
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 291-297.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150362
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Xin-Guo1,2( ), YAN Jie1, CHEN Zi-Meng1, ZHU Lin1, XU Guo-Wang1,2, HUANG Chu-Yun1,2(
), YAN Jie1, CHEN Zi-Meng1, ZHU Lin1, XU Guo-Wang1,2, HUANG Chu-Yun1,2( ), LV Hui1,2
), LV Hui1,2
Received:2015-08-10
Revised:2015-09-16
Published:2016-03-20
Online:2016-02-24
Supported by:CLC Number:
MA Xin-Guo, YAN Jie, CHEN Zi-Meng, ZHU Lin, XU Guo-Wang, HUANG Chu-Yun, LV Hui. First-principles Calculation on Pt- and Au-modified Anatase TiO2(101) Surface[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(3): 291-297.
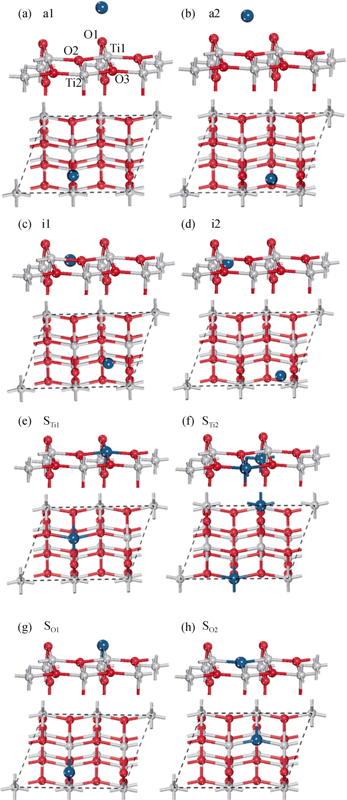
Fig. 1 The structure model of anatase TiO2(101) surface modified noble metal from side and top view(a) and (b) indicate the adsorption above surface; (c) and (d) indicate the adsorption between surface atoms; (e) and (f) indicate the adsorption at Ti vacancy; (g) and (h) indicate the adsorption at O vacancy. Small black and gray spheres represent the O and Ti atoms, respectively. Big blue spheres represent the noble metal atoms
| Metal | Type | 1×1 | 1×2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | a1 | 3.511 | 1.858 |
| a2 | 3.854 | ― | |
| i1 | ― | 1.416 | |
| i2 | ― | 2.323 | |
| Au | a1 | 2.423 | 1.398 |
| a2 | 2.405 | ― | |
| i1 | ― | 1.455 | |
| i2 | ― | 2.624 |
Table 1 Adsorption energies of noble metal adsorbing above surface or adsorbing between surface atoms (eV)
| Metal | Type | 1×1 | 1×2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | a1 | 3.511 | 1.858 |
| a2 | 3.854 | ― | |
| i1 | ― | 1.416 | |
| i2 | ― | 2.323 | |
| Au | a1 | 2.423 | 1.398 |
| a2 | 2.405 | ― | |
| i1 | ― | 1.455 | |
| i2 | ― | 2.624 |
| Metal | Type | 1×1 | 1×2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O rich | Ti rich | O rich | Ti rich | ||
| Pt | STi1 | -0.237 | 10.064 | -0.161 | 4.990 |
| STi2 | -0.490 | 9.810 | -0.331 | 4.820 | |
| SO1 | 5.548 | 0.398 | 2.812 | 0.237 | |
| SO2 | 6.043 | 0.893 | 2.950 | 0.375 | |
| Au | STi1 | 1.248 | 11.548 | 0.600 | 5.751 |
| STi2 | 1.956 | 12.256 | 0.907 | 6.057 | |
| SO1 | 5.501 | 0.351 | 2.793 | 0.218 | |
| SO2 | 6.179 | 1.029 | 3.067 | 0.492 | |
Table 2 The adsorption energies of noble metal adsorbing at Ti or O vacancies in TiO2(101) surface (eV)
| Metal | Type | 1×1 | 1×2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O rich | Ti rich | O rich | Ti rich | ||
| Pt | STi1 | -0.237 | 10.064 | -0.161 | 4.990 |
| STi2 | -0.490 | 9.810 | -0.331 | 4.820 | |
| SO1 | 5.548 | 0.398 | 2.812 | 0.237 | |
| SO2 | 6.043 | 0.893 | 2.950 | 0.375 | |
| Au | STi1 | 1.248 | 11.548 | 0.600 | 5.751 |
| STi2 | 1.956 | 12.256 | 0.907 | 6.057 | |
| SO1 | 5.501 | 0.351 | 2.793 | 0.218 | |
| SO2 | 6.179 | 1.029 | 3.067 | 0.492 | |
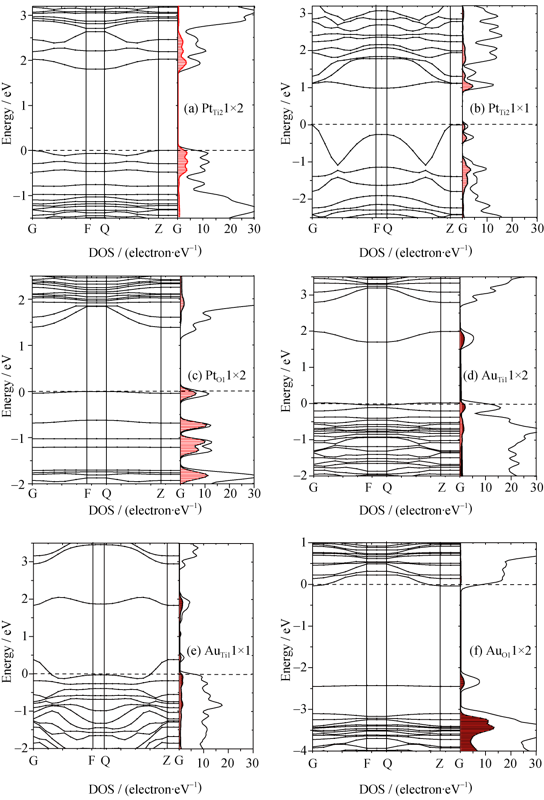
Fig. 3 The energy band structures and the density of states of TiO2(101) surface modified noble metal, whose shaded parts indicate the density of states of the impurity atoms and the standard dotted lines indicate the Fermi level
| [1] | LINSEBIGLER A L, LU G, YATES J T.Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: principles, mechanisms, and selected results.Chem. Rev., 1995, 95(3): 735-751. |
| [2] | CHEN X B, SHEN S H, GUO L J, et al. Semiconductor-based photocatalytic hydrogen generation. Chem. Rev., 2010, 110(11): 6503-6570. |
| [3] | DIEBOLD U.The surface science of titanium dioxide.Surf. Sci. Rep., 2003, 48(5-8): 53-229. |
