|
|
Rapid Development and Critical Issues of Secondary Lithium-air Batteries
GUO Xiang-Xin, HUANG Shi-Ting, ZHAO Ning, CUI Zhong-Hui, FAN Wu-Gang, LI Chi-Lin, LI Hong
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 113–123
 Abstract
Abstract(
2148 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(791KB)(
3614
)
Rechargeable lithium-air batteries have been the focus in recent years, owing to their great potential for achieving super-high specific energy density. Many researchers have carried out investigations on crucial issues such as reaction mechanism, cycle life, overpotential, rate capability, and significant progresses have been made. Based on these efforts, in combination with our own experience, this paper summarizes recent development of secondary lithium-air batteries, and our opinions on the critical scientific issues which are urgently required to solve in view of real application.
|
|
|
Fabrication and Excellent Catalytic Performance of Three-dimensional Ordered Mesoporous Molybdenum Oxides
DU Yu-Cheng, ZHENG Guang-Wei, MENG Qi, WANG Li-Ping, FAN Hai-Guang, DAI Hong-Xing
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 124–130
 Abstract
Abstract(
956 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(676KB)(
2133
)
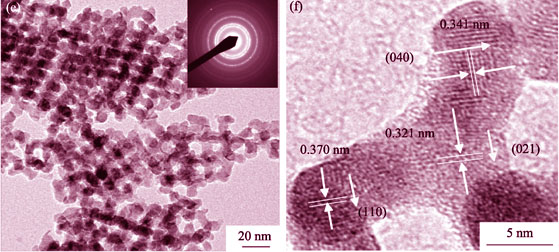
Three-dimensional (3D) ordered and wormhole-like MoO3 mesoporous structures were synthesized based on ultrasound-assisted vacuum impregnation method. Carbon template was used in the synthesis process, which was prepared by using mesoporous molecular sieve KIT-6. Hexaammonium molybdate acted as molybdenum source. The as-prepared MoO3 samples were characterized by transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetric analysis/differenctial scanning calorimetry (TG/DSC), and N2 adsorption-desorption measurement. The catalytic performance of MoO3 mesoporous structure was evaluated by hydrogen temperature-programmed reduction (H2-TPR), and complete oxidation of toluene and carbon monoxide (CO). It was found that the initiation temperatures of toluene were 203℃, 215℃ and 225℃, respectively, and the initiation temperatures of CO were 114℃, 158℃ and 180℃, respectively, with their conversion rates of 50%, 90% and 100%, respectively. The well catalytic performance was attributed to 3D ordered mesoporous structure and high surface area of as-obtained MoO3 materials.
|
|
|
Effects of pH on the Structure of Titania Prepared via Ionic Liquid-assisted Hydrothermal Method
WANG Kai, ZHANG Li-Juan, XU Zhi-Jian, QI Bin, DI Lan-Bo, ZHANG Xiu-Ling
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 131–136
 Abstract
Abstract(
863 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(501KB)(
2422
)
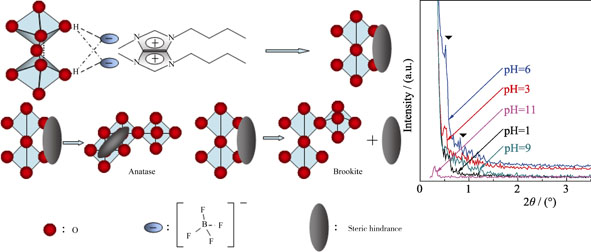
The mesoporous anatase TiO2 material was prepared by ionic liquid-assisted hydrothermal method using tetrabutyl titanate as titanium source and ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimida-zolium tetrafluoroborate ([C4MIM]BF4) as template. The pH values of the starting suspensions were adjusted from 1 to 11 using HCl or NH3·H2O solution. The influence of pH on the ionic liquid-water system for the preparation of titanium dioxide was investigated. The obtained TiO2 samples were characterized with X-ray diffraction (XRD) and N2 adsorption-desorption measurements, respectively. The results showed that the addition of ionic liquid inhibited the formation of the brookite TiO2, and increasing pH values enhanced the crystallization. When the pH was changed at a wide range (pH=1~9), the pore size distributions of the samples were relatively narrow, and the average pore diameter was reduced from 6.6 nm to 5.0 nm by increasing pH value. At the same time, the average size of the TiO2 nanoparticles in the samples was controlled at about 9 nm by using ionic liquid-assisted hydrothermal method. This is consistent with the results of the transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses.
