
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 173-197.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170352
Special Issue: 乘风破浪的新能源材料
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Song-Can, TANG Feng-Qiu, WANG Lian-Zhou
Received:2017-07-21
Published:2018-02-26
Online:2018-01-26
About author:WANG Song-Can(1988), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: s.wang3@uq.edu.au
CLC Number:
WANG Song-Can, TANG Feng-Qiu, WANG Lian-Zhou. Visible Light Responsive Metal Oxide Photoanodes for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting: a Comprehensive Review on Rational Materials Design[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(2): 173-197.

Fig. 2 Theoretical photocurrent densities of several semiconductors under AM 1.5 G illumination Reproduced with permission from Ref. [45]. Copyright 2013 American Chemical Society

Fig. 3 I-t curves of a bare WO3 photoanode (a) and a Co-Pi modified WO3 photoanode (b) Inset: SEM image demonstrating charge transfer and separation between the Co-Pi layer, WO3, and FTO substrate Reproduced with permission from Ref. [55]. Copyright 2011 American Chemical Society
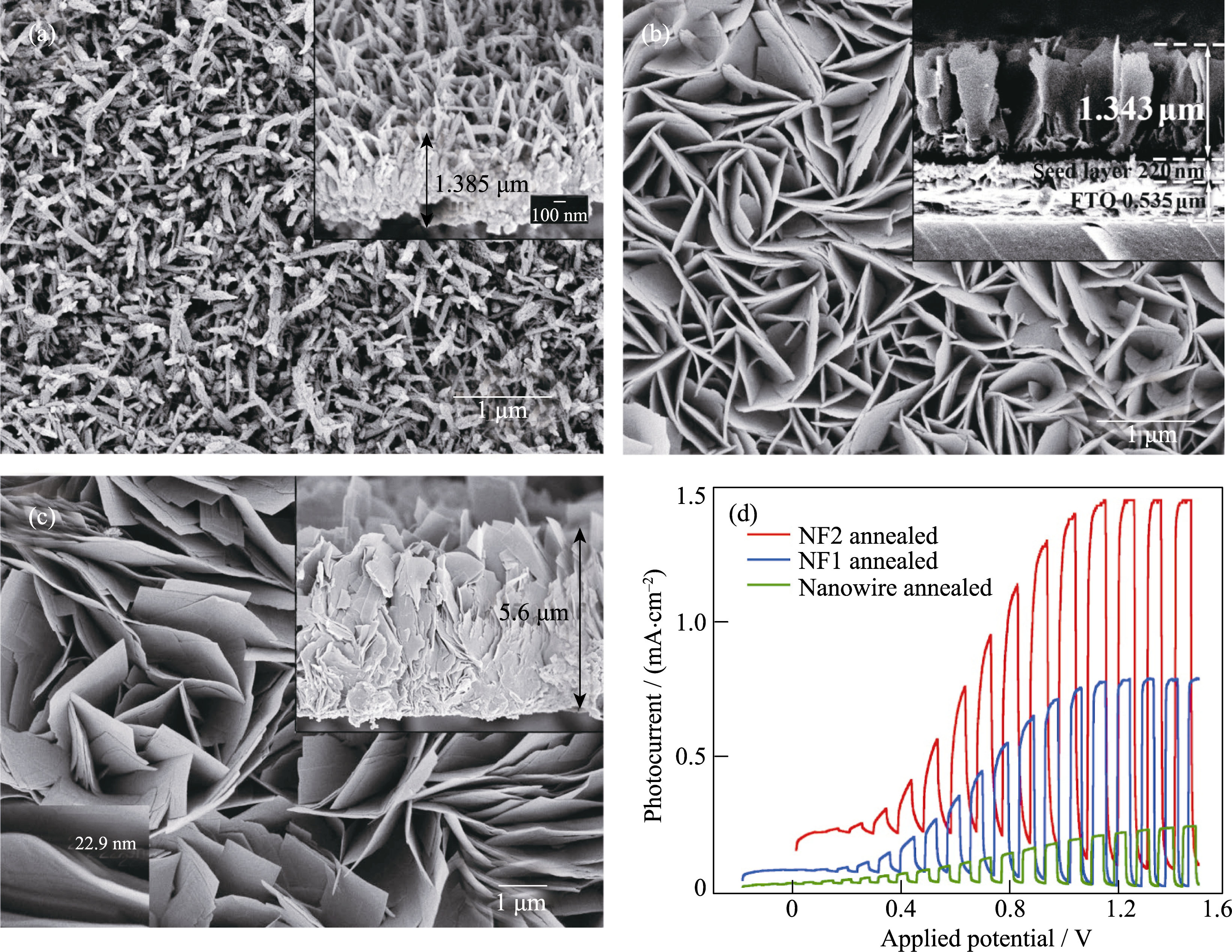
Fig. 4 FESEM images of the as-prepared WO3 films (a) Nanowires; (b) Nanoflakes-1 (NF1); (c) Nanoflakes-2 (NF2) Insets: film cross section; (d) Photocurrent density vs applied potential curves Reproduced with permission from Ref. [60]. Copyright 2011 American Chemical Society

Fig. 5 (a) Schematic illustration of crystal facet orientation of the 1-step-16 h, 1-step-8 h and 2-step-16 h WO3 photoanodes; (b) Photocurrent density vs applied potential curves; (c) I-t curves of the 1-step-16 h, 1-step-8 h and 2-step-16 h WO3 photoanodes Reproduced with permission from Ref. [73]. Copyright 2016 Elsevier
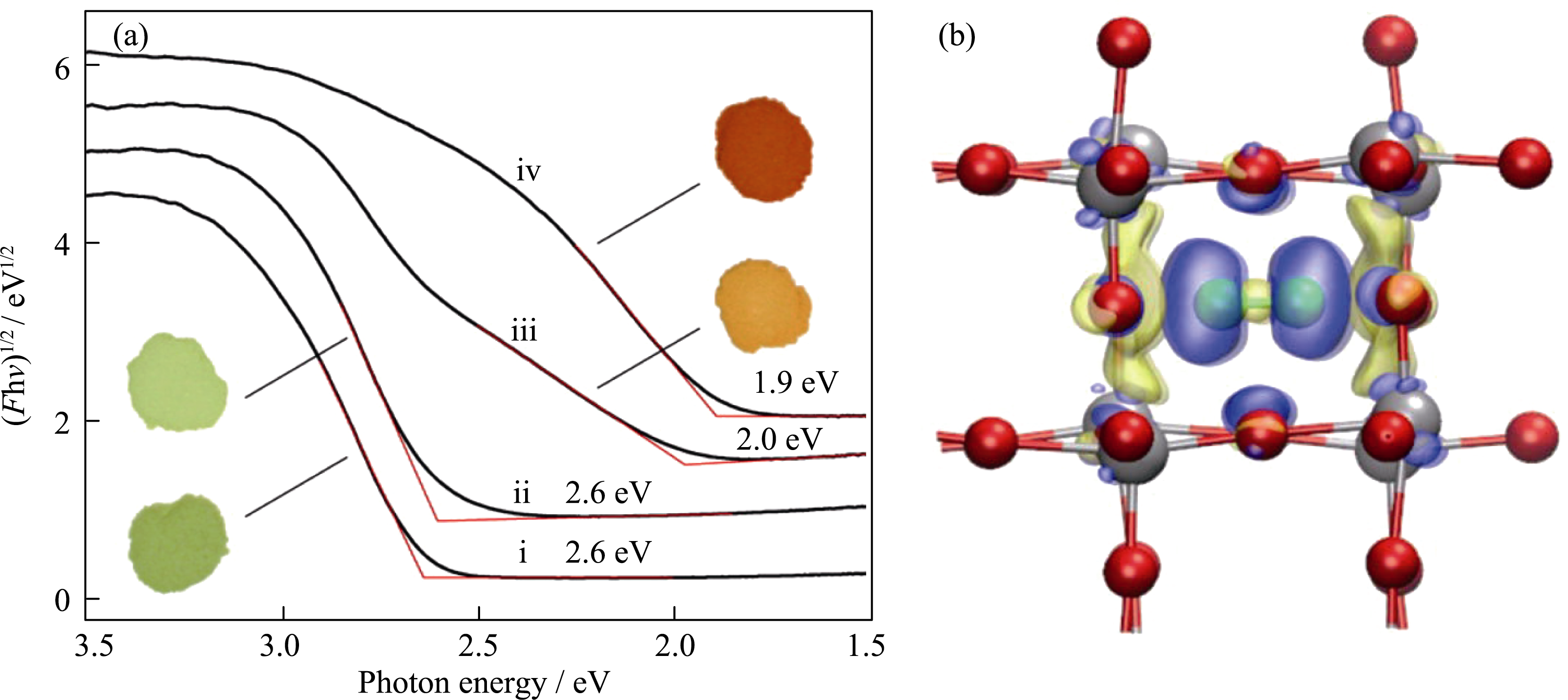
Fig. 6 (a) Diffuse reflectance spectra and digital images of (i) pure monoclinic WO3, (ii) 0.034N2·WO3, (iii) 0.039N2·WO3, and (iv) 0.039N2·WO3; (b) A model of electron density difference for monoclinic WO3 with incorporating N2. Yellow: electron loss; blue: electron gain; silver sphere: W; red sphere: O; green sphere: N Reproduced with permission from Ref. [76]. Copyright 2012 American Chemical Society
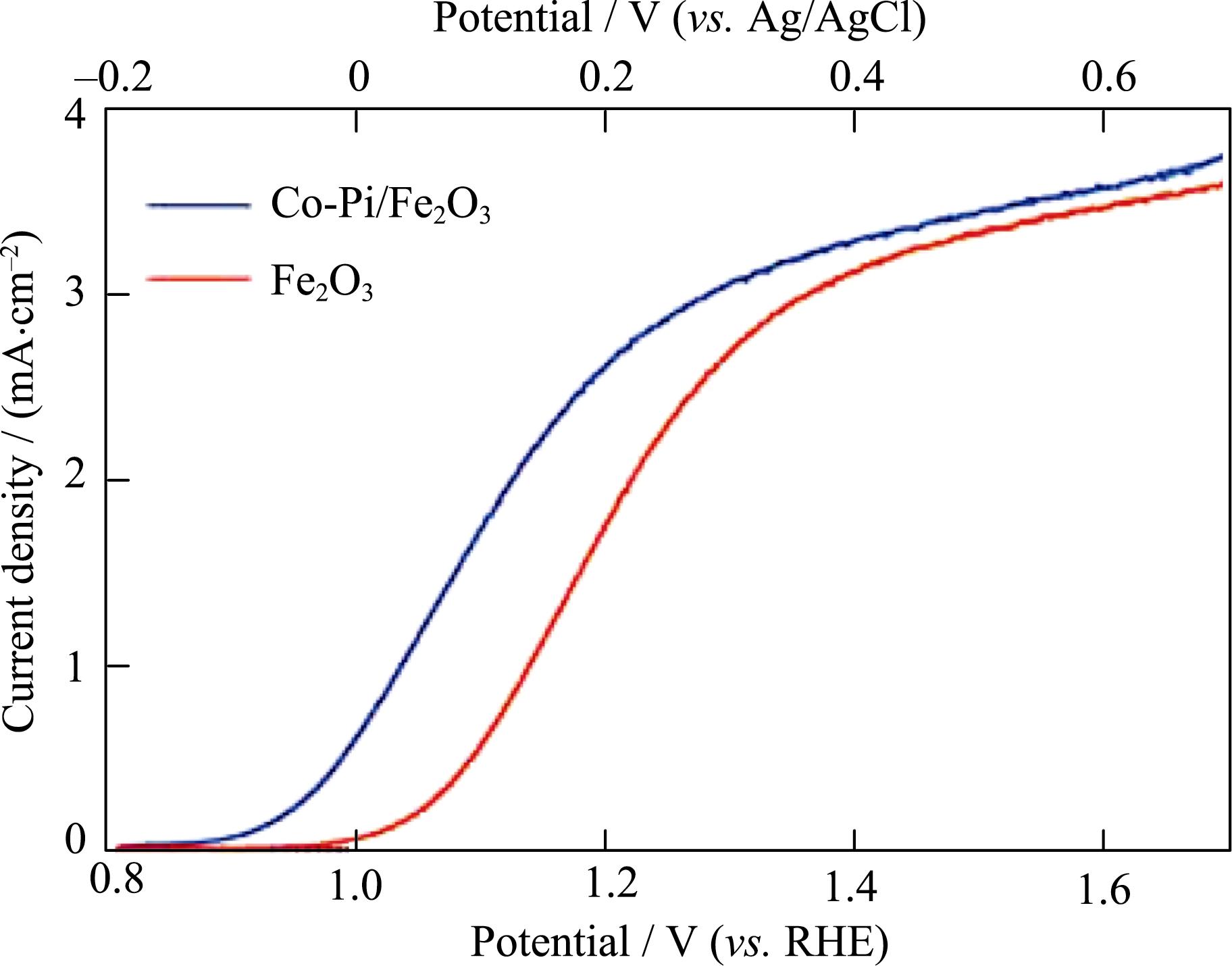
Fig. 7 Dark-current (dotted) and photocurrent (solid) densities of bare α-Fe2O3 and Co-Pi/α-Fe2O3 photoanodes modified by photo-assisted electrodeposition Reproduced with permission from Ref. [112]. Copyright 2011 Royal Society of Chemistry

Fig. 8 (a) Photocurrent density vs applied potential curves of α-Fe2O3 photoanodes sintered at 400, 700, and 800℃ in the dark (dotted curves) and under AM 1.5 G illumination (solid curves) with inset showing enlarged curves photocurrent density vs applied potential curves of α-Fe2O3 photoanodes sintered at 700 and 800℃; (b) XPS survey data for the α-Fe2O3 photoanodes sintered at 400, 700, and 800℃; (c) Absorption coefficient as a function of wavelength and the digital images of the α-Fe2O3 photoanodes sintered at 400, 700, and 800℃ Reproduced with permission from Ref. [120]. Copyright 2010 American Chemical Society
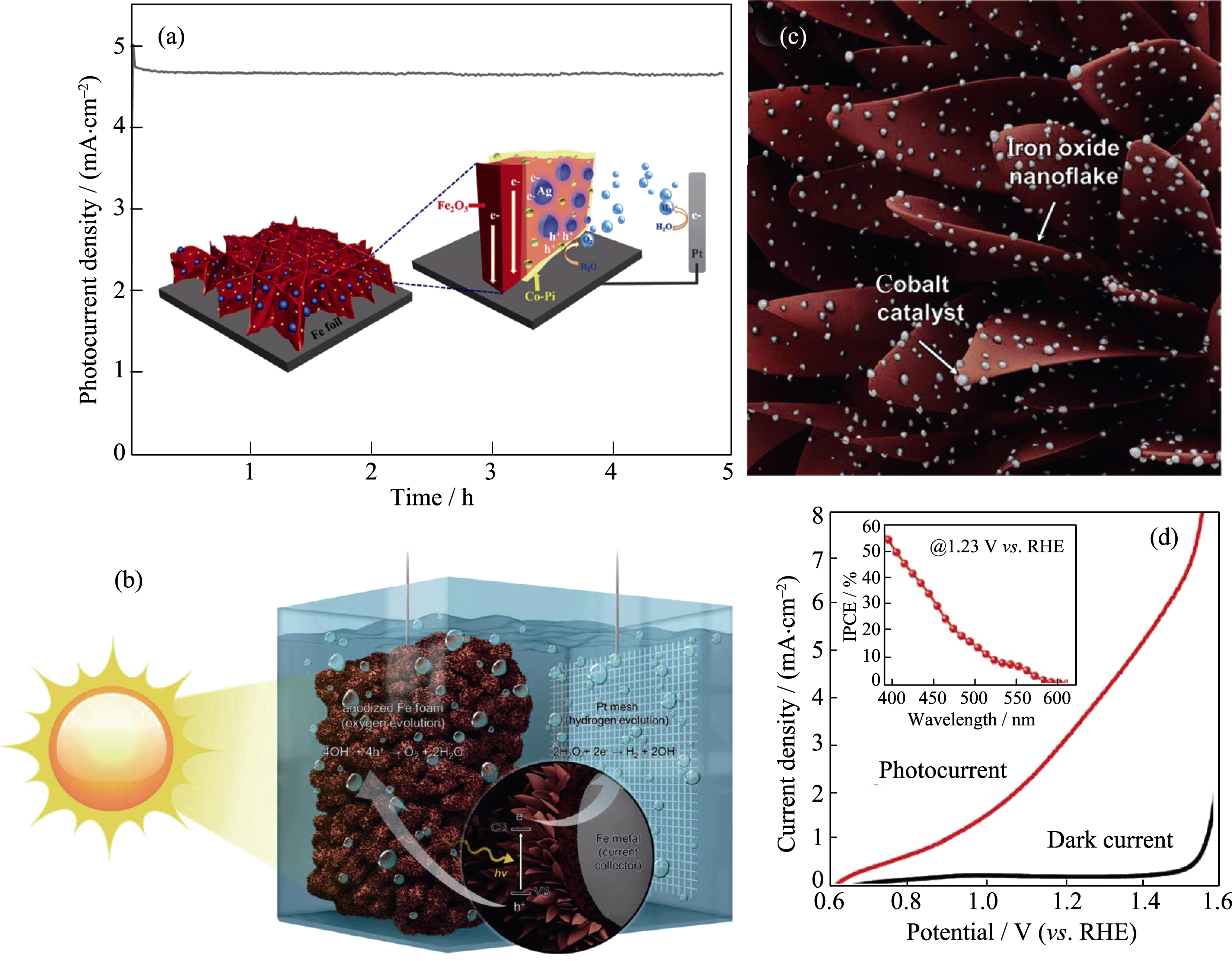
Fig. 9 (a) I-t curve of a Co-Pi/Ag/α-Fe2O3 photoanode with inset showing schematic of a Co-Pi/Ag/α-Fe2O3 photoanode for efficient PEC water splitting; (b) Schematic of an AFF photoanode for PEC water splitting; (c) Schematic of Co based OECs decorated on the surfaces of an AFF photoanode; (d) Photocurrent density vs applied potential curves of a Co based OECs modified AFF photoanode with inset showing IPCE curve measured at 1.23 V (vs RHE) Reproduced with permission from Ref. [130-131]. Copyright 2016 and 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim

Fig. 10 Band diagram schematic of the BiVO4 samples (a) 1% W-doped BiVO4; (b) W doped BiVO4 homojunction; (c) W doped BiVO4 reverse homojunction; (d) Gradient W doped BiVO4; (e) Carrier separation efficiency curves Reproduced with permission from Ref. [147]. Copyright 2013 Nature Publishing Group
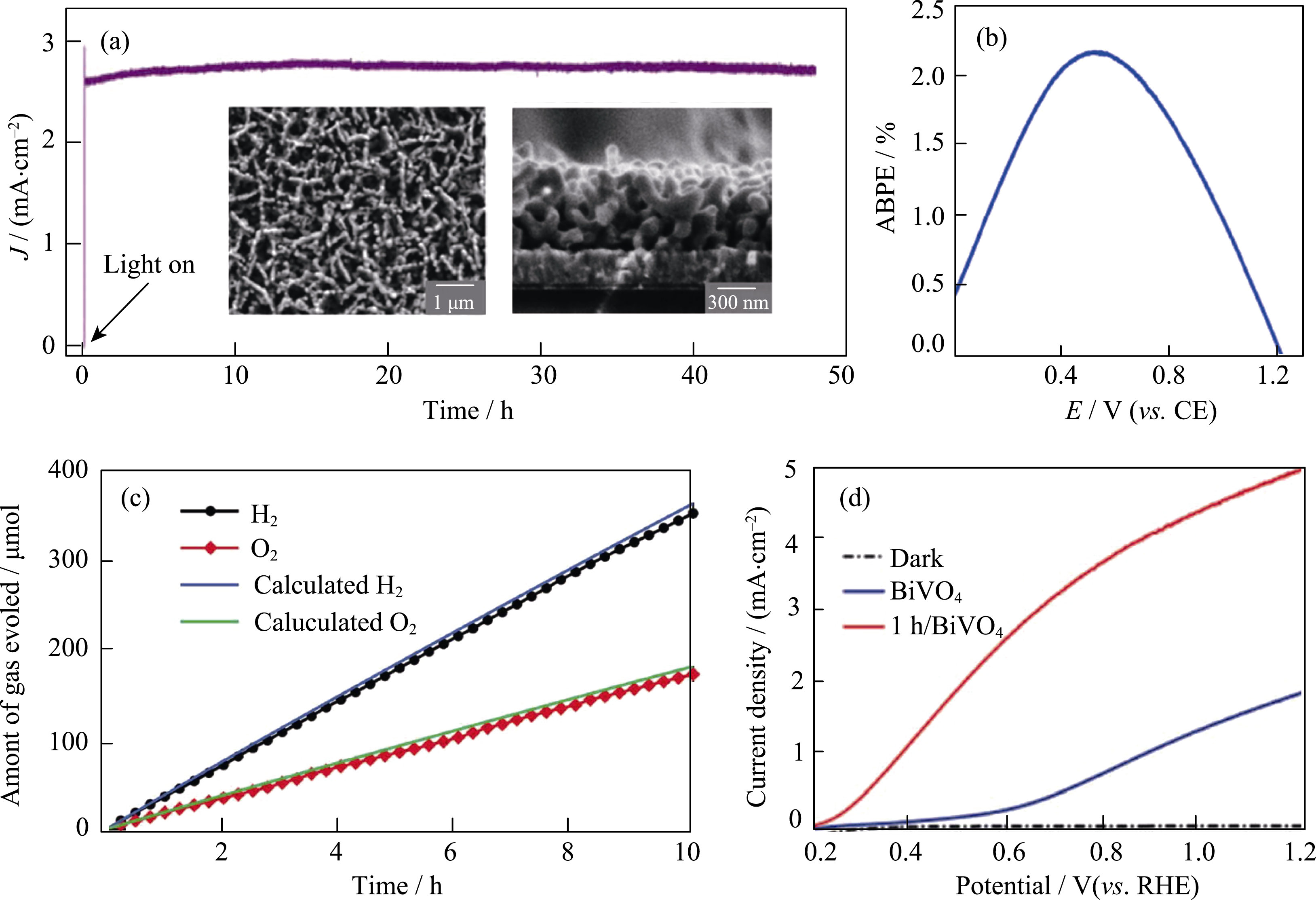
Fig. 11 (a) I-t curve of nanoporous BiVO4/FeOOH/NiOOH photoanode measured at 0.6 V (vs counter electrode) with insets showing: surface and cross-sectional SEM images of nanoporous BiVO4. Reproduced with permission from Ref.[153]. Copyright 2014, American Association for the Advancement of Science. (b) Applied bias photon-to-current efficiency (ABPE) of N2-treated BiVO4/FeOOH/NiOOH photoanode obtained using a two-electrode configuration (CE: counter electrode). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [154]. Copyright 2015 Nature Publishing Group. Distributed under a CC-BY 4.0 license. (c) H2 (black circle) and O2 evolution (red square) using two BiVO4/NiFeOx-Bi photoanodes. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [155]. Copyright 2015 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (d) Photocurrent density vs applied potential curves of BiVO4 and molecular Co4O4 cubane modified BiVO4 photoanodes under AM 1.5 G illumination. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [156]. Copyright 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim

Fig. 12 (a) Schematic of the WO3 NRs/BiVO4/Co-Pi junction, the charge transfer and separation in the junction for PEC water splitting; (b) Cross-sectional SEM image of a WO3 NRs/BiVO4 photoanode; (c) Photocurrent density (vs applied potential) curves of the WO3 NRs/BiVO4/Co-Pi junction under 1 sun and 3 sun illumination, respectively Reproduced with permission from Ref. [166]. Copyright 2015 Nature Publishing Group. Distributed under a CC-BY 4.0 license
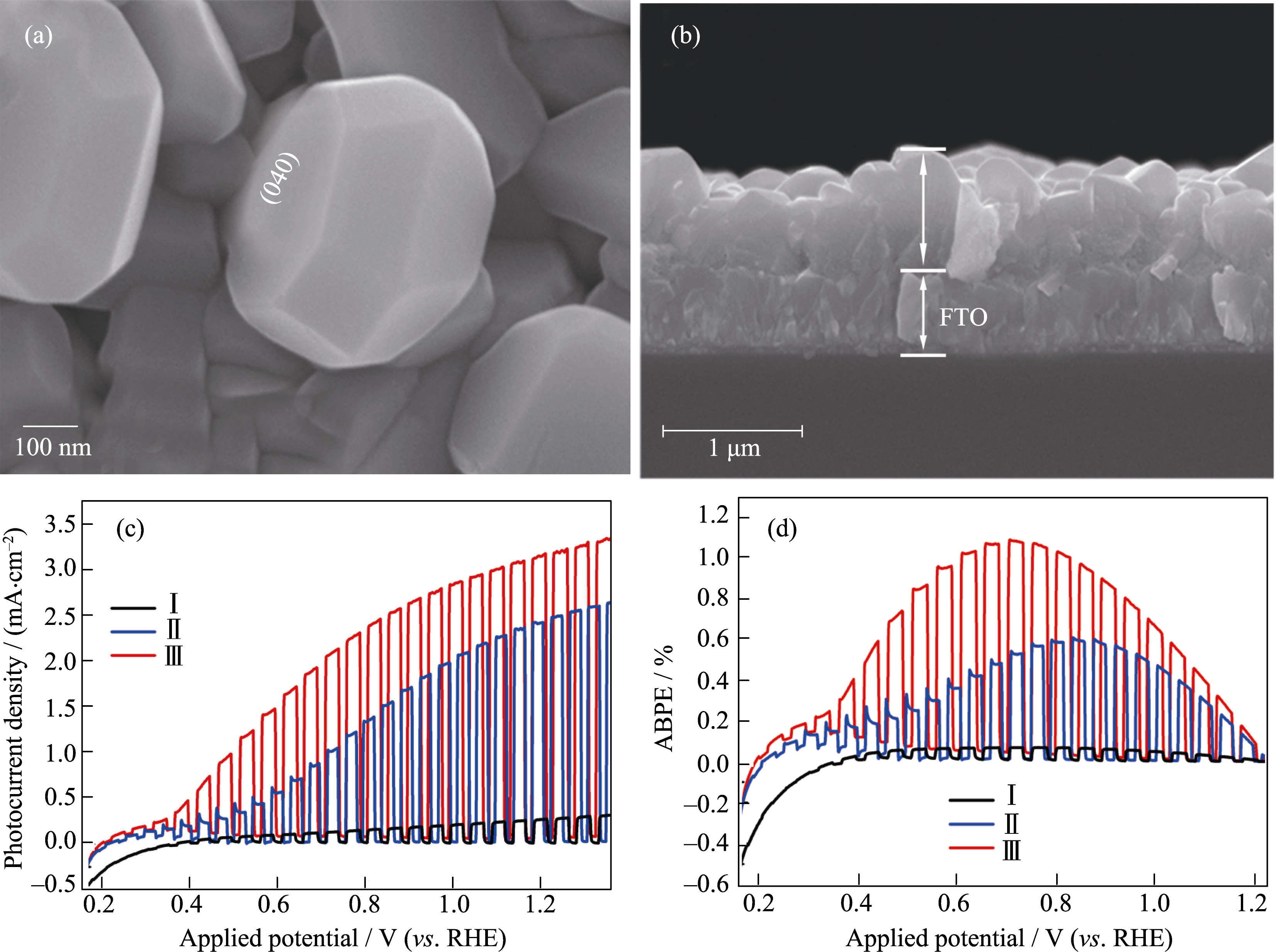
Fig. 13 SEM images of BVO-{040}-V: (a) top view and (b) cross-sectional view, (c) photocurrent density vs applied potential curves and (d) the corresponding PEC water splitting efficiency curves of I: BVO-{040}-V, II: electrochemically treated BVO-{040}-V, and III: electrochemically treated BVO-{040}-V/CoBi photoanodes Reproduced with permission from Ref. [151]. Copyright 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim

Fig. 14 (a) Photostability measurement of the 800℃-BM-700℃ and the previously reported nanoworm BiVO4 photoanodes; (b) Photostability and electrochemical stability of the 800℃- BM-700℃ photoanode; (c) Long-term stability measurement of the NiFe-OECs modified 800℃-BM-700℃ photoanode at 0.6 V (vs RHE) under AM 1.5 G illumination Reproduced with permission from Ref. [196]. Copyright 2016 Nature Publishing Group
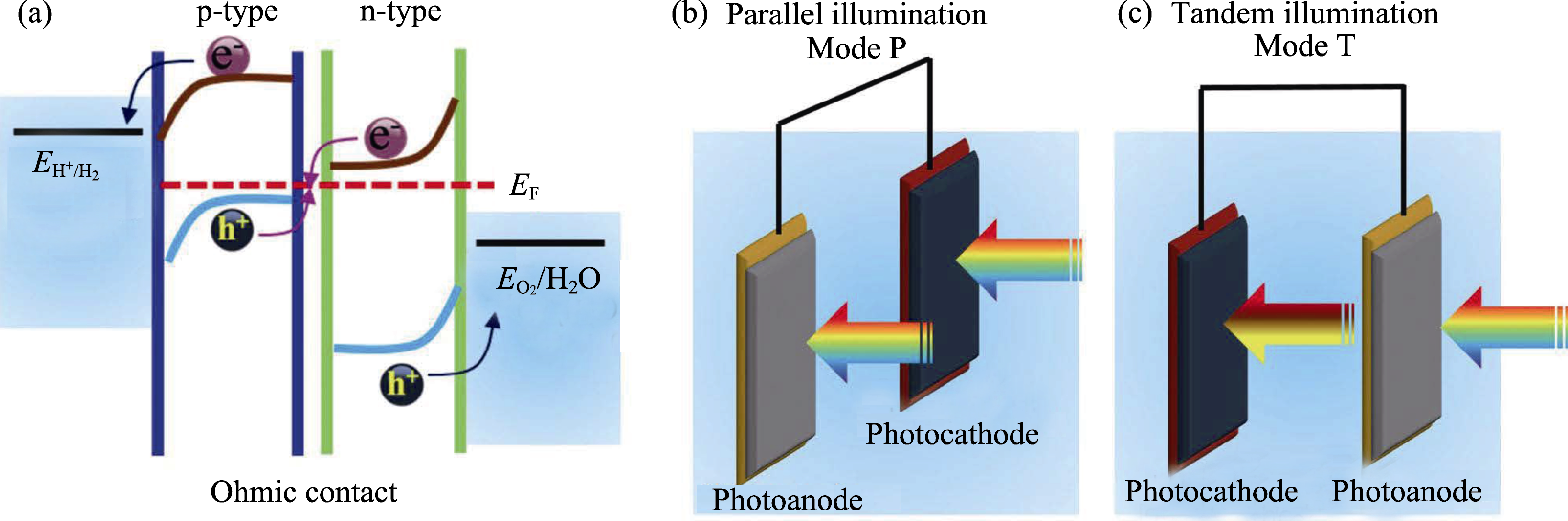
Fig. 15 (a) Mechanism of a PEC tandem system with Ohmic contact, a schematic of the wired PEC tandem system in (b) a parallel illumination mode (Mode P) and (c) a tandem illumination mode (Mode T) Reproduced with permission from Ref. [197]. Copyright 2016 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim

