
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 408-412.DOI: 10.15541/jim.20140523
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHEN Yan-Zhong1, 2, LI Jing2, WANG Dan-Jun2, FU Feng2, XUE Gang-Lin1
Received:2014-10-14
Revised:2014-12-18
Published:2015-04-29
Online:2015-03-26
About author:ZHEN Yan-Zhong. E-mail: zyz943@163.com
CLC Number:
ZHEN Yan-Zhong, LI Jing, WANG Dan-Jun, FU Feng, XUE Gang-Lin. Synthesis of α-MoO3 Nanobelt and Its Photocatalytic Oxidative Desulfurization(Photo-ODS) Activity of Simulation Fuel[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(4): 408-412.
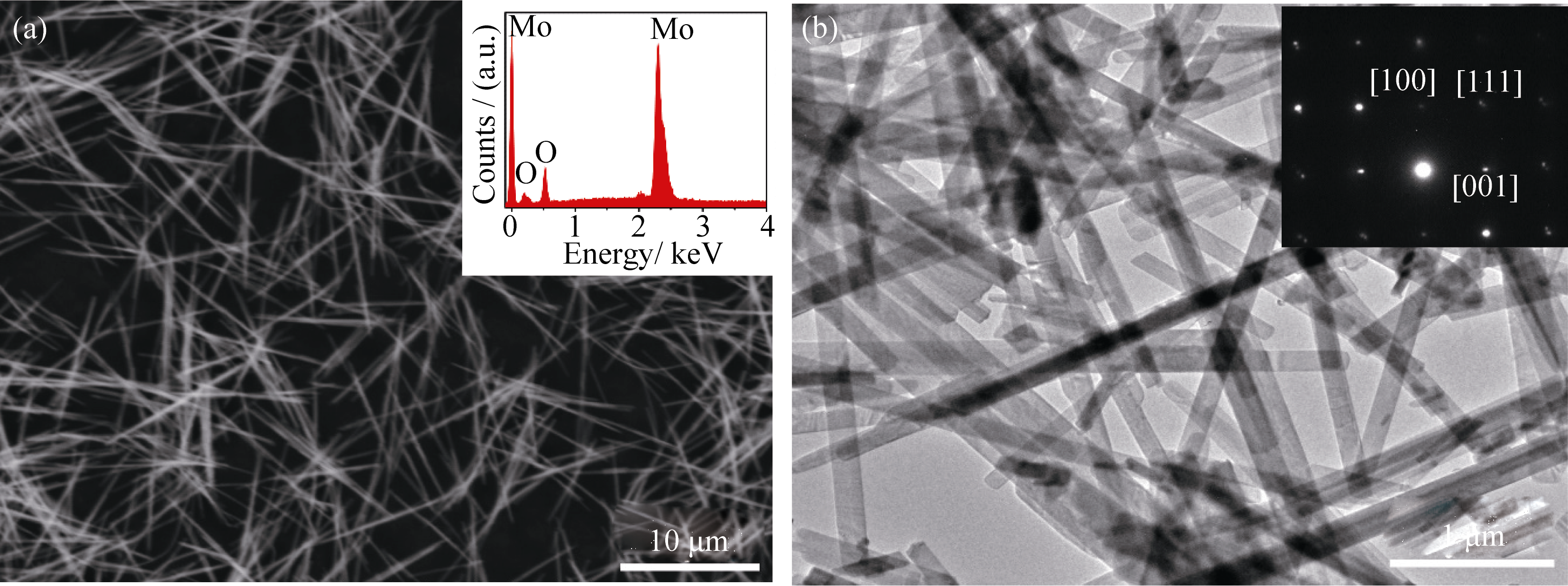
Fig. 2 SEM image (a) (with an inset showing the corresponding EDS spectrum) and TEM image (b) (with an inset showing the corresponding SAED pattern) of α-MoO3 nanobelts
| [1] | GRANGER P, PARVULESCU V I.Catalytic NOx abatement systems for mobile sources: from three-way to lean burn after-treatment technologies.Chemical Reviews, 2011, 111(5): 3155-3207. |
| [2] | LIU P, RODRIGUEZ J A, ASAKURA T, et al.Desulfurization reactions on Ni2P(001) and α-Mo2C(001) surfaces: complex role of P and C sites.Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 2005, 109: 4575-4583. |
| [3] | ZHANG WEI, XIAO JING, WANG XUN, et al.Oxidative desulfurization using in-situ-generated peroxides in diesel by light irradiation.Energy and Fuels, 2014, 28(8): 5339-5344. |
| [4] | SHIRAISHI Y, TAKI Y, HIRAI T, et al. Visible light-induced desulfurization technique for light oil.Chemical Communications, 1998(23): 2601-2602. |
| [5] | SHIRAISHI Y, HIRAI T, KOMASAWA I.TiO2-mediated photocatalytic desulfurization process for light oils using an organic two-phase system.Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 2002, 35(5): 489-492. |
| [6] | NA PING, ZHAO BAO-LIN, GU LIN-YUAN, et al.Deep desulfurization of model gasoline over photoirradiated titanium-pillared montmorillonite.Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2009, 70(12): 1465-1470. |
| [7] | SAMOKHVALOV A.Desulfurization of real and model liquid fuels using light: photocatalysis and photochemistry.Catalysis Reviews, 2012, 54(3): 281-343. |
| [8] | LI FA-TANG, LIU YING, SUN ZHI-MIN, et al.Photocatalytic oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene under simulated sunlight irradiation with mixed-phase Fe2O3 prepared by solution combustion.Catalysis Science and Technology, 2012, 2(7): 1455. |
| [9] | WANG CHAO, ZHU WEN-SHUAI, XU YE-CHAI, et al.Preparation of TiO2/g-C3N4 composites and their application in photocatalytic oxidative desulfurization.Ceramics International, 2014, 40(8): 11627-11635. |
| [10] | ZHANG WEI, ZHANG HONG, XIAO JING, et al, Carbon nanotube catalysts for oxidative desulfurization of a model diesel fuel using molecular oxygen.Green Chemistry, 2014, 16: 211-220. |
| [11] | CHEN DE-LIANG, LIU MIN-NA, YIN LI, et al.Single-crystalline MoO3 nanoplates: topochemical synthesis and enhanced ethanol-sensing performance.Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(25): 9332-9342. |
| [12] | GAO BIN, FAN HUI-QING, ZHANG XIAO-JUN.Hydrothermal synthesis of single crystal MoO3 nanobelts and their electrochemical properties as cathode electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries.Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2012, 73(3): 423-429. |
