
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (9): 950-958.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200675
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHU Yuxing1( ), LIU Hairui1,2, YAN Shuang1(
), LIU Hairui1,2, YAN Shuang1( )
)
Received:2020-11-26
Revised:2020-12-31
Published:2021-09-20
Online:2021-01-25
Contact:
YAN Shuang, lecturer. E-mail: yanye150@outlook.com
About author:CHU Yuxing(1994-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 434611816@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
CHU Yuxing, LIU Hairui, YAN Shuang. Preparation and Gas Sensing Properties of SnO2/NiO Composite Semiconductor Nanofibers[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 950-958.
| Sample | Ni/% | Sn/% |
|---|---|---|
| NiO NFs | 100 | 0 |
| SnO2/NiO-1 NFs | 76.79 | 23.21 |
| SnO2/NiO-2 NFs | 25.46 | 74.54 |
| SnO2/NiO-3 NFs | 0.51 | 99.49 |
| SnO2/NiO-4 NFs | 0.08 | 99.92 |
Table 1 Relative molar percentages of Ni and Sn in NiO NFs and SnO2/NiO NFs samples
| Sample | Ni/% | Sn/% |
|---|---|---|
| NiO NFs | 100 | 0 |
| SnO2/NiO-1 NFs | 76.79 | 23.21 |
| SnO2/NiO-2 NFs | 25.46 | 74.54 |
| SnO2/NiO-3 NFs | 0.51 | 99.49 |
| SnO2/NiO-4 NFs | 0.08 | 99.92 |
| Sample | Grain size, D/nm | Grain boundary density, $\delta $/(×109, mm-2) |
|---|---|---|
| SnO2/NiO-1 NFs | 11.1 | 8.12 |
| SnO2/NiO-2 NFs | 7.4 | 18.46 |
| SnO2/NiO-3 NFs | 6.3 | 25.16 |
| SnO2/NiO-4 NFs | 6.3 | 25.16 |
Table 2 Respective grain size (D) and grainboundary density (δ) of SnO2/NiO NFs samples
| Sample | Grain size, D/nm | Grain boundary density, $\delta $/(×109, mm-2) |
|---|---|---|
| SnO2/NiO-1 NFs | 11.1 | 8.12 |
| SnO2/NiO-2 NFs | 7.4 | 18.46 |
| SnO2/NiO-3 NFs | 6.3 | 25.16 |
| SnO2/NiO-4 NFs | 6.3 | 25.16 |
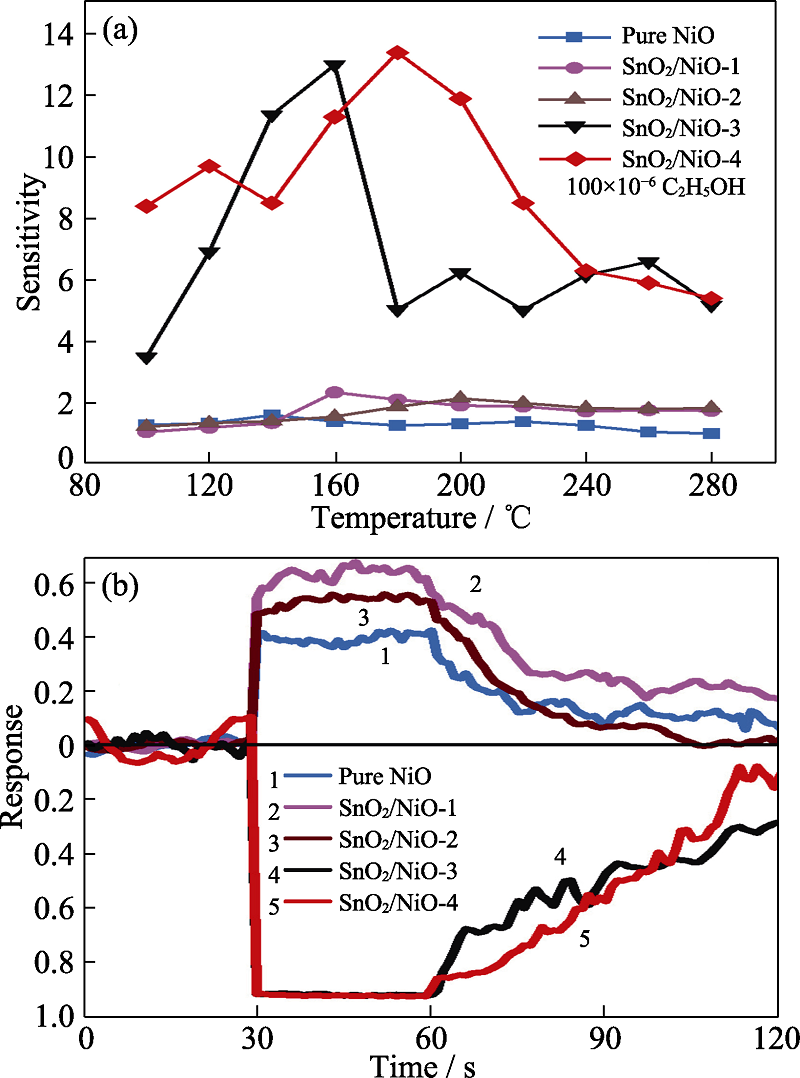
Fig. 5 (a) Sensitivity curves of NiO NFs, SnO2/NiO-1 NFs, SnO2/NiO-2 NFs, SnO2/NiO-3 NFs, and SnO2/NiO-4 NFs to ethanol gas at different temperatures, and (b) response recovery curve to 100×10-6 ethanol gas (volume fraction) at the optimal working temperature
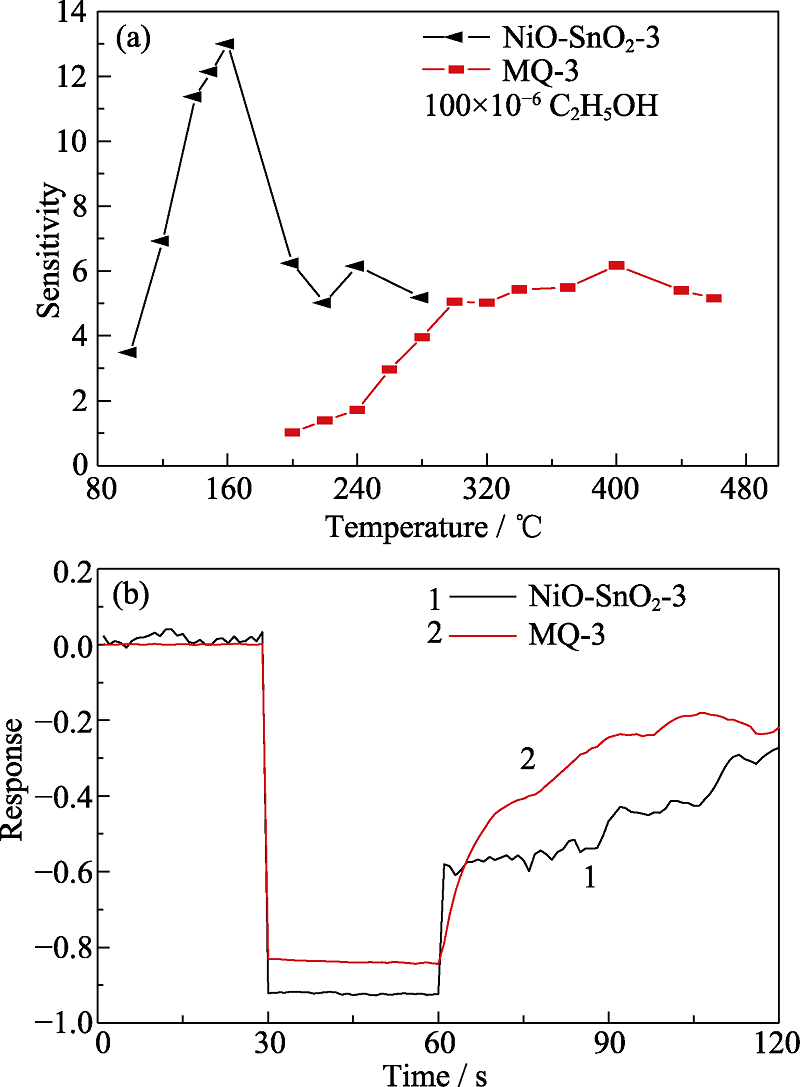
Fig. 7 (a) Sensitivity curves of SnO2/NiO-3 NFs and MQ-3 to 100×10-6 ethanol gas at different working temperatures, and (b) response recovery curve to 100×10-6 ethanol gas at the optimal working temperature
| Materials | Temperature/ ℃ | Response/(100 mg·L-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical SnO2 | 300 | 24.1 | [ |
| ZnO-SnO2 nanofibers | 300 | 18.0 | [ |
| Horseshoe-shaped SnO2 | 225 | 17.3 | [ |
| NiO-decorated SnO2nanorods | 300 | 30.0 | [ |
| SnO2/NiO composite nanofibers | 160 | 13.0 | This work |
Table 3 Comparison of the characteristics of some SnO2-based ethanol sensors reported in the literature with this work
