无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (12): 1367-1376.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240273 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240273
所属专题: 【结构材料】陶瓷基复合材料(202506)
由博杰1( ), 李博1,2, 李旭勤3, 马雪寒1, 张毅1(
), 李博1,2, 李旭勤3, 马雪寒1, 张毅1( ), 成来飞1
), 成来飞1
收稿日期:2024-06-04
修回日期:2024-08-08
出版日期:2024-08-19
网络出版日期:2024-08-19
通讯作者:
张 毅, 副研究员. E-mail: zhangyit@nwpu.edu.cn作者简介:由博杰(2001-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: youbojie@mail.nwpu.edu.cn
基金资助:
YOU Bojie1( ), LI Bo1,2, LI Xuqin3, MA Xuehan1, ZHANG Yi1(
), LI Bo1,2, LI Xuqin3, MA Xuehan1, ZHANG Yi1( ), CHENG Laifei1
), CHENG Laifei1
Received:2024-06-04
Revised:2024-08-08
Published:2024-08-19
Online:2024-08-19
Contact:
ZHANG Yi, associate professor. E-mail: zhangyit@nwpu.edu.cnAbout author:YOU Bojie (2001-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: youbojie@mail.nwpu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
SiCf/SiC复合材料热冲击损伤是航空发动机热端部件应用中需要解决的关键问题。本研究利用全自动精准控温的热冲击设备, 在1200 ℃测试了2D SiCf/SiC的热冲击性能, 拟探究热冲击损伤与面内剪切性能退化之间的相关性。结果表明, 随着热冲击次数增加, 2D SiCf/SiC涂层表面出现硼硅酸盐玻璃(BSG)气泡, SiC基体氧化, BN界面脱黏加剧, 但并未影响基体开裂、纤维桥联等损伤机制。因此, 2D SiCf/SiC的面内剪切应力-应变曲线依然呈双线性。热冲击产生的热膨胀失配及SiC基体氧化导致面剪模量由78.5 GPa降低至63.6 GPa, 面剪比例极限应力由128.9 MPa降低至99.3 MPa, 面剪强度由205.8 MPa降低至187.3 MPa。根据面内剪切混合定律, BN界面脱黏加剧是剪切模量退化的关键因素。基体开裂应力公式表明, 氧化后SiC基体体积分数下降, 进一步降低了面剪比例极限应力。基于修正刚体块滑移模型, 利用纤维台阶间距能够有效预测面剪强度的下降规律, 且理论计算结果与实际值误差小于20%。
中图分类号:
由博杰, 李博, 李旭勤, 马雪寒, 张毅, 成来飞. 2D SiCf/SiC中温热冲击损伤与面内剪切性能退化规律[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1367-1376.
YOU Bojie, LI Bo, LI Xuqin, MA Xuehan, ZHANG Yi, CHENG Laifei. Thermal Shock Damage and In-plane Shear Performance Degradation of 2D SiCf/SiC at Medium Temperature[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1367-1376.

