|
|
Processing, Microstructure and Properties of ZrC Ceramic Composites
WANG Dong, WANG Yu-Jin
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 449–458
 Abstract
Abstract(
1512 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(568KB)(
3230
)
ZrC ceramic composites have been proposed for a variety of applications in super-hard, thermal protection and new energy fields due to their excellent properties, such as high melting point, low density and good ablation resistance. The preparation techniques for ZrC cements, composite ceramics and fiber reinforced ZrC composites are reviewed, including powder sintering, precursor infiltration and pyrolysis and reactive melt infiltration. The effects of processing on microstructure of ZrC composite are discussed. Mechanical properties and ablation properties of ZrC ceramic composites are summarized. The problems, low toughness and spalling of ablation layer, for ZrC cements, composite ceramics and fiber reinforced ZrC composites are proposed, respectively. Finally, the trend of researches on ZrC ceramic composites is also prospected.
|
|
|
Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of C/C-ZrC Composites
SHEN Xue-Tao, LI Wei, LI Ke-Zhi
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 459–466
 Abstract
Abstract(
1091 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(787KB)(
1669
)
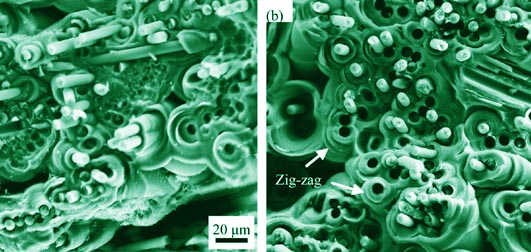
C/C-ZrC composites were obtained by subsequent steps: immersing carbon felts into ZrOCl2 aqueous solution, heat treatment, densification by thermal gradient chemical vapor infiltration with methane gas and graphitization. Three-point bending tests were performed to evaluate the mechanical properties of the composites. The results show that the flexural strength and elastic modulus increase with increasing ZrC contents. Carbon/carbon (C/C) composites containing 12.08wt% ZrC achieve a flexural strength of 42.5 MPa and a modulus of 9.6 GPa, increasing by 70.0% and 43.3%, respectively, as comparison with the flexural strength and modulus of C/C composites. Micro-size ZrC particles with weak anchoring strength between them are unfavorable to the strength of carbon matrices, but they are not the main determinant of the strength of the composites. Submicro- and nano-size ZrC particles in carbon matrices owning good interface anchoring strength with carbon matrices can enhance the strength and elastic modulus of carbon matrices, improving the final mechanical properties of the composites.
|
|
|
Investigation of Elastic Properties, Hardness and Thermal Conductivity of New Superhard Material z-BC2N
WANG Jun-Peng, LI Feng, AO Jing, JIAO Li-Na, LI Chun-Mei, CHEN Zhi-Qian
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 467–473
 Abstract
Abstract(
798 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(555KB)(
1857
)
Based on the first-principles calculations, the elastic anisotropic properties, stress-strain relationship, hardness and minimum thermal conductivity of the superhard material z-BC2N were investigated. Results show that the Pugh criterion B/G is 0.87, Poisson ratio is 0.084, and the universal elastic anisotropy index AU equals to 0.09992. The ultimate tensile strength along [100] crystal orientation is up to 180 GPa while the shear intensity ofdirection peaks at 160 GPa, and 77.07 GPa for the Vickers hardness of z-BC2N. Based on Cahill model the calculated minimum thermal conductivity is 6.811 W/(m·K). Those data indicate that z-BC2N belongs to brittle material with excellent mechanical properties such as the outstanding tensile strength and shear intensity, its bulk modulus is exactly isotropic and the Young's modulus witnesses a significant trend to be isotropic. Besides, z-BC2N possesses a lower minimum thermal conductivity compared with diamond.
|
|
|
Influence of Hydrogen Dilution on Two-phase Structure and Electrical Properties of Hydrogenated Silicon Thin Films
LU Yuan-Yuan, LI He-Jun, YANG Guan-Jun
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 474–478
 Abstract
Abstract(
685 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(448KB)(
1129
)
Hydrogenated silicon thin films with two-phase structure were prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) at different hydrogen dilution ratios (R) and their microstructure and electrical properties were investigated. The results indicated that the film was amorphous when R was 10. As R increased, the film presented two-phase structure, and the thickness of the amorphous layer tended to thin and the transition to crystalline from amorphous started earlier. From XRD results, both crystallinity and average grain size of the films increased firstly and then decreased with increase of R, and at maximum values when R was 28.6. The change rule of dark conductivity and carrier density agreed with the change rule of crystallinity and average grain size, which showed a close positive relationship between electrical properties and the microstructure.