|
|
|
Preparation of Organic/Inorganic Membrane by PDMS Low-temperature Pyrolysis
YU Jiao-Zhu, LI Lin, JIN Xin, DING Ling-Hua, WANG Tong-Hua
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 137–142
 Abstract
Abstract(
1034 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(537KB)(
1788
)
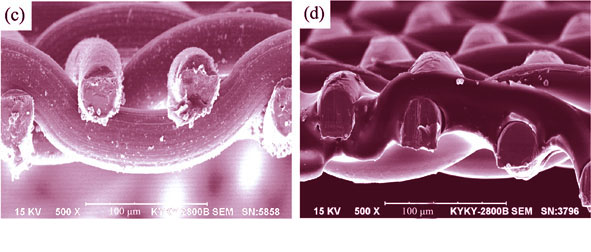
The organic/inorganic membranes were prepared via low-temperature pyrolysis of polymers. Firstly, polymeric membranes were prepared by dip-coating method using PDMS as the precursor and stainless steel as the support. Then they were pyrolyzed at 350–480℃ under inert atmosphere. The effects of preparation conditions on the gas separation performance of the organic/inorganic membranes were investigated. Chemical structure changes of PDMS in the pyrolysis process were studied by TG and FT-IR. The morphology of organic/inorganic membrane was characterized by SEM. The results showed that the organic/inorganic membranes with good gas separation performance could be successfully prepared by low-temperature pyrolysis of PDMS. The membrane retains part flexibility of PDMS, and presents good thermostability and high gas permselectivity. The gas separation performance and membrane layer structure of organic/inorganic membranes are greatly affected by the preparation conditions such as the PDMS concentration, coating times, pyrolysis temperature and properties of support. The gas separation performances prepared under the optimum condition are that the O2 permeation flux of 21.2 GPU(1 GPU=7.501×10-12m3(STP)/(m2?s?Pa)) and O2/N2 selectivity of 2.28.
|
|
|
Effect of Coagulation Bath in Phase Inversion on Microstructure of Hollow Fiber Porous Al2O3 Support
CHEN Yuan-Yuan, SHI Zhen-Zhou, ZHANG Chun, GU Xue-Hong
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 143–148
 Abstract
Abstract(
795 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(498KB)(
2393
)
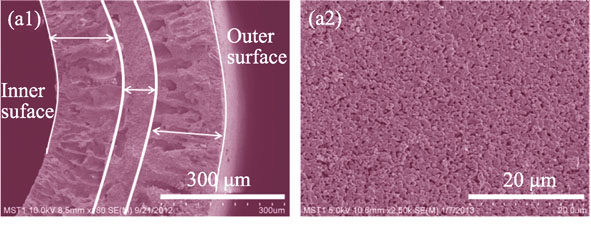
Al2O3 hollow fiber porous supports with asymmetric structures were prepared by phase inversion method. The effects of ethanol/water solution with different contents as internal and external coagulation baths on the microstructure and performance of as-synthesized hollow fiber supports were investigated. The results indicated that the finger-like voids on inner side of support extended outwards and the pore size increased as well with the increasing of ethanol content in external coagulation bath when using water as internal coagulation bath. The three-point bending strength of the support increased firstly and then decreased, meanwhile pure water flux and N2 permeance decreased firstly and then increased. The internal coagulation also had an effect on the structure of hollow fiber porous supports. When using ethanol and water as internal and external coagulation baths, respectively, the as-synthesized hollow fiber supports possessed sponge-like layer on inner side and finger-like voids on outer side. The N2 permeance and pure water flux were about 6.85×10-5 mol/(s·m2·Pa) and 4.5 m3/(m2·h) for the hollow fiber supports.
