|
|
Research Progress of the Sealing Glass for Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell
LUO Ling-Hong, YU Hui, HUANG Zu-Zhi
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 113–121
 Abstract
Abstract(
1116 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(568KB)(
2937
)
Sealing glass plays a crucial role in the intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell (IT-SOFC). A sealing glass should have a combination of desired thermal, chemical and mechanical properties and good adhesive ability with other cell’s components in order to prevent gas leakage during the working of the IT-SOFC. It has to be a long-term thermal stability and interface chemical stability with other cell’s components at the operating temperatures with an oxidizing or reducing atmospheres, respectively. In this paper, the research progress of the sealing glass in recent ten years was reviewed. From the point of the properties of sealing glass and the interfacial reactions with other cell’s components, relations of the composition-structure-property were discussed. Main problems on current research of sealing glass of IT-SOFC were put forward.
|
|
|
Electrochemical Performance of 0.7LiFePO4ּ0.3Li3V2(PO4)3/C Cathode Materials Using Polyethylene Glycol as Carbon Source
MA Ping-Ping, LIU Zhi-Jian, XIA Jian-Hua, LU Zhi-Chao
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 122–128
 Abstract
Abstract(
960 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(632KB)(
2638
)
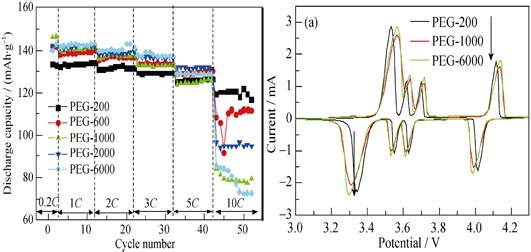
Different molecular weight of polyethylene glycol (PEG), including PEG-200, PEG-600, PEG-1000, PEG-2000 and PEG-6000, were used as carbon sources and reduction agents for preparation of 0.7LiFePO4?0.3Li3V2(PO4)3/C composites via spay-drying followed solid-state reaction approach. The structure and morphology of the 0.7LiFePO4?0.3Li3V2(PO4)3/C composite samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction(XRD), Raman spectroscope and field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM). The diffraction peaks of the synthesized compound were composed of both orthorhombic LiFePO4 and monoclinic Li3V2(PO4)3, indicating the synthesized compound is a mixture phase of LiFePO4 and Li3V2(PO4)3. The structure of residual carbon was characterized by Raman spectroscope. A lower intensity ratio of the ID/IG band for PEG-200 in Raman spectrum indicated more graphite clusters in the structure of carbon, which would enhance the electronic conductivity of the residual carbon. The composites showed higher discharge capacity, better rate capability and cyclic performance. Even at a high charge-discharge rate of 10C, it still maintained a discharge capacity of 120 mAh/g in the potential range of 2.0-4.3 V.
|
|
|
Effect of FePO4 Coating on Performance of Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 as Cathode Material for Li-ion Battery
LI Zhong, HONG Jian-He, HE Gang, Lü Lu
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 129–134
 Abstract
Abstract(
988 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(497KB)(
1520
)
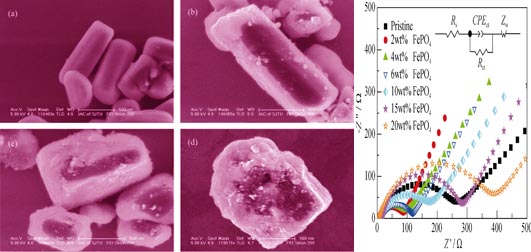
Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 with a rod-like morphology was prepared by a carbonate co-precipitation method followed by a high-temperature solid state reaction, and coated with different amounts of FePO4. XRD results and SEM images show that the particles of Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 are uniformly coated with amorphous FePO4. The amorphous FePO4 layer not only inhibits the reaction between Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 and electrolyte, but also acts as lithium ion receptor during the initial charging process. So, the surface modification of Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 with FePO4 reduces the initial irreversible capacity loss, and improves cyclic and rate performance. Specific electrochemical performance can be achieved by adjusting the amount of FePO4. Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 coated with 2wt% FePO4 exhibits the highest initial charge and discharge capacity, 325.9 and 258.4 mAh/g at 0.05C rate, respectively. The material coated with 4wt% FePO4 shows high discharge capacity and good cycle stability. And with the increase of FePO4 amounts, the initial coulombic efficiency increases greatly, reaching 97.4% for the sample coated with 20wt% FePO4.