| Materials | Temperature/ ℃ | Response/(100 mg·L-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical SnO2 | 300 | 24.1 | [ |
| ZnO-SnO2 nanofibers | 300 | 18.0 | [ |
| Horseshoe-shaped SnO2 | 225 | 17.3 | [ |
| NiO-decorated SnO2nanorods | 300 | 30.0 | [ |
| SnO2/NiO composite nanofibers | 160 | 13.0 | This work |
| [1] | YAMAZOE NOBORU, SHIMANOE KENGO. Receptor function and response of semiconductor gas sensor. Journal of Sensors, 2009, 2009:875704. |
| [2] |
BARSAN N, KOZIEJ D, WEIMAR U. Metal oxide-based gas sensor research: How to? Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2007, 121(1):18-35.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
MORAN-LAZARO J P, GUILLEN-LOPEZ E S, LOPEZ-URIAS F, et al. Synthesis of ZnMn2O4 nanoparticles by a microwave-assisted colloidal method and their evaluation as a gas sensor of propane and carbon monoxide. Sensors, 2018, 18(3):701.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LEE JEONGSEOK, LEE SE-HYEONG, BAK SO-YOUNG, et al. Improved sensitivity of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticle-decorated ZnO nanowire gas sensor for CO. Sensors, 2019, 19(8):1903.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
WANG XU, LI SIHAN, XIE LILI, et al. Low-temperature and highly sensitivity H2S gas sensor based on ZnO/CuO composite derived from bimetal metal-organic frameworks. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(10):15858-15866.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LEONARDI S G, MIRZAEI A, BONAVITA A, et al. A comparison of the ethanol sensing properties of alpha-iron oxide nanostructures prepared via the Sol-Gel and electrospinning techniques. Nanotechnology, 2016, 27(7):075502.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
MIRZAEI ALI, PARK SUNGHOON, SUN GUN-JOO, et al. Fe2O3/Co3O4 composite nanoparticle ethanol sensor. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2016, 69(3):373-380.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHOI SEUNGBOK, BONYANI MARYAM, SUN GUN-JOO, et al. Cr2O3 nanoparticle-functionalized WO3 nanorods for ethanol gas sensors. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 432:241-249.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHOU XINYUAN, WANG YING, WANG JINXIAO, et al. Amplifying the signal of metal oxide gas sensors for low concentration gas detection. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(9):2841-2847.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HU WEIYE. Vehicle alcohol detection system based on Internet of things technology. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 452:042156.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WEI BEE-YU, HSU MING-CHIH, SU PI-GUEY, et al. A novel SnO2 gas sensor doped with carbon nanotubes operating at room temperature. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2004, 101(1/2):81-89.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SHARMA HEMLATA JAYPRAKSH, SONWANE NAYANA DAMODHAR, KONDAWAR SUBHASH BABURAO. Electrospun SnO2/polyaniline composite nanofibers based low temperature hydrogen gas sensor. Fibers and Polymers, 2015, 16(7):1527-1532.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
