无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 295-302.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250217 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250217
郭文静1( ), 王广舒1, 彭凯1, 张旭海1, 曾宇乔1(
), 王广舒1, 彭凯1, 张旭海1, 曾宇乔1( ), 蒋建清1,2
), 蒋建清1,2
收稿日期:2025-05-20
修回日期:2025-06-30
出版日期:2025-07-31
网络出版日期:2025-07-31
通讯作者:
曾宇乔, 教授. E-mail: zyuqiao@seu.edu.cn作者简介:郭文静(2001-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 18352295088@163.com
基金资助:
GUO Wenjing1( ), WANG Guangshu1, PENG Kai1, ZHANG Xuhai1, ZENG Yuqiao1(
), WANG Guangshu1, PENG Kai1, ZHANG Xuhai1, ZENG Yuqiao1( ), JIANG Jianqing1,2
), JIANG Jianqing1,2
Received:2025-05-20
Revised:2025-06-30
Published:2025-07-31
Online:2025-07-31
Contact:
ZENG Yuqiao, professor. E-mail: zyuqiao@seu.edu.cnAbout author:GUO Wenjing (2001-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 18352295088@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
镍锰层状双金属氢氧化物(NiMn-LDH)具有环境友好、理论比电容高和循环稳定性好等诸多优点, 是混合超级电容器(Hybrid supercapacitors, HSCs)的理想正极材料。但其电子电导能力不佳, 导致实际比电容和倍率性能较差。尤其是在mg·cm-2量级载量下, NiMn-LDH在50 A·g-1及以上大电流密度时的比电容远低于1500 F·g-1, 难以满足HSCs的实用要求。本研究提出了一种简单易行的两步电沉积工艺来制备新型高比电容、高倍率性能的NiMnx-LDH@Ni95Cu5电极。通过改变沉积液中金属离子配比来调节电沉积在Ni95Cu5枝晶泡沫表面NiMn-LDH的Mn/Ni原子比, 并研究其对NiMn-LDH成分、元素价态、晶体结构、形貌、能带结构和电化学性能的影响。优化后NiMn0.6-LDH@Ni95Cu5电极展现出最佳的结晶性、最小的带隙以及良好的电化学性能, 即便在载量高于2 mg·cm-2的条件下, 1 A·g-1的比电容也可达2365 F·g-1, 50 A·g-1的比电容达1803 F·g-1, 且在20 A·g-1下循环3000 次后电容保持率仍可达88.8%。本研究为设计下一代高性能HSCs电极提供了新思路。
中图分类号:
郭文静, 王广舒, 彭凯, 张旭海, 曾宇乔, 蒋建清. 高倍率性能NiMnx-LDH@Ni95Cu5电极的快速制备与性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(3): 295-302.
GUO Wenjing, WANG Guangshu, PENG Kai, ZHANG Xuhai, ZENG Yuqiao, JIANG Jianqing. High Rate Capability NiMnx-LDH@Ni95Cu5 Electrode: Fast Fabrication and Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(3): 295-302.
| Electrode | Concentration of Ni(NO3)2/ (mol·L-1) | Concentration of Mn(NO3)2/ (mol·L-1) | Mn2+/Ni2+ (in atom) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiMn0.3-LDH@Ni95Cu5 | 0.160 | 0.040 | 0.25 |
| NiMn0.6-LDH@Ni95Cu5 | 0.150 | 0.050 | 0.33 |
| NiMn0.8-LDH@Ni95Cu5 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 1.00 |
表1 锚定NiMnₓ-LDH的沉积液配方
Table 1 Plating solutions used for anchoring NiMnx-LDH
| Electrode | Concentration of Ni(NO3)2/ (mol·L-1) | Concentration of Mn(NO3)2/ (mol·L-1) | Mn2+/Ni2+ (in atom) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiMn0.3-LDH@Ni95Cu5 | 0.160 | 0.040 | 0.25 |
| NiMn0.6-LDH@Ni95Cu5 | 0.150 | 0.050 | 0.33 |
| NiMn0.8-LDH@Ni95Cu5 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 1.00 |
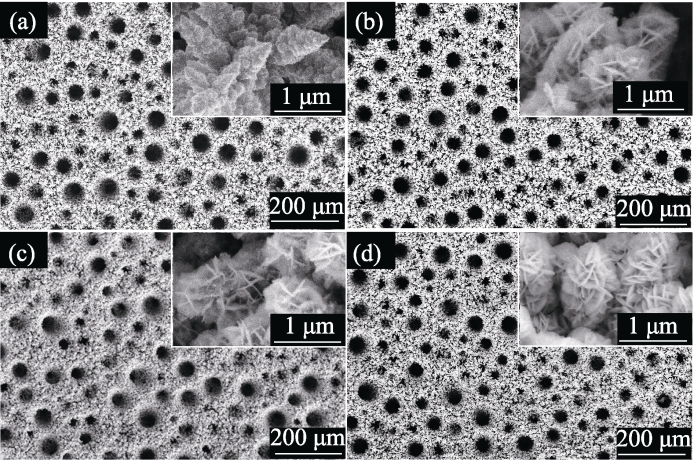
图2 (a) Ni95Cu5枝晶泡沫基底、(b) NiMn0.3-LDH@Ni95Cu5、(c) NiMn0.6-LDH@Ni95Cu5和(d) NiMn0.8-LDH@Ni95Cu5电极的表面SEM照片(插图为微米孔壁四周沉积物的高倍率SEM照片)