| [4] | COQUET R, HOWARD K L, WILLOCK D J.Theory and simulation in heterogeneous gold catalysis.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008, 37(9): 2046-2076. |
| [5] | COLEMAN H M, CHIANG K, AMAL R.Effects of Ag and Pt on photocatalytic degradation of endocrine disrupting chemicals in water.Chem. Engin. J., 2005, 113(1): 65-72. |
| [6] | KOZLOVA E A, VORONTSOV A V.Influence of mesoporous and platinum-modified titanium dioxide preparation methods on photocatalytic activity in liquid and gas phase.Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2007, 77(1/2): 35-45. |
| [7] | LI C M, ZHANG S T, ZHANG B S, et al. Photohole-oxidation- assisted anchoring of ultra-small Ru clusters onto TiO2 with excellent catalytic activity and stability. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(7): 2461-2467. |
| [8] | METE E, UNER D, GÜLSEREN O, et al. Pt-incorporated anatase TiO2(001) surface for solar cell applications: first-principles density functional theory calculations. Phys. Rev. B, 2009, 79(12): 125418-125432. |
| [9] | METE E, GÜLSEREN O, ELLIALTIOĞLU Ş. Modification of TiO2(001) surface electronic structure by Au impurity investigated with density functional theory.Phys. Rev. B, 2009, 80(3): 035422-035430. |
| [10] | MÁRQUEZ A M, PLATA J J, ORTEGA Y, et al. Structural defects in W-doped TiO2(101) anatase surface: density functional study. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(34): 16970-16976. |
| [11] | ZHANG M, JIN Z, ZHANG Z, et al. Study of strong interaction between Pt and TiO2 under oxidizing atmosphere. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2005, 250(1-4): 29-34. |
| [12] | PERKAS N, POL V G, POL S V, et al. Golden-induced crystallization of SiO2 and TiO2 powders. Cryst. Growth Des., 2006, 6: 293-296. |
| [13] | MA X G, TANG C Q, HUANG J Q, et al. First-principle calculations on the geometry and relaxation structure of anatase TiO2(101) surface. Acta Phys. Sin., 2006, 55(8): 4208-4214. |
| [14] | MA X G, JIANG J J, LIANG P.Theory study of native point defects on anatase TiO2(101) surface.Acta Phys. Sin., 2008, 57(12): 3120-3125. |
| [15] | VANDERBILT D.Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism.Phys. Rev. B, 1990, 41(11): 7892-7895. |
| [16] | PERDEW J P.Density-functional approximation for the correlation energy of the inhomogeneous electron gas.Phys. Rev. B, 1986, 33: 8822-8824. |
| [17] | SEGALL M D, LINDAN P L D, PROBERT M J, et al. First-principles simulation: ideas, illustrations and the CASTEP code. J. Phys.: Condens Matter, 2002, 14(11): 2717-2744. |
| [18] | VITTADINI A, SELLONI A.Small gold clusters on stoichiometric and defected TiO2 anatase (101) and their interaction with CO: A density functional study.J. Chem. Phys., 2002. 117(1): 353-361. |
| [19] | WANG Y, HWANG G S.Adsorption of Au atoms on stoichiometric and reduced TiO2(110) rutile surfaces: a first principles study.Surf. Sci., 2003, 542(1/2): 72-80. |
| [20] | IDDIR H, SKAVYSH V, ÖĞÜT S, et al. Preferential growth of Pt on rutile TiO2. Phys. Rev. B. 2006, 73(4): 041403-041406. |
| [21] | IDDIR H, ÖĞÜT S, BROWNING N D, et al. Adsorption and diffusion of Pt and Au on the stoichiometric and reduced TiO2 rutile (110) surfaces. Phys. Rev. B, 2005, 72(8): 081407-081410. |
| [22] | OKAZAKI K, MORIKAWA Y, TANAKA S, et al. Electronic structures of Au on TiO2(110) by first-principles calculations. Phys. Rev. B, 2004, 69(23): 235404-235411. |