Fig. 16 (a) Current density-voltage (J-V) curves of the BiVO4 photoanodes with (solid lines) and without (dashed lines) Co-Pi OECs under AM 1.5 G illumination. The |J|-V curves of the Cu2O photocathode is measured with the coverage of the corresponding BiVO4 photoanode (dotted line with the same colour). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [199]. Copyright 2014 American Chemical Society. (b) J-V curves of various α-Fe2O3 photoanodes. The |J|-V curve of the Si photocathode is measured behind the α-Fe2O3 photoanode. (c) Schematic of overall unassisted water splitting by α-Fe2O3 photoanode and amorphous Si photocathode in wired Mode T. (d) Photocurrent stability measurement of the PEC tandem system in (c). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [202]. Copyright 2015 Nature Publishing Group. Distributed under a CC-BY 4.0 license
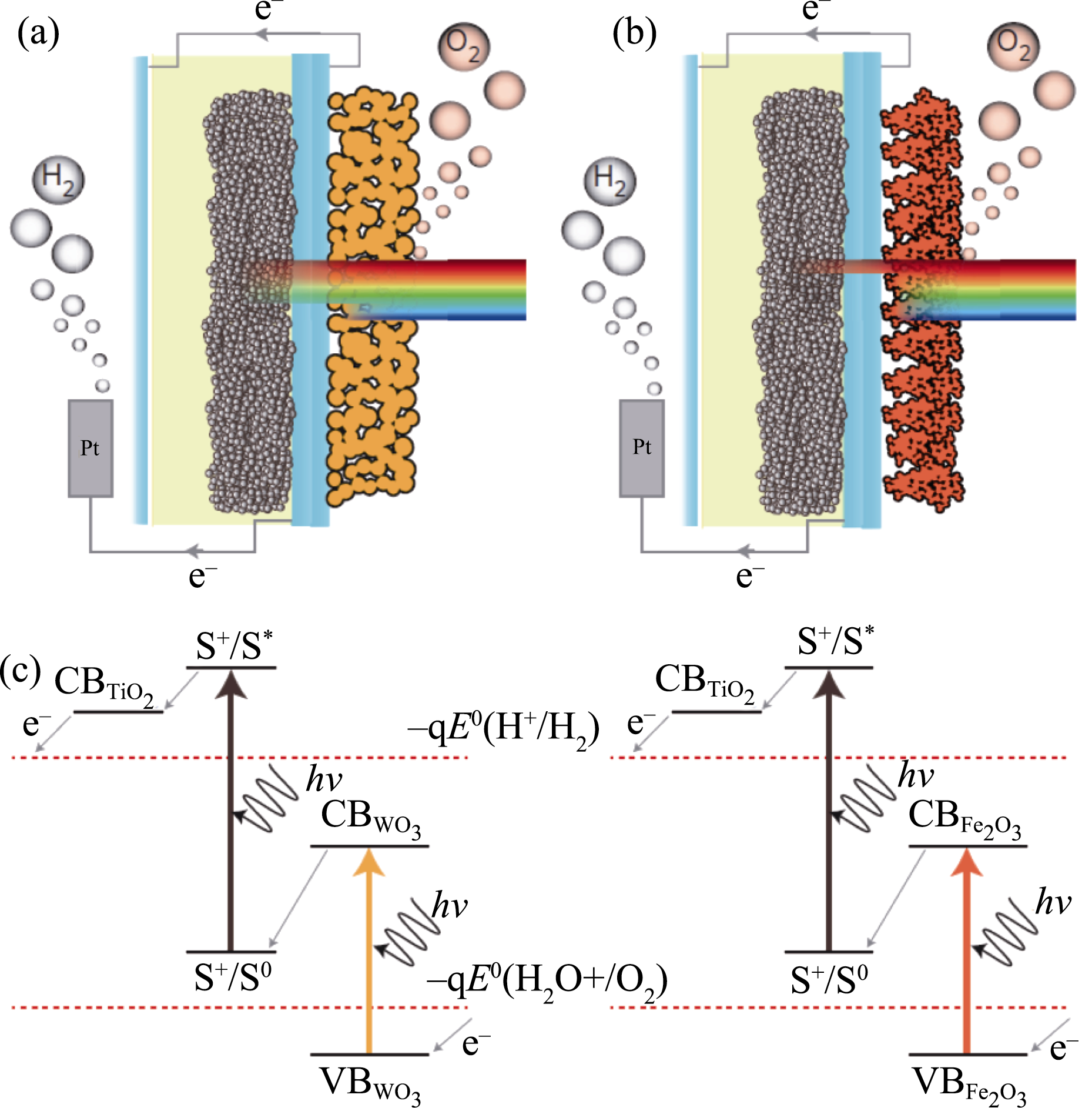
Fig. 17 General schemes of a WO3/DSSC tandem system (a) and a Fe2O3/DSSC tandem system (b); Working mechanism of the WO3/DSSC and Fe2O3/DSSC tandem systems (c) Reproduced with permission from Ref. [207]. Copyright 2012 Nature Publishing Group conducting substrate for the front photoanode to enhance solar light utilization, an impressive STH efficiency of 7.1% was achieved[209].
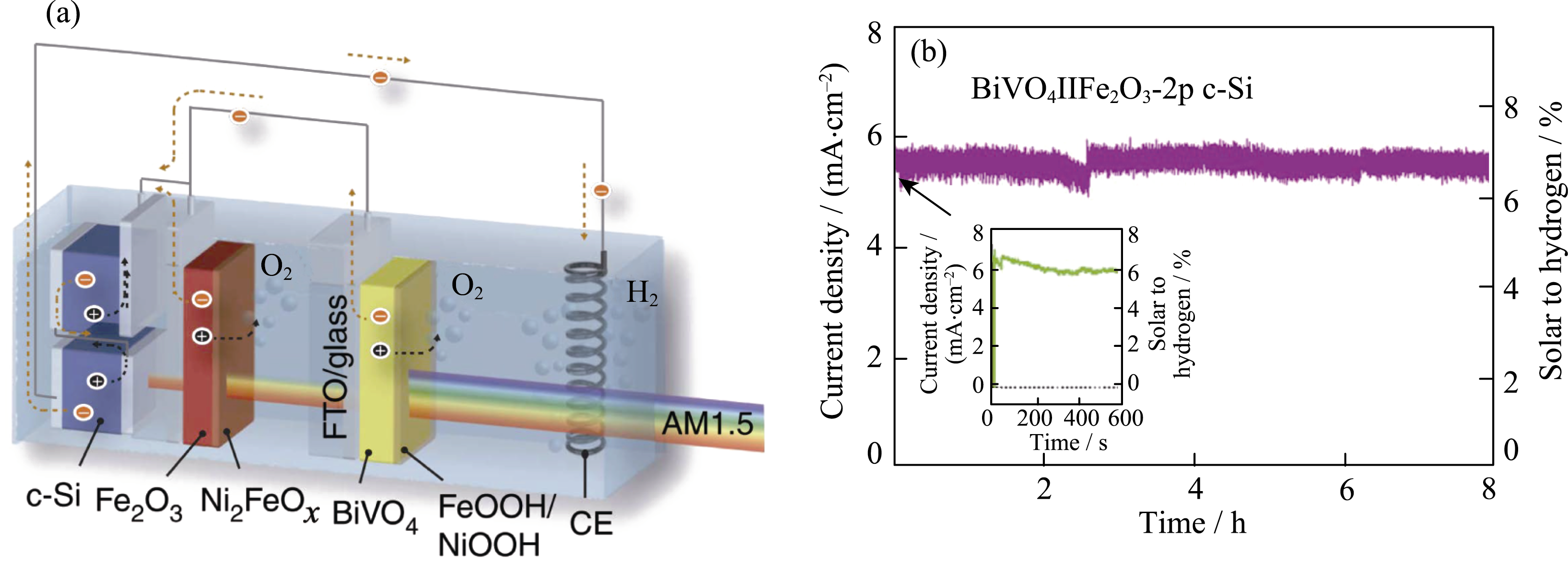
Fig. 18 (a) Scheme of a PEC/PV tandem cell with modified BiVO4/α-Fe2O3 dual photoanodes and two parallel-connected c-Si cells; (b) Stability of unassisted water splitting with inset showing: data recorded for short term illumination Reproduced with permission from Ref. [211]. Copyright 2016 Nature Publishing Group. Distributed under a CC-BY 4.0 license

Fig. 19 Schematics of (a) BiVO4/PSC tandem device with PSC behind the BiVO4 photoanode in air, (b) BiVO4/PSC tandem device with a beam splitter, and (c) wireless artificial leaf of BiVO4/PSC tandem device, (d) stability measurement of the BiVO4/PSC tandem device in (b) Reproduced with permission from Ref. [212-214]. Copyright 2015 American Chemical Society. Distributed under an ACS AuthorChoice License. Copyright 2016 American Association for the Advancement of Science. Distributed under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license Copyright 2015 American Chemical Society
| [1] | KITOUS A, KERAMIDAS K, VANDYCK T, et al.GECO 2016: Global Energy and Climate Outlook: Road from Paris: Impact of Climate Policies on Global Energy Markets in the Context of the UNFCCC Paris Agreement, EUR 27952 EN, Publications Office of the European Union: KITOUS A, 2016. 25-83. DOI: 10.2790/89230. |
| [2] | LEWIS N S, NOCERA D G.Powering the planet: chemical challenges in solar energy utilization.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2006, 103(43): 15729-15735. |
| [3] | GRATZEL M.Photoelectrochemical cells.Nature, 2001, 414(6861): 338-344. |
| [4] | FUJISHIMA A, HONDA K.Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode.Nature, 1972, 238(5358): 37-38. |
| [5] | FAUNCE T, STYRING S, WASIELEWSKI M R, et al.Artificial photosynthesis as a frontier technology for energy sustainability.Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, 6(4): 1074-1076. |
| [6] | YANG Y, WANG S, LI Y, et al.Strategies for efficient solar water splitting using carbon nitride.Chem. Asian J., 2017, 12(13): 1421-1434. |
| [7] | CHEN J, ZHAO D, DIAO Z, et al.Ferrites boosting photocatalytic hydrogen evolution over graphitic carbon nitride: a case study of (Co, Ni)Fe2O4 modification.Sci. Bull., 2016, 61(4): 292-301. |
| [8] | HAN Y, ZHANG L, WANG Y, et al.Photoelectrocatalytic activity of an ordered and vertically aligned TiO2 nanorod array/BDD heterojunction electrode.Sci. Bull., 2017, 62(9): 619-625. |
| [9] | LIM M, ZHOU Y, WANG L Z, et al.Development and potential of new generation photocatalytic systems for air pollution abatement: an overview.Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng., 2009, 4(4): 387-402. |
| [10] | ZHANG W, ZOU L D, WANG L Z.Photocatalytic TiO2/adsorbent nanocomposites prepared via wet chemical impregnation for wastewater treatment: a review.Appl. Catal. a-Gen., 2009, 371(1/2): 1-9. |
| [11] | GARCIA-SEGURA S, BRILLAS E.Applied photoelectrocatalysis on the degradation of organic pollutants in wastewaters.J. Photochem. Photobiol. C, 2017, 31: 1-35. |
| [12] | LIU J, HAN L, MA H, et al.Template-free synthesis of carbon doped TiO2 mesoporous microplates for enhanced visible light photodegradation.Sci. Bull., 2016, 61(19): 1543-1550. |
| [13] | KUMAR B, LLORENTE M, FROEHLICH J, et al.Photochemical and photoelectrochemical reduction of CO2.Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2012, 63: 541-569. |
| [14] | RONGE J, BOSSEREZ T, MARTEL D, et al.Monolithic cells for solar fuels.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43(23): 7963-7981. |
| [15] | SUN Z, WANG S, LI Q, et al.Enriching CO2 activation sites on graphitic carbon nitride with simultaneous introduction of electron- transfer promoters for superior photocatalytic CO2-to-fuel conversion.Adv. Sustainable Syst., 2017, 1(3/4): 1700003. |
| [16] | MEI B, MUL G, SEGER B.Beyond water splitting: efficiencies of photo-electrochemical devices producing hydrogen and valuable oxidation products.Adv. Sustainable Syst., 2017, 1(1/2): 1600035. |
| [17] | ZONG X, HAN J, SEGER B, et al.An integrated photoelectrochemical-chemical loop for solar-driven overall splitting of hydrogen sulfide.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(17): 4399-4403. |
| [18] | ZONG X, CHEN H J, SEGER B, et al.Selective production of hydrogen peroxide and oxidation of hydrogen sulfide in an unbiased solar photoelectrochemical cell.Energy Environ. Sci., 2014, 7(10): 3347-3351. |
| [19] | SKUBI K L, BLUM T R, YOON T P.Dual catalysis strategies in photochemical synthesis.Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(17): 10035-10074. |
| [20] | KONDRATENKO E V, MUL G, BALTRUSAITIS J, et al.Status and perspectives of CO2 conversion into fuels and chemicals by catalytic, photocatalytic and electrocatalytic processes.Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, 6(11): 3112-3135. |
| [21] | FAGNONI M, DONDI D, RAVELLI D, et al.Photocatalysis for the formation of the C-C bond.Chem. Rev., 2007, 107(6): 2725-2756. |
| [22] | WANG S, YUN J H, WANG L.Nanostructured semiconductors for bifunctional photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical energy conversion.Semicond. Semimetals, 2017, 97: 315-347. |
| [23] | HISATOMI T, KUBOTA J, DOMEN K.Recent advances in semiconductors for photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical water splitting.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43(22): 7520-7535. |
| [24] | PREVOT M S, SIVULA K.Photoelectrochemical tandem cells for solar water splitting.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(35): 17879-17893. |