|
|
|
Microwave Absorption Properties of Double-layer Absorbing Coatings Based on Ni0.4Co0.2Zn0.4Fe2O4 and BaTiO3 Nanofibers
LI Jia-Le, XIANG Jun, YE Qin, LIU Min, SHEN Xiang-Qian
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 479–486
 Abstract
Abstract(
955 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(595KB)(
1996
)
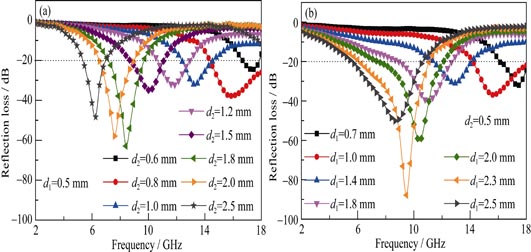
BaTiO3 (BTO) nanofibers (NFs) and Ni0.4Co0.4Zn0.4Fe2O4 (NCZFO) NFs with average diameters of about 180 nm and 220 nm, respectively, were prepared by electrospinning method. Their phase structures, surface morphologies and electromagnetic parameters were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field mission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) and vector network analyzer. Microwave absorption properties of both single- and double-layer silicone rubber based absorbing coatings with either 70wt% BTO NFs or NCZFO NFs as microwave absorbents were evaluated according to the transmission line theory in the frequency range of 2–18 GHz. The results show that the double-layer absorbing coatings with the NCZFO NFs/silicone rubber composite (S1) as matching layer and the BTO NFs/silicone rubber composite (S2) as absorbing layer display superior microwave absorbing performance compared to the single-layer ones due to the proper combination of magnetic loss of NCZFO NFs and dielectric loss of BTO NFs, and the improved impedance matching characteristics. The double-layer absorbing coatings have a reflection loss (RL) of less than –20 dB over the frequency range of 4.9–18 GHz through appropriately adjusting the thicknesses of the absorbing layer and matching layer. When the thicknesses of the absorbing layer and the matching layer are 2.3 and 0.5 mm, respectively, the minimum RL reaches –87.8 dB at 9.5 GHz and the absorption bandwidth with the RL values below –20 dB is up to 5 GHz. The optimal NCZFO NFs/BTO NFs double-layer absorbing coatings can become a novel microwave absorption material with strong-absorption and broad-band.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Monodispersed and Spherical YAG Powder for Transparent Ceramic by Spray Drying
ZHANG Le, ZHOU Tian-Yuan, YANG Hao, QIAO Xue-Bin, WANG Zhong-Ying, ZHANG Jian, TANG Ding-Yuan
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 487–492
 Abstract
Abstract(
1003 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(635KB)(
2934
)
YAG transparent ceramic powders were prepared by spray drying method with anhydrous ethanol suspension. The morphology, size, forming performance and crushing behavior of granulated particles with different PVB binder contents, the pore distribution in green compacts as well as the microstructure and optical properties of sintered ceramics were investigated by SEM, mercury injection, EDS and UV-Visible-Infrared transmission spectroscopy. The optimal content of PVB is 1.0wt%. The granulated particles exhibit excellent forming performance with mono-dispersed and fully dense aggregates. They have high spherical degree and high chemical uniformity. Their mean size is ~40 μm. The granulated particels are completely crushed under 75 MPa pressure and form uniform and compact structure of green compacts. The sintered YAG transparent ceramics have good optical properties with homogeneous microstructure and without pore and defects.