|
|
|
Growth Process of SiC Grains Prepared by High-energy Microwave Irradiation
HUANG Shan, WANG Ji-Gang, LIU Song, LI Fan
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 149–154
 Abstract
Abstract(
789 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(549KB)(
1619
)
High-energy vacuum microwave irradiation was directly applied to synthesize silicon carbide (SiC). Results indicated that the well-crystallized β-SiC grains can be obtained rapidly and conveniently via microwave approach, even simply constituents covering silica dioxide powders and artificial graphite were employed as raw materials. Based on the comprehensive micro-structural characterizations, the formation of β-SiC, under high-energy vacuum microwave irradiation, could be properly explained by the mechanism of two-dimension nucleation and growth. Besides, the technology of electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD) was particularly used to characterize the crystal plane of the observed SiC grains. The corresponding calculation of Euler angles suggested that the fastest-growing crystal planes {211} should be overlapped gradually, and the evolution from {211} to {220} crystal planes should be realized through the formation of {421} transformation plane. The most stable crystal planes of {111} became the regular hexagonal planes in the end, which can be explained by the Bravis rule. Correspondingly, the {220} crystal planes were finally existed as the side-planes of SiC grains. The detailed EBSD investigation provided the experimental evidences for the evolution of crystal planes in the growth process.
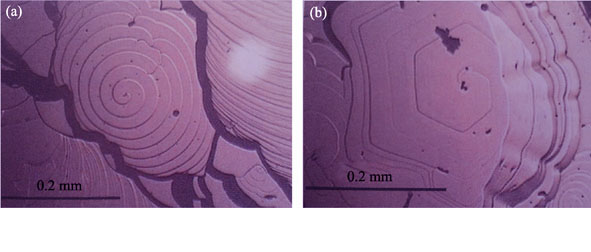
|
|
|
p-type Sodium-doped Zinc Oxide Nanowire Arrays Grown by High-pressure Pulsed Laser Deposition
QIU Zhi-Wen, YANG Xiao-Peng, HAN Jun1 ZENG Xue-Song, LI Xin-Hua, CAO Bing-Qiang
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 155–161
 Abstract
Abstract(
792 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(693KB)(
1647
)
Sodium-doped ZnO (ZnO:Na) nanowire arrays were grown with high-pressure pulsed laser deposition (HP-PLD). The influence of growth pressure and thickness of gold catalyst layer on the growth of ZnO:Na nanowires were systemically studied. It is found that c-orientated ZnO nanowire arrays grow on single crystal silicon substrates under the optimized condition, e.g. gold catalyst layer’s thickness of 4.2 nm, growth pressure of 3.33×104 Pa and growth temperature of 875 ℃. X-ray diffraction pattern and X-ray photoelectron spectroscope analyses indicate that Na is introduced into ZnO nanowires successfully. Optical fingerprints of sodium-related acceptors in the low-temperature (15 K) photoluminescence spectrum are observed, such as neutral acceptor-bound exciton emission (3.356 eV, A0X), free-electron to neutral-acceptor emission (3.312 eV, (e, A0)), and donor-to-acceptor pair emission (3.233 eV, DAP). ZnO:Na nanowire arrays grown on ZnO:Al/sapphire substrates form the pn junction. The corresponding I-V curve measurements exhibit a clear rectifying behavior of pn homojunction, which further indicates that such ZnO:Na nanowire is of p-type conductivity.
