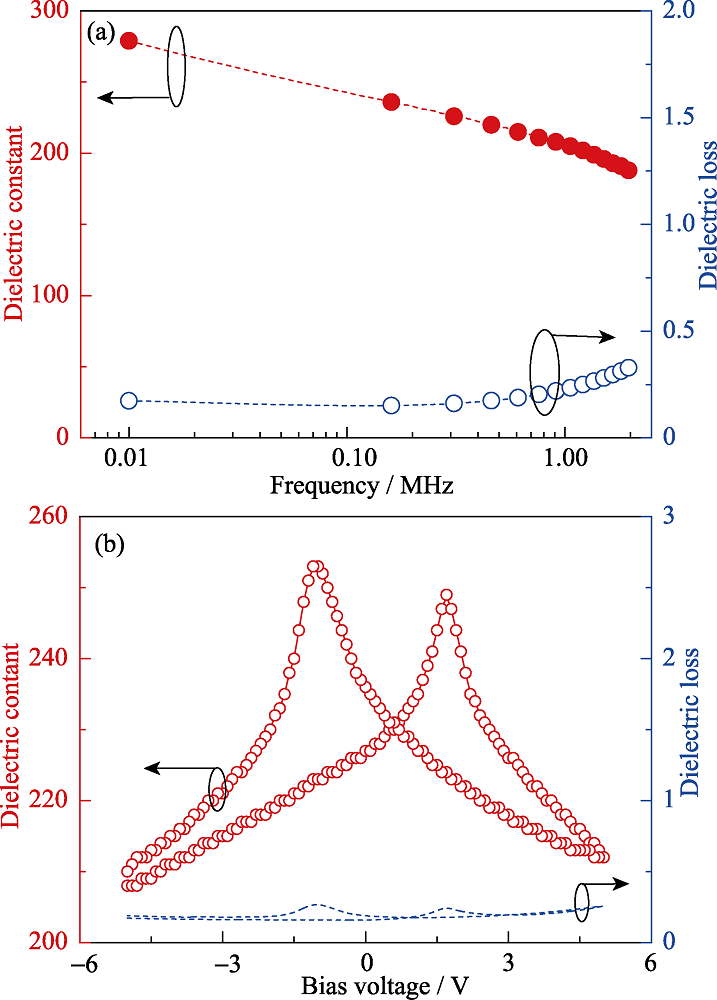
Fig. 2 (a) Frequency dependence of dielectric constant and dielectric loss of BFO thin film in Pt/BFO/LSCO heterostructures, and (b) voltage dependence of dielectric constant and dielectric loss of BFO thin film in Pt/BFO/LSCO heterostructures
| [1] | WEN Z, LI C, WU D,et al. Ferroelectric-field-effect-enhanced electroresistance in metal/ferroelectric/semiconductor tunnel junctions. Nature Mater., 2013, 12(7): 617-621. |
| [2] | TIAN B B, LIU Y, CHEN L F, et al. Space-charge effect on electroresistance in metal-ferroelectric-metal capacitors. Sci. Rep., 2015, 5: 18297-1-9. |
| [3] | ABUWASIB M, LU H, LI T, et al. Scaling of electroresistance effect in fully integrated ferroelectric tunnel junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2016, 108(15): 152904-1-5. |
| [4] | SILVA J P B, KAMAKSHI K, SEKHAR K C,et al. Light-controlled resistive switching in laser-assisted annealed Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3 thin films. Physica. Status. Solidi. A, 2016, 213(4): 1082-1087. |
| [5] | BARRIONUEVO D, ZHANG L, ORTEGA N,et al. Enhanced tunneling electroresistance in Pt/PZT/LSMO ferroelectric tunnel junctions in presence of magnetic field. Integr. Ferroelectr., 2016, 174(1): 174-185. |
| [6] | WANG C, JIN K J, XU Z T, et al. Switchable diode effect and ferroelectric resistive switching in epitaxial BiFeO3 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2011, 98(19): 192901-1-3. |
| [7] | XU H M, WANG H C, SHEN Y, ,et al. Photocatalytic and magnetic behaviors of BiFeO3 thin films deposited on different substrates. J. Appl. Phys., 2014, 116(17): 174307-1-5. |
| [8] | MOUBAH R, ROUSSEAU O, COLSON D,et al. Photoelectric effects in single domain BiFeO3 crystals. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2012, 22(22): 4814-4818. |
| [9] | LI M, ZHUGE F, ZHU X, ,et al. Nonvolatile resistive switching in metal/La-doped BiFeO3/Pt sandwiches. Nanotech., 2010, 21(42): 425202-1-5. |
| [10] | ZHU H, ZHANG Y, JIANG A, ,et al. Effect of poling process on resistive switching in Au/BiFeO3/SrRuO3 structures. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2016, 109(25): 252901-1-4. |
| [11] | HONG S, CHOI T, JEON J H,et al. Large resistive switching in ferroelectric BiFeO3 nano-island based switchable diodes. Adv. Mater., 2013, 25(16): 2339-2343. |
| [12] | YAMADA H, GARCIA V, FUSIL S,et al. Giant electroresistance of super-tetragonal BiFeO3-based ferroelectric tunnel junctions. ACS Nano., 2013, 7(6): 5385-5390. |
| [13] | LIN Y B, YAN Z B, LU X B, ,et al. Temperature-dependent and polarization-tuned resistive switching in Au/BiFeO3/SrRuO3 junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, 104(14): 143503-1-5. |
| [14] | WANG Y, JIANG Q H, HE H C, et al. Multiferroic BiFeO3 thin films prepared via a simple Sol-Gel method. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, 88(14): 142503-1-3. |