|
|
|
Comparative Study on Kinetics of Chlorine Evolution Reaction for Ru-La-O Oxide Coatings
LONG Ping, XU Li-Kun, CUI Xiu-Fang, JIN Guo
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 493–499
 Abstract
Abstract(
878 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(508KB)(
1659
)
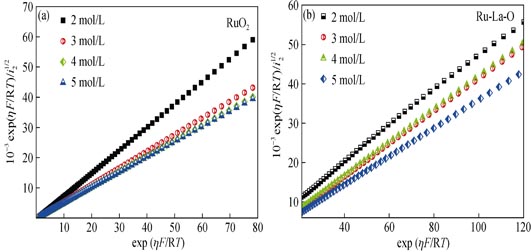
The Ti/RuO2 and Ti/Ru-La-O oxide coatings were prepared by thermal decomposition of the metal chlorides in the precursor solution. The specific adsorption of Clˉ on coatings, the effect of La on the chlorine evolution reactions (ClER) and the kinetic mechanism were investigated by using differential capacity (DC) and polarization curves (PC). Results show that the coating surface exhibits significantly specific adsorption of Clˉ in NaCl neutral solution, which has an influence on the kinetics of the chlorine evolution process, resulting in an increase of the Tafel slope and a decrease of the reaction order. The addition of lanthanum reduces the overpotential of Ti/RuO2 coating and enhances the exchange current density, which improves the chlorine evolution reaction of the coatings. Both kinetic mechanisms of recombination and electrochemical desorption of adsorbed intermediate species for the coatings are comparatively studied. It is confirmed that the Chlorine evolution reaction on Ru-La-O oxide coatings in NaCl neutral solution is controlled by the process of.
|
|
|
Effect of Microwave Sintering on Electrical Properties of PLZT Ceramics
LONG Lian-Jun, XU Jian-Mei, GONG Yan-Sheng, WU Ming-Yang, CUI Xin-You
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 500–504
 Abstract
Abstract(
736 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(464KB)(
1494
)
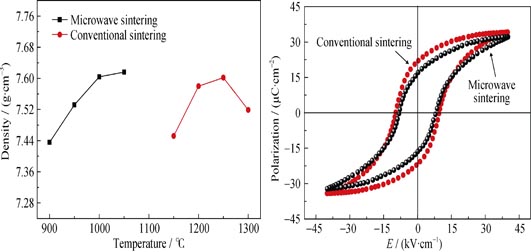
Lead lanthanum zirconate titanate(PLZT) powders synthesized by partial co-precipitation method were used to fabricate PLZT ceramics by conventional muffle furnace or by microwave muffle furnace. The crystal structure, microstructure, electrical properties of PLZT ceramics prepared by these two methods were investigated. The results show that the PLZT ceramics sintered by these two methods are pure perovskite structure. Microwave sintered PLZT ceramics possess smaller grain, more uniform size and less holes than do the conven tional prepared. The microwave sintering temperature is much lower than that by the conventional method, and the duration time is also much less, while the electrical properties of the ceramics sintered by these two methods are similar. The best properties of PLZT ceramics can be gained by microwave sintering at 1000℃ with dielectric constant and piezoelectric constant of 2512 and 405 pC/N. The remnant polarization is 16.5 kV/cm, and the coercive field is 8.2 μC/cm2. The dielectric constant and piezoelectric constant of PLZT ceramics sintered by conventional method at 1250℃ reach the maximum values of 2822 and 508 pC/N. The remnant polarization is 21.6 kV/cm and the coercive field is 9.6 μC/cm2.
|
|
|
Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of PPy/GO-RuO2 Film Electrode for Micro-supercapacitor
ZHU Ping, CAI Ting, HAN Gao-Yi, XIONG Ji-Jun
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 505–510
 Abstract
Abstract(
1120 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(457KB)(
1887
)
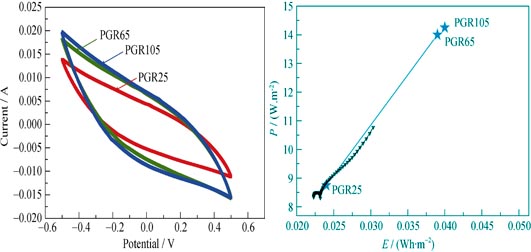
To address the issue that RuO2 was difficult to deposit directly on the micro-3D-structure metal current collector due to its high deposition potential, this study was engaged to prepare RuO2 composite film by the fractional electro-deposition method. PPy/GO film was firstly deposited on nickel current collector as substrate, then RuO2 particles were deposited on the substrate after heat-treatment, finally the RuO2 composite film was carried on a second heat-treatment. By means of scanning electron microscope (SEM), it can be found that the porous structures of RuO2 composite film multiply with the increase of heat-treatment temperature, so that the pore structure of the membrane electrode is improved. By means of X-ray energy dispersive spectroscope (EDS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), the results indicate that there exists amorphous RuO2·xH2O in the film, which ensures the great specific capacity of the membrane electrode. The electrochemical testing results indicate that the electrochemical performance of membrane electrode is optimal when heat-treatment temperature reaches 105℃, with specific capacitance of 28.5 mF/cm2, energy density of 0.04 Wh/m2 and power density of 14.25 W/m2. The RuO2 composite film prepared by using step-by-step electro-deposition method is a type of excellent electrode material for micro-supercapacitor.