图1 热冲击循环试验及控温曲线
Fig. 1 Thermal shock test and temperature control curves (a) Thermal shock test furnace; (b) Principle of test; (c) Cycling curve; (d) Single cycle
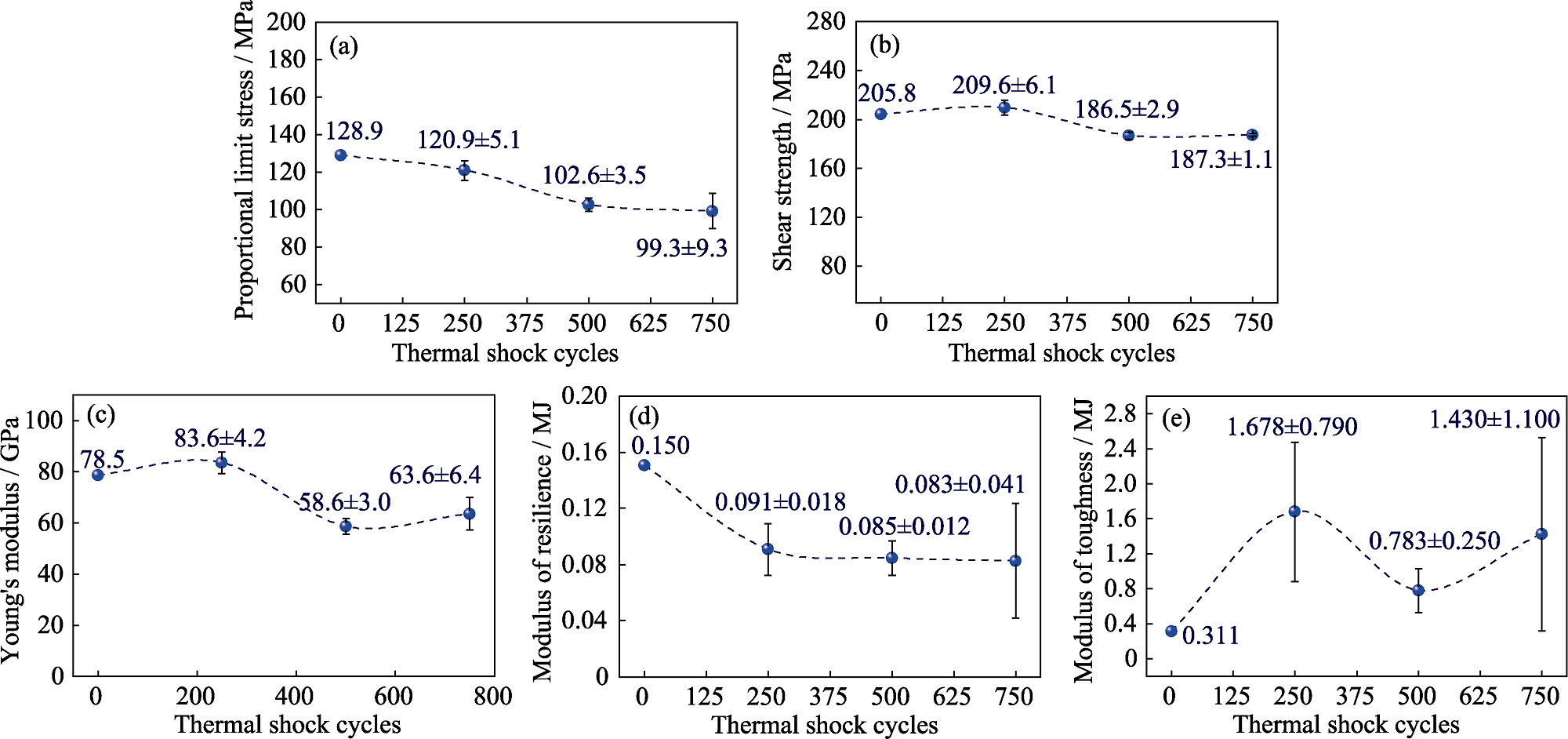
图3 2D SiCf/SiC面内剪切性能
Fig. 3 In-plane shear properties of 2D SiCf/SiC (a) Proportional limit stress; (b) Shear strength; (c) Young’s modulus; (d) Modulus of resilience; (e) Modulus of toughness
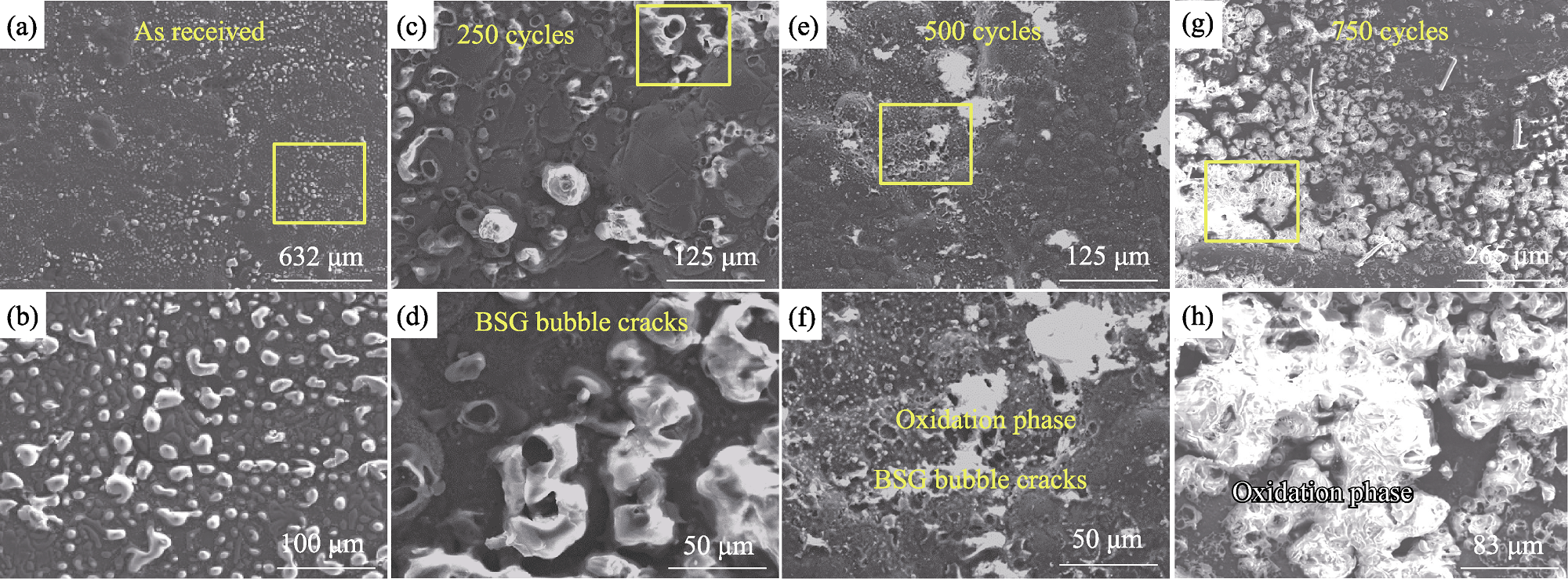

图4 2D SiCf/SiC表面微结构演化
Fig. 4 Microstructure evolution of 2D SiCf/SiC surfaces (a, b) As-received; (c, d) After 250 cycles; (e, f) After 500 cycles; (g, h) After 750 cycles
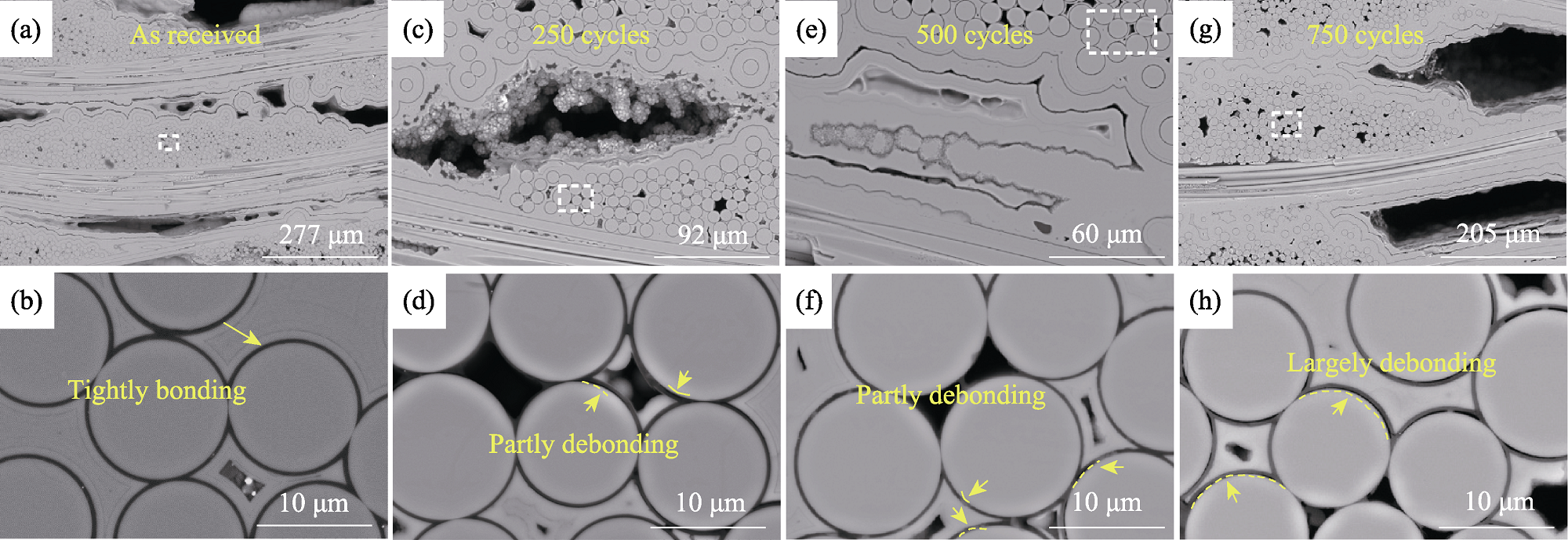
图6 2D SiCf/SiC截面微结构演化
Fig. 6 Cross-sectional microstructure evolution of 2D SiCf/SiC (a, b) As-received; (c, d) After 250 cycles; (e, f) After 500 cycles; (g, h) After 750 cycles

图7 2D SiCf/SiC剪切界面脱黏和台阶间距演变
Fig. 7 Debonding and step spacing evolution at 2D SiCf/SiC shear interface (a, b) As-received; (c, d) After 250 cycles; (e, f) After 500 cycles; (g, h) After 750 cycles
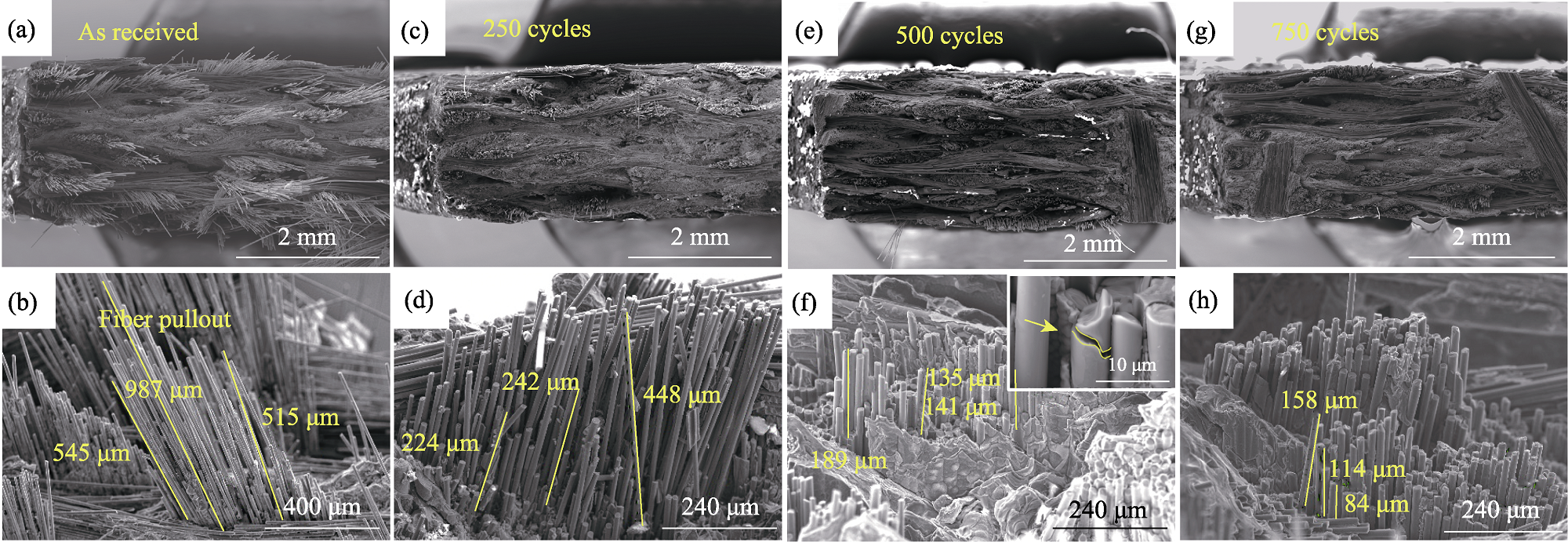

图8 2D SiCf/SiC的断口微结构形貌
Fig. 8 Fracture microstructure morphologies of 2D SiCf/SiC (a, b) As-received; (c, d) After 250 cycles; (e, f) After 500 cycles; (g, h) After 750 cycles
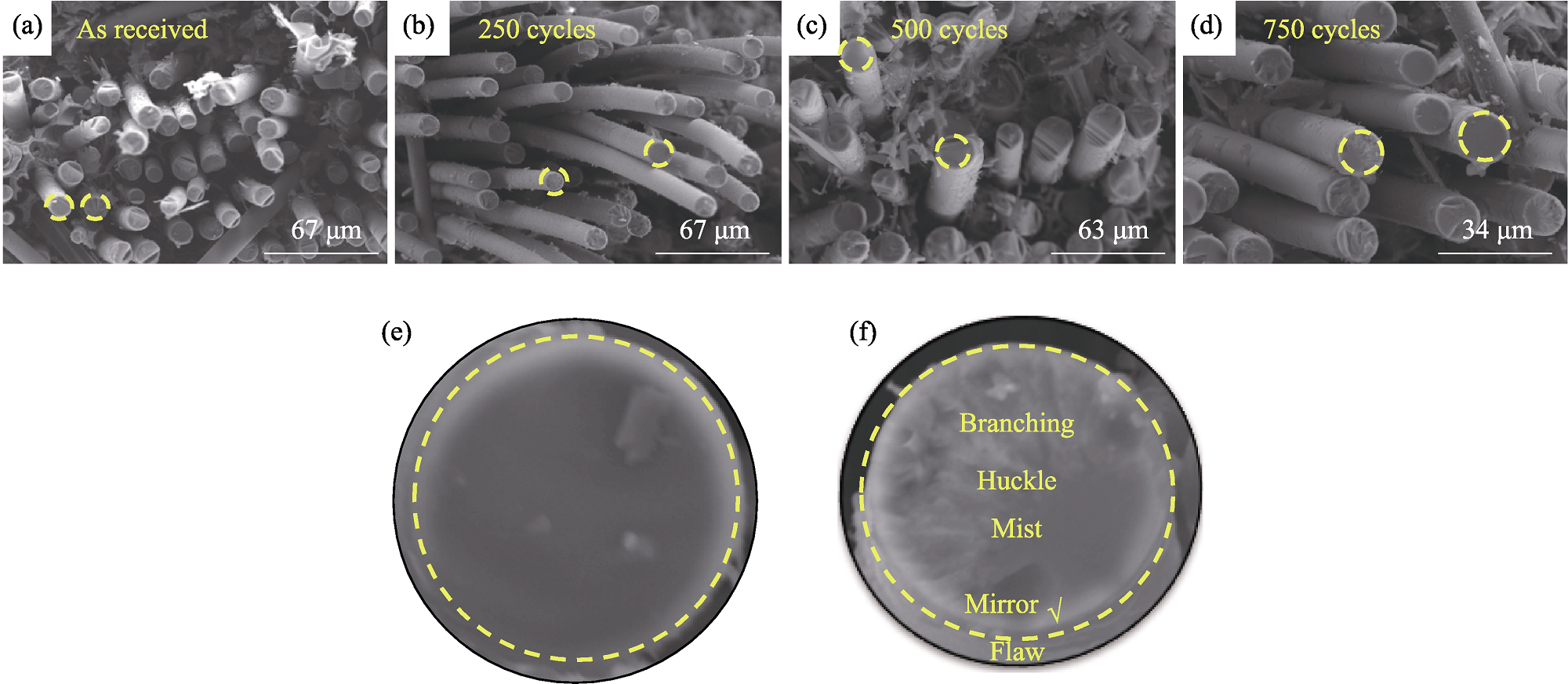
图9 2D SiCf/SiC纤维断口形貌
Fig. 9 Fracture morphologies of 2D SiCf/SiC fibers (a) As-received; (b) After 250 cycles; (c) After 500 cycles; (d) After 750 cycles; (e) Brittle fracture; (f) Toughness fracture

图10 热冲击及剪切界面脱黏机制
Fig. 10 Mechanisms of thermal shock and shear interface debonding (a)Thermal shock interface debonding; (b) Shear strain relationship
| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Poisson’s ration of SiC fiber | vf | 0.20 |
| Poisson’s ration of SiC matrix | vm | 0.17 |
| Fiber volume fraction | Vf/% | 0.35 |
| Matrix cracking energy | ${{\Gamma }_{\text{m}}}~$/(N·m-1) | 6.0 |
| Interface sliding stress | ${{\tau }_{\text{s}}}$/MPa | 9.2 |
| Thickness of plain woven layer | ${{t}_{\text{layer}}}$/mm | 0.2 |
| SiC fiber diameter | ${{d}_{\text{f}}}$/μm | 12.0 |
| SiC fiber modulus | ${{E}_{\text{f}}}$/GPa | 386.7 |
| SiC matrix modulus | ${{E}_{\text{m}}}$/GPa | 350.0 |
| SiC fiber shear modulus | ${{G}_{\text{f}}}/$GPa | 161.1 |
| SiC matrix shear modulus | ${{G}_{\text{m}}}$/GPa | 149.6 |
| BN interface shear modulus | ${{G}_{\text{I}}}$/GPa | 110.0 |
表1 参数数值统计
Table 1 Parameter value statistics
| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Poisson’s ration of SiC fiber | vf | 0.20 |
| Poisson’s ration of SiC matrix | vm | 0.17 |
| Fiber volume fraction | Vf/% | 0.35 |
| Matrix cracking energy | ${{\Gamma }_{\text{m}}}~$/(N·m-1) | 6.0 |
| Interface sliding stress | ${{\tau }_{\text{s}}}$/MPa | 9.2 |
| Thickness of plain woven layer | ${{t}_{\text{layer}}}$/mm | 0.2 |
| SiC fiber diameter | ${{d}_{\text{f}}}$/μm | 12.0 |
| SiC fiber modulus | ${{E}_{\text{f}}}$/GPa | 386.7 |
| SiC matrix modulus | ${{E}_{\text{m}}}$/GPa | 350.0 |
| SiC fiber shear modulus | ${{G}_{\text{f}}}/$GPa | 161.1 |
| SiC matrix shear modulus | ${{G}_{\text{m}}}$/GPa | 149.6 |
| BN interface shear modulus | ${{G}_{\text{I}}}$/GPa | 110.0 |
| Thermal shock cycles | Percentage of debonding/ % | Theoretical value/ GPa | Actual value/ GPa | Error/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 80.4 | 78.5 | -2.4 |
