|
|
Research Progress in Atomistic Simulation on Ferroelectricity and Electromechanical Coupling Behavior of Nanoscale Ferroelectrics
WANG Xiao-Yuan, YAN Ya-Bin, SHIMADA Takahiro, KITAMURA Takayuki
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 561–570
 Abstract
Abstract(
1655 )
 HTML
HTML(
20)
 PDF
PDF(454KB)(
3072
)
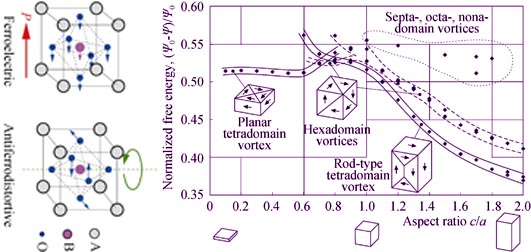
For nanoscale ferroelectric materials, their geometrical structures and characteristic sizes strongly affect the ferroelectricity, which are dominant factors for the reliability of functional materials in micro-electronics. Numerical simulation is an effective tool instead of the experimental method to investigate the physical properties of ferroelectrics. Particularly, when the characteristic sizes of these materials shrink to several nanometers, it may be the only option because no experimental testing system is available due to the restriction in specimen fabrication and measurement precision. In this paper, recent progresses in numerical simulations on the ferroelectricity of typical 2D, 1D and 0D nano-ferroelectrics are reviewed, especially researches on the polarization distribution, phase transition, critical size, and electromechanical coupling behavior of nanoscale ferroelectrics. Finally, the potential research emphases on numerical simulation of the nanoscale ferroelectrics are prospected.
|
|
|
Effects of Fiber Thickness and Volume Fraction on the Strain Performance of Piezoelectric Fiber Composites
CHEN Zi-Qi, ZHU Song, LIN Xiu-Juan, XIONG Wei, ZHOU Ke-Chao, ZHANG Dou
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 571–575
 Abstract
Abstract(
933 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(360KB)(
1540
)
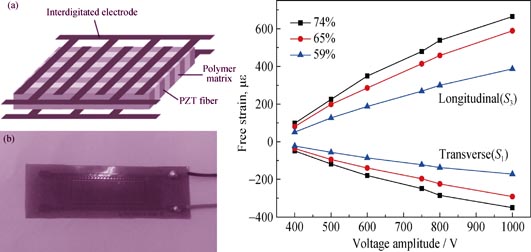
Piezoelectric fiber composite is an emerging smart material and exhibits much broader applications than traditional piezoelectric ceramics, especially in light-weight and curved structures. Piezoelectric fiber composites with different fiber thickness and volume fraction were fabricated. The effects of structural parameters, i.e. different fiber thickness and volume fraction, on the strain properties and actuation performance of piezoelectric fiber composites were investigated at different excitation voltages at frequency of 0.1 Hz. The results indicated that the free strain and tip displacement decreased with the increasing thickness of piezoelectric fiber. When 1000 V voltage was applied, the free strain and tip displacement for the composite with fiber thickness of 200 μm were 665 με and 1.9 mm, respectively, which were much higher than those of composite with fiber thickness of 300 μm or 400 μm. Piezoelectric fiber composites exhibited orthotropic actuation properties, and higher free strains with larger fiber volume fraction. The longitudinal and transverse free strains of composites with 74% fiber volume fraction were 2.04 and 1.72 times magnitudes of composites with 59% fiber volume fraction, respectively. The transverse effect coefficient, the ratio between transverse and longitudinal free strains, decreased from 0.519 to 0.451 when the fiber volume fraction decreased from 74% to 59%.