CHO SOO-YEON, YOO HAE-WOOK, KIM JU YE, et al. High-resolution p-type metal oxide semiconductor nanowire array as an ultrasensitive sensor for volatile organic compounds. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(7):4508-4515.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MOON YOUNG KOOK, JEONG SEONG-YONG, KANG YUN CHAN, et al. Metal oxide gas sensors with Au nanocluster catalytic overlayer: Toward tuning gas selectivity and response using a novel bilayer sensor design. ACS Applied Materials Interfaces, 2019, 11(35):32169-32177.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
AMIRI VAHID, ROSHAN HOSSEIN, MIRZAEI ALI, et al. Nanostructured metal oxide-based acetone gas sensors: a review. Sensors, 2020, 20(11):3096.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
NUNDY SRIJITA, EOM TAE-YIL, KANG JUN-GU, et al. Flower-shaped ZnO nanomaterials for low-temperature operations in NOX gas sensors. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(5):5706-5714.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SHAALAN N M, YAMAZAKI T, KIKUTA T, et al. Influence of morphology and structure geometry on NO2 gas-sensing characteristics of SnO2 nanostructures synthesized via a thermal evaporation method. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2011, 153(1):11-16.
DOI URL |
| [18] | GAIDAN IBRAHIM, ASBIA SALIM, BRABAZON DERMOT, et al. TiO2 gas sensor to detect the propanol at room temperature. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2017, 1896(1):1-5. |
| [19] |
YAN SHUANG, WU QINGSHENG. A novel structure for enhancing the sensitivity of gas sensors -α-Fe2O3 nanoropes containing a large amount of grain boundaries and their excellent ethanol sensing performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(11):5982-5990.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ZHANG JIAN, ZENG DAWEN, ZHU QIANG, et al. Effect of grain-boundaries in NiO nanosheet layers room-temperature sensing mechanism under NO2. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(31):17930-17939.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
