
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 434-442.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150488
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHU Kai-Ping1, SUN Jing2, YE Song1, ZHOU Jie1, WANG Hui1, WANG De-Ping1
Received:2015-10-10
Published:2016-04-20
Online:2016-03-25
About author:ZHU Kai-Ping(1991–), male, candidate of master degree. E-mail: zkp10580@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHU Kai-Ping, SUN Jing, YE Song, ZHOU Jie, WANG Hui, WANG De-Ping. A Novel Hollow Hydroxyapatite Microspheres/Chitosan Composite Drug Carrier for Controlled Release[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(4): 434-442.

Fig. 2 Surface SEM images of the hollow HA microspheres (a) Dried at 60℃; (b) Sintered at 600℃ The inset in (a) and (b) show the high magnification image of the surface
| Sample | SA/(m2·g-1) | PV/(cm3·g-1) | PS/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60℃ | 55.32 | 0.21 | 15.38 |
| 600℃ | 31.17 | 0.17 | 28.29 |
Table 1 The surface characteristics and pore structure parameters of the microspheres
| Sample | SA/(m2·g-1) | PV/(cm3·g-1) | PS/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60℃ | 55.32 | 0.21 | 15.38 |
| 600℃ | 31.17 | 0.17 | 28.29 |
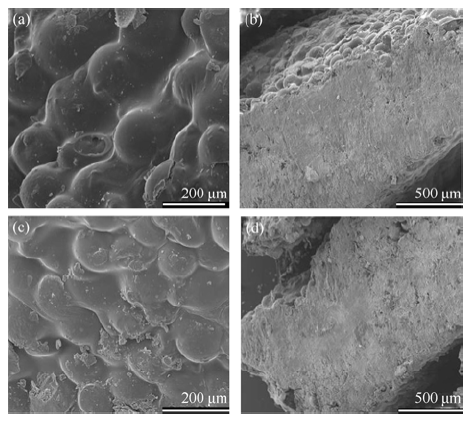
Fig. 7 SEM images of the surface and the cross-section of the CS-coated composite drug carrier (a) Surface of the CS (20 g/L)-coated; (b) Cross-section of the CS (20 g/L)- coated; (c) Surface of the CS (30 g/L)-coated; (d) Cross-section of the CS (30 g/L)-coated

Fig. 8 The cumulative release percentage of vancomycin from the hollow HA microspheres, CS (20 g/L)-coated and CS (30 g/L)-coated composite drug carrier into PBS as a function of time

Fig. 9 The cumulative release percentage of vancomycin into PBS with different pH from the hollow HA microspheres (a), the CS (20 g/L)- coated composite drug carrier (b) and the CS (30 g/L)-coated composite drug carrier (c)