|
|
|
Fabrication of High Tc BaTiO3-(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 Lead-free Positive Temperature Coefficient of Resistivity Ceramics
LENG Sen-Lin, JIA Fei-Hu, ZHONG Zhi-Kun, YANG Qin-Fang, LI Guo-Rong, ZHENG Liao-Ying
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 576–580
 Abstract
Abstract(
932 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(406KB)(
1899
)
High curie temperature (Tc) (1-xmol%)BaTiO3-xmol%(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3(BBNTx) lead-free positive temperature coefficient of resistivity(PTCR) ceramics were prepared by the conventional solid state reaction sintering method. XRD patterns showed that all BBNTx samples had a single tetragonal phase perovskite structure. The SEM results showed that as the content of BNT increased from 1mol% to 60mol%, the average grain size monotonously decreased. The 0.2mol% Nb-doped BBNT1 ceramic sintered in air had low room-temperature resistivity (ρ25) of ~102 Ω·cm and high resistivity jump (maximum resistivity [ρmax]/minimum resistivity [ρmin]) of ~4.5 orders of magnitude with Tc at about 150℃. The 0.3mol% Nb-doped BBNTx(10≤x≤60) ceramics, sintered in N2, also showed distinct PTCR effect with Tc between 180℃ and 235℃. As the BNT content increased, the ρ25 of the BBNTx rapidly increased with the resistivity jump decrease.
|
|
|
Influence of Ball Milling Speed on Microstructure and Optical Transparency of Nd:YAG Ceramics
LIU Jing, LIU Jun, LI Jiang, LIN Li, PAN Yu-Bai, CHENG Xiao-Nong, GUO Jing-Kun
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 581–587
 Abstract
Abstract(
1362 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(611KB)(
1662
)
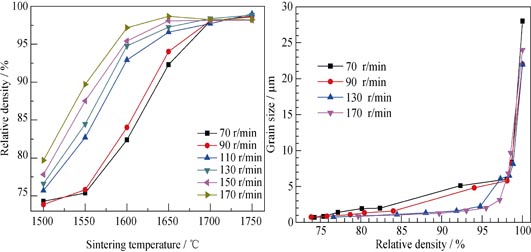
Transparent 1.0at%Nd:YAG ceramics were fabricated by the solid-state reaction and vacuum sintering method using Y2O3, α-Al2O3 and Nd2O3 as starting powders. These powders were mixed in ethanol with MgO and TEOS as sintering aids and ball milled at different speeds for 10 h. Effects of ball milling speed on the particle size of powder mixtures as well as the densification process, the microstructure and the optical transparency of Nd:YAG ceramics were mainly investigated. It is showed that coarse powders can be ground into fine particles with increase of the ball milling speed up to 130 r/min. Porosities of the sintered Nd:YAG ceramics decrease with the increase of ball milling speed. Al-rich secondary phase can be observed in the microstructure of Nd:YAG ceramics when the ball milling speed is over-high, and it will cause a decrease in the optical transmittance. For the sample sintered at 1760℃ for 50 h from the powder mixture ball milled at 130 r/min, the in-line transmittance reaches 83% at 1064 nm and there are almost no pores at the grain boundaries and inner grains.
|
|
|
Preparation and Performance of Ce:YAG Phosphor-in-glass
ZHANG Yan, LIU Sheng, XU Hong-Jie, WANG Lian-Jun, JIANG Wan
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 588–592
 Abstract
Abstract(
1332 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(381KB)(
2306
)
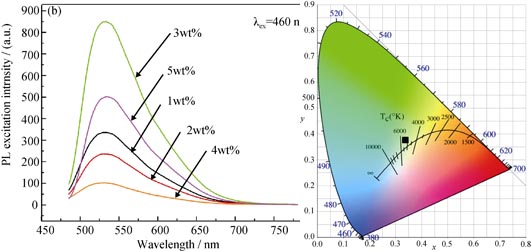
One-step spark plasma sintering (SPS) process was introduced to fabricate Ce:YAG phosphor-in-silica-glass (PiSG), of which the composite powder of glass powder/commercial Ce:YAG phosphor was directly obtained by ball mill grinding. The phase, microstructures, absorption spectrum and photoluminescence properties of PiSG samples were investigated by XRD, SEM, UV-Vis spectrophotometer, fluorescence spectrophotometer, etc. The results showed that the as-sintered PiSG sample had amorphous phase and the Ce:YAG phosphor particles was uniformly distributed in glass matrix with no size change, indicating that Ce:YAG phosphor particles were well preserved in silica glass matrix without any decomposition reaction. There was a strong absorption peak around 460 nm and a broad emission band peaked at 530 nm of PiSG sample. The properties of PiSG samples were studied by adjusting the phosphor concentration, demonstrating that the photoluminescence intensity reached the highest when Ce:YAG phosphor concentration was 3wt%. Besides, the optimized 3wt% PiSG based LED modules fell into white light range(0.33, 0.38) under 800 mA current drive.