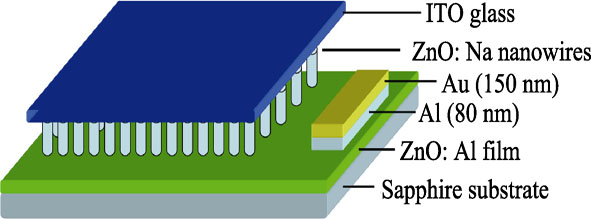
|
|
|
Influence of F/Cl Ratio on the Crystal Growth and Luminescence Properties of PbFCl Crystals
ZHANG Guo-Qing, YANG Fan, WU Yun-Tao, SUN Dan-Dan, SHANG Shan-Shan, REN Guo-Hao
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 162–166
 Abstract
Abstract(
762 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(449KB)(
1549
)
Lead fluoride chloride (PbFCl) crystal has been proposed for dual readout application as it has excellent properties. In this study, the PbFCl crystals were grown with different F/Cl ratios in the raw materials by modified Bridgman method. It is observed that excessive PbCl2 in the raw materials is helpful to grow transparent crystals, meanwhile it may enhance the cleavage. The excessive PbF2 or PbCl2 only modifies the cell parameters, not the phase of PbFCl crystal. The emission peaks in X-ray excited luminescence spectra do not depend on the F/Cl ratio in the raw materials. The UV cut-off edge of transmittance shifts from 300 nm to 275 nm when extra PbCl2 was added. According to the emission weighted transmittance of the samples, the crystals grown with F/Cl=1:1.25 in the raw materials show the best dual readout properties among all the samples.
|
|
|
Preparation of Bi4Si3O12-based Glass-ceramics and Effect of Heat Treatments on Optical Properties
WANG Chen-Yang, HU Guan-Qin, WANG Hong, ZHAO Jing-Tai
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 167–171
 Abstract
Abstract(
742 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(390KB)(
1524
)
Bi4Si3O12-based glass-ceramics with different crystalline volume fractions and transparency were prepared by the two-step heat-treatment of Bi2O3-SiO2 based glass. The experimental results show that the two-step heat-treatment is favorable to control the amount and size of crystallized grains in BSO-based glass-ceramics, which correspondingly affects the transparency and optical properties of the obtained glass-ceramics. The transmission spectra of these samples indicate that the transparency of BSO-based glass-ceramic (annealed at 600℃ for 1 h, then heated to 800℃ and held for 1 h) can reach 73.1% (> 500 nm). The BSO-based glass-ceramics maintain similar optical property as that of BSO single crystal, that is, the emission of such glass-ceramics is located in visible light wavelength of 380–680 nm, and their optical intensities are almost proportional to the crystalline volume fraction. The optical intensity of BSO-based glass-ceramic at low temperature (14 K) is increased by 12 times as against that at room temperature.
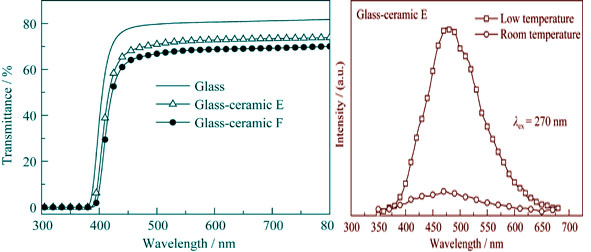
|
|
|
A Comparative Study of Vacuum and Air Plasma Sprayed Bioactive Akermanite Coating
YI De-Liang, WU Cheng-Tie, MA Xu-Bing, JI Heng, ZHENG Xue-Bin, CHANG Jiang
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 172–178
 Abstract
Abstract(
832 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(639KB)(
1348
)
Air plasma-sprayed akermanite coating is a new type orthopedic implant coating material with high bonding strength and excellent bioactivity. However, its crystallinity is low which affects its chemical stability. In this study, high crystallinity akermanite coating has been prepared using vacuum plasma spray (VPS) method. VPS akermanite coating possesses improved apatite mineralization ability compared with APS coating. An apatite layer has formed on VPS akermanite coating surface after 6 d of immersion into simulated body fluid (SBF), and the thickness of apatite layer on VPS coating is 4 times thicker than that on APS akermanite coating. The ionic release of VPS coating is significantly lower than that of APS coating, showing improved chemical stability. Furthermore, bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs) adhere to and spread well on the surface of both VPS and APS akermanite coating surface without significant difference. The proliferation rate of BMSCs is significantly higher on VPS and APS akermanite coating surface than on HA coating. Our results suggest that vacuum plasma sprayed (VPS) akermanite coating is more suitable as orthopedic implant material due to its improved bioactivity and chemical stability.