Fig. 2 Surface SEM images of (a) Ni95Cu5, (b) NiMn0.3-LDH@Ni95Cu5, (c) NiMn0.6-LDH@Ni95Cu5, and (d) NiMn0.8-LDH@Ni95Cu5 with insets showing high-resolution SEM images of the deposits around the micropore walls
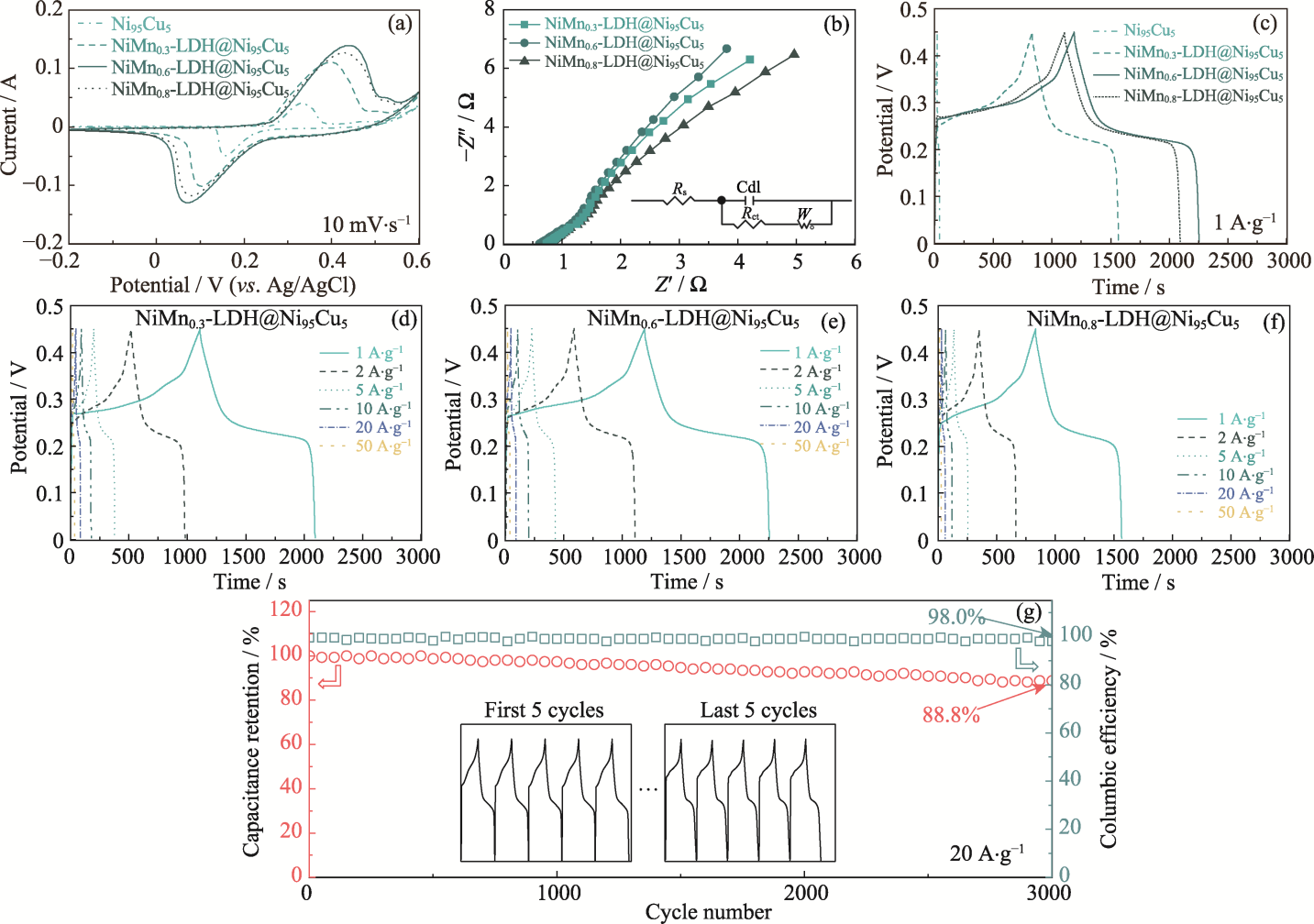
图4 不同电极的电化学性能
Fig. 4 Electrochemical performance of different electrodes (a) CV curves at a scan rate of 10 mV·s-1; (b) Nyquist plots with inset showing equivalent circuit; (c) GCD curves at 1 A·g-1; (d-f) Rate capabilities of (d) NiMn0.3-LDH@Ni95Cu5, (e) NiMn0.6-LDH@Ni95Cu5 and (f) NiMn0.8-LDH@Ni95Cu5; (g) Cycling GCD tests of NiMn0.6-LDH@Ni95Cu5 electrode at 20 A·g-1
| Electrode | Loading density/ (mg·cm-2) | Specific capacitance/ (F·g-1) | Rate capability |
|---|---|---|---|
| This work | 2.3 | 2365 (1 A·g-1) | 76.2% (1-50 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH@MXene[S1] | 1.5 | 1530 (2 A·g-1) | 58.8% (1-15 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH@rGO[S2] | 1.3 | 1500 (1 A·g-1) | 45.3% (1-10 A·g-1) |
| Ni-Mn-LDH@MXene[S3] | 2 | 1288.8 (1 A·g-1) | 62.6% (1-10 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH@PC[S4] | 3.2 | 1634 (1 A·g-1) | 60.5% (1-10 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH/NCF[S5] | 2 | 2128.3 (0.5 A·g-1) | 70.1% (0.5-10 A·g-1) |
| Carbon-NiMn-LDH/NF[S6] | 2 | 1916 (0.5 A·g-1) | 79.5% (0.5-10 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH@Ni foam[S7] | 1.2 | 1511 (2.5 A·g-1) | 80.1% (2.5-48 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH/rGO[S8] | 1.8 | 1250 (1 A·g-1) | 36% (1-5 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH@MXene[S9] | 1.2 | 1575 (0.5 A·g-1) | 68.9% (0.5-10 A·g-1) |
表S1 NiMn0.6-LDH@Ni95Cu5的电化学性能与文献的比较
Table S1 Comparison of electrochemical properties of NiMn0.6-LDH@Ni95Cu5 with other literature
| Electrode | Loading density/ (mg·cm-2) | Specific capacitance/ (F·g-1) | Rate capability |
|---|---|---|---|
| This work | 2.3 | 2365 (1 A·g-1) | 76.2% (1-50 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH@MXene[S1] | 1.5 | 1530 (2 A·g-1) | 58.8% (1-15 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH@rGO[S2] | 1.3 | 1500 (1 A·g-1) | 45.3% (1-10 A·g-1) |
| Ni-Mn-LDH@MXene[S3] | 2 | 1288.8 (1 A·g-1) | 62.6% (1-10 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH@PC[S4] | 3.2 | 1634 (1 A·g-1) | 60.5% (1-10 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH/NCF[S5] | 2 | 2128.3 (0.5 A·g-1) | 70.1% (0.5-10 A·g-1) |
| Carbon-NiMn-LDH/NF[S6] | 2 | 1916 (0.5 A·g-1) | 79.5% (0.5-10 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH@Ni foam[S7] | 1.2 | 1511 (2.5 A·g-1) | 80.1% (2.5-48 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH/rGO[S8] | 1.8 | 1250 (1 A·g-1) | 36% (1-5 A·g-1) |
| NiMn-LDH@MXene[S9] | 1.2 | 1575 (0.5 A·g-1) | 68.9% (0.5-10 A·g-1) |
| [1] | LIBICH J, MÁCA J, VONDRÁK J, et al. Supercapacitors: properties and applications. Journal of Energy Storage, 2018, 17: 224. |