| [25] | QU Y, DUAN X.Progress, challenge and perspective of heterogeneous photocatalysts.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42(7): 2568-2580. |
| [26] | GAN J, LU X, TONG Y.Towards highly efficient photoanodes: boosting sunlight-driven semiconductor nanomaterials for water oxidation.Nanoscale, 2014, 6(13): 7142-7164. |
| [27] | GANNOUNI M, BEN ASSAKER I, CHTOUROU R.Photoelectrochemical cell based on n-CuIn5S8 film as photoanodes for photocatalytic water splitting.Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(23): 7252-7259. |
| [28] | XIA Z M, ZHOU X M, LI J, et al.Protection strategy for improved catalytic stability of silicon photoanodes for water oxidation.Sci. Bull., 2015, 60(16): 1395-1402. |
| [29] | LICHTERMAN M F, SUN K, HU S, et al.Protection of inorganic semiconductors for sustained, efficient photoelectrochemical water oxidation.Catal. Today, 2016, 262: 11-23. |
| [30] | WANG L, SASAKI T.Titanium oxide nanosheets: graphene analogues with versatile functionalities.Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(19): 9455-9486. |
| [31] | MA Y, WANG X, JIA Y, et al.Titanium dioxide-based nanomaterials for photocatalytic fuel generations.Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(19): 9987-10043. |
| [32] | LIU Y, TIAN L, TAN X, et al.Synthesis, properties, and applications of black titanium dioxide nanomaterials.Sci. Bull., 2017, 62(6): 431-441. |
| [33] | AROUTIOUNIAN V M, ARAKELYAN V M, SHAHNAZARYAN G E.Metal oxide photoelectrodes for hydrogen generation using solar radiation-driven water splitting.Sol. Energy, 2005, 78(5): 581-592. |
| [34] | ZONG X, THAWEESAK S, XU H, et al.A scalable colloidal approach to prepare hematite films for efficient solar water splitting.Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15(29): 12314-12321. |
| [35] | ZHENG X L, SONG J P, LING T, et al.Strongly coupled nafion molecules and ordered porous CdS networks for enhanced visible- light photoelectrochemical hydrogen evolution.Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(24): 4935-4942. |
| [36] | WANG G, YANG X, QIAN F, et al.Double-sided CdS and CdSe quantum dot co-sensitized ZnO nanowire arrays for photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation.Nano Lett., 2010, 10(3): 1088-1092. |
| [37] | CAO S Y, YAN X Q, KANG Z, et al.Band alignment engineering for improved performance and stability of ZnFe2O4 modified CdS/ZnO nanostructured photoanode for PEC water splitting.Nano Energy, 2016, 24: 25-31. |
| [38] | ZHONG Y J, LI Z S, ZHAO X, et al.Enhanced water-splitting performance of perovskite SrTaO2N photoanode film through ameliorating interparticle charge transport.Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(39): 7156-7163. |
| [39] | XIAO M, WANG S, THAWEESAK S, et al.Tantalum (oxy)nitride: narrow bandgap photocatalysts for solar hydrogen generation.Engineering, 2017, 3(3): 365-378. |
| [40] | ZHEN C, CHEN R Z, WANG L Z, et al.Tantalum (oxy)nitride based photoanodes for solar-driven water oxidation.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4(8): 2783-2800. |
| [41] | XIAO M, LUO B, LYU M, et al.Single-crystalline nanomesh tantalum nitride photocatalyst with improved hydrogen-evolving performance.Adv. Energy Mater., 2017, DOI: 10.1002/aenm. 201701605. |
| [42] | SUN K, SHEN S, LIANG Y, et al.Enabling silicon for solar-fuel production.Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(17): 8662-8719. |
| [43] | WANG T, GONG J.Single-crystal semiconductors with narrow band gaps for solar water splitting.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(37): 10718-10732. |
| [44] | BAE D, SEGER B, VESBORG P C, et al.Strategies for stable water splitting via protected photoelectrodes.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46(7): 1933-1954. |
| [45] | LIU C, DASGUPTA N P, YANG P.Semiconductor nanowires for artificial photosynthesis.Chem. Mater., 2014, 26(1): 415-422. |
| [46] | LI H, ZHOU Y, TU W, et al.State-of-the-art progress in diverse heterostructured photocatalysts toward promoting photocatalytic performance.Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25(7): 998-1013. |
| [47] | WANG H, ZHANG L, CHEN Z, et al.Semiconductor heterojunction photocatalysts: design, construction, and photocatalytic performances.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43(15): 5234-5244. |
| [48] | MONIZ S J A, SHEVLIN S A, MARTIN D J, et al. Visible-light driven heterojunction photocatalysts for water splitting - a critical review.Energy Environ. Sci., 2015, 8(3): 731-759. |
| [49] | KUDO A, MISEKI Y.Heterogeneous photocatalyst materials for water splitting.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38(1): 253-278. |
| [50] | YANG Y, NIU S, HAN D, et al.Progress in developing metal oxide nanomaterials for photoelectrochemical water splitting.Adv. Energy Mater., 2017, 7(19): 1700555. |
| [51] | QIU W T, HUANG Y C, WANG Z L, et al.Effective strategies towards high-performance photoanodes for photoelectrochemical water splitting.Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2017, 33(1): 80-102. |
| [52] | CHEN Z B, JARAMILLO T F, DEUTSCH T G, et al.Accelerating materials development for photoelectrochemical hydrogen production: standards for methods, definitions, and reporting protocols.J. Mater. Res., 2010, 25(1): 3-16. |
| [53] | DONG P, HOU G, XI X, et al.WO3-based photocatalysts: morphology control, activity enhancement and multifunctional applications.Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2017, 4(3): 539-557. |
| [54] | ANIK M, CANSIZOGLU T.Dissolution kinetics of WO3 in acidic solutions.J. Appl. Electrochem., 2006, 36(5): 603-608. |
| [55] | SEABOLD J A, CHOI K S.Effect of a cobalt-based oxygen evolution catalyst on the stability and the selectivity of photo-oxidation reactions of a WO3 photoanode.Chem. Mater., 2011, 23(5): 1105-1112. |
| [56] | HUANG J, DING Y, LUO X, et al.Solvation effect promoted formation of p-n junction between WO3 and FeOOH: a high performance photoanode for water oxidation.J. Catal., 2016, 333: 200-206. |
| [57] | HUANG J, ZHANG Y, DING Y.Rationally designed/constructed CoOx/WO3 anode for efficient photoelectrochemical water oxidation.ACS Catal., 2017, 7(3): 1841-1845. |
| [58] | LIU R, LIN Y, CHOU L Y, et al.Water splitting by tungsten oxide prepared by atomic layer deposition and decorated with an oxygen- evolving catalyst.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50(2): 499-502. |
| [59] | LIU Y, LI J, LI W, et al.Enhanced photoelectrochemical performance of WO3 film with HfO2 passivation layer.Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(29): 8856-8863. |
| [60] | SU J, FENG X, SLOPPY J D, et al.Vertically aligned WO3 nanowire arrays grown directly on transparent conducting oxide coated glass: synthesis and photoelectrochemical properties.Nano Lett., 2011, 11(1): 203-208. |
