无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 274-282.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230391 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20230391
所属专题: 【结构材料】核用陶瓷(202506)
收稿日期:2023-08-29
修回日期:2023-11-08
出版日期:2024-03-20
网络出版日期:2023-11-10
通讯作者:
田志林, 副教授. E-mail: tianzhlin@mail.sysu.edu.cn;作者简介:邱子豪(2000-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: qiuzh28@mail2.sysu.edu.cn
基金资助:
QIU Zihao( ), TIAN Zhilin(
), TIAN Zhilin( ), ZHENG Liya, LI Bin(
), ZHENG Liya, LI Bin( )
)
Received:2023-08-29
Revised:2023-11-08
Published:2024-03-20
Online:2023-11-10
Contact:
TIAN Zhilin, associate professor. E-mail: tianzhlin@mail.sysu.edu.cn;About author:QIU Zihao(2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: qiuzh28@mail2.sysu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
熔盐电解是核能领域乏燃料干法后处理的关键技术。高温下熔盐会对盛装乏燃料的坩埚造成严重的腐蚀, 因此, 研发具有耐高温和抗腐蚀的坩埚材料是发展干法后处理技术的关键。Si3N4凭借其优异的高温热学和力学性能, 成为干法后处理工艺中坩埚的理想候选材料。然而在实际服役条件下, Si3N4面临高温熔盐和水氧的侵蚀, 其失效行为尚不明确。因此, 本工作选取Si3N4为研究对象, 在氩气和水氧(5%H2O-10%O2-85%Ar)环境中, 开展了LiCl-KCl和NaCl-2CsCl熔盐对Si3N4的腐蚀行为研究。研究发现, 在氩气环境中, Si3N4在LiCl-KCl熔盐中出现轻微的晶界腐蚀, 而NaCl-2CsCl熔盐对其腐蚀并不明显。在5%H2O-10%O2-85%Ar水氧耦合环境中, LiCl-KCl熔盐优先腐蚀Si3N4中的晶界相, 而NaCl-2CsCl熔盐的腐蚀比氩气环境更为严重。高温水氧环境显著加剧了熔盐对Si3N4陶瓷的腐蚀程度, 同时晶界相成为Si3N4最易受到腐蚀的部位。此外, LiCl-KCl和NaCl-2CsCl熔盐在Si3N4表面的润湿性与抗腐蚀性之间并无直接关联。上述研究结果揭示了Si3N4在高温熔盐-水氧环境下的腐蚀机制, 为乏燃料干法后处理工艺中关键材料的选择提供了参考。
中图分类号:
邱子豪, 田志林, 郑丽雅, 李斌. Si3N4陶瓷在高温熔盐-水氧环境下的腐蚀行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 274-282.
QIU Zihao, TIAN Zhilin, ZHENG Liya, LI Bin. Corrosion Behavior of Si3N4 Ceramic in High-temperature Molten Salt-water Vapor Environment[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 274-282.