| [2] | TIAN X D, LI X, YANG T, et al. Recent advances on synthesis and supercapacitor application of binary metal oxide. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(5): 459. |
| [3] | YANG E D, LI B L, ZHANG K, et al. ZnCo2O4-ZnO@C@CoS core-shell composite: preparation and application in supercapacitors. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 485. |
| [4] | LI X J, DU D F, ZHANG Y, et al. Layered double hydroxides toward high-performance supercapacitors. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(30): 15460. |
| [5] | KANG G Y, CHEN Y, LI J J. Comparison on structure and electrochemical performances of NiAl-LDH, CoAl-LDH and NiCoAl-LDH. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(11): 1230. |
| [6] | HALL D S, LOCKWOOD D J, BOCK C, et al. Nickel hydroxides and related materials: a review of their structures, synthesis and properties. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2015, 471(2174): 20140792. |
| [7] | CHEN H, WANG J M, PAN T, et al. The structure and electrochemical performance of spherical Al-substituted α-Ni(OH)2 for alkaline rechargeable batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 143(1/2): 243. |
| [8] | SINGH D. Characteristics and effects of γ-NiOOH on cell performance and a method to quantify it in nickel electrodes. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1998, 145(1): 116. |
| [9] | OESTEN R, WOHLFAHRT-MEHRENS M, STRÖBELE S, et al. Structural aspects of undoped and doped nickel hydroxides. Ionics, 1996, 2(3/4): 293. |
| [10] | PAN X, ZHAO L, LIU H, et al. Hierarchical structure Ni3S2/Ni(OH)2 nanoarrays towards high-performance supercapacitors. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2022, 309: 122974. |
| [11] | QU R, TANG S, QIN X, et al. Expanded graphite supported Ni(OH)2 composites for high performance supercapacitors. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 728: 222. |
| [12] | ZHANG Z, HUO H, WANG L, et al. Stacking fault disorder induced by Mn doping in Ni(OH)2 for supercapacitor electrodes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 412: 128617. |
| [13] | WANG Z, WANG H, WANG Y, et al. High-performance supercapacitor materials based on NiMn-LDH layered structures with MXene layers. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2024, 1008: 176785. |
| [14] | LIANG H, LIN J, JIA H, et al. Hierarchical NiCo-LDH/NiCoP@NiMn-LDH hybrid electrodes on carbon cloth for excellent supercapacitors. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(31): 15040. |
| [15] | DONG X, GUO L, DONG X, et al. Nickel manganese hydroxide on hierarchically porous phenolic resin as a high-performance electrode material for supercapacitors. Materials Research Bulletin, 2023, 168: 112449. |