| [61] | LI W, DA P, ZHANG Y, et al.WO3 nanoflakes for enhanced photoelectrochemical conversion.ACS Nano, 2014, 8(11): 11770-11777. |
| [62] | ZHAO Z, BUTBUREE T, LYV M, et al.Etching treatment of vertical WO3 nanoplates as a photoanode for enhanced photoelectrochemical performance.RSC Adv., 2016, 6(72): 68204-68210. |
| [63] | AMANO F, LI D, OHTANI B.Fabrication and photoelectrochemical property of tungsten (VI) oxide films with a flake-wall structure.Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(16): 2769-2771. |
| [64] | YANG J, LI W Z, LI J, et al.Hydrothermal synthesis and photoelectrochemical properties of vertically aligned tungsten trioxide (hydrate) plate-like arrays fabricated directly on FTO substrates.J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(34): 17744-17752. |
| [65] | KALANUR S S, HWANG Y J, CHAE S Y, et al.Facile growth of aligned WO3 nanorods on FTO substrate for enhanced photoanodic water oxidation activity.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(10): 3479-3488. |
| [66] | LIU Y, ZHAO L, SU J, et al.Fabrication and properties of a branched (NH4)xWO3 nanowire array film and a porous WO3 nanorod array film.ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7(6): 3532-3538. |
| [67] | WANG N, WANG D, LI M, et al.Photoelectrochemical water oxidation on photoanodes fabricated with hexagonal nanoflower and nanoblock WO3.Nanoscale, 2014, 6(4): 2061-2066. |
| [68] | KAFIZAS A, FRANCÀS L, SOTELO-VAZQUEZ C, et al. Optimizing the activity of nanoneedle structured WO3 photoanodes for solar water splitting: direct synthesis via chemical vapor deposition.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121(11): 5983-5993. |
| [69] | BISWAS S K, BAEG J O.A facile one-step synthesis of single crystalline hierarchical WO3 with enhanced activity for photoelectrochemical solar water oxidation.Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(8): 3177-3188. |
| [70] | XIE Y P, LIU G, YIN L C, et al.Crystal facet-dependent photocatalytic oxidation and reduction reactivity of monoclinic WO3 for solar energy conversion.J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(14): 6746-6751. |
| [71] | ZHENG J Y, SONG G, HONG J, et al.Facile fabrication of WO3 nanoplates thin films with dominant crystal facet of (002) for water splitting.Cryst. Growth Des., 2014, 14(11): 6057-6066. |
| [72] | ZHANG J J, ZHANG P, WANG T, et al.Monoclinic WO3 nanomultilayers with preferentially exposed (002) facets for photoelectrochemical water splitting.Nano Energy, 2015, 11: 189-195. |
| [73] | WANG S C, CHEN H J, GAO G P, et al.Synergistic crystal facet engineering and structural control of WO3 films exhibiting unprecedented photoelectrochemical performance.Nano Energy, 2016, 24: 94-102. |
| [74] | LIU X, WANG F, WANG Q.Nanostructure-based WO3 photoanodes for photoelectrochemical water splitting.Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14(22): 7894-7911. |
| [75] | SUN Y, MURPHY C J, REYES-GIL K R, et al. Photoelectrochemical and structural characterization of carbon-doped WO3 films prepared via spray pyrolysis.Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(20): 8476-8484. |
| [76] | MI Q, PING Y, LI Y, et al.Thermally stable N2-intercalated WO3 photoanodes for water oxidation.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(44): 18318-18324. |
| [77] | COLE B, MARSEN B, MILLER E, et al.Evaluation of nitrogen doping of tungsten oxide for photoelectrochemical water splitting.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112(13): 5213-5220. |
| [78] | LIU Y, LI J, LI W, et al.Enhancement of the photoelectrochemical performance of WO3 vertical arrays film for solar water splitting by gadolinium doping.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, 119(27): 14834-14842. |
| [79] | LIU Q, LIU Y, LI C, et al.Hydrothermal Sm-doped tungsten oxide vertically plate-like array photoelectrode and its enhanced photoelectrocatalytic efficiency for degradation of organic dyes.J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2016, 28(5): 4004-4013. |
| [80] | SARNOWSKA M, BIENKOWSKI K, BARCZUK P J, et al.Highly efficient and stable solar water splitting at (Na)WO3 photoanodes in acidic electrolyte assisted by non-noble metal oxygen evolution catalyst.Adv. Energy Mater., 2016, 6(14): 1600526. |
| [81] | WANG G M, LING Y C, WANG H Y, et al.Hydrogen-treated WO3 nanoflakes show enhanced photostability.Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5(3): 6180-6187. |
| [82] | ZHAO J, OLIDE E, OSTERLOH F E.Enhancing majority carrier transport in WO3 water oxidation photoanode via electrochemical doping.J. Electrochem. Soc., 2015, 162(1): H65-H71. |
| [83] | MA M, ZHANG K, LI P, et al.Dual oxygen and tungsten vacancies on a WO3 photoanode for enhanced water oxidation.Angew. Chem., 2016, 128(39): 11998-12002. |
| [84] | WANG F, DI VALENTIN C, PACCHIONI G.Doping of WO3 for photocatalytic water splitting: hints from density functional theory.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116(16): 8901-8909. |
| [85] | WANG S, YUN J H, LUO B, et al.Recent progress on visible light responsive heterojunctions for photocatalytic applications.J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2017, 33(1): 1-22. |
| [86] | HOU Y, ZUO F, DAGG A P, et al.Branched WO3 nanosheet array with layered C3N4 heterojunctions and CoOx nanoparticles as a flexible photoanode for efficient photoelectrochemical water oxidation.Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(29): 5043-5049. |
| [87] | HE H, BERGLUND S P, XIAO P, et al.Nanostructured Bi2S3/WO3 heterojunction films exhibiting enhanced photoelectrochemical performance.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(41): 12826-12834. |
| [88] | ZHANG J, MA H, LIU Z.Highly efficient photocatalyst based on all oxides WO3/Cu2O heterojunction for photoelectrochemical water splitting.Appl. Catal., B, 2017, 201: 84-91. |
| [89] | LI H, ZHAO F, ZHANG J, et al.A g-C3N4/WO3 photoanode with exceptional ability for photoelectrochemical water splitting.Mater. Chem. Front., 2017, 1(2): 338-342. |
| [90] | ZHANG J, LIU Z, LIU Z.Novel WO3/Sb2S3 heterojunction photocatalyst based on WO3 of different morphologies for enhanced efficiency in photoelectrochemical water splitting.ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(15): 9684-9691. |
| [91] | ZHAO Z, BUTBUREE T, PEERAKIATKHAJOHN P, et al. Carbon quantum dots sensitized vertical WO3 nanoplates with enhanced photoelectrochemical properties.Chemistry Select, 2016, 1(11): 2772-2777. |
| [92] | SOLARSKA R, KROLIKOWSKA A, AUGUSTYNSKI J.Silver nanoparticle induced photocurrent enhancement at WO3 photoanodes.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010, 49(43): 7980-7983. |