|
|
|
Growth and Characterization of Er3+-doped Relaxor-based Ferroelectric Crystal PMNT
XIANG Jun-Tao, DU Peng, LUO Lai-Hui, FANG Yi-Quan, ZHAO Xue-Yang, HU Xu-Bo, CHEN Hong-Bing
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 135–140
 Abstract
Abstract(
926 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(444KB)(
1930
)
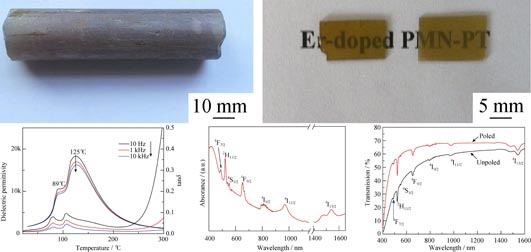
According to the molar ratio of 0.71Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.26PbTiO3-0.03Pb(Er1/2Nb1/2)O3, Er3+-doped PMNT polycrystalline material was prepared by two-step solid-state synthesis at elevated temperature. Er3+-doped PMNT relaxor-based ferroelectric crystal with size of φ25 mm × 100 mm was grown from the stoichiometric melts by vertical Bridgman method. In the ferroelectric crystal with perovskite structure, Er3+ ions were doped into the crystal lattice via one composition of the ternary solid solution compound. The dielectric, piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties and up-conversion emission performance of Er3+-doped PMNT crystal wafers were investigated systematically. It is verified that Er3+-doped PMNT crystal presents the similar electrical properties to those of undoped PMNT crystal. Under the excitation of 980 nm, the crystal also exhibits a strong up-conversion fluorescence emission characteristic to Er3+ ions doped in the medium, and the emission intensity will be enhanced after being poled.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Macroporous Mayenite Monoliths
GUO Xing-Zhong, CAI Xiao-Bo, SONG Jie, YANG Hui
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 141–146
 Abstract
Abstract(
899 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(533KB)(
1582
)
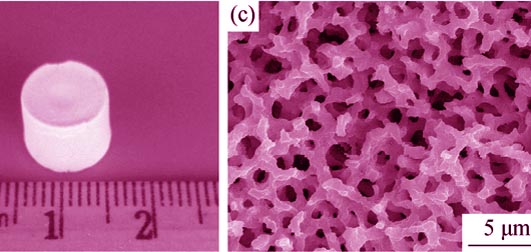
Macroporous mayenite monoliths were successfully prepared via Sol-Gel process accompanied by phase separation using calcium chloride dihydrate and aluminum chloride hexahydrate as raw materials, propylene oxide (PO) as a gelation agent, and poly (ethylene oxide) with average molecular weight of 100,000 as a phase separation inducer. In addition, glycol was used as a chelating agent and formamide as a drying control chemical additive. Macroporous monoliths were characterized by scanning electron microscope(SEM), mercury porosimetry, and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The result shows that the addition of PEO induces phase separation; the amount of PEO and the ratio of ethanol to water have an important effect on porous structure, and monolithic mayenite with co-continuous marcoporous structure is obtained at appropriate addition of PEO and solvent as well as gelation temperature. The dried gels are amorphous, and transform to Ca12Al14O32Cl2 after heat-treatment at 1000℃ in air, while the co-continuous macropores are retained. The monolith after heat-treatment has narrow pore size distribution of 1-2 μm and porosity of 73.0%. The monoliths before and after heat-treatment possess smooth and dense skeletons.
|
|
|
Preparing Porous Si-based Ceramic Core Using Thermosetting Silicon Resin Injection Method
YANG Zhi-Gang, YU Jian-Bo, LI Chuan-Jun, XUAN Wei-Dong, ZHANG Zhen-Qiang, DENG Kang, REN Zhong-Ming
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 147–152
 Abstract
Abstract(
779 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(480KB)(
1409
)
The porous Si-based ceramic core was prepared using injection method, where quartz glass powders were used as original materials and thermosetting silicon resin was used as plasticizer. The effect of sintering temperature and holding time on the properties of the samples were examined. It was found that the process of devitrification was accelerated with the increase of sintering temperature while the glass phase transforms into cristobalite gradually. When sintering temperature was at 1250℃, the amount of cristobalite increased with the extension of holding time. Linear shrinkage rate and weight loss of the samples slightly increased with the increase of sintering temperature. But the holding time showed less effect on linear shrinkage rate and weight loss of the samples. In fact, the weight loss of the sample was mainly caused by decomposition of silicon resin. The sample sintered at 1250℃ for 10 h showed linear shrinkage of 0.93%, the porosity of 32.8% and bending strength of 9.08 MPa.