| [16] | ZHANG Z, HUO H, YU Z, et al. Unraveling the reaction mechanism of low dose Mn dopant in Ni(OH)2 supercapacitor electrode. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 61: 497. |
| [17] | HSU S C, CHIANG H H, HUANG T Y, et al. Morphology evolution and electrochemical behavior of NixMn1-x(OH)2 mixed hydroxides as high-performance electrode for supercapacitor. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 403: 139692. |
| [18] | ZHAO J, CHEN J, XU S, et al. Hierarchical NiMn layered double hydroxide/carbon nanotubes architecture with superb energy density for flexible supercapacitors. Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24(20): 2938. |
| [19] | KIDIE A E, DHAKAL G, SAHOO S, et al. Interlayer spacing-controlled carnation flower-like microstructure of nickel-manganese layered double hydroxide for enhancing hybrid supercapacitor performance. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2024, 133: 550. |
| [20] | YANG Y, XU X, LI W, et al. Multi-color materials NiMn LDH loaded on activated carbon as electrode for electrochemical performance investigation. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 611: 155562. |
| [21] | HOU Z, YU J, ZHOU X, et al. Enhanced performance of hybrid supercapacitors by the synergistic effect of Co(OH)2 nanosheets and NiMn layered hydroxides. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 646: 753. |
| [22] | SHAO Y L, EL-KADY M F, SUN J Y, et al. Design and mechanisms of asymmetric supercapacitors. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(18): 9233. |
| [23] | GUO X L, ZHANG J M, XU W N, et al. Growth of NiMn LDH nanosheet arrays on KCu7S4 microwires for hybrid supercapacitors with enhanced electrochemical performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(39): 20579. |
| [24] | LU L, FAN J W, LEI W, et al. Multiple metal (Cu, Mn, Fe) centered species simultaneously combined nitrogen-doped graphene as an electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction in alkaline and neutral solutions. ChemCatChem, 2018, 10(11): 2471. |
| [25] | XUE Q, PEI Z X, HUANG Y, et al. Mn3O4 nanoparticles on layer-structured Ti3C2 MXene towards the oxygen reduction reaction and zinc-air batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(39): 20818. |
| [26] | ZHANG A T, ZHENG W, YUAN Z, et al. Hierarchical NiMn-layered double hydroxides@CuO core-shell heterostructure in-situ generated on Cu(OH)2 nanorod arrays for high performance supercapacitors. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 380: 122486. |
| [27] | GAO G, WANG K, WANG X T. Peony flower-like CuxS@NiMn LDH heterostructure as an efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(4): 1347. |
| [28] | WU Y T, LIU Q J, WANG J R, et al. Effectively morphology-controlled NiMn layered double hydroxide microflowers by conductive silver nanowires for supercapacitor electrodes. Electrochimica Acta, 2023, 460: 142623. |