| [93] | SHEN S H, LINDLEY S A, CHEN X Y, et al.Hematite heterostructures for photoelectrochemical water splitting: rational materials design and charge carrier dynamics.Energy Environ. Sci., 2016, 9(9): 2744-2775. |
| [94] | HUANG Z Q, LIN Y J, XIANG X, et al.In situ probe of photocarrier dynamics in water-splitting hematite (α-Fe2O3) electrodes.Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5(10): 8923-8926. |
| [95] | WHEELER D A, WANG G M, LING Y C, et al.Nanostructured hematite: synthesis, characterization, charge carrier dynamics, and photoelectrochemical properties.Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5(5): 6682-6702. |
| [96] | CUMMINGS C Y, MARKEN F, PETER L M, et al.New insights into water splitting at mesoporous α-Fe2O3 films: a study by modulated transmittance and impedance spectroscopies.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(2): 1228-1234. |
| [97] | JUN H, IM B, KIM J Y, et al.Photoelectrochemical water splitting over ordered honeycomb hematite electrodes stabilized by alumina shielding.Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5(4): 6375-6382. |
| [98] | BARROSO M, COWAN A J, PENDLEBURY S R, et al.The role of cobalt phosphate in enhancing the photocatalytic activity of α-Fe2O3 toward water oxidation.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(38): 14868-14871. |
| [99] | QIU Y, LEUNG S F, ZHANG Q, et al.Efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting with ultrathin films of hematite on three-dimensional nanophotonic structures.Nano Lett., 2014, 14(4): 2123-2129. |
| [100] | ZHANG P, WANG T, CHANG X, et al.Synergistic cocatalytic effect of carbon nanodots and Co3O4 nanoclusters for the photoelectrochemical water oxidation on hematite.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(19): 5851-5855. |
| [101] | FECKL J M, DUNN H K, ZEHETMAIER P M, et al.Ultrasmall Co3O4 nanocrystals strongly enhance solar water splitting on mesoporous hematite.Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2015, 2(18): 1500358. |
| [102] | KIM J Y, YOUN D H, KANG K, et al.Highly conformal deposition of an ultrathin FeOOH layer on a hematite nanostructure for efficient solar water splitting.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(36): 10854-10858. |
| [103] | YU Q, MENG X G, WANG T, et al.Hematite films decorated with nanostructured ferric oxyhydroxide as photoanodes for efficient and stable photoelectrochemical water splitting.Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25(18): 2686-2692. |
| [104] | TAMIRAT A G, SU W N, DUBALE A A, et al.Photoelectrochemical water splitting at low applied potential using a NiOOH coated codoped (Sn, Zr) α-Fe2O3 photoanode.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(11): 5949-5961. |
| [105] | CAI L, ZHAO J, LI H, et al.One-step hydrothermal deposition of Ni: FeOOH onto photoanodes for enhanced water oxidation.ACS Energy Letters, 2016, 1(3): 624-632. |
| [106] | DU C, YANG X, MAYER M T, et al.Hematite-based water splitting with low turn-on voltages.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(48): 12692-12695. |
| [107] | XU Y F, WANG X D, CHEN H Y, et al.Toward high performance photoelectrochemical water oxidation: combined effects of ultrafine cobalt iron oxide nanoparticle.Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(24): 4414-4421. |
| [108] | CESAR I, KAY A, GONZALEZ MARTINEZ J A, et al. Translucent thin film Fe2O3 photoanodes for efficient water splitting by sunlight: nanostructure-directing effect of Si-doping.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(14): 4582-4583. |
| [109] | CESAR I, SIVULA K, KAY A, et al.Influence of feature size, film thickness, and silicon doping on the performance of nanostructured hematite photoanodes for solar water splitting.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113(2): 772-782. |
| [110] | ZHONG D K, SUN J, INUMARU H, et al.Solar water oxidation by composite catalyst/α-Fe2O3 photoanodes.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(17): 6086-6087. |
| [111] | ZHONG D K, GAMELIN D R.Photoelectrochemical water oxidation by cobalt catalyst ("Co-Pi")/α-Fe2O3 composite photoanodes: oxygen evolution and resolution of a kinetic bottleneck.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(12): 4202-4207. |
| [112] | ZHONG D K, CORNUZ M, SIVULA K, et al.Photo-assisted electrodeposition of cobalt-phosphate (Co-Pi) catalyst on hematite photoanodes for solar water oxidation.Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, 4(5): 1759-1764. |
| [113] | TILLEY S D, CORNUZ M, SIVULA K, et al.Light-induced water splitting with hematite: improved nanostructure and iridium oxide catalysis.Angew. Chem., 2010, 122(36): 6549-6552. |
| [114] | HAHN N T, MULLINS C B.Photoelectrochemical performance of nanostructured Ti- and Sn-doped α-Fe2O3 photoanodes.Chem. Mater., 2010, 22(23): 6474-6482. |
| [115] | KLEIMAN-SHWARSCTEIN A, HU Y S, FORMAN A J, et al.Electrodeposition of α-Fe2O3 doped with Mo or Cr as photoanodes for photocatalytic water splitting.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112(40): 15900-15907. |
| [116] | KLEIMAN-SHWARSCTEIN A, HUDA M N, WALSH A, et al.Electrodeposited aluminum-doped α-Fe2O3 photoelectrodes: experiment and theory.Chem. Mater., 2010, 22(2): 510-517. |
| [117] | KUMAR P, SHARMA P, SHRIVASTAV R, et al.Electrodeposited zirconium-doped α-Fe2O3 thin film for photoelectrochemical water splitting.Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(4): 2777-2784. |
| [118] | FU Y, DONG C L, LEE W Y, et al.Nb-doped hematite nanorods for efficient solar water splitting: electronic structure evolution vs morphology alteration.ChemNanoMat, 2016, 2(7): 704-711. |
| [119] | LING Y, WANG G, WHEELER D A, et al.Sn-doped hematite nanostructures for photoelectrochemical water splitting.Nano Lett., 2011, 11(5): 2119-2125. |
| [120] | SIVULA K, ZBORIL R, LE FORMAL F, et al.Photoelectrochemical water splitting with mesoporous hematite prepared by a solution-based colloidal approach.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(21): 7436-7444. |
| [121] | BRILLET J, GRATZEL M, SIVULA K.Decoupling feature size and functionality in solution-processed, porous hematite electrodes for solar water splitting.Nano Lett., 2010, 10(10): 4155-4160. |
| [122] | LI M, YANG Y, LING Y, et al.Morphology and doping engineering of Sn-doped hematite nanowire photoanodes.Nano Lett., 2017, 17(4): 2490-2495. |
| [123] | LI C, LI A, LUO Z, et al.Surviving high-temperature calcination: ZrO2-induced hematite nanotubes for photoelectrochemical water oxidation.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(15): 4150-4155. |
| [124] | ANNAMALAI A, SUBRAMANIAN A, KANG U, et al.Activation of hematite photoanodes for solar water splitting: effect of FTO deformation.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, 119(7): 3810-3817. |