|
|
|
Properties of Multiferroic PrBi4Fe0.5Co0.5Ti3O15 Ceramics
CHEN Chun-Xia, LI Hao-Ran, ZHENG Ren-Kui
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 511–515
 Abstract
Abstract(
2655 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(478KB)(
1332
)
PrBi4Fe0.5Co0.5Ti3O15 compounds were prepared either by conventional solid-state reaction method or by two-step method. X-ray diffraction analyses indicate that the PrBi4Fe0.5Co0.5Ti3O15 samples which were synthesized by the conventional solid-state reaction method favors the formation of single phase four-layer Aurivillius phase more easily than the samples prepared by the two-step method. The multiferroic properties of the samples at room temperature were demonstrated by ferroelectric and magnetic measurements. The samples exhibit significantly enhanced magnetic properties by Pr/Co co-substitution. The remnant magnetization (2Mr) of the samples prepared by the conventional solid-state reaction and two-step methods are 0.315 and 0.576 Am2/kg, respectively, approximately five orders larger than that of the reported Bi5FeTi3O15 ceramics (2.7×10-6 Am2/kg) and two orders of the reported Co-doped Bi5FeTi3O15 ceramics (7.8×10-3 Am2/kg).
|
|
|
Electrospinning Gelatin/Chitosan/Hydroxyapatite/Graphene Oxide Composite Nanofibers with Antibacterial Properties
LIANG Hong-Pei, WANG Ying-Bo, SU Zhi, LU Xiong, WANG Shuai
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 516–522
 Abstract
Abstract(
1332 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(583KB)(
1823
)
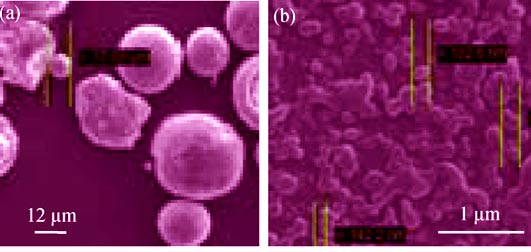
Gelatin/chitosan/hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide composite nanofibers were prepared by electrospinning. The effect of composition on fiber morphology and antibacterial properties were investigated. The results show that increasing of gelatin concentration results in the increase of fiber diameter and then heavy fiber adhesion, showing ideal concentration scope of 15%-20%. Increasing chitosan concentration leads to thin fibers, with optimum concentration at 1%, while increasing hydroxyapatite (HA) concentration increases the ionic concentration of eletrospinning solution, leading to the decrease of beads and fiber adhesion. Nanofibers with smooth morphology are obtained when the diameter of HA particles is 12 μm and at concentration of 5%. And the addition of graphene oxide (GO) enhances uniform, smooth and antibacterial property of the composite nanofibers, which enables the gelatin/chitosan/hydrox- yapatite/GO fibers good antibacterial effect against both Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.
|
|
|
Influence of Micro-nano Structure of Haydroxyapatite Particles on Protein Adsorption
FU Ya-Kang, ZHOU Xue, XIAO Dong-Qin, SHI Feng, LU Xiao-Ying, WENG Jie
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 523–528
 Abstract
Abstract(
893 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(465KB)(
1552
)
Hydroxyapatite (HAP) particles were hydrothermally synthesized with the surface morphologies adjusted by cyclohexane-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6-hexacarboxylic acid (H6E) as the template. HAP particles were characterized by XRD, BET, SEM and FTIR. The protein adsorption-desorption behaviors of positively charged lysozyme (LYS), fibrinogen (FN) and negatively charged bovine serum albumin (BSA) on these HAP particles were examined. The results indicate that using H6E as a template to fabricate micro-nano structures on HAP particles through hydrothermal reaction is simple and controllable. HAP particles with micro-nano structures show selective protein adsorption-desorption properties for different proteins. The protein-loaded shell-like HAP particle (HAP50-protein) shows an excellent protein release behavior in vitro.