TURGUT ERDAL, COBAN OMER, SARITAS SEVDA, et al. Oxygen partial pressure effects on the RF sputtered p-type NiO hydrogen gas sensors. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 435:880-885.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZENG QINGHAO, CUI YANFA, ZHU LIANFENG, et al. Increasing oxygen vacancies at room temperature in SnO2 for enhancing ethanol gas sensing. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2020, 111:104962.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LI XIN, ZHANG HANG, FENG CHANGHAO, et al. Novel cage-like α-Fe2O3/SnO2 composite nanofibers by electrospinning for rapid gas sensing properties. RSC Advanced., 2014, 4(52):27552-27555.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
JAYABABU NAGABANDI, POLOJU MADHUKAR, SHRUTHI JULAKANTI, et al. Semi shield driven p-n heterostructures and their role in enhancing the room temperature ethanol gas sensing performance of NiO/SnO2 nanocomposites. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(12):15134-15142.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WEI ZHIJIE, ZHOU QU, WANG JINGXUAN, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of SnO2 nanoneedle-anchored NiO microsphere and its gas sensing performances. Nanomaterials, 2019, 9(7):1015.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
GUO JING, ZHANG JUN, ZHU MIN, et al. High-performance gas sensor based on ZnO nanowires functionalized by Au nanoparticles. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2014, 199:339-345.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
LONG JING, XIONG WEI, WEI CHENGYIRAN, et al. Directional assembly of ZnO nanowires via three-dimensional laser direct writing. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(7):5159-5166.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LIU BILU, LIU QINGFENG, REN WENCAI, et al. Synthesis of single-walled carbon nanotubes, their ropes and books. Comptes Rendus Physique, 2010, 11(5/6):349-354.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SCHOTTLE MARIUS, XIA QINGBO, CHENG YEN THENG, et al. Integrated polyphenol-based hydrogel templating method for functional and structured oxidic nanomaterials. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(11):4716-4723.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
LIU ZICHEN, MURPHY ALEXANDER WILLIAM ALLEN, KUPPE CHRISTIAN, et al. WS2 nanotubes, 2D nanomeshes, and 2D in-plane films through one single chemical vapor deposition route. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(4):3896-3909.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
BAI SHOULI, GUO WENTAO, SUN JIANHUA, et al. Synthesis of SnO2-CuO heterojunction using electrospinning and application in detecting of CO. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2016, 226:96-103.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
YAN SHUANG, WU QINGSHENG. Micropored Sn-SnO2/carbon heterostructure nanofibers and their highly sensitive and selective C2H5OH gas sensing performance. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2014, 205:329-337.