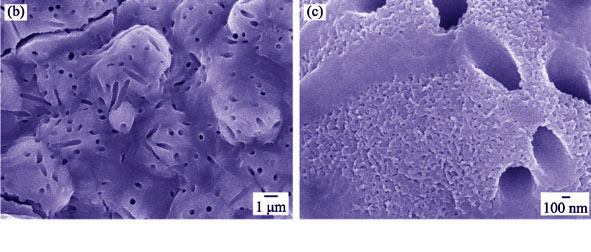
|
|
|
Surface Topology and Cytocompatibility of Polyphosphate Macroporous Ceramics with Recoating
LIU Bin, DONG Yin-Sheng, WU Hong-Yan, SU Jing, LIN Ping-Hua, GUO Zong-Ke
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 179–184
 Abstract
Abstract(
756 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(794KB)(
1478
)
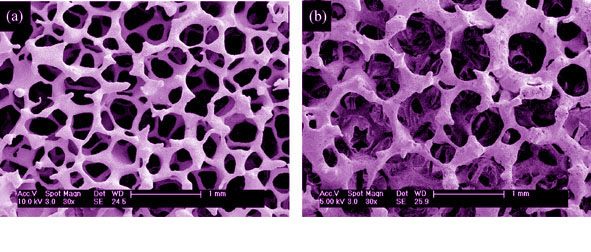
Polyphosphate porous ceramics were prepared and then recoated with thinner slurry. Macroporous characteristics, surface topology and cytocompatibility of samples before and after being recoated was evaluated using scan emission microscope (SEM), the Archimedes drainage method and the cells cultivation test in vitro. The results show that the pore wall thickness of samples increases with the increase of coating times, which slighty decreases their porosity. After being coated for 3 times, however, the macroporous morphology does not change obviously and the porosity is still more than 80%. Simultaneously, plenty of micropores with about 1–2 μm diameter are observed on the wall surfaces of samples. Furthermore, these surfaces are in favor of rabbit bone mesenchymal stem cells (RBMSC) adhesion, spreading and proliferation. These results indicate that the recoating process, especially repeated for 3 times, alters the surface topology of samples and enhances their cytocompatibility, but not sacrifices their macroporous characteristics.
|
|
|
Preparation and Sintering of High Active and Ultrafine B4C-SiC Composite Powders
ZHANG Zhi-Xiao, DU Xian-Wu, WANG Wei-Min, FU Zheng-Yi, WANG Hao
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 185–190
 Abstract
Abstract(
721 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(675KB)(
1429
)
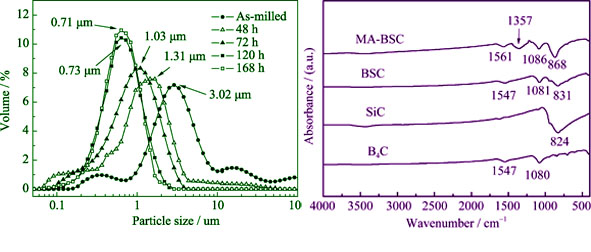
High active and ultrafine B4C-SiC composite powders were prepared by the coarse powders of B4C and SiC through the technology of mechanical alloying. Under testing techniques of X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, laser particle size analysis and infrared absorption spectrum, by which studied the influences of ball to powder weight ratio, process control agents and milling time on composite powders, the best technological conditions of MA for preparing B4C-SiC ultrafine composite powders could be confirmed. After studying order-disorder transformation of the composite powders during the process of MA, hot pressing sintering was adopted to verify the sintering activity of the composite powders. The results indicate that the lattice unordered B4C-50wt% SiC ultrafine composite powders can be obtained when the ball to powder weight ratio is 30:1, process control agents 2wt%, milling time 120 h and the rotation speed 250 r/min. While the composite powders are sintered at 1900℃ with pressure of 30 MPa, the density of samples is 2.62 g/cm3 and the relative density of samples attains 93%. The relative density of samples sintered with the composite powders is 8.1% higher than that of samples sintered with ordinary mixing powders. B4C-SiC ultrafine composite powders prepared by mechanical alloying possess extremely high sintering activity.