| 250 | 5.56 | 78.2 | 83.6 | 6.9 |
| 500 | 13.90 | 74.6 | 58.6 | -21.4 |
| 750 | 56.10 | 50.0 | 63.6 | 27.2 |
表2 剪切模量计算理论值与实际值对比
Table 2 Comparison of theoretical and actual values for shear modulus calculation
| Thermal shock cycles | Percentage of debonding/ % | Theoretical value/ GPa | Actual value/ GPa | Error/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 80.4 | 78.5 | -2.4 |
| 250 | 5.56 | 78.2 | 83.6 | 6.9 |
| 500 | 13.90 | 74.6 | 58.6 | -21.4 |
| 750 | 56.10 | 50.0 | 63.6 | 27.2 |
| Thermal shock cycles | Fiber step spacing/ mm | Theoretical value/ MPa | Actual value/ MPa | Error/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 79.0 | 178.6 | 205.8 | 15.2 |
| 250 | 97.5 | 193.4 | 209.6 | 8.4 |
| 500 | 49.0 | 162.6 | 186.5 | 14.7 |
| 750 | 67.3 | 170.8 | 187.3 | 9.7 |
表3 面内剪切强度计算理论值与实际值对比
Table 3 Comparison of theoretical and actual shear strength values
| Thermal shock cycles | Fiber step spacing/ mm | Theoretical value/ MPa | Actual value/ MPa | Error/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 79.0 | 178.6 | 205.8 | 15.2 |
| 250 | 97.5 | 193.4 | 209.6 | 8.4 |
| 500 | 49.0 | 162.6 | 186.5 | 14.7 |
| 750 | 67.3 | 170.8 | 187.3 | 9.7 |
| [1] |
PADTURE N P. Advanced structural ceramics in aerospace propulsion. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(8):804.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | NASLAIN R. Design, preparation and properties of non-oxide CMCs for application in engines and nuclear reactors: an overview. Composites Science and Technology, 2004, 64(2):155. |
| [3] | WANG X, GAO X, ZHANG Z, et al. Advances in modifications and high-temperature applications of silicon carbide ceramic matrix composites in aerospace: a focused review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(9):4671. |