DOI URL |
| [33] | DONG SHUWEN, WU DI, GAO WENYUAN, et al. Multi- dimensional templated synthesis of hierarchical Fe2O3/NiO composites and their superior ethanol sensing properties promoted by nanoscale p-n heterojunctions. Dalton Transitions, 2020, 49(4):1300-1310. |
| [34] |
RHEINGANS BASTIAN, MITTEMEIJER ERIC J. Modelling precipitation kinetics: evaluation of the thermodynamics of nucleation and growth. Calphad, 2015, 50:49-58.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
LI LU, BAO ZHILONG, YE XUNHENG, et al. Nucleation, growth, and aggregation of Au nanocrystals on liquid surfaces. Chinese Physics Letters, 2020, 37(2):028102.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
WANG XIAOMING, PHILLIPS BRIAN L, BOILY JEAN-FRANCOIS, et al. Phosphate sorption speciation and precipitation mechanisms on amorphous aluminum hydroxide. Soil Systems, 2019, 3(1):20.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
AYED RIHAB BEN, AJILI MEJDA, GARCIA JORGE M, et al. Physical properties investigation and gas sensing mechanism of Al: Fe2O3 thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Superlattices and Microstructures, 2019, 129:91-104.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
MIRZAEI ALI, LEE JAE-HYOUNG, MAJHI SANJIT MANOHAR, et al. Resistive gas sensors based on metal-oxide nanowires. Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 126(24):241102.
DOI URL |
| [39] | GUMBI SIFISO W, MKWAE PRINCE S, KORTIDIS IOANNIS, et al. Electronic and simple oscillatory conduction in ferrite gas sensors: gas-sensing mechanisms, long-term gas monitoring, heat transfer, and other anomalies. ACS Applied Materiale Interfaces, 2020, 12(38):43231-43249. |
| [40] |
ZHOU XIAOMING, FU WUYOU, YANG HAIBIN, et al. Novel SnO2 hierarchical nanostructures: synthesis and their gas sensing properties. Materials Letters, 2013, 90(1):53-55.
DOI URL |
| [41] | SONG XIAOFENG, LIU LI. Characterization of electrospun ZnO-SnO2 nanofibers for ethanol sensor. Sensors & Actuators A Physical, 2009, 154(1):175-179. |
| [42] | LU GEYU, ZHANG BO, SUN YANGFENG, et al. Horseshoe-shaped SnO2 with annulus-like mesoporous forethanol gas sensing application. Sensors & Actuators B Chemical, 2017, 240:1321-1329. |
| [43] |
SUN GUN-JOO, LEE JAE KYUNG, LEE WAN IN, et al. Ethanol sensing properties and dominant sensing mechanism of NiO-decorated SnO2 nanorod sensors. Electronic Materials Letters, 2017, 13(3):260-269.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
DEY ANANYA. Semiconductor metal oxide gas sensors: a review. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2018, 229:206-217.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
BARSAN NICOLAE, WEIMAR UDO. Conduction model of metal oxide gas sensors. Journal of Electroceramics, 2001, 7(3):143-167.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
GAO HONGYU, YU QI, ZHANG SUFANG, et al. Nanosheet- assembled NiO microspheres modified by Sn2+ ions isovalent interstitial doping for xylene gas sensors. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2018, 269:210-222.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
HAO PEI, QIU GE, SONG PENG, et al. Construction of porous LaFeO3 microspheres decorated with NiO nanosheets for high response ethanol gas sensors. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 515:146025.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
LI ZHOU, YI JIANXIN. Enhanced ethanol sensing of Ni-doped SnO2 hollow spheres synthesized by a one-pot hydrothermal method. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2017, 243:96-103.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
GUAN YUE, WANG DAWEI, ZHOU XIN, et al. Hydrothermal preparation and gas sensing properties of Zn-doped SnO2 hierarchical architectures. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2014, 191:45-52.