| [125] | FRANKING R, LI L, LUKOWSKI M A, et al.Facile post-growth doping of nanostructured hematite photoanodes for enhanced photoelectrochemical water oxidation.Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, 6(2): 500-512. |
| [126] | WANG D, CHANG G, ZHANG Y, et al.Hierarchical three-dimensional branched hematite nanorod arrays with enhanced mid-visible light absorption for high-efficiency photoelectrochemical water splitting.Nanoscale, 2016, 8(25): 12697-12701. |
| [127] | LIU J, CAI Y Y, TIAN Z F, et al.Highly oriented Ge-doped hematite nanosheet arrays for photoelectrochemical water oxidation.Nano Energy, 2014, 9: 282-290. |
| [128] | KIM J Y, MAGESH G, YOUN D H, et al.Single-crystalline, wormlike hematite photoanodes for efficient solar water splitting.Sci. Rep., 2013, 3: 2681. |
| [129] | GUO X L, WANG L L, TAN Y W.Hematite nanorods Co-doped with Ru cations with different valence states as high performance photoanodes for water splitting.Nano Energy, 2015, 16: 320-328. |
| [130] | PEERAKIATKHAJOHN P, YUN J H, CHEN H, et al.Stable hematite nanosheet photoanodes for enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting.Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(30): 6405-6410. |
| [131] | KANG J S, NOH Y, KIM J, et al.Iron oxide photoelectrode with multidimensional architecture for highly efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(23): 6583-6588. |
| [132] | HOU Y, ZUO F, DAGG A, et al.A three-dimensional branched cobalt-doped α-Fe2O3 nanorod/MgFe2O4 heterojunction array as a flexible photoanode for efficient photoelectrochemical water oxidation.Angew. Chem., 2013, 125(4): 1286-1290. |
| [133] | LIN Y, ZHOU S, SHEEHAN S W, et al.Nanonet-based hematite heteronanostructures for efficient solar water splitting.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(8): 2398-2401. |
| [134] | SIVULA K, FORMAL F L, GRÄTZEL M. WO3-Fe2O3 photoanodes for water splitting: a host scaffold, guest absorber approach.Chem. Mater., 2009, 21(13): 2862-2867. |
| [135] | HOU Y, ZUO F, DAGG A, et al.Visible light-driven α-Fe2O3 nanorod/graphene/BiV1-xMoxO4 core/shell heterojunction array for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting.Nano Lett., 2012, 12(12): 6464-6473. |
| [136] | XU Y F, RAO H S, CHEN B X, et al.Achieving highly efficient photoelectrochemical water oxidation with a TiCl4 treated 3D antimony-doped SnO2 macropore/branched α-Fe2O3 nanorod heterojunction photoanode.Adv. Sci., 2015, 2(7): 1500049. |
| [137] | MIAO C, JI S, XU G, et al.Micro-nano-structured Fe2O3: Ti/ZnFe2O4 heterojunction films for water oxidation.ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2012, 4(8): 4428-4433. |
| [138] | AHMED M G, KANDIEL T A, AHMED A Y, et al.Enhanced photoelectrochemical water oxidation on nanostructured hematite photoanodes via p-CaFe2O4/n-Fe2O3 heterojunction formation.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, 119(11): 5864-5871. |
| [139] | DENG J, LV X, LIU J, et al.Thin-layer Fe2TiO5 on hematite for efficient solar water oxidation.ACS Nano, 2015, 9(5): 5348-5356. |
| [140] | BASSI P S, ANTONY R P, BOIX P P, et al.Crystalline Fe2O3/Fe2TiO5 heterojunction nanorods with efficient charge separation and hole injection as photoanode for solar water oxidation.Nano Energy, 2016, 22: 310-318. |
| [141] | LI C, WANG T, LUO Z, et al.Enhanced charge separation through ALD-modified Fe2O3/Fe2TiO5 nanorod heterojunction for photoelectrochemical water oxidation.Small, 2016, 12(25): 3415-3422. |
| [142] | PARK Y, MCDONALD K J, CHOI K S.Progress in bismuth vanadate photoanodes for use in solar water oxidation.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42(6): 2321-2337. |
| [143] | HUANG Z F, PAN L, ZOU J J, et al.Nanostructured bismuth vanadate-based materials for solar-energy-driven water oxidation: a review on recent progress.Nanoscale, 2014, 6(23): 14044-14063. |
| [144] | ABDI F F, SAVENIJE T J, MAY M M, et al.The origin of slow carrier transport in BiVO4 thin film photoanodes: a time-resolved microwave conductivity study.J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2013, 4(16): 2752-2757. |
| [145] | TOLOD K, HERNÁNDEZ S, RUSSO N. Recent advances in the BiVO4 photocatalyst for sun-driven water oxidation: top-performing photoanodes and scale-up challenges.Catalysts, 2017, 7(1): 13. |
| [146] | BERGLUND S P, RETTIE A J, HOANG S, et al.Incorporation of Mo and W into nanostructured BiVO4 films for efficient photoelectrochemical water oxidation.Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14(19): 7065-7075. |
| [147] | ABDI F F, HAN L, SMETS A H, et al.Efficient solar water splitting by enhanced charge separation in a bismuth vanadate-silicon tandem photoelectrode.Nat. Commun., 2013, 4: 2195. |
| [148] | WANG G, LING Y, LU X, et al.Computational and photoelectrochemical study of hydrogenated bismuth vanadate.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(21): 10957-10964. |
| [149] | QIN D D, WANG T, SONG Y M, et al.Reduced monoclinic BiVO4 for improved photoelectrochemical oxidation of water under visible light.Dalton Trans., 2014, 43(21): 7691-7694. |
| [150] | WANG G, YANG Y, LING Y, et al.An electrochemical method to enhance the performance of metal oxides for photoelectrochemical water oxidation.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4(8): 2849-2855. |
| [151] | WANG S, CHEN P, YUN J H, et al.An electrochemically treated BiVO4 photoanode for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(29): 8500-8504. |
| [152] | BU Y Y, TIAN J, CHEN Z W, et al.Optimization of the photo-electrochemical performance of Mo-doped BiVO4 photoanode by controlling the metal-oxygen bond state on (020) facet.Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2017, 4(10): 1601235. |
| [153] | KIM T W, CHOI K S.Nanoporous BiVO4 photoanodes with dual-layer oxygen evolution catalysts for solar water splitting.Science, 2014, 343(6174): 990-994. |
| [154] | KIM T W, PING Y, GALLI G A, et al.Simultaneous enhancements in photon absorption and charge transport of bismuth vanadate photoanodes for solar water splitting.Nat. Commun., 2015, 6: 8769. |
| [155] | KUANG Y, JIA Q, NISHIYAMA H, et al.A front-illuminated nanostructured transparent BiVO4 photoanode for >2% efficient water splitting.Adv. Energy Mater., 2016, 6(2): 1501645. |
| [156] | WANG Y, LI F, ZHOU X, et al.Highly efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting with an immobilized molecular Co4O4 cubane catalyst.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(24): 6911-6915. |
| [157] | YE K-H, WANG Z, GU J, et al.Carbon quantum dots as a visible light sensitizer to significantly increase the solar water splitting performance of bismuth vanadate photoanodes.Energy Environ. Sci., 2017, 10(3): 772-779. |
| [158] | ZHONG M, HISATOMI T, MINEGISHI T, et al.Bulky crystalline BiVO4 thin films for efficient solar water splitting.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4(25): 9858-9864. |