| [4] | LIU B, LI F, LIU Y, et al. Experimental and numerical studies on low-velocity impact of laminated C/SiC structures. Composite Structures, 2024, 329: 117765. |
| [5] | LIU B, HAN Y, LI F, et al. High-velocity impact damage by projectile and tension after impact behavior at 1300 ℃ for SiC/SiC with environment barrier coating. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2024, 296: 109858. |
| [6] | WANG H, SINGH R N. Thermal shock behaviour of ceramics and ceramic composites. International Materials Reviews, 2013, 39(6):228. |
| [7] | WU S, CHENG L, ZHANG L, et al. Thermal shock damage of a 3D-SiC/SiC composite. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2005, 7(11):1046. |
| [8] | BHATT R T, SOLA-LOPEZ F, HALBIG M C, et al. Thermal stability of CVI and MI SiC/SiC composites with Hi-Nicalon™-S fibers. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(8):3383. |
| [9] | ZHANG C, WANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Thermal shock resistance of a two-dimensional silicon carbon fiber reinforced SiC matrix composite. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2013, 16(1):65. |
| [10] | LIU X, GUO X, XU Y, et al. Cyclic thermal shock damage behavior in CVI SiC/SiC high pressure turbine twin guide vanes. Materials, 2021, 14(20):6104. |
| [11] | 段宏宇, 王贺权, 张佳平, 等. 不同热震工况下2.5D编织陶瓷基复合材料力学性能及损伤. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(7):4184. |
| [12] | 胡庆宽, 许琦鹏, 万志慧, 等. SiC/SiC复合编织管的抗热冲击性能与失效机理研究. 应用力学学报, 2024, 41(2):288. |