| Element/(%, in atom) | N | O | Al | Si | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32.77 | 13.73 | 3.55 | 44.72 | 5.23 |
| 2 | 27.10 | 12.44 | 4.90 | 47.63 | 7.93 |
表1 Si3N4陶瓷晶界相的元素组成
Table 1 Composition of grain boundary phase in Si3N4
| Element/(%, in atom) | N | O | Al | Si | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32.77 | 13.73 | 3.55 | 44.72 | 5.23 |
| 2 | 27.10 | 12.44 | 4.90 | 47.63 | 7.93 |
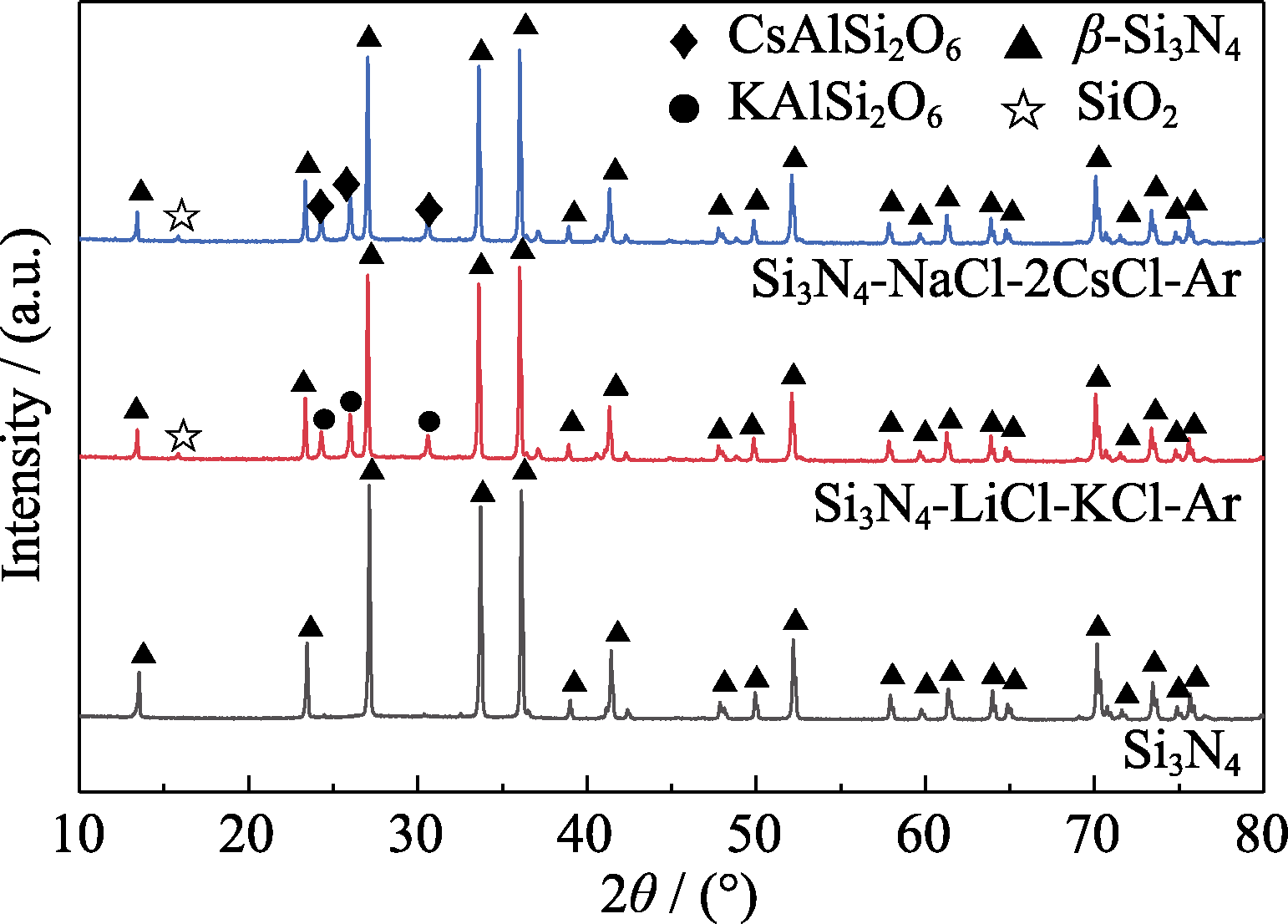
图9 Si3N4陶瓷在氩气气氛LiCl-KCl和NaCl-2CsCl熔盐中腐蚀100 h后的XRD图谱
Fig. 9 XRD patterns of Si3N4 after corrosion in LiCl-KCl and NaCl-2CsCl molten salt under Ar atmosphere for 100 h
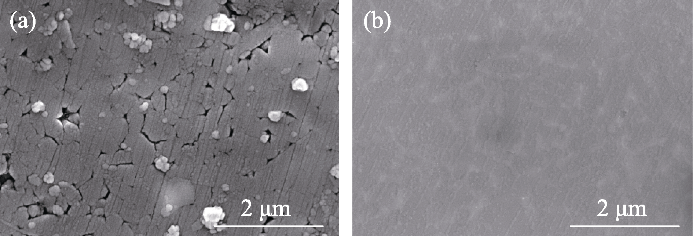
图10 Si3N4陶瓷在氩气气氛中经过(a) LiCl-KCl和(b) NaCl- 2CsCl熔盐腐蚀100 h后的表面形貌
Fig. 10 Surface microstructures of Si3N4 after corrosion in (a) LiCl-KCl and (b) NaCl-2CsCl molten salt under Ar atmosphere for 100 h
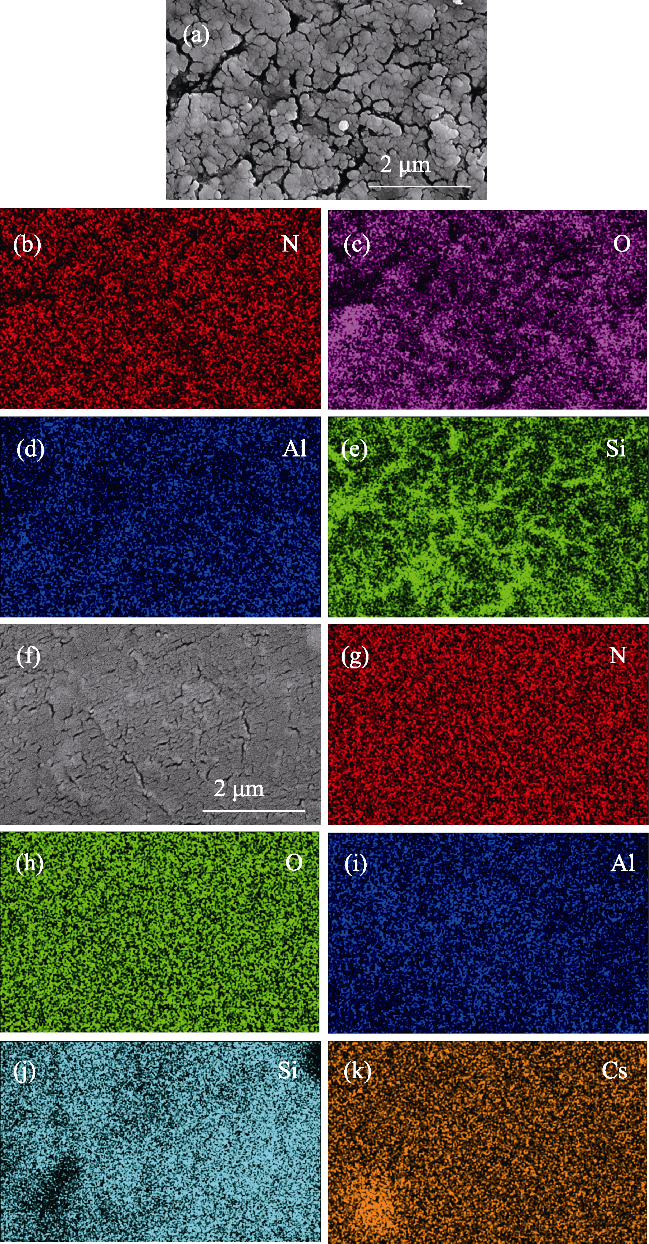
图11 Si3N4陶瓷在氩气气氛中经过(a~e) LiCl-KCl和(f~k) NaCl- 2CsCl熔盐腐蚀100 h后的能谱面扫描分析
Fig. 11 EDS mappings of Si3N4 after corrosion in (a-e) LiCl-KCl and (f-k) NaCl-2CsCl molten salt under Ar atmosphere for 100 h

图12 Si3N4陶瓷在5%H2O-10%O2-85%Ar气氛LiCl-KCl和NaCl-2CsCl熔盐中腐蚀100 h后的XRD图谱
Fig. 12 XRD patterns of Si3N4 after corrosion in LiCl-KCl and NaCl-2CsCl molten salt under 5%H2O-10%O2-85%Ar atmosphere for 100 h

图13 Si3N4陶瓷在5%H2O-10%O2-85%Ar气氛中经过(a) LiCl- KCl和(b) NaCl-2CsCl熔盐腐蚀100 h后的表面形貌
Fig. 13 Surface microstructures of Si3N4 after corrosion in (a) LiCl-KCl and (b) NaCl-2CsCl molten salt under 5%H2O-10%O2-85%Ar for 100 h

图15 Si3N4陶瓷在5%H2O-10%O2-85%Ar气氛中经过(a~e) LiCl- KCl和(f~k) NaCl-2CsCl熔盐腐蚀100 h后的能谱面扫描分析
Fig. 15 EDS mappings of Si3N4 after corrosion in (a-e) LiCl- KCl and (f-k) NaCl-2CsCl molten salt under 5%H2O-10%O2-85%Ar for 100 h

图S3 Si3N4陶瓷(a) X1-Si3N4, (b) X2-Si3N4, (c) Y1-Si3N4, (d) Y2-Si3N4在氩气和水氧气氛LiCl-KCl和NaCl-2CsCl中腐蚀100 h后表面的三维形貌
Fig. S3 3D morphologies of the surface of (a) X1-Si3N4, (b) X2-Si3N4, (c) Y1-Si3N4, (d) Y2-Si3N4 after corrosion for 100 h