| [159] | HONG S J, LEE S, JANG J S, et al.Heterojunction BiVO4/WO3 electrodes for enhanced photoactivity of water oxidation.Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, 4(5): 1781-1787. |
| [160] | SU J, GUO L, BAO N, et al.Nanostructured WO3/BiVO4 heterojunction films for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting.Nano Lett., 2011, 11(5): 1928-1933. |
| [161] | PIHOSH Y, TURKEVYCH I, MAWATARI K, et al.Nanostructured WO3/BiVO4 photoanodes for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting.Small, 2014, 10(18): 3692-3699. |
| [162] | RAO P M, CAI L, LIU C, et al.Simultaneously efficient light absorption and charge separation in WO3/BiVO4 core/shell nanowire photoanode for photoelectrochemical water oxidation.Nano Lett., 2014, 14(2): 1099-1105. |
| [163] | SHI X, CHOI I Y, ZHANG K, et al.Efficient photoelectrochemical hydrogen production from bismuth vanadate-decorated tungsten trioxide helix nanostructures.Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 4775. |
| [164] | XIA L, BAI J, LI J, et al.A highly efficient BiVO4/WO3/W heterojunction photoanode for visible-light responsive dual photoelectrode photocatalytic fuel cell.Appl. Catal., B, 2016, 183: 224-230. |
| [165] | LEE M G, KIM D H, SOHN W, et al.Conformally coated BiVO4 nanodots on porosity-controlled WO3 nanorods as highly efficient type II heterojunction photoanodes for water oxidation.Nano Energy, 2016, 28: 250-260. |
| [166] | PIHOSH Y, TURKEVYCH I, MAWATARI K, et al.Photocatalytic generation of hydrogen by core-shell WO3/BiVO4 nanorods with ultimate water splitting efficiency.Sci. Rep., 2015, 5: 11141. |
| [167] | SAITO R, MISEKI Y, SAYAMA K.Highly efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting using a thin film photoanode of BiVO4/SnO2/WO3 multi-composite in a carbonate electrolyte.Chem. Commun., 2012, 48(32): 3833-3835. |
| [168] | BAEK J H, KIM B J, HAN G S, et al.BiVO4/WO3/SnO2 double- heterojunction photoanode with enhanced charge separation and visible-transparency for bias-free solar water-splitting with a perovskite solar cell.ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(2): 1479-1487. |
| [169] | CHENG B Y, YANG J S, CHO H W, et al.Fabrication of an efficient BiVO4-TiO2 heterojunction photoanode for photoelectrochemical water oxidation.ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(31): 20032-20039. |
| [170] | AN X, LI T, WEN B, et al.New insights into defect-mediated heterostructures for photoelectrochemical water splitting.Adv. Energy Mater., 2016, 6(8): 1502268. |
| [171] | HESS L H, COOPER J K, LOIUDICE A, et al.Probing interfacial energetics and charge transfer kinetics in semiconductor nanocomposites: new insights into heterostructured TiO2/BiVO4 photoanodes.Nano Energy, 2017, 34: 375-384. |
| [172] | ZHOU L, ZHAO C, GIRI B, et al.High light absorption and charge separation efficiency at low applied voltage from Sb-doped SnO2/BiVO4 core/shell nanorod-array photoanodes.Nano Lett., 2016, 16(6): 3463-3474. |
| [173] | RESASCO J, ZHANG H, KORNIENKO N, et al.TiO2/BiVO4 nanowire heterostructure photoanodes based on type II band alignment.ACS Cent Sci, 2016, 2(2): 80-88. |
| [174] | YE K H, CHAI Z S, GU J W, et al.BiOI-BiVO4 photoanodes with significantly improved solar water splitting capability: p-n junction to expand solar adsorption range and facilitate charge carrier dynamics.Nano Energy, 2015, 18: 222-231. |
| [175] | YANG J S, WU J J.Low-potential driven fully-depleted BiVO4/ZnO heterojunction nanodendrite array photoanodes for photoelectrochemical water splitting.Nano Energy, 2017, 32: 232-240. |
| [176] | MONIZ S J A, ZHU J, TANG J. 1D Co-Pi modified BiVO4/ZnO junction cascade for efficient photoelectrochemical water cleavage.Adv. Energy Mater., 2014, 4(10): 1301590. |
| [177] | SU J Y, BAI Z W, HUANG B L, et al.Unique three dimensional architecture using a metal-free semiconductor cross-linked bismuth vanadate for efficient photoelectrochemical water oxidation.Nano Energy, 2016, 24: 148-157. |
| [178] | KIM E S, KANG H J, MAGESH G, et al.Improved photoelectrochemical activity of CaFe2O4/BiVO4 heterojunction photoanode by reduced surface recombination in solar water oxidation.ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6(20): 17762-17769. |
| [179] | CHANG X, WANG T, ZHANG P, et al.Enhanced surface reaction kinetics and charge separation of p-n heterojunction Co3O4/BiVO4 photoanodes.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(26): 8356-8359. |
| [180] | XI G, YE J.Synthesis of bismuth vanadate nanoplates with exposed {001} facets and enhanced visible-light photocatalytic properties.Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(11): 1893-1895. |
| [181] | WANG D, JIANG H, ZONG X, et al.Crystal facet dependence of water oxidation on BiVO4 sheets under visible light irradiation.Chem. Eur. J., 2011, 17(4): 1275-1282. |
| [182] | KIM C W, SON Y S, KANG M J, et al.(040)-crystal facet engineering of BiVO4 plate photoanodes for solar fuel production.Adv. Energy Mater., 2016, 6(4): 1501754. |
| [183] | ZHU Y K, REN J, YANG X F, et al.Interface engineering of 3D BiVO4/Fe-based layered double hydroxide core/shell nanostructures for boosting photoelectrochemical water oxidation.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(20): 9952-9959. |
| [184] | LIU G, YANG H G, PAN J, et al.Titanium dioxide crystals with tailored facets.Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(19): 9559-9612. |
| [185] | LI R, ZHANG F, WANG D, et al.Spatial separation of photogenerated electrons and holes among {010} and {110} crystal facets of BiVO4.Nat. Commun., 2013, 4: 1432. |
| [186] | LI R G, HAN H X, ZHANG F X, et al.Highly efficient photocatalysts constructed by rational assembly of dual-cocatalysts separately on different facets of BiVO4.Energy Environ. Sci., 2014, 7(4): 1369-1376. |
| [187] | CHEN S, WANG L W.Thermodynamic oxidation and reduction potentials of photocatalytic semiconductors in aqueous solution.Chem. Mater., 2012, 24(18): 3659-3666. |
| [188] | LICHTERMAN M F, SHANER M R, HANDLER S G, et al.Enhanced stability and activity for water oxidation in alkaline media with bismuth vanadate photoelectrodes modified with a cobalt oxide catalytic layer produced by atomic layer deposition.J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2013, 4(23): 4188-4191. |
| [189] | MCDOWELL M T, LICHTERMAN M F, SPURGEON J M, et al.Improved stability of polycrystalline bismuth vanadate photoanodes by use of dual-layer thin TiO2/Ni coatings.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118(34): 19618-19624. |
| [190] | KIM T W, CHOI K S.Improving stability and photoelectrochemical performance of BiVO4 photoanodes in basic media by adding a ZnFe2O4 layer.J Phys Chem Lett, 2016, 7(3): 447-451. |