|
|
|
Rapid in situ Crystallization and Catalytic Performance of Cu3(BTC)2-based Film on Copper Mesh
HUA Cheng-Jiang, WANG Ming-Hui, LUAN Guo-You, LIU Yan, WU Hua
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 529–534
 Abstract
Abstract(
961 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(493KB)(
2086
)
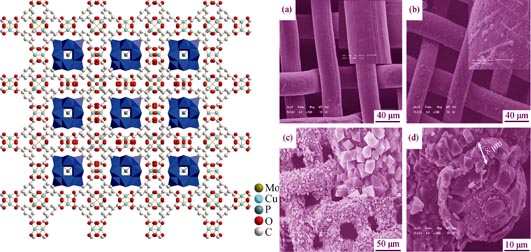
Cu3(BTC)2-based (BTC=1, 3, 5-benzenetricarboxylic acid) metal-organic framework film was synthesized on the surface of copper mesh through in situ crystallization at room temperature. In this film, Keggin-type H3PMo12O40 was embedded in partial cavity of Cu3(BTC)2. The film was characterized by X-Ray powder diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR). The surface of copper fiber was evenly covered by the film. It can be estimated that the thickness of film is about 8 μm. In the synthesis process, the role of copper is not only a support, but also a copper source. H2O2 played an important role in synthesis process of membrane, and adding proper H2O2 could accelerate reactive speed effectively. As a heterogeneous catalyst, the catalytic property of the sample was tested through rhodamine B degradation. The film exhibited good catalytic performance in the reaction of rhodamine B degradation. After reaction for 100 min, the degradation degree of rhodamine B reached 98%. The catalyst was reused for three times, and every time it exhibited good catalytic performances during the processes.
|
|
|
Effects of Solution pH on Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B Using Bismuth Tungstate Prepared by Low-temperature Combustion Method
YU Zhong-Xiong, XIANG Lei, ZHONG Fang-Long, LI Yan-Wen, MO Ce-Hui, CAI Quan-Ying, HUANG Xian-Pei, WU Xiao-Lian, ZHAO Hai-Ming
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 535–541
 Abstract
Abstract(
1134 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(568KB)(
2078
)
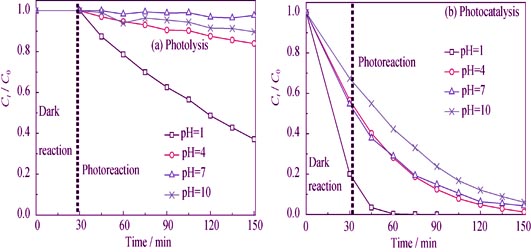
Bismuth tungstate (Bi2WO6) was synthesized by low-temperature combustion method (LCM) and characterized by diffuse reflectance spectroscope (DRS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and Zeta potential. The effects of solution pH and acidity regulator types on the photocatalytic degradation of RhB by LCM-Bi2WO6 were investigated. Results showed that LCM-Bi2WO6 was an orthorhombic crystal and its wavelength of maximum absorption, forbid bandwidth, lattice size and isoelectric point were 455 nm, 2.72 eV, 14.7 nm and 3.43, respectively. Stronger adsorption and photodegradation of RhB (25 mg/L, pH=4) using LCM-Bi2WO6 as photocatalyst was observed, compared with using TiO2 or Bi2WO6 prepared by hydrothermal method as photocatalyst. Adsorption and photodegradation of RhB by LCM-Bi2WO6 satisfied the pseudo-second-order kinetic equations and first order kinetic equations, respectively. Equilibrated adsorption capacity (7.48-21.93 mg/g) and photodegradation rate constants (0.0197-0.1181 min-1) of RhB by LCM-Bi2WO6 were positively related to solution pH. Photocatalytic degradation of RhB by LCM-Bi2WO6 was mainly triggered by free hydroxyl groups (·OH). Blue shifts of RhB ultraviolet-visible spectrum indicated its degradation through ethyl removal and conjugated groups break pathway. Weaker adsorption (qe=6.03 mg/g) and photodegradation (kv=0.115 min-1) of RhB by LCM-Bi2WO6 using H2SO4 as acidity regulator were observed compared with using HCl (qe=21.93 mg/g, kv=0.115 min-1) as acidity regulator, because of SO42- strong adsorption to LCM-Bi2WO6.