| [1] |
BORGES SILVERIO L, LAMAS W D Q. An analysis of development and research on spent nuclear fuel reprocessing. Energy Policy, 2011, 39(1): 281.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ROTHWELL G. Spent nuclear fuel storage: what are the relationships between size and cost of the alternatives? Energy Policy, 2021, 150: 112126.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Chen H Y, TAYLOR R, JOBSON M, et al. Development and validation of a flowsheet simulation model for neptunium extraction in an advanced PUREX process. Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 2016, 34(4): 297.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LEE C H, KIM T J, PARK S, et al. Effect of cathode material on the electrorefining of U in LiCl-KCl molten salts. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2017, 488: 210.
DOI URL |
| [5] | SIMPSON M. Developments of spent nuclear fuel pyroprocessing technology at Idaho National Laboratory. 2012. INL/EXT-12-25124. |
| [6] |
HOSHIKAWA T, KAWAMURA F, SAWA T, et al. A new concept of nuclear fuel reprocessing by applying ion-exchange technology. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 1998, 32(3): 365.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
JANG J, LEE M, KIM G Y, et al. Cesium and strontium recovery from LiCl-KCl eutectic salt using electrolysis with liquid cathode. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2022, 54(10): 3957.
DOI URL |
| [8] | ZHANG H, JIANG K, LI W, et al. Electrochemical extraction of fission element samarium from molten NaCl-2CsCl eutectic salt using the liquid gallium cathode. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2023, 11(23): 8685. |
| [9] |
YOO T S, FREDRICKSON G L, TESKE G M. Uranium exchange kinetics in a molten LiCl-KCl/Cd system at 500 °C. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2018, 508: 521.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