|
|
|
Fabrication and Irradiation of Nanocrystalline Yttrium-stabilized Cubic ZrO2 Film
WANG Ka, WAN Kang, ZHANG Jing, CHEN Lin, CHEN Qiong, CHANG Yong-Qin, LONG Yi
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 593–598
 Abstract
Abstract(
847 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(542KB)(
1926
)
Nanocrystalline cubic yttrium-stabilized ZrO2 films (YSZ) were prepared on silicon substrate via Sol-Gel combined with spin-coating method. The as-grown films were characterized by optical microscope, SEM, XRD and TEM. It was found that preparation parameters have obvious effect on quality of the YSZ film. The quality of YSZ thin films can be greatly improved by adding PVA as dispersing agent, adopting the grading drying process and increasing the spin speed. Smooth films without any cracks can be obtained by optimum growth conditions. XRD result shows that the film is cubic structure with no other phase. The thickness of the YSZ film is about 60 nm, and its average grain-size is 9.4 nm. When the samples are irradiated by Xe ions with low dose at room-temperature, microscopic cracks are detected in the YSZ films. As the ion irradiation dose increases, the irradiation-induced cracks are gradually recovered, which might attribute to the thermal spike effect on the film. In addition, the average grain-size of the YSZ film grows with irradiation dose increasing.
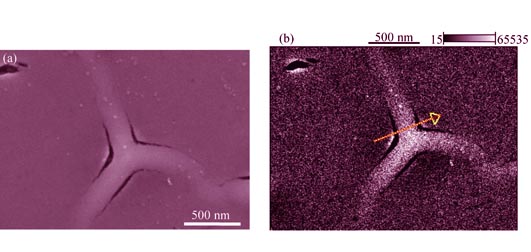
|
|
|
Facile Preparation Carbon-Doped TiO2 Nanotube Electrodes and Its Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Response
ZHAO Peng, LI Zhong, CUI Xiao-Li
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 599–604
 Abstract
Abstract(
834 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(477KB)(
2559
)
Nanostructured carbon-doped titanium dioxide were fabricated by thermal treatment of anodized titanium dioxide nanotube with the presence of NaHCO3. The resulted samples were characterized via X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and photoelectrochemistry methods. Anatase type TiO2 nanotubes and almost no influence from C doping were observed from XRD and SEM results. XPS spectra showed that the O was partly replaced by C in the resulted carbon-doped titanium dioxide nanotubes. Enhanced photocurrents were identified for the C-TiO2 nanotube and 1.7 times was observed in comparison to the TiO2. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy indicates the decrease of charge transfer resistance and flat band potential also negative shift from -0.28 V to -0.38 V. Needle- shaped dye sensitized solar cells were developed by using anodized Ti and Pt wire. Improved photovoltaic performance was demonstrated by the photocurrent density-photovoltage curves for DSSCs when the anodized Ti wire was thermal treated with the presence of NaHCO3. The short-circuit current and energy conversion efficiency were up to 0.17 mA/cm2 and 3.8%, respectively.