|
|
|
Effects of the Diluent Content on Microstructure of Submicron ZrB2 by Combustion Synthesis
LA Pei-Qing, HAN Shao-Bo, LU Xue-Feng, WEI Yu-Peng
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 191–196
 Abstract
Abstract(
729 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(543KB)(
1264
)
Submicron ZrB2 powders were prepared by combustion synthesis using NaCl as the diluent and B2O3, Mg and ZrO2 as raw materials. The samples were analyzed by SEM, EDS, XRD and particle size analyzer. The results show that adiabatic temperature of the system decreases with the diluent content increase. The products are aggregates which contain a small amount of larger-sized particles and a large number of small-sized particles. The average particle size of products drops from 305 nm to 160 nm as the value of k, i.e. molar ratio of the diluent, increases from 0.5 to 1.5. The products after leaching mainly consist of ZrB2 and ZrO2, and the content of the latter decreases with the increase of k. NaCl plays very important roles, such as providing a liquid medium, promoting the mass transfer, improving the purity of the products, and reducing the combustion temperature of the system, inhibiting growth of particles by giving a coating on the surface, and leading to small-sized particles.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of Si/C Composite Anode by Electrostatic Spinning Method
QU Chao-Qun, WANG Yu-Hui, JIANG Tao, BIE Xiao-Fei
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 197–202
 Abstract
Abstract(
959 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(459KB)(
1832
)
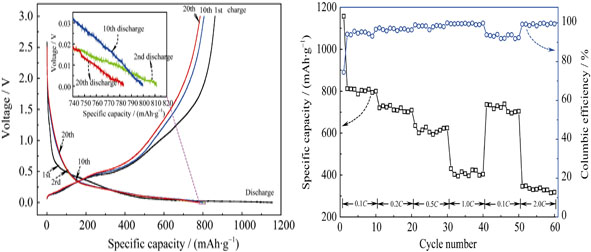
Si/C composite anode material was successfully fabricated by an electrospinning method using PVP as macromolecule polymer collocation. The carbon derived from sintering PVP at high temperature plays a role in buffering size skeleton of silicon, which can effectively improve the volume expansion and pulverization problem of silicon at charge-discharge. The structure and morphology of the as-prepared samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectrum (Raman) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The results show that the distribution of composite material is fibrous with diameter in the range of 300–400 nm. A “wheat like” structure is formed by Si particles distributed on the amorphous carbon fibers. The electrochemical test demonstrates that the irreversible capacity at first charge-discharge process is 294.9 mAh/g, which is due to the formation of solid electrolyte interface (SEI) film between the electrode and electrolyte. In addition, this composite material has very high columbic efficiency and excellent cycle stability, both at a low (0.1C, 0.2C and 0.5C) and high (1.0C and 2.0C) rates.