SONG Y, JIAO S, HU L, et al. The cathodic behavior of Ti(III) ion in a NaCl-2CsCl melt. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2016, 47(1): 804.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
TAKEUCHI M, ARAI Y, KASE T, et al. Corrosion study of a highly durable electrolyzer based on cold crucible technique for pyrochemical reprocessing of spent nuclear oxide fuel. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2013, 432(1): 35.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SAKAMURA Y, INOUE T, IWAI T, et al. Chlorination of UO2, PuO2and rare earth oxides using ZrCl4 in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2005, 340(1): 39.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
TAKEUCHI M, KATO T, HANADA K, et al. Corrosion resistance of ceramic materials in pyrochemical reprocessing condition by using molten salt for spent nuclear oxide fuel. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2005, 66(2): 521.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZHANG B, XIE W Q, LIN H Z. Preparation of SiC coated graphite composite powders by nitriding combustion synthesis. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2023, 12(10): 1930.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
RILEY F L. Silicon nitride and related materials. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2000, 83(2): 245.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
AN L Q, SHI R W, MAO X J, et al. Fabrication of AlON transparent ceramics with Si3N4 sintering additive. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2023, 12(7): 1361.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
XU S S, ZHOU X N, ZHI Q, et al. Anisotropic, biomorphic cellular Si3N4 ceramics with directional well-aligned nanowhisker arrays based on wood-mimetic architectures. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11: 656.