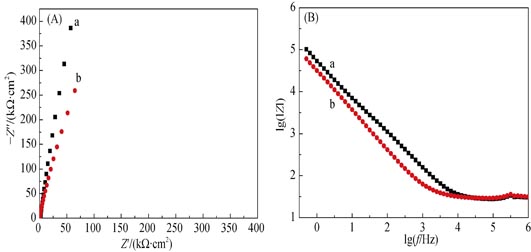
|
|
|
Synthesis of TiO2 Nanoparticles Using Hydrogel as Template and TiO2 Microspheres Using Microfluidic
DING Xue-Qiang, ZHANG Cheng, DONG Li-Min, WANG Chen, LIANG Tong-Xiang
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 605–609
 Abstract
Abstract(
981 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(406KB)(
2839
)
Poly (acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) and polyethylene glycol/polyacrylic acid as templates and acrylic acid as an inhibitor were used to prepare TiO2 nanoparticles. Hydrogel with low speed of absorption and network structure suppressed the speed of hydrolysis of tetrabutyl titanate and growth rate of TiO2 nanoparticles. The as-prepared titanium dioxide nanoparticles have anatase phase structure with a narrow size distribution. As compared with poly (acrylamide-co-acrylic acid), polyethylene glycol/polyacrylic acid has lower expansion rate of water-absorption and higher stability of precursor solution. Using microfluidic process, precursor solution of polyethylene glycol/polyacrylic acid is chosen to prepare TiO2 microspheres. These as-prepared TiO2 microspheres have a uniform size distrubition and good sphericity, which crystal structure is anatase phase after calcination.
|
|
|
Preparation of Porous Core/Shell Structure Fe2O3/Al Nanothermite Membrane by Template Method
ZHENG Guo-Qiang, ZHANG Wen-Chao, XU Xing, SHEN Rui-Qi, DENG Ji-Ping, YE Ying-Hua
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 610–614
 Abstract
Abstract(
915 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(416KB)(
2469
)
A three-dimensionally ordered macroporous(3DOM) α-Fe2O3 membrane was prepared by inversing polystyrene(PS) spheres colloidal crystal template, and nano aluminum was then introduced into the 3DOM α-Fe2O3 skeleton using magnetron sputtering method. Scanning electron microscope(SEM) images show that nano Al coats on surface of α-Fe2O3 skeleton uniformly, and pore structure converts into a kind of diamond from previously suborbicular after aluminizing with wall thickness increasing from 32 nm to 100 nm. Simultaneously, elemental analysis of the membrane is investigated via energy dispersive spectrum(EDS). Differential scanning calorimety(DSC) results indicate that onset temperature of the Fe2O3/Al nanothermite membrane is 490℃, and thermite reaction between Al and Fe2O3 can be divided into solid-solid reaction and liquid-solid reaction. The total heat release is 1374.7 J/g. Ignition performance of the energetic membrane is investigated by laser ignition test. Sparks spatter outward with dazzling light can be observed for 2.6 ms, demonstrating that Fe2O3/Al nanothermite membrane can be ignited normally.

|
|
|
Directly Synthesis of ZSM-22 Particles by Adding Polyurethane Foam in Ionic Liquid-directed Dry-gel-conversion
WEN Hai-Meng, SONG Jun, WANG Chong-Qing, ZHOU Yu, WANG Jun
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 615–620
 Abstract
Abstract(
951 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(443KB)(
2056
)
Pure-silica ZSM-22 particles with millimeter size were directly synthesized by adding polyurethane foam (PU foam) in ionic liquid-directed dry-gel-conversion process, where the dry gel was prepared under the unusual acidic condition for hydrolyzing the silica precursor with 1,3-alkylimidazolium ionic liquid as the structure directing agent (SDA). Both the PU foam and the ionic liquid-directed dry-gel-conversion process played essential roles in the formation of macroscopic morphology, because only powder-like sample could be obtained in the absence of foam, and moreover, no such special morphology could be achieved on ZSM-22 zeolite prepared by the PU foam-added traditional hydrothermal synthetic route. Various synthetic parameters were systematically studied, including the influence of PU foam, adding time and adding amount of PU foam, as well as the crystallization time. Pure phase ZSM-22 particles with the highest crystallinity can be obtained by adding appropriate volume of PU foam after microwave aging. Finally, the directly synthesized ZSM-22 particles were modified by impregnating CuO, which exhibited superior N2O adsorption property to the CuO-impregnated post-molded ZSM-22 particles with binding materials. The results indicate that there is an important influence of the macro-morphology on the adsorption performance of zeolites.