| [29] | WANG X, ZHANG J, YANG S, et al. Interlayer space regulating of NiMn layered double hydroxides for supercapacitors by controlling hydrothermal reaction time. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 295: 1. |
| [30] | CHEN F, CHEN C, HU Q, et al. Synthesis of CuO@CoNi LDH on Cu foam for high-performance supercapacitors. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 401: 126145. |
| [31] | WANG R, LANG J, LIU Y, et al. Ultra-small, size-controlled Ni(OH)2 nanoparticles: elucidating the relationship between particle size and electrochemical performance for advanced energy storage devices. NPG Asia Materials, 2015, 7(6): e183. |
| [32] | ZHAO Y, LI B, WANG Q, et al. NiTi-Layered double hydroxides nanosheets as efficient photocatalysts for oxygen evolution from water using visible light. Chemical Science, 2014, 5(3): 951. |
| [1] | 冯星哲, 马董云, 王金敏. 多孔NiMn-LDH纳米片薄膜的溶剂热生长及其电致变色性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1391-1396. |
| [2] | 王洋, 范广新, 刘培, 尹金佩, 刘宝忠, 朱林剑, 罗成果. 钾离子掺杂提高锂离子电池正极锰酸锂性能的微观机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1023-1029. |
| [3] | 付宇坤, 曾敏, 饶先发, 钟盛文, 张慧娟, 姚文俐. 锂离子电池高镍LiNi0.8Mn0.2O2正极材料的微波合成及其Co、Al共改性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 718-724. |
| [4] | 王琦, 彭大春, 马倩, 何月德, 刘洪波. 炭包覆LiFePO4纳米片的制备及电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(12): 1349-1354. |
| [5] | 刘双宇, 徐 丽, 陈 新, 韩 钰, 刘海镇, 盛 鹏, 王 博, 赵广耀. 石墨烯负载团簇结构CoFe2O4及其电化学储锂性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(9): 904-908. |
| [6] | 侯 渊, 张邦文, 邢瑞光, 布林朝克. 一步合成还原氧化石墨烯/MnO2复合材料及其电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(8): 855-860. |
| [7] | 何月德, 简志敏, 刘洪波, 肖海河. 微扩层鳞片石墨负极材料的制备及电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(9): 931-936. |
| [8] | 刘建华, 张施露, 于 美, 安军伟, 李松梅. 石墨烯接枝聚吡咯复合物的原位合成及其电容特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(4): 403-408. |
| [9] | 刘 玲, 袁中直, 邱彩霞, 程思洁, 刘金成. 新型锂离子电池材料FeS2/VGCF的合成与电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(12): 1291-1295. |
| [10] | 高兆辉, 张 浩, 曹高萍, 韩敏芳, 杨裕生. 模板法制备介孔VN纳米电极材料及其电容性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(12): 1261-1265. |
| [11] | 郭德超, 曾燮榕, 邓 飞, 邹继兆, 盛洪超. 碳纳米管/微膨石墨复合负极材料的制备及电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(10): 1035-1041. |
| [12] | 甘卫平, 马贺然, 李 祥. 超级电容器用(RuO2/Co3O4)·nH2O复合薄膜电极的制备及其性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(8): 823-828. |
| [13] | 吕 岩, 王志永, 张 浩, 房 进, 曹高萍, 施祖进, 王碧燕. 电弧法制备石墨烯的孔结构和电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(7): 725-728. |
| [14] | 杜 嬛,王成扬,陈明鸣,焦 旸. 纳米Fe3O4- 活性炭混合超级电容器电化学性能的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(6): 1193-1198. |
| [15] | 时志强,赵朔,陈明鸣,王妹先,王成扬. 预炭化对KOH活化石油焦的结构及电容性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(4): 799-804. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||