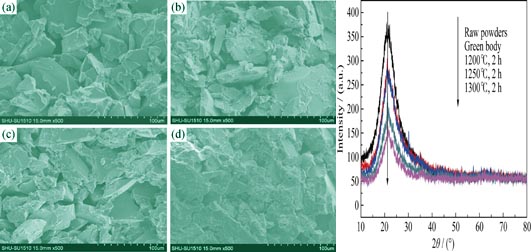
|
|
|
Densification Behavior of Thermal Gradient CVI of Large-scale C/C Composites
LI Yan, CUI Hong, ZHANG Hua-Kun, JI A-Lin, JIE Yu-Jie
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 153–158
 Abstract
Abstract(
927 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(547KB)(
1991
)
Using integral carbon felt as reinforced perform, large-scale C/C composites were prepared by thermal gradient-chemical vapor infiltration (TG-CVI) with two temperature controlling ways, namely keeping constant temperature of the inner wall or outer wall of the samples. The results indicated that, for keeping constant temperature of the outer wall, the composite density was merely 0.64 g/cm3, showing high-low-high distribution across the wall. Meanwhile, its structure comprised rough laminar and smooth laminar. For keeping constant temperature of the inner wall, the density of the sample showed evenly distribution across the wall and increased to 0.98 g/cm3, and densification efficiency was 73.79%, higher than that of the former. Under this temperature controlling way, the composite comprised only rough laminar carbon with superior properties. Compared to the outer wall temperature controlling, the composite prepared by the inner wall temperature controlling, needed higher temperature and more appropriate temperature gradient during densification, which was consistent well with the ideal densification model. Moreover, the inner wall temperature controlling way enabled the large-scale C/C composite densification from inner side to outside wall, and achieved uniform density distribution, high densification efficiency and excellent microstructure.
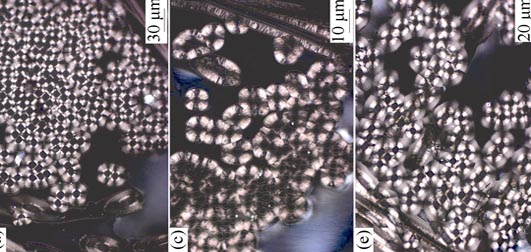
|
|
|
Effect of Silicon Source on Biomorphic SiC Fibers Converted from Natural Fibers
YUAN Wen-Yu, CHENG Lai-Fei,WU Heng, LIU Yong-Sheng
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 159–164
 Abstract
Abstract(
658 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(533KB)(
1492
)
Converting the natural fibers into biomorphic ceramics has been a novel and promising method to produce porous ceramics. This research explored a novel preparation method of biomorphic SiC fibers (SiCf), and its silicon source’s effects on the production. The results suggest that the silicon in vapor, compared to melting silicon, can provide much slower reaction velocity which can enable the reaction more controllable, leading to stronger mechanical properties of the final product, the SiC fiber. Besides, different kinds of silicon sources have great difference in influence on the reaction rate, temperature, grain size and purity. Among the silicon sources, SiO is an ideal source of the porous SiC fiber.