|
|
|
Component Optimization and Performance of Ti-Al-Si-Ox deNOx Catalyst Carrier
SHEN Yue-Song, ZONG Yu-Hao, SUI Guo-Rong, HAN Bing, ZHU She-Min
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 542–548
 Abstract
Abstract(
656 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(505KB)(
2607
)
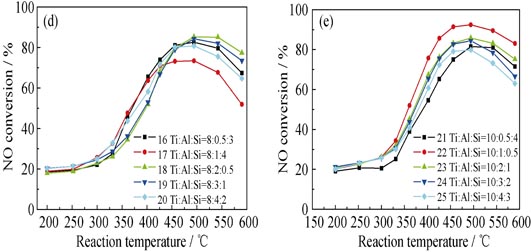
A series of Ti-Al-Si-Ox deNOx catalyst carriers were prepared by extrusion method and tested for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3. The Ti-Al-Si-Ox formulas were designed and optimized by orthogonal experiments, and the specific surface area, pore volume and size distributions, micro-morphology and solid-phase structure of the carriers were characterized by N2-BET, ESEM and XRD, respectively. Moreover, the water adsorption, open porosity and bulk density of the carriers were measured by Archimedes method. Results showed that the catalytic activity for NH3-SCR of NO and the axial crush strength of the TiAl0.2Si0.1Ox carrier matched the best when the Ti/Al/Si molar ratio was equal to 1:0.2:0.1. Under gas hourly space velocity (GHSV) of 7200 h-1, the TiAl0.2Si0.1Ox obtained more than 80% NO removal in active temperature range of 450-550℃, and obtained the maximum catalytic activity of 85.8% at 494℃. The axial crushing strength of the TiAl0.2Si0.1Ox was 6.17 MPa, its specific surface area was 89.1 m2/g, its open porosity was 63.0%, its water adsorption was 48.3%, the most probable meso pore distribution was 8.1 nm and the second probable pore distribution was 3.7 nm. In conclusion, the TiAl0.2Si0.1Ox deNOx catalyst carrier possesses excellent performance.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Er3+-doped ZnWO4
ZHOU Yu, ZHANG Zhi-Jie, XU Jia-Yue, CHU Yao-Qing, YOU Ming-Jiang
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 549–554
 Abstract
Abstract(
893 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(400KB)(
1317
)
Er3+-doped ZnWO4 nanorods with different doping concentrations were synthesized by a hydrothermal method. The as-prepared products were characterized by XRD, TEM and DRS. The photocatalytic activities of the as-prepared ZnWO4 samples were evaluated by photo-degradation of RhB under simulated solar light irradiation and the effects of Er3+ doping on the photocatalytic activity of ZnWO4 were investigated. The result showed that the sample with the doping concentration of 2mol% exhibited the best photocatalytic performance, which could be ascribed to the promoted charge separation efficiency of Er3+-doped ZnWO4.
|
|
|
Preparation of Perfective TAPO-5 Membrane through Tertiary Growth with Amorphous Seed
LIU Xu-Guang, MA Xin, LIU Yong, ZHANG Bao-Quan
2015 Vol. 30 (5): 555–560
 Abstract
Abstract(
604 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(504KB)(
2223
)
TAPO-5 membranes were synthesized through a tertiary growth method. Its perfection significantly depends on the adopted seed and itself poly-crystalline structure. Amorphous seed synthesized at a low crystallization temperature (393 K), obviously favors producing the perfective TAPO-5 membrane. TAPO-5 crystal seed, however, induces the growth of its membrane with a larger extent of cracks (i.e., grain boundary defect), destructing itself perfection. Those diverse results are associated with the disparate seeds layers deposited by a spreading-wetting method, and consistently demonstrated by SEM, XRD, and single gas (He) permeation test. A typical feature of the amorphous TAPO-5 seed layer is its dispersive distribution pattern in the macro holes of support. A continuous layer, however, is observed for the TAPO-5 crystal seed layer. The amorphous seed is explained as a prior seed for the perfective TAPO-5 membrane.
|
|