| [191] | TOMA F M, COOPER J K, KUNZELMANN V, et al.Mechanistic insights into chemical and photochemical transformations of bismuth vanadate photoanodes.Nat. Commun., 2016, 7: 12012. |
| [192] | XIE J, GUO C, YANG P, et al.Bi-functional ferroelectric BiFeO3 passivated BiVO4 photoanode for efficient and stable solar water oxidation.Nano Energy, 2017, 31: 28-36. |
| [193] | LUO W J, YANG Z S, LI Z S, et al.Solar hydrogen generation from seawater with a modified BiVO4 photoanode.Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, 4(10): 4046-4051. |
| [194] | PILLI S K, FURTAK T E, BROWN L D, et al.Cobalt-phosphate (Co-Pi) catalyst modified Mo-doped BiVO4 photoelectrodes for solar water oxidation.Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, 4(12): 5028-5034. |
| [195] | ZHONG D K, CHOI S, GAMELIN D R.Near-complete suppression of surface recombination in solar photoelectrolysis by "Co-Pi" catalyst-modified W: BiVO4.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(45): 18370-18377. |
| [196] | KUANG Y, JIA Q, MA G, et al.Ultrastable low-bias water splitting photoanodes via photocorrosion inhibition and in situ catalyst regeneration.Nature Energy, 2016, 2(1): 16191. |
| [197] | ZHANG K, MA M, LI P, et al.Water splitting progress in tandem devices: moving photolysis beyond electrolysis.Adv. Energy Mater., 2016, 6(15): 1600602. |
| [198] | PEERAKIATKHAJOHN P, YUN J H, WANG S C, et al.Review of recent progress in unassisted photoelectrochemical water splitting: from material modification to configuration design.J. Photonics Energy, 2017, 7(1): 012006. |
| [199] | BORNOZ P, ABDI F F, TILLEY S D, et al.A bismuth vanadate-cuprous oxide tandem cell for overall solar water splitting.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118(30): 16959-16966. |
| [200] | JIANG F, GUNAWAN, HARADA T, et al.Pt/In2S3/CdS/ Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film as an efficient and stable photocathode for water reduction under sunlight radiation.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(42): 13691-13697. |
| [201] | LIU B, WU C H, MIAO J, et al.All inorganic semiconductor nanowire mesh for direct solar water splitting.ACS Nano, 2014, 8(11): 11739-11744. |
| [202] | JANG J W, DU C, YE Y, et al.Enabling unassisted solar water splitting by iron oxide and silicon.Nat. Commun., 2015, 6: 7447. |
| [203] | HU S, XIANG C X, HAUSSENER S, et al.An analysis of the optimal band gaps of light absorbers in integrated tandem photoelectrochemical water-splitting systems.Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, 6(10): 2984-2993. |
| [204] | REECE S Y, HAMEL J A, SUNG K, et al.Wireless solar water splitting using silicon-based semiconductors and earth-abundant catalysts.Science, 2011, 334(6056): 645-648. |
| [205] | KHASELEV O, TURNER J A.A monolithic photovoltaic-photoelectrochemical device for hydrogen production via water splitting.Science, 1998, 280(5362): 425-427. |
| [206] | LICHT S, WANG B, MUKERJI S, et al.Efficient solar water splitting, exemplified by RuO2-catalyzed AlGaAs/Si photoelectrolysis.J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104(38): 8920-8924. |
| [207] | BRILLET J, YUM J H, CORNUZ M, et al.Highly efficient water splitting by a dual-absorber tandem cell.Nat. Photonics, 2012, 6(12): 824-828. |
| [208] | SHI X J, ZHANG K, SHIN K, et al.Unassisted photoelectrochemical water splitting beyond 5.7% solar-to-hydrogen conversion efficiency by a wireless monolithic photoanode/dye-sensitised solar cell tandem device.Nano Energy, 2015, 13: 182-191. |
| [209] | SHI X, JEONG H, OH S J, et al.Unassisted photoelectrochemical water splitting exceeding 7% solar-to-hydrogen conversion efficiency using photon recycling.Nat. Commun., 2016, 7: 11943. |
| [210] | DING C, QIN W, WANG N, et al.Solar-to-hydrogen efficiency exceeding 2.5% achieved for overall water splitting with an all earth-abundant dual-photoelectrode.Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, 16(29): 15608-15614. |
| [211] | KIM J H, JANG J W, JO Y H, et al.Hetero-type dual photoanodes for unbiased solar water splitting with extended light harvesting.Nat. Commun., 2016, 7: 13380. |
| [212] | CHEN Y S, MANSER J S, KAMAT P V.All solution-processed lead halide perovskite-BiVO4 tandem assembly for photolytic solar fuels production.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(2): 974-981. |
| [213] | QIU Y, LIU W, CHEN W, et al. Efficient solar-driven water splitting by nanocone BiVO4-perovskite tandem cells. Sci. Adv., 2016, 2(6): e1501764-1-9. |
| [214] | KIM J H, JO Y, KIM J H, et al.Wireless solar water splitting device with robust cobalt-catalyzed, dual-doped BiVO4 photoanode and perovskite solar cell in tandem: a dual absorber artificial leaf.ACS Nano, 2015, 9(12): 11820-11829. |
| [215] | JIA J, SEITZ L C, BENCK J D, et al.Solar water splitting by photovoltaic-electrolysis with a solar-to-hydrogen efficiency over 30%.Nat. Commun., 2016, 7: 13237. |
| [216] | LHERMITTE C R, BARTLETT B M.Advancing the chemistry of CuWO4 for photoelectrochemical water oxidation.Acc. Chem. Res., 2016, 49(6): 1121-1129. |
| [217] | KANG D, PARK Y, HILL J C, et al.Preparation of Bi-based ternary oxide photoanodes BiVO4, Bi2WO6, and Bi2Mo3O12 using dendritic Bi metal electrodes.J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2014, 5(17): 2994-2999. |
| [218] | LIU Q, HE J, YAO T, et al.Aligned Fe2TiO5-containing nanotube arrays with low onset potential for visible-light water oxidation.Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 5122. |
| [219] | GUO W, CHEMELEWSKI W D, MABAYOJE O, et al.Synthesis and characterization of CuV2O6 and Cu2V2O7: two photoanode candidates for photoelectrochemical water oxidation.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, 119(49): 27220-27227. |
| [220] | KIM M W, JOSHI B, YOON H, et al.Electrosprayed copper hexaoxodivanadate (CuV2O6) and pyrovanadate (Cu2V2O7) photoanodes for efficient solar water splitting.J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 708: 444-450. |
| [221] | SEABOLD J A, NEALE N R.All first row transition metal oxide photoanode for water splitting based on Cu3V2O8.Chem. Mater., 2015, 27(3): 1005-1013. |
| [222] | WANG W, ZHANG Y J, WANG L, et al.Facile synthesis of Fe3+/Fe2+ self-doped nanoporous FeVO4 photoanodes for efficient solar water splitting.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(6): 2478-2482. |
| [223] | BISWAS S K, BAEG J O.Enhanced photoactivity of visible light responsive W incorporated FeVO4 photoanode for solar water splitting.Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(34): 14451-14457. |
| [1] | HU Xue-Mei, GU Zheng-Ying, LI Xiao-Min, GAO Xiang-Dong, SHI Ying. Hybrid Photoanodes Based on Nanoporous Lithium Titanate Nanostructures in Dye-sensitized Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(10): 1037-1042. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||