| [13] | GUO H, WANG B, JIA P, et al. In-plane shear behaviours of a 2D-SiC/SiC composite under various loading conditions. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(9):11562. |
| [14] | YAN K F, ZHANG C Y, QIAO S R, et al. Failure and strength of 2D-C/SiC composite under in-plane shear loading at elevated temperatures. Materials & Design, 2011, 32(6):3504. |
| [15] | 郭洪宝, 王波, 贾普荣, 等. 平纹编织陶瓷基复合材料面内剪切细观损伤行为研究. 力学学报, 2016, 48: 361. |
| [16] | 冯宇琦, 王龙, 李艳芬, 等. 平纹陶瓷基复合材料面内剪切解析模型. 中国科技论文, 2022, 17(4):361. |
| [17] | DUAN J, LI Y, LI F, et al. Corrosion behavior of LSI-based 3D needled C/SiC composites subjected to burner rig test. Corrosion Science, 2022, 197: 109982. |
| [18] | LI Y, XIAO P, LI Z, et al. Oxidation behavior of C/C composites with SiC/ZrSiO4-SiO2 coating. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(2):397. |
| [19] | WANG X, SONG Z, CHENG Z, et al. Tensile creep properties and damage mechanisms of 2D-SiCf/SiC composites reinforced with low-oxygen high-carbon type SiC fiber. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(14):4872. |
| [20] | LI B, CHEN X, TIAN L, et al. In-situ formation of the BSG bubbles toward SiC/SiC composites protection mechanisms under thermal shock treatment. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 26: 7097. |
| [21] | SUN G, ZHANG C, ZHANG Q, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of SiCf/SiC composite prepared by chemical vapor infiltration. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(24):36983. |
| [22] | HAY R S. Growth stress in SiO2 during oxidation of SiC fibers. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 111(6):063527. |