|
|
|
Influence of TiO2 Content on the Tensile and Actuation Properties of Piezoelectric Fiber Composites
CHEN Hai-Yan, LIN Xiu-Juan, CHEN Zi-Qi, ZHOU Ke-Chao, ZHANG Dou
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 165–170
 Abstract
Abstract(
839 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(470KB)(
1573
)
Piezoelectric fiber composites (PFCs) composed of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) fibers with interdigitated electrodes (IDEs) were prepared by viscous polymer processing technique. The influence of TiO2 content in epoxy resin on the electrical impedance, tensile properties and actuation performance of PFCs was investigated and characterized. The experimental results showed that the resonant frequency of PFCs was influenced by TiO2 content in the epoxy resin heavily. With the increase of TiO2 content in epoxy resin, tensile strength and longitudinal free strain of PFCs were enhanced firstly and then decreased. When the TiO2 content in epoxy resin was increased to 3wt%, the tensile strength reached the maximun value, 77.50 MPa. The longitudinal free strain of PFCs reached 1783.7 με when PFCs with 3wt% TiO2 in epoxy resin were under the excitation voltage range of -500 V to +1500 V at 0.1 Hz. Both tensile properties and actuation performance of PFCs decreased when TiO2 content increased from 3wt% to 5wt%. PFCs exhibited different actuation performance when excitation electric field with different frequencies was applied to PFCs. With the increase of excitation frequency, the longitudinal free strain values of PFCs displayed an obvious decrease at first and then decreased slowly when excitation frequency was over 5 Hz.
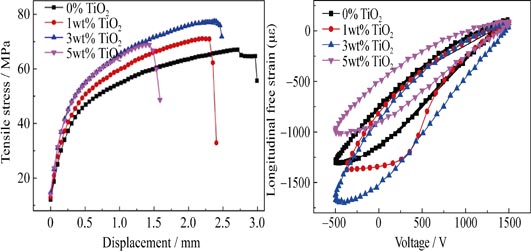
|
|
|
Preparation of La-doped TiO2 Ultrafiltration Membrane by Templating of Block Copolymer
CHEN Tao-Tao, LI Dan, JING Wen-Heng, FAN Yi-Qun, XING Wei-Hong
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 171–176
 Abstract
Abstract(
697 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(517KB)(
2169
)
La-doped TiO2 ultrafiltration membrane was prepared via a block copolymer assisted polymeric Sol-Gel process. The effects of La doping on the mechanical property of TiO2 gel, the crystal phase transformation and mesostructure of TiO2 materials were investigated by dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), N2 adsorption-desorption, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS) analysis. Results showed that the mechanical strength of the formed gel was significantly improved by the introduction of lanthanum, by which the risk of the membrane cracking could be reduced largely. X-ray diffraction analysis showed that La doping inhibited the TiO2 crystal phase transformation and the anatase phase could still keep stable at 800℃. Furthermore, the BET surface area and porosity of the materials were also increased. The optimal La doping amount was 0.74 g, and the formed TiO2 sol particle size was 10 nm. Futher more, the filtration experiments showed that the La-doped TiO2 ultrafiltration membrane possessed a pore size of 2.3 nm, while the pore size of the La-undoped TiO2 membrane was 2.7 nm.
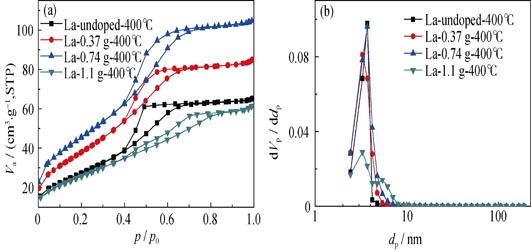
|
|
|
(Y, Lu)AG:Ce Phosphors Synthesized by Stearate Melting Method and Their Fluorescence Properties
LI Jin-Sheng, SUN Xu-Dong, LI Xiao-Dong, LIU Shao-Hong, ZHU Qi
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 177–182
 Abstract
Abstract(
967 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(507KB)(
1756
)
[(Y1-xLux)1-yCey]3Al5O12 (x=0-0.5, y=0.005-0.03) garnet powders were prepared by a novel stearate melting method. The phosphor powders were analyzed by XRD, SEM, BET and PL-PLE. The results show that phase-pure garnet can be obtained upon calcination at a relatively low temperature of 800℃, without involvement of YAlO3 (YAP) and Y4Al2O9 (YAM) intermediate phases. The resultant [(Y1-xLux)1-yCey]3Al5O12 phosphor powders are well dispersed, and show the highest emission at 544 nm under excitation wavelength at 455 nm. The emission intensity increases with increasing calcination temperature, due to improved crystallinity of the powder and removal of surface defects at high temperatures. The quenching concentration of Ce3+ is found to be 1.5% and the quenching mechanism is proposed to be Ce-Ce interactions and lattice defects. PL band of the phosphor red shifts with the increase of Ce3+ content, while the strongest excitation and emission bands are blue shift with increasing Lu3+ doping, due to combination effects of centroid shift and crystal field splitting of the Ce3+ 5d energy levels.