|
|
|
Optimization of the Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Anode by Tape Casting
LUO Ting, SHI Jian, WANG Shao-Rong, ZHAN Zhong-Liang
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 203–208
 Abstract
Abstract(
712 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1016KB)(
1927
)
The scandia-stabilized zirconia (SSZ) electrolyte supported by Ni-YSZ anode was prepared by tape casting and co-firing techniques. In order to improve the electrochemical activity, a Ni-SSZ anode active layer was introduced between the supporting anode and the electrolyte film. The anode activity was optimized by adjusting the thickness and mass ratio of SSZ: NiO in the active layer. The pore distribution and porosity of supporting anode were optimized by comparing the performance of cells with different content of pore former in the supporting anode. As a result, the thickness of active layer was optimized to be 35 μm, with w(SSZ):w(NiO)=1:1, and 10wt% carbon as anode pore former. The composite cathode of LSM-SSZ was prepared by screen printing and sintering method, and the maximum power density of single cell as high as 0.96 W/cm2 was obtained at 750℃. The performance was about 2.3 times higher than what previously reported by our group.
|
|
|
Study on the High Temperature Stability of YbyCo4Sb12/Yb2O3 Composite Thermoelctric Material
DING Juan, LIU Rui-Heng, GU Hui, CHEN Li-Dong
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 209–214
 Abstract
Abstract(
754 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(493KB)(
1557
)
YbyCo4Sb12/Yb2O3 filled skutterudite composite with nominal compositions of y=0.6 was synthesized, in which the Yb2O3 particles in nanometer and/or micrometer sizes dispersed mainly on the grain boundary. The high temperature stability of the composite was investigated. It was found that the thermoelectric properties (electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient and thermal conductivity) and the microstructure features (grain size, amount and dispersion of oxide particles) , Yb filling fractions were almost unchanged after heat treatment at 873 K for 30 d, resulting in almost unchanged maximum ZT values of about 1.2. A large number of dislocations were observed in the grain interior. The stress generated by dislocations is considered the major factor to effectively prevent the “escape” of Yb ions from the Sb-cages and to block the migration of the Yb2+ ions and O2- ions, thus preventing the generation of oxide particles.
|
|
|
Influence of Cu on Transport Properties of Thermoelectric Thin Film Fabricated via Magnetron Co-sputtering Method
CAO Li-Li, WANG Yao, DENG Yuan, LUO Bing-Wei, ZHU Wei, SHI Yong-Ming,LIN Zhen
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 215–219
 Abstract
Abstract(
1362 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(364KB)(
2332
)
A simple magnetron co-sputtering method was used to fabricate Cu dispersed Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 thin films, and the co-sputtering method was beneficial to the preferential growth of Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 thin films along c-axis. Cu atoms were well-dispersed in the nano-structured materials. The electrical conductivity sharply increased with the increasing content of Cu due to the effect of Cu on transport property. For Cu target sputtering power of 20 W, a maximum power factor of 20 μW/(cm?K2) with an electrical conductivity of 15 × 104 S/m at 355 K were achieved.
|
|
|
Microstructure and Ionic Conductivity of Sb-doped Li7La3Zr2O12 Ceramics
CAO Zhen-Zhu, REN Wei, LIU Jin-Rong, LI Guo-Rong, GAO Yan-Fang, FANG Ming-Hao, HE Wei-Yan
2014 Vol. 29 (2): 220–224
 Abstract
Abstract(
1899 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(2445KB)(
3597
)
The garnet-related oxides Li7-xLa3Zr2-xSbxO12 (x = 0, 0.075) were prepared by solid-state reaction method. Crystal structure, microstructure, conductivity, and element distribution were characterized for the pure and Sb-doped Li7La3Zr2O12. Ionic conductivity of the Li7La3Zr2O12 is enhanced by Sb doping. An amorphous Li-La-Zr-Al-O thin film which is formed on the grain boundary of Sb-doped samples not only suppresses the abnormal grain growth but also eliminates the pores on the grain boundary. The ionic conductivity of Sb doped Li7-xLa3Zr2-xSbxO12 ceramic with x = 0.075 sintered at 1160℃ reaches about 3.40×10-4 S/cm.
|
|