| [23] | WANG Y, ZHANG L, CHENG L, et al. Characterization of tensile behavior of a two-dimensional woven carbon/silicon carbide composite fabricated by chemical vapor infiltration. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 497(1/2):295. |
| [24] | MAZERAT S, EL-MORSLI J, SARRAZIN R, et al. Oxidation embrittlement of SiC fibers at intermediate temperatures. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(7):4465. |
| [25] | ZHANG Y, ZHANG L, LIU Y, et al. Oxidation effects on in-plane and interlaminar shear strengths of two-dimensional carbon fiber reinforced silicon carbide composites. Carbon, 2016, 98: 144. |
| [26] | NANCE J, SUBHASH G, SANKAR B, et al. Measurement of residual stress in silicon carbide fibers of tubular composites using Raman spectroscopy. Acta Materialia, 2021, 217: 117164. |
| [27] | GAO X, LEI B, ZHANG Y, et al. Identification of microstructures and damages in silicon carbide ceramic matrix composites by deep learning. Materials Characterization, 2023, 196: 112608. |
| [28] | AVESTON J, KELLY A. Theory of multiple fracture of fibrous composites. Journal of Materials Science, 1973, 8: 352. |
| [29] | MA X, ZHAO L, ZHANG Y, et al. Uncertainty analysis and B-basis value of tensile strength of 2D SiC/SiC composite. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 24: 7058. |
| [30] | PETERS P W M, MARTIN E, PLUVINAGE P. Influence of porosity and fibre coating on engineering elastic moduli of fibre-reinforced ceramics (SiC/SiC). Composites, 1995, 26(2):108. |
| [31] | BERTRAND S, FORIO P, PAILLER R, et al. Hi-nicalon/SiC minicomposites with (pyrocarbon/SiC)n nanoscale multilayered interphases. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2004, 82(9):2465. |