DOI URL |
| [1] | XIAO Zichen, HE Shihao, QIU Chengyuan, DENG Pan, ZHANG Wei, DAI Weideren, GOU Yanzhuo, LI Jinhua, YOU Jun, WANG Xianbao, LIN Liangyou. Nanofiber-modified Electron Transport Layer for Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 828-834. |
| [2] | DING Ningning, SUN Jianhua, WEI Xu, SUN Lixia. Monitoring Ammonia at Room Temperature of p-Aminobenzene Sulfonic Acid Modified MoO3/PPy Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1245-1253. |
| [3] | ZHONG Xiaolan, LIU Xueqing, DIAO Xungang. Electrochromic Devices Based on Tungsten Oxide and Nickel Oxide: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(2): 128-139. |
| [4] | ZHU Zhengwang,FENG Rui,LIU Yang,ZHANG Yang,XIE Wenhan,DONG Lijie. Preparation and Property of CoFe2O4 Nanofibers with Fishbone-like Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 1011-1016. |
| [5] | ZHAO Zhankui, LI Tao, LU Shuhan, WANG Minggang, ZHANG Jingjing, CHENG Daowen, WU Chen, CHI Yue, WANG Hongli. Magnetic Properties and Resistivity of Soft Magnetic Composites Regulated by SPS Enhanced Interface Reaction Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(11): 1223-1226. |
| [6] | Zhi-Jun MA, Chang-Ye MANG, Hai-Tao ZHAO, Zhi-Hao GUAN, Liang CHENG. Comparison of Electromagnetism Behavior of Different Content Cobalt-zinc Ferrite Loaded with Graphene [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(4): 407-416. |
| [7] | LI Xiao-Ping, LI Yue-Jun, CAO Tie-Ping, SUN Da-Wei, WANG Xia, XI Xiao-Tian. Facile Synthesis of Bi/Bi2MoO6/TiO2 Composite Nanofibers with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity under Visible Light [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(11): 1193-1199. |
| [8] | DU Hai-Ying, YAO Peng-Jun, WANG Jing, SUN Yan-Hui, YU Nai-Sen, ZHANG Tao, DONG Liang. Preparation and Gas Sensing Property of SnO2/ZnO Composite Hetero-nanofibers Using Two-step Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(4): 453-461. |
| [9] | ZENG Yan-Fei, XIN Guo-Xiang, BULIN Chao-Ke, ZHANG Bang-Wen. One-step Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide/NiO as Supercapacitor Electrodes Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1070-1076. |
| [10] | LI Xiang, GE Wu-Jie, WANG Hao, QU Mei-Zhen. Research Progress on the Capacity Fading Mechanisms of High-Nickel Ternary Layered Oxide Cathode Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(2): 113-121. |
| [11] | ZHAI Li-Li, ZHANG Jiang, LI Xuan-Ke, CONG Ye, DONG Zhi-Jun, YUAN Guan-Ming. F127 Template on Pore Structure and Electrochemical Performances of Mesoporous SnO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(6): 588-596. |
| [12] | HAN Dan-Dan, JING Xiao-Yan, XU Peng-Cheng, TAN Ao, CHENG Zhen-Yu. Optimizing the Charge Transfer Process by Synthesizing NiO Microspheres on Ni Foam through Microwave-assisted Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(6): 667-672. |
| [13] | YANG Qi, HU Wen-Bin. Amorphous SnO2-C Composite Fibers and Their Electrochemical Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(8): 861-866. |
| [14] | BI Jun, WU Yan-Bo, ZHAO Heng-Yan, WEI Bin-Bin. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of La2CoFeO6 Bamboo-like Hollow Nanofibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(10): 1031-1036. |
| [15] | LI Yue-Jun, CAO Tie-Ping, MEI Ze-Min. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of BaTiO3/TiO2 Heterostructured Nanofibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(7): 741-746. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||