|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Mixed-conducting Supported Hollow Fiber Membrane
LIU Zheng-Kun, ZHU Jia-Wei, JIN Wan-Qin
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 621–626
 Abstract
Abstract(
846 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(485KB)(
1743
)
Sr0.7Ba0.3Fe0.9Mo0.1O3-δ (SBFM) hollow fiber supports were prepared by dry-wet spinning technology. SrCo0.8Fe0.2O3-δ doped Nb2O5 (SCFNb) was selected as membrane material, SCFNb/SBFM supported hollow fiber membranes were successfully prepared by a combined spin-spraying and co-sintering method. XRD, SEM, thermal expansion technique, oxygen permeability and membrane reaction tests were utilized to characterize the crystal phase structures, microstructure, sintering behavior, oxygen permeation flux, and reaction performance of membranes and/or supports, respectively. XRD patterns show that the membranes and supports are composed of perovskite main phase. SEM images indicate that the support has an asymmetric structure with a sponge-like microporous/finger-like porous structure. The membrane surface is dense and crack-free, and the membrane layer with a thickness of about 5 μm is well bonded with the support. At 900℃, the oxygen permeation flux of the membrane is 0.74 mL/(cm2·min). No degradation of performance is observed in the membrane reactor under partial oxidation of methane during continuously operating for 200 h at 850℃, and the oxygen permeation flux can reach 4.5 mL/(cm2·min). It is demonstrated that the SCFNb/SBFM supported hollow fiber membrane exhibits high oxygen permeation flux and good stability of the membrane reactor.
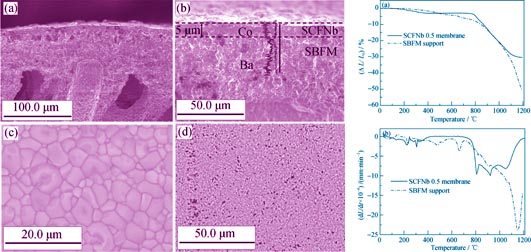
|
|
|
Effect of Sealing Treatments on the Corrosion Behavior of Micro-arc Oxidation Coating on Aluminum Alloy in Acid NaCl Solution
YE Zuo-Yan, LIU Dao-Xin, LI Chong-Yang, ZHANG Xiao-Hua, ZANG Xiao-Ming, LEI Ming-Xia
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 627–632
 Abstract
Abstract(
1124 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(496KB)(
1788
)
Ceramic coatings were fabricated on 7A85 aluminum alloy by unipolar positive pulsed micro-arc oxidation (MAO) treatment for enhancing corrosion resistance. A bi-layer coating was formed with large pores between the layers. The outer layer contained several micro pores and cracks. Therefore, cerium nitrate, potash bichromate and SiO2 sol were adopted to seal the MAO coatings. Scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffraction and electrochemistry instrument were used to investigate the effect of sealing treatments on the surface morphology, coating structure and corrosion resistance of MAO coatings. Results show that the MAO coating can not protect aluminum alloy from acid NaCl solution for the existing of defects. The defects can be sealed by precipitations produced by cerium nitrate and potash bichromate sealing treatment, and corrosion resistance of the MAO coating is improved. However, the sealed coatings also fail in the acid NaCl solution for dissolution of the precipitation. After sealing with SiO2 sol, the MAO coating is covered with a SiO2 gel layer has become a compact barrier layer to protect aluminum substrate from corrosion in acid NaCl solution.