| [32] | RAJAN V P, ZOK F W. Matrix cracking of fiber-reinforced ceramic composites in shear. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2014, 73: 3. |
| [33] | KEITH W P, KEDWARD K T. Shear damage mechanisms in a woven, nicalon-reinforced ceramic-matrix composite. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2005, 80(2):357. |
| [1] | 汤哲鹏, 张中伟, 房金铭, 彭雨晴, 李爱军, 张丹. 模型孔中化学气相渗透过程的热解碳沉积模拟[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(3): 298-304. |
| [2] | 李 艳, 崔 红, 张华坤, 嵇阿琳, 介玉洁. 热梯度CVI制备大尺寸C/C复合材料的致密化行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(2): 153-158. |
| [3] | 张守阳,颜夏峰,李贺军,李 伟,郭领军. 乙醇热解制备炭/炭复合材料工艺探索及组织特征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(5): 1073-1076. |
| [4] | 王东生,于 涛,胡 安,吴 迪,李爱东,刘治国. 氮氢混合气氛对SrBi2Ta2O9铁电薄膜和粉末性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(4): 737-740. |
| [5] | 张亚妮,张立同,成来飞,徐永东. 炭/碳化硅复合材料在高温燃气环境中的铰链传动与摩擦行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(3): 501-508. |
| [6] | 张亚妮,张立同,成来飞,徐永东. 复合材料在传动过程中的摩擦磨损行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(2): 298-304. |
| [7] | 袁 明,黄政仁,董绍明,朱云洲,江东亮. 温度脉冲方法制备碳/碳化硅复合材料界面的微观结构与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(2): 305-310. |
| [8] | 陈招科,熊翔,肖鹏,李国栋,黄伯云. 低温化学气相渗透法制备Cf/TaC复合材料的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(2): 287-292. |
| [9] | 徐国忠,李贺军,白瑞成,陈拂晓,胡志彪. 新技术制备 C/C复合材料及特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(6): 1385-1390. |
| [10] | 刘谊,刘永胜,张立同,成来飞,徐永东. CVI制备Si3N4p/Si3N4透波材料表征与性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(4): 979-985. |
| [11] | 刘永胜,成来飞,张立同,徐永东,刘谊. CVI制备C/Si3N4复合材料及其表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2005, 20(5): 1208-1214. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||