| [15] | TRASSIN M, CLARKSON J D, BOWDEN S R, et al. Interfacial coupling in multiferroic-ferromagnet heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B, 2013, 87(13): 134426-1-6. |
| [16] | QI X, TSAI PC, CHEN YC, et al. Ferroelectric properties and dielectric responses of multiferroic BiFeO3 films grown by RF magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2008, 41(23): 232001-1-5. |
| [17] | WU J, WANG J.BiFeO3 thin films of (111)-orientation deposited on SrRuO3 buffered Pt/TiO/SiO/Si(100) substrates.Acta Mater., 2010, 58(5): 1688-1697. |
| [18] | HAO Y L, LIU B T, PENG Z W,et al. Effect of retained temperature on the structure and property of BiFeO3 thin film prepared by off-axis magnetron sputtering method. J. Synth. Cryst., 2013, 42(2): 246-250. |
| [19] | FAN X M, LIAN J S, GUO Z X,et al. Microstructure and photoluminescence properties of ZnO thin films grown by PLD on Si(111) substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2005, 239(2): 176-181. |
| [20] | WANG C, CHEN Z, HU H,et al. Effect of the oxygen pressure on the microstructure and optical properties of ZnO films prepared by laser molecular beam epitaxy. Phys. B, 2009, 404(21): 4075-4082. |
| [21] | NAGARAJ B, AGGARWAL S, RAMESH R.Influence of contact electrodes on leakage characteristics in ferroelectric thin films.J. Appl. Phys., 2001, 90(1): 375-382. |
| [22] | SHANG D S, WANG Q, CHEN L D, et al. Effect of carrier trapping on the hysteretic current-voltage characteristics in Ag/La0.7Ca0.3 MnO3/Pt heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B, 2006, 73(24): 245427-1-7. |
| [23] | WANG S Y, CHENG B L, WANG C,et al. Reduction of leakage current by Co doping in Pt/Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3/Nb-SrTiO3 capacitor. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 84(20): 4116-4118. |
| [24] | CHEN X, WU G, JIANG P, et al. Colossal resistance switching effect in Pt/spinel-MgZnO/Pt devices for nonvolatile memory applications. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009, 94(3): 033501-1-3. |
| [25] | ZHU H, ZHANG Y Q, WANG P F,et al. Resistive switching effect and conduction mechanism of BiFeO3 thin films. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc., 2017, 45(4): 467-471. |
| [26] | EBRAHIMPOUR Z, MANSOUR N.Annealing effects on electrical behavior of gold nanoparticle film: conversion of ohmic to non-ohmic conductivity.Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 394: 240-247. |
| [1] | HE Guoqiang, ZHANG Kaiheng, WANG Zhentao, BAO Jian, XI Zhaochen, FANG Zhen, WANG Changhao, WANG Wei, WANG Xin, JIANG Jiapei, LI Xiangkun, ZHOU Di. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: Au Underrated K40 Microwave Dielectric Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [2] | LI Junsheng, ZENG Liang, LIU Rongjun, WANG Yanfei, WAN Fan, LI Duan. Functional Strontium Tantalum Oxynitride Ceramics: Efficient Synthesis, Densification and Dielectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 885-892. |