| [23] | MA X G, TANG C Q, YANG X H.Effect of relaxation on the energetics and structure of anatase TiO2(101) surface.Surf. Rev. Lett., 2006, 13(6): 825-831. |
| [1] | SUN Jing, LI Xiang, MAO Xiaojian, ZHANG Jian, WANG Shiwei. Effect of Lauric Acid Modifier on the Hydrolysis Resistance of Aluminum Nitride Powders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 826-832. |
| [2] | FAN Xiaoxuan, ZHENG Yonggui, XU Lirong, YAO Zimin, CAO Shuo, WANG Kexin, WANG Jiwei. Organic Pollutant Fenton Degradation Driven by Self-activated Afterglow from Oxygen-vacancy-rich LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ Long Afterglow Phosphor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 481-488. |
| [3] | JIA Xianghua, ZHANG Huixia, LIU Yanfeng, ZUO Guihong. Cu2O/Cu Hollow Spherical Heterojunction Photocatalysts Prepared by Wet Chemical Approach [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 397-404. |
| [4] | MA Binbin, ZHONG Wanling, HAN Jian, CHEN Liangyu, SUN Jingjing, LEI Caixia. ZIF-8/TiO2 Composite Mesocrystals: Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 937-944. |
| [5] | CAO Qingqing, CHEN Xiangyu, WU Jianhao, WANG Xiaozhuo, WANG Yixuan, WANG Yuhan, LI Chunyan, RU Fei, LI Lan, CHEN Zhi. Visible-light Photodegradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride on Self-sensitive Carbon-nitride Microspheres Enhanced by SiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 787-792. |
| [6] | CAI Heqing, HAN Lu, YANG Songsong, XUE Xinyu, ZHANG Kou, SUN Zhicheng, LIU Ruping, HU Kun, WEI Yan. Fe3O4-DMSA-PEI Magnetic Nanoparticles with Small Particle Size: Preparation and Gene Loading [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 517-524. |
| [7] | WANG Zhaoyang, QIN Peng, JIANG Yin, FENG Xiaobo, YANG Peizhi, HUANG Fuqiang. Sandwich Structured Ru@TiO2 Composite for Efficient Photocatalytic Tetracycline Degradation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 383-389. |
| [8] | WU Lin, HU Minglei, WANG Liping, HUANG Shaomeng, ZHOU Xiangyuan. Preparation of TiHAP@g-C3N4 Heterojunction and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [9] | LING Jie, ZHOU Anning, WANG Wenzhen, JIA Xinyu, MA Mengdan. Effect of Cu/Mg Ratio on CO2 Adsorption Performance of Cu/Mg-MOF-74 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1379-1386. |
| [10] | SUN Chen, ZHAO Kunfeng, YI Zhiguo. Research Progress in Catalytic Total Oxidation of Methane [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1245-1256. |
| [11] | MA Xinquan, LI Xibao, CHEN Zhi, FENG Zhijun, HUANG Juntong. BiOBr/ZnMoO4 Step-scheme Heterojunction: Construction and Photocatalytic Degradation Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [12] | CHEN Hanxiang, ZHOU Min, MO Zhao, YI Jianjian, LI Huaming, XU Hui. 0D/2D CoN/g-C3N4 Composites: Structure and Photocatalytic Performance for Hydrogen Production [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [13] | XUE Hongyun, WANG Congyu, MAHMOOD Asad, YU Jiajun, WANG Yan, XIE Xiaofeng, SUN Jing. Two-dimensional g-C3N4 Compositing with Ag-TiO2 as Deactivation Resistant Photocatalyst for Degradation of Gaseous Acetaldehyde [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [14] | WEN Zhiqin, HUANG Binrong, LU Taoyi, ZOU Zhengguang. Pressure on the Structure and Thermal Properties of PbTiO3: First-principle Study [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 787-794. |
| [15] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||