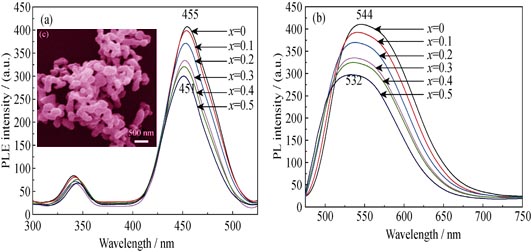
|
|
|
Preparation of TiO2: Er3+ Hollow Spheres and Its Photocatalytic Properties
QU Xiao-Fei, LIU Lu-Ying, LI Xue-Qin, DU Fang-Lin
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 183–188
 Abstract
Abstract(
916 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(493KB)(
1593
)
Using tetrabutyl titanate, erbium oxide and nitric acid as raw materials, TiO2: Er3+ hollow spheres were prepared with carbon spheres as template. The structures and morphologies of the obtained samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The photocatalytic activities were studied by degradation of organic pollutants (rhodamine B, methylene blue, alizarin red, methyl orange) using UV-Vis spectrophotometer. The factors, such as Er3+ dopant concentration, pH of the dye solution, on the photocatalytic activities were discussed. The results showed that uniform and well crystallized TiO2: Er3+ hollow spheres in an anatase phase, with diameter of 120 nm could be obtained via carbon-template method followed by a heat treatment at 600℃ for 3 h. The specific surface area of the TiO2: Er3+ hollow spheres was about 60.5 m2/g. When the Er3+ dopant concentration was 0.5 mol% of Ti4+ ions in TiO2, the photocatalytic activity of catalyst on the methyl orange was better than the other samples. Among the four different organic pollutants, the photocatalytic activity on the alizarin red was best. TiO2: 0.5mol%Er3+ showed the better photocatalytic properties than the undoped TiO2. The photodegradation efficiency of alizarin red with TiO2: 0.5mol%Er3+ was 30% higher than that with the undoped TiO2 under UV light irradiation.
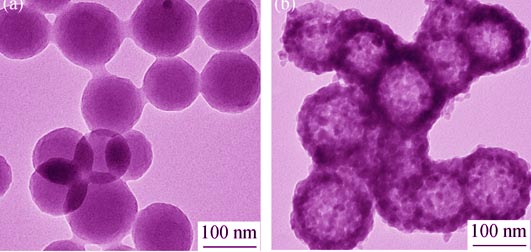
|
|
|
Influence of Calcination Temperature on Nano-TiO2 Photocatalyst Synthesized by Gliding Arc Plasma
LIU Shi-Xin, LI Xiao-Song, DENG Xiao-Qing, SUN Zhi-Guang, ZHU Ai-Min
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 189–194
 Abstract
Abstract(
749 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(577KB)(
1333
)
TiO2 nanopowders with different morphologies and initial anatase contents (fA) were synthesized by gliding arc plasma. X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and physisorption instruments were employed to investigate the effects of calcination temperature on phase composition, crystal size, morphology and specific surface area (SBET) of the TiO2 nanopowders. Photocatalytic oxidation of methylene blue was utilized to evaluate the activities of calcined TiO2 nanopowders. The results indicate that the anatase-rutile transformation temperature of as-synthesized TiO2 nanopowders is around 650℃, and the anatase-rutile transformation rate depends on the calcination temperature, morphology and the initial fA. With the increase of calcination temperature, the anatase crystal size slightly increases and SBET slightly decreases for spherical particles, while for non-spherical particles, the anatase crystal size increases and SBET decreases rapidly. With the increase of fA, the variation of photocatalytic apparent rate constant (k) of TiO2 nanopowder presents three profiles: when fA is below 70%, k slowly increases; when fA ranges from 70% to 85%, k rapidly increases; when fA is beyond 85%, k rapidly decreases.