| [3] | XIE Bing, CAI Jinxia, WANG Tongtong, LIU Zhiyong, JIANG Shenglin, ZHANG Haibo. Research Progress of Polymer-based Multilayer Composite Dielectrics with High Energy Storage Density [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 137-147. |
| [4] | LI Wangguo, LIU Dianguang, WANG Kewei, MA Baisheng, LIU Jinling. High Entropy Oxide Ceramics (MgCoNiCuZn)O: Flash Sintering Synthesis and Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1289-1294. |
| [5] | LIANG Hanqin, YIN Jinwei, ZUO Kaihui, XIA Yongfeng, YAO Dongxu, ZENG Yuping. Mechanical and Dielectric Properties of Hot-pressed Si3N4 Ceramics with BaTiO3 Addition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 535-540. |
| [6] | WANG Lu, KONG Wen-Jie, LUO Hang, ZHOU Xue-Fan, ZHOU Ke-Chao, ZHANG Dou. Dielectric and Energy Storage Property of Dielectric Nanocomposites with BaTiO3 Nanofibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1059-1064. |
| [7] | XIE Hui, YUAN Shu-Juan, KANG Bao-Juan, LU Bo, CAO Shi-Xun, ZHANG Jin-Cang. Giant Magnetodielectric Effect and Magnetic Properties of Ho0.5Pr0.5FeO3 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(1): 77-80. |
| [8] | LIU Hao, SHEN Chun-Ying, LU Zheng-Dong, QIU Tai. Microwave Dielectric Properties of the (1-x)(Mg0.9Co0.1)TiO3-x(Ca0.61La0.26)TiO3 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(6): 664-668. |
| [9] | ZHAO Li, SHEN Chun-Ying, QIU Tai. Studieson the (1- x)Mg0.7Zn0.3TiO3-xCa0.61La0.26TiO3Microwave Dielectric Ceramics System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(2): 219-224. |
| [10] | LU Zheng-Dong,SHEN Chun-Ying,LI Liang,YANG Jian,QIU Tai. Study on the (1-x)(Mg0.7Zn0.3)TiO3-x(Ca0.61Nd0.26)TiO3 Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(3): 332-336. |
| [11] | QIN Wen-Feng,XIONG Jie,LI Yan-Rong. Structure and Properties of BST/BZT/BST Multilayer Film [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(3): 247-250. |
| [12] | CHU Rui-Qing, HAO Ji-Gong, XU Zhi-Jun, ZANG Guo-Zhong. Preparation and Characterization of (K0.5Na0.5)0.94-2xLi0.06SrxNb0.98Sb0.02O3 Lead-free Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(11): 1164-1168. |
| [13] | ZHANG Hai-Long,LI Jing-Feng,ZHANG Bo-Ping. Dielectric Constant Anomaly in PZT/Ag Functional Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(2): 448-452. |
| [14] | HUANG Ji-Quan,DU Pi-Yi,WENG Wen-Jian,HAN Gao-Rong. Preparation of BaTiO3-Acetylene Black Composite with a Super High Dielectric Constant [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2005, 20(5): 1106-1112. |
| [15] | WANG Juan,ZHANG Chang-Rui,FENG Jian. Effects of Poly(Ethylene glycol) on Properties of Nanoporous Silica Film [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2005, 20(2): 435-441. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||