Fig. 11 SEM image of the CS (20 g/L)-coated HA microspheres after immersing in PBS with the high pH 8.5. Red arrows indicate the hollow HA microspheres; black arrows indicate the chitosan gel
| [1] | GIANNOUDIS PV, DINOPOULOS H, TSIRIDIS E.Bone substitutes: an update.Injury, 2005, 36(S3): S20-S27. |
| [2] | MOORE W R, GRAVES S E, BAIN G I.Synthetic bone graft substitutes.ANZ J Surg., 2001, 71(6): 354-361. |
| [3] | LAURENCIN C, KHAN Y, EL-AMIN S F. Bone graft substitutes.Expert. Rev. Med. Devices, 2006, 3(1): 49-57. |
| [4] | LIU X, XIE Z P, HUANG W H, et al.Bioactive borate glass scaffolds: in vitro and in vivo evaluation for use as a drug delivery system in the treatment of bone infection.J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med., 2010, 21(2): 575-582. |
| [5] | WANG Y N, CHEN H, DENG C L, et al.The applications of surfactant template on the preparing of nano-hydroxyapatite.China Ceram., 2009, 45(4): 21-24. |
| [6] | ZHAO W R, CHEN H R, LI Y S, et al.Uniform rattle-type hollow magnetic mesoporous spheres as drug delivery carriers and their sustained-release property.Adv. Funct. Mater., 2008, 18(18): 2780-2788. |
| [7] | HUANG W H, RAHAMAN M N, DAY D E, et al.Strength of hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres prepared by a glass conversion process.J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med., 2009, 20(1): 123-129. |
| [8] | ZHU KAI-PING, WANG DE-PING, FAN HONG-YUAN, et al.In-situ transformation of borate glass and its effect on pH value of soaking-liquid.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(10): 1069-1074. |
| [9] | HUYNH D P, IM G J, CHAE S Y, et al.Controlled release of insulin from pH/temperature-sensitive injectable pentablock copolymer hydrogel.J. Control Release, 2009, 137(1): 20-24. |
| [10] | BARON R, NEFF L, LOUVARD D, et al.Cell-mediated extracellular acidification and bone resorption: evidence for a low pH in resorbing lacunae and localization of a 100-kD lysosomal membrane protein at the osteoclast ruffled border.J. Cell Biol., 1985, 101(6): 2210-2222. |
| [11] | ZHANG X, JIA W T, GU Y F, et al.Teicoplanin-loaded borate bioactive glass implants for treating chronic bone infection in a rabbit tibia osteomyelitis model.Biomaterials, 2010, 31(22): 5865-5874. |
| [12] | JIA W T, ZHANG X, LUO S H, et al.Novel borate glass/chitosan composite as a delivery vehicle for teicoplanin in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis.Acta Biomaterialia, 2010, 6(3): 812-819. |
| [13] | CARREIRA A S, GONCALVES F A M M, MENDONCA P V, et al. Temperature and pH responsive polymers based on chitosan: applications and new graft copolymerization strategies based on living radical polymerization.Carbohydrate Polymers, 2010, 80(3): 618-630. |
| [14] | YAO A H, AI F R, LIU X, et al.Preparation of hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres by the conversion of borate glass at near room temperature.Materials Research Bulletin, 2010, 45(1): 25-28. |
| [15] | CU X, ZHAO C J, GU Y F, et al.A novel injectable borate bioactive glass cement for local delivery of vancomycin to cure osteomyelitis and regenerate bone.J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med., 2014, 25(3): 733-745. |
| [16] | JIANG F, WANG D P, YE S, et al.Strontium-substituted, luminescent and mesoporous hydroxyapatite microspheres for sustained drug release.J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med., 2014, 25(2): 391-400. |
| [17] | LIN K L, LIU P Y, WEI L, et al.Strontium substituted hydroxyapatite porous microspheres: surfactant-free hydrothermal synthesis, enhanced biological response and sustained drug release.Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 222(15): 49-59. |
| [18] | SING K S W, EVERETT D H, HAUL R A W, et al. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity.Pure Appl. Chem., 1985, 57(4): 603-619. |
| [19] | WANG Y C, DENG P H, ZHANG S X, et al.Research on the phase, morphology and textual properties of the hollow HAP microspheres at different sintering temperatures.Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41(S2): 19-22. |
| [20] | XIA W, CHANG J.Well-ordered mesoporous bioactive glasses (MBG): a promising bioactive drug delivery system. J. Controlled Release, 2006, 110(3): 522-530. |
| [21] | XIAO W, FU H L, RAHAMAN M N, et al.Hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres: a novel bioactive and osteoconductive carrier for controlled release of bone morphogenetic protein-2 in bone regeneration.Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9(9): 8374-8383. |
| [22] | ZHAO Q S, CHENG X J, JI Q X, et al.Effect of organic and inorganic acids on chitosan/ glycerophosphate thermosensitive hydrogel.Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2009, 50(1): 111-118. |
| [23] | SUNGWOO K, SATORU K N, BUMGARDNER J D, et al.A chitosan/ β-glycerophosphate thermo-sensitive gel for the delivery of ellagic acid for the treatment of brain cancer.Biomaterials, 2010, 31(14): 4157-4166. |
| [24] | CHENG Y H, YANG S H, LIU C C, et al.Thermosensitive hydrogel made of ferulic acid-gelatin and chitosan glycerophosphate.Carbohydrate Polymers, 2013, 92(2): 1512-1519. |
| [1] | CHEN Xinli, LI Yan, WANG Weisheng, SHI Zhiwen, ZHU Liqiang. Gelatin/Carboxylated Chitosan Gated Oxide Neuromorphic Transistor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 421-428. |
| [2] | FU Hai-Li, ZHANG Wen, ZHANG Hua, SONG Shao-Bo, LI Wei. Preparation and Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan/Organic Laponite Nanocomposites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(5): 479-484. |
| [3] | LIANG Hong-Pei, WANG Ying-Bo, SU Zhi, LU Xiong, WANG Shuai. Electrospinning Gelatin/Chitosan/Hydroxyapatite/Graphene Oxide Composite Nanofibers with Antibacterial Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(5): 516-522. |
| [4] | LI Jian, HAN Zhi-Jun, WEI Yan, NIU Lu-Lu, LIU Yu, LU Guo-Yun, HUANG Di. In situ Biomimetic Fabrication and Characterization of Nano-hydroxyapatite/ Chitosan Composite Microspheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(12): 1327-1332. |
| [5] | WANG Xiao-Ying, LIU Bo, TANG Yu-Feng, SU Han-Jie, HAN Yang, SUN Run-Cang. New Progress on Rectorite/Polymer Nanocomposites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(2): 113-121. |
| [6] | ZHENGXiong-Fei, ZHAI Wen-Jie, LIANG Ying-Chun, SUN Tao. Fabrication ofChitosan-nanohydroxyapatite Scaffolds viaLow-temperature Deposition Manufacturing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(1): 12-16. |
| [7] | WANG Xiao-Ying,DU Yu-Min,SUN Run-Cang,LIU Chuan-Fu. Antimicrobial Activity of Quaternized Chitosan/Organic Rectorite Nanocomposite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(6): 1236-1242. |
| [8] | WANG Ying-Bo,LU Xiong,FENG Bo,QU Shu-Xin,WENG Jie,CHEN Jian-Min. Investigation of HA/chitosan Composite Coatings Prepared by Sol-Gel on Alkali Treated Titanium Surfaces [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(6): 1241-1245. |
| [9] | LU Xiao-Ying,WANG,Xiu-Hong,QU Shu-Xin,WENG Jie. Preparation of Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Hybrids [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(2): 332-336. |
| [10] | JIANG Liu-Yun,LI Yu-Bao,ZHANG Li,WANG Xue-Jiang. Study on Nano-hydroxyapatite/Chitosan-Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composite Scaffold [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(1): 135-140. |
| [11] | ZHANG Li,LI Yu-Bao,ZHOU Gang,LU Guo-Yu,ZUO Yi. Setting Mechanism of Nano-hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(5): 1197-1202. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||