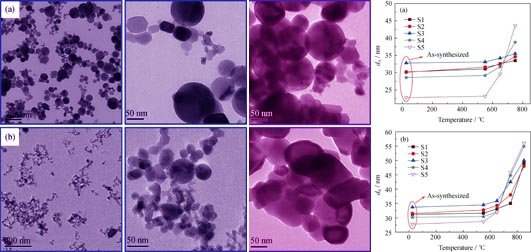
|
|
|
Influence of Alcohol on Performance of Ce0.65Zr0.35O2 and Its Corresponding Pd-only Catalyst in Ageing System
HUANG Li -Hua, CHEN Shan-Hu, GONG Mao-Chu, CHEN Yao-Qiang
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 195–201
 Abstract
Abstract(
672 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(506KB)(
1548
)
CZ oxygen storage material was prepared by co-precipitation method. The ethanol-water, propyl alcohol-water, ethylene glycol-water, and glycerol-water ageing systems were used to age the precipitate. CZ was characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and nitrogen sorption techniques. Their corresponding Pd/CZ were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), oxygen storage capacity (OSC), and hydrogen temperature-programmed reduction (H2-TPR) techniques. The results showed that the CZ prepared in ethanol-water and propyl alcohol-water ageing system exhibited large BET surface and pore size, high pore volume, as well as excellent thermal stability. The propyl alcohol-water imparted CZ the highest thermal stability, with BET surface of 28 m2/g and pore volume 0.1 mL/g after ageing. The corresponding aged Pd/CZ showed prominent catalytic performance. The T50 and T90 of C3H8, CO and NO were lower than those over the catalysts prepared in ethylene glycol-water and glycerol-water ageing system obviously.
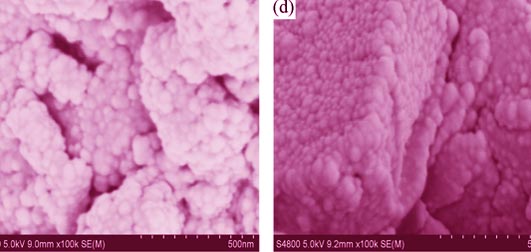
|
|
|
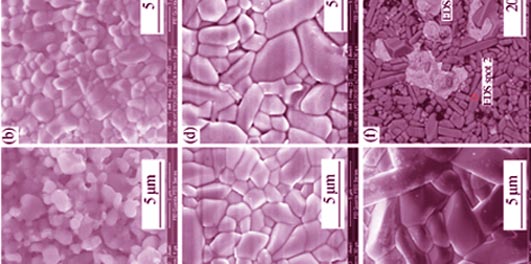
Microwave Dielectric Properties of BiMg2VO6 Ceramic with Low Sintering Temperature
XIE Hui-Dong, XI Hai-Hong, LI Fei, CHEN Chao
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 202–206
 Abstract
Abstract(
1095 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(460KB)(
2164
)
A low firing microwave dielectric ceramic BiMg2VO6 was prepared via conventional solid state reaction method. The chemical compatibility, phase, morphology, density and microwave dielectric properties of the ceramic in the sintering temperature range of 720~840℃ were studied. The infrared reflectivity spectra of the ceramic were measured. Results showed that the BiMg2VO6 ceramics did not react with Ag at 780℃ and the relative densities of the samples were greater than 93.8% at every sintering temperature conditions. Ceramic sintered at 780℃ for 2 h showed the optimum microwave dielectric properties with permittivity of 13.34, Q×f value of 15610 GHz (f= 8.775 GHz) and temperature coefficient value of -87.2×10-6/℃. The optical frequency permittivity was 3.4 and the extrapolated value to microwave frequency was 13.5. The optimum microwave dielectric properties and low sintering temperature of BiMg2VO6 ceramic enable it a promising candidate for low temperature co-fired ceramic applications.
|
|
|
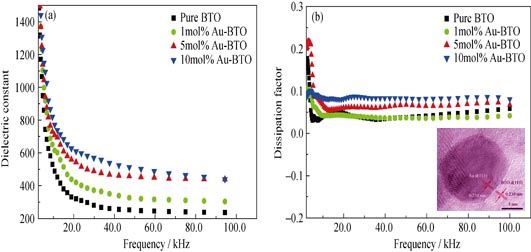
Dielectric Properties of Au-BaTiO3 Nanocomposite Films Prepared by Sol-Gel Method
WU Ying-Jie, WANG Hai-Ling, NING Xing-Kun, WANG Zhan-Jie, WANG Qiang
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 207–213
 Abstract
Abstract(
982 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(557KB)(
1359
)
Au-BaTiO3 nanocomposite thin films were prepared on Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si substrates by a Sol-Gel method and their crystal structure, microstructure and dielectric properties were investigated. Au nanoparticles with diameter of 5-22 nm are distributed in the BaTiO3 matrix. Au concentration has great effects on the surface morphology and dielectric properties of the composite thin films, and the optimal concentration of Au is about 5mol%. The composite thin films have crystallized into the perovskite phase after annealing at 550℃, and their dielectric constant is equivalent with that of the pure BaTiO3 thin films annealed at 700℃. The enhanced crystallization of Au-BaTiO3 composite film is attributed to the addition of Au nanoparticles, which can promote the decomposition of the intermediate phase and induce a heterogeneous nucleation of the perovskite phase. Thus, the annealing temperature of the composite films is drastically reduced and their dielectric properties are improved significantly with the addition of Au nanoparticles.