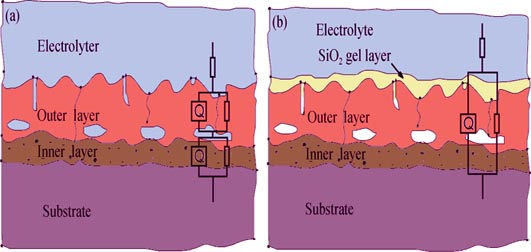
|
|
|
Mechanical Property and Deformation Behavior of SOFCs
LIANG Ling-Jiang, LI Kai, YAN Dong, MA Ben, YANG Jia-Jun, PU Jian, CHI Bo, LI Jian
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 633–638
 Abstract
Abstract(
1124 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(446KB)(
2350
)
Anode-supported planar solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) were successfully fabricated by tape casting, screen printing, and co-sintering technologies. Evaluated by the ring-on-ring and double-torsion technique, the flexure strength and fracture toughness of the single-cell are 156.69 MPa and 2.51 MPa•m1/2, respectively. And after the anode support being reduced from ceramic (NiO/YSZ) to cermet (Ni/YSZ), the flexure strength and fracture toughness change to be 104.48 MPa and 3.95 MPa•m1/2, respectively. Cell flexural deformation test indicates that with reduction of the anode support, the flexural deformation increases, the force for flattening cell increases (from 108 N to 184 N), and the rupture-resisting performance is enhanced. In conclusion, with notable improvement of cell fracture toughness after anode support reduction, the adverse influence caused by flexural deformation can be effectively mitigated and the comprehensive mechanical property can be improved.
|
|
|
Optimization of Electrode Material and Connecting Process for Mg-Si-Sn Based Thermoelectric Device
CHEN Geng, LIU Tao-Xiang, TANG Xin-Feng, SU Xian-Li, YAN Yong-Gao
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 639–646
 Abstract
Abstract(
1080 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(783KB)(
1975
)
Metal (Ni, Cu, Ag, Al) electrode was connected with Mg-Si-Sn based thermoelectric materials by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) process. Microstructure of interface, sintering process and transport properties, including electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient, of electrode materials were investigated. The results showed that composites of Ni-Al /Al (60:40) and Cu-Al/Cu (45:55) displayed high electrical conductivity, high thermal conductivity and suitable thermal expansion coefficient to Mg-Si-Sn based materials. It is indicated that the two composites have potential to be used as good electrode materials for, and to be connected by SPS sintering to, Mg-Si-Sn based materials.
|
|
|
Effect of Silicon Anode Additives on Lithium Ion Batteries
FENG Ming-Yan, TIAN Jian-Huan, LIU Yuan-Yuan, SHAN Zhong-Qiang
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 647–652
 Abstract
Abstract(
1265 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(571KB)(
2509
)
Silicon anode of lithium ion batteries was fabricated with different binders and conductive additives (acetylene black, SuperP, VulcanXC-72, BP2000), and the electrochemical performance was investigated in detail. The effect of morphology and addition amount of conductive additives on the electrochemical performance of silicon electrode were investigated. Then, the appropriate type and content of binder in the silicon electrode was optimized. The morphology of silicon electrodes were characterized by scanning electron microscope(SEM). Electrochemical performances of the silicon electrodes were measured by constant current charge-discharge and cyclic voltammetry(CV). The results shows that SuperP hasuperPlectrical conducitivity and good electrical conductivity, a suitable surface area of 75.8 m2/g and average particle size of 39.24 nm, which can improve cycling performance and rate performance of the silicon electrode. With 15wt% SuperP and 15wt% CMC, the electrode exhibits a reversible capacity of 1143.8 mAh/g after 50 cycles.