| [13] | WANG ZHI-YU, MADHAVI SRINIVASAN, LOU XIONG-WEN.Ultralong α-MoO3 nanobelts: synthesis and effect of binder choice on their lithium storage properties.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(23): 12508-12513. |
| [14] | SHAKIR I, CHOI J H, SHAHID M, et al.MoO3-MWCNT nanocomposite photocatalyst with control of light-harvesting under visible light and natural sunlight irradiation.Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(38): 20549-20553. |
| [15] | JIANG JIAN-BO, LIU JIN-LONG, PENG SAN-JUN, et al.Facile synthesis of α-MoO3 nanobelts and their pseudocapacitive behavior in an aqueous Li2SO4 solution.Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(7): 2588-2594. |
| [16] | SHAKIR I, SHAHID M, KANG D J.MoO3 and Cu0. 33MoO3 nanorods for unprecedented UV/visible light photocatalysis.Chemical Communications, 2010, 46(24): 4324-4326. |
| [17] | CHENG LIANG, SHAO MING-WANG, WANG XIU-HUA, et al.Single-crystalline molybdenum trioxide nanoribbons: photocatalytic, photoconductive, and electrochemical properties.Chemistry-A European Journal, 2009, 15(10): 2310-2316. |
| [18] | CHEN YU-PING, LU CHUN-LIANG, XU LIN, et al.Single- crystalline orthorhombic molybdenum oxide nanobelts: synthesis and photocatalytic properties.Crystal Engineering Communications, 2010, 12(11): 3740-3747. |
| [19] | ZHAO YE, LIU JING-GUO, ZHOU YA, et al.Preparation of MoO3 nanostructures and their optical properties.Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2003, 15(35): L547-L552. |
| [20] | THONGTEM T, PHURUANGRAT A, THONGTEM S.Free surfactant synthesis of microcrystalline CdS by solvothermal reaction.Materials Letters, 2007, 61(14/15): 3235-3238. |
| [21] | SINAIM H, HAM D J, LEE J S, et al.Free-polymer controlling morphology of α-MoO3 nanobelts by a facile hydrothermal synthesis, their electrochemistry for hydrogen evolution reactions and optical properties.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 516: 172-178. |
| [22] | ZHAO DI-SHUN, LIU CUI-WEI, MA SI-GUO.Oxdain deulurztion from fluld catalytic cracking gasoline via photocatalysis.Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(4): 692-696. |
| [23] | TONG HUA, OUYANG SHUXIN, BI YING-PU, et al.Nano- photocatalytic materials: possibilities and challenges.Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(2): 229-251. |
| [24] | SHEN GUO-ZHEN, CHEN DI.One-dimensional nanostructures for photodetectors.Recent Patents on Nanotechnology, 2010, 4(1): 20-31. |
| [25] | CHATTERJEE S, BHATTACHARYYA K, AYYUB P, et al.Photocatalytic properties of one-dimensional nanostructured titanates.The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(20): 9424-9430. |
| [26] | LIN FENG, LI CAN, WANG DON GE, et al.Photocatalytic oxidation of thiophene on BiVO4 with dual co-catalysts Pt and RuO2 under visible light irradiation using molecular oxygen as oxidant.Energy and Environmental Science, 2012, 5(4): 6400-6406. |
| [1] | FENG Guanzheng, YANG Jian, ZHOU Du, CHEN Qiming, XU Wentao, ZHOU Youfu. Mechanism for Hydrothermal-carbothermal Synthesis of AlN Nanopowders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 104-110. |