|
|
|
Comparative Study on Planar-silicon and Nano-silicon Si/PCBM Inorganic-organic Hybrid Junctions
LIU Wei-Feng, BIAN Ji-Ming, LUO Ying-Lin, QIAO Jian-Kun, ZHAO Chun-Yi
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 214–218
 Abstract
Abstract(
916 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(346KB)(
1190
)
Inorganic-organic heterojunction devices based on organic polymer and inorganic semiconductors has attracted extensive attention for high performance hybrid solar cell applications, due to the combined advantage of high carrier mobility of inorganic semiconductors and easy processing, strong absorption of organic polymers. In this study, both planar-Si and nano-Si were combined with spin-coated [6, 6]-phenyl C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM) organic film to form Si/PCBM inorganic/organic hybrid junctions. A comparative study was performed through quantitative electrical analysis of planar-Si/PCBM and nano-Si/PCBM, respectively. In general, both devices exhibited a rectifying diode-like behavior. However, a higher turn-on voltage and smaller current density were observed from nano-Si/ PCBM junctions, which was in contradiction with the expectation from the view of junction area. The corresponding mechanisms were further investigated with measurements of impedance spectroscopy (IS). Our results indicated that this abnormal electrical characteristic of nano-Si/PCBM compared with normal p-n junction was highly associated with the parasitic effects caused by the defect states at the junction interface.
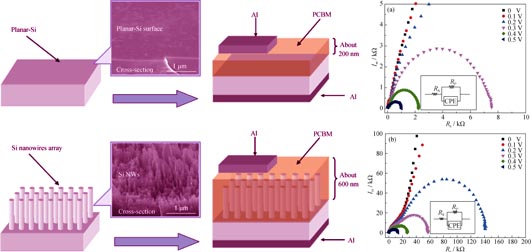
|
|
|
Effect of Polarization on Mechanical Properties of Lead Zirconate Titanate Ceramics
YU Yao, WANG Xu-Sheng, LI Yan-Xia, YAO Xi
2015 Vol. 30 (2): 219–224
 Abstract
Abstract(
1328 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(759KB)(
2010
)
This study concerns two following commercial lead zirconate titanate (PZT) materials, “soft” PZT-5H and “hard” PZT-8 piezoelectric ceramics. Young’s modulus and internal friction versus temperature at different vibration frequencies were investigated by means of Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) before and after polarization. The phase transition temperatures (Tc) of PZT-5H and PZT-8 ceramics were 438 K and 550 K. PZT-8 ceramic had higher Young’s modulus than PZT-5H ceramic at ferroelectric phase, which resulted from the increase of internal local stress in PZT-8 ceramic. After polarization, the Young’s modulus of both PZT ceramics increased, the influence of the piezoelectric effect was investigated. A relaxation peak emerges in internal friction curve of each PZT sample. Considering the hard ceramic, this peak is a pure relaxation mechanism controlled by oxygen vacancies diffusion. Considering the soft ceramic, the relaxation peak can be related to viscous motion of domain walls and the interaction between domain walls and point defects. The activation energy of the relaxation peak increased after polarization, which resulted from the increased local internal stress and directional arranged space charges caused by polarization.
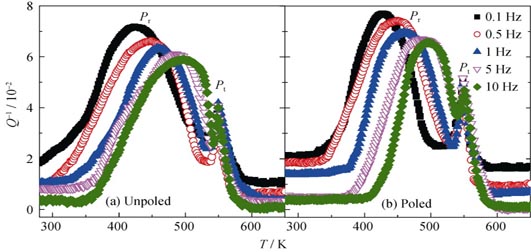
|
|