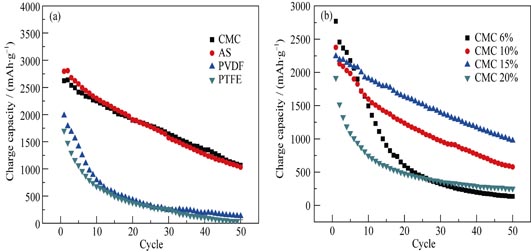
|
|
|
Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Red Phosphorus/Carbon Composites
TIAN Li-Yuan, YAO Zhi-Heng, LI Feng, WANG Yong-Long, YE Shi-Hai
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 653–661
 Abstract
Abstract(
1513 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(722KB)(
2672
)
Effect of different fabrication methods, composition of electrolytes and various carbon substrates on the electrochemical performance of red phosphorus/carbon composites were studied. The red phosphorus (red P)/active carbon (AC) composites synthesized via ball milling method exhibited a low coulombic efficiency and cyclic capacity in the initial cycle, meaning poor utilization ratio of red P. It was found that the optimal electrolyte was 1 mol/L LiPF6 in an ethyl carbonate (EC)/ethyl methyl carbonate (EMC)/dimethyl carbonate (DMC) mixed solvent. Red P/conductive carbon black (BP2000) and red P/AC composites were synthesized by a vapor deposition method. The morphology, structure and electrochemical performance of the as-prepared composites were characterized by thermal gravity analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), BET surface analysis and cyclic voltammetry (CV). Electrochemical results reveal that the red P/AC composite (45%P) has a good reversibility with charge/discharge potential plateau at 1.0 V and 0.75 V. The initial discharge/charge special capacity is 1500 and 1200 mAh/g (calculated based on the weight of composites), respectively, showing initial coulombic efficiency of 82.5%. In the subsequent cycles the coulombic efficiency is over 97.5%. The stable cyclic capacity is related to 2.8-electron reaction. Relying on the stable discharge capacity in the second cycle, the capacity retention is calculated to be 75.0% after 50 cycles. The as-prepared red P/AC composites exhibit high cyclic capacity and good cyclic stability, which can be attributed to the uniform dispersion of amorphous red P in the porous structure of AC substrate, especially in the micropores.
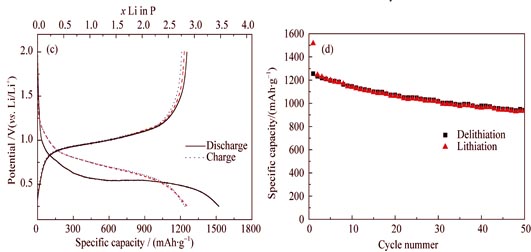
|
|
|
Enhanced Capacitive Properties of All-solid-state Symmetric Graphene Supercapacitors by Incorporating Nitrogen-doping and SnO2 Nanoparticles
YU Jian-Hua, XU Li-Li, ZHANG Wu-Shou, ZHU Qian-Qian, WANG Xiao-Xia, DONG Li-Feng
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 662–666
 Abstract
Abstract(
986 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(406KB)(
1340
)
Graphene and N-doped graphene were synthesized by a solvothermal process, and their composites with SnO2 nanoparticles were prepared by a facile one-pot chemical solution method. The corresponding films were fabricated by a blade coating process and followed by heat treatment at 400℃ for 1 h. All-solid-state supercapacitors were fabricated with graphene based films and a polymer gel of polyvinyl alcohol/H3PO4 as electrodes and electrolyte, respectively. The capacitance performance of the as-fabricated supercapacitors was characterized. The results suggest that compared with graphene, N-doped graphene exhibits larger crystalline size, lower specific surface area, yet superior capacitance performance, and the incorporation of SnO2 nanoparticles on graphene and N-doped graphene sheets enhances their capacitive characteristics.
|
|
|
Microstructure and Property of TiB2 Reinforced Reaction-bonded B4C Composites
LIN Qing-Qing, DONG Shao-Ming, HE Ping, ZHOU Hai-Jun, HU Jian-Bao
2015 Vol. 30 (6): 667–672
 Abstract
Abstract(
1352 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(332KB)(
2294
)
Dense B4C composites were fabricated by reaction bonding technique based on vacuum infiltration of silicon melt into green preforms made of microporous carbon, B4C and Ti powders. Phase assemblage and microstructure of the composites were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy dispersive spectrum (EDS) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The flexural strength and fracture toughness of the composite with 15wt% Ti in its preform were 313 MPa and 5.40 MPa•m1/2, respectively. The in-situ generated TiB2 played a positive role in strengthening and toughening material.
|
|