| [2] | WANG Tingting, SHI Shumei, LIU Chenyuan, ZHU Wancheng, ZHANG Heng. Synthesis of Hierarchical Porous Nickel Phyllosilicate Microspheres as Efficient Adsorbents for Removal of Basic Fuchsin [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1330-1336. |
| [3] | SONG Keke, HUANG Hao, LU Mengjie, YANG Anchun, WENG Jie, DUAN Ke. Hydrothermal Preparation and Characterization of Zn, Si, Mg, Fe Doped Hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1091-1096. |
| [4] | WANG Shu-Jiang, YANG Yong-Heng, WEN Chun-Yang, ZHANG Guo-Kui, YUAN Chun-Hui. Preparation and Property of Nano-Ag/illite Composite Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(5): 570-576. |
| [5] | JIA Si-Qi, JIANG Zheng, CHI Li-Na, YE Ying, HU Shuang-Shuang. Synthesis and Photoelectrocatalytic Performance of Sb2S3 Nanorods from Natural Stibnite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(11): 1213-1218. |
| [6] | YANG Kun-Kun, YANG Shao-Hua, ZHAO Ping, ZHAO Yan-Long. Hydrothermal Synthesis of FeS2/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite with Enhanced Discharge Performance for Thermal Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 691-698. |
| [7] | GUO Yu, LI Dong-Xin, WU Hong-Mei, JIN Yu-Jia, ZHOU Li-Dai, CHEN Qiang-Qiang. Preparation, Characterization and Catalytic Performance of Supported Titanium Silicalite-1 Zeolite Membrane Catalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(6): 631-636. |
| [8] | ABUBAKER Abutartour, LOTFIA El-Majdoub, SHI Ya-Sai, LI Ni-Li, XU Qing-Hong. A New Porous Zirconium Phosphonate Hybride Material and Its Adsorption Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(3): 305-312. |
| [9] | LI Li-Cheng, HE Tian-Tian, ZHAO Xue-Juan, QIAN Qi, WANG Lei, LI Xiao-Bao. Self Supported Synthesis of Porous Molybdenum-titanium Oxide and the Resulting Structural Transformation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(11): 1198-1204. |
| [10] | YAN Hui, Qi Lu, ZHANG Ding, WANG Zheng-De, LIU Yun-Ying, WANG Xiao-Xia, ZHU Tie-Yong. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Spherical Li4Ti5O12 as Anode Material for Lithium-ion Secondary Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(11): 1242-1248. |
| [11] | XIE Hui-Dong, LI Fei, CHEN Chao, XI Hai-Hong, SHI Ling. Microwave Dielectric Properties of LaPO4 Ceramics Synthesized by a Hydrothermal Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(8): 882-886. |
| [12] | GAO Er-Ping, WANG Wen-Zhong. Synthesis and Visible-light Photocatalytic Activities of Bi2Sn2O7 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(1): 87-92. |
| [13] | SHI Guo-Dong, SONG Jun, YANG Liu-Liu, ZHANG Li-Xiong. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Flower-like Hierarchical TiO2 Microspheres from Titanium Sulfate and Hexafluorosilicic Acid [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(8): 891-896. |
| [14] | LI Yue-Jun, CAO Tie-Ping, MEI Ze-Min. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of BaTiO3/TiO2 Heterostructured Nanofibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(7): 741-746. |
| [15] | XIAO Dong-Qin, WANG Dong-Wei, REN Jun-Chen, DUAN Ke, YAO Ning, LU Xiong, ZHENG Xiao-Tong, WENG Jie. Synthesis and Characterization of Copper-substituted Hydroxyapatite Micrspheres [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(7): 769-775. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||