DOI |
| [18] |
HERRMANN M. Corrosion of silicon nitride materials in aqueous solutions. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2013, 96(10): 3009.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LIU M Q, NEMAT-NASSER S. The microstructure and boundary phases of in-situ reinforced silicon nitride. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1998, 254(1): 242.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
CINIBULK M K, THOMAS G, JOHNSON S M. Grain-boundary- phase crystallization and strength of silicon nitride sintered with a YSIAlON glass. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1990, 73(6): 1606.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
PIERCE L A, MIESKOWSKI D M, SANDERS W A. Effect of grain-boundary crystallization on the high-temperature strength of silicon nitride. Journal of Materials Science, 1986, 21(4): 1345.
DOI URL |
| [22] | GABRIEL S-S, JUAN S, SOKRATES T P, et al. Localization of yttrium segregation within YSZ grain boundary dislocation cores. Physica Status Solidi A, 2018, 215: 1800349. |
| [1] | 梁锐辉, 钟鑫, 洪督, 黄利平, 牛亚然, 郑学斌. Yb2O3改性硅黏结层的环境障涂层体系耐高温水氧腐蚀行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 425-432. |
| [2] | 刘建, 王凌坤, 许保亮, 赵倩, 王耀萱, 丁艺, 张胜泰, 段涛. 熔盐法低温合成掺钕ZrSiO4陶瓷的物相演变和化学稳定性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 910-916. |
| [3] | 胡佳军, 王凯, 侯鑫广, 杨婷, 夏鸿雁. 熔盐法合成高导热磷化硼及其热管理性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 933-940. |
| [4] | 张叶, 姚冬旭, 左开慧, 夏咏锋, 尹金伟, 曾宇平. 原位引入BN-SiC燃烧合成Si3N4-BN-SiC复合材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 574-578. |
| [5] | 刘平平, 钟鑫, 张乐, 李红, 牛亚然, 张翔宇, 李其连, 郑学斌. 硅酸镱环境障涂层抗熔盐腐蚀行为与机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1267-1274. |
| [6] | 舒朝琴, 朱敏, 朱钰方. 熔盐法制备含钴氯磷灰石及其抗氧化性能和细胞相容性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1225-1235. |
| [7] | 吴爱军, 朱敏, 朱钰方. 含铜硅酸钙纳米棒复合水凝胶用于肿瘤治疗和皮肤伤口愈合性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(11): 1203-1216. |
| [8] | 张文进, 申倩倩, 薛晋波, 李琦, 刘旭光, 贾虎生. 具有高度有序氧空位的α-Fe2O3纳米带的制备及光电催化水氧化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1290-1296. |
| [9] | 万朋, 李勉, 黄庆. 熔盐辅助合成Dy3Si2C2包裹SiC粉体及其陶瓷的烧结行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(1): 49-54. |
| [10] | 刘雅兰, 柴之芳, 石伟群. 干法后处理含盐废物陶瓷固化技术研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(3): 271-276. |
| [11] | 周鑫, 马垒, 刘涛, 郭永斌, 王岛, 董培林. Si3N4/FePd/Si3N4薄膜的晶体结构和磁性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(8): 909-913. |
| [12] | 王洪达, 周海军, 董绍明, 王震, 胡建宝, 冯倩. SiCf/SiC复合材料耐高温氟熔盐腐蚀性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(11): 1133-1140. |
| [13] | 王贺云, 刘 茜, 周 遥, 周真真,刘光辉. 碳纤维复合Si3N4陶瓷材料的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(9): 1003-1008. |
| [14] | 胡海龙, 姚冬旭, 夏咏锋, 左开慧, 曾宇平. 反应烧结制备Si3N4/SiC复相陶瓷及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(6): 594-598. |
| [15] | 吴 星, 栗海峰, 周金玲, 霍敏锋, 程 呈, 沈绪根, 严春杰. 固相-熔盐法非平衡骤热骤冷工艺制备高纯BiFeO3及性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(11): 1151-1155. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||