
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 81-87.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200394
Previous Articles Next Articles
XIE Xue1,2,WU Jianrong2,CAI Xiaojun2,HAO Junnian2,ZHENG Yuanyi1,2( )
)
Received:2020-07-14
Revised:2020-08-13
Published:2021-01-20
Online:2020-08-28
About author:XIE Xue (1992-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: xiexue_moderation@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
XIE Xue, WU Jianrong, CAI Xiaojun, HAO Junnian, ZHENG Yuanyi. Photothermal/pH Responsive B-CuS-DOX Nanodrug for Chemo-photothermal Synergistic Therapy of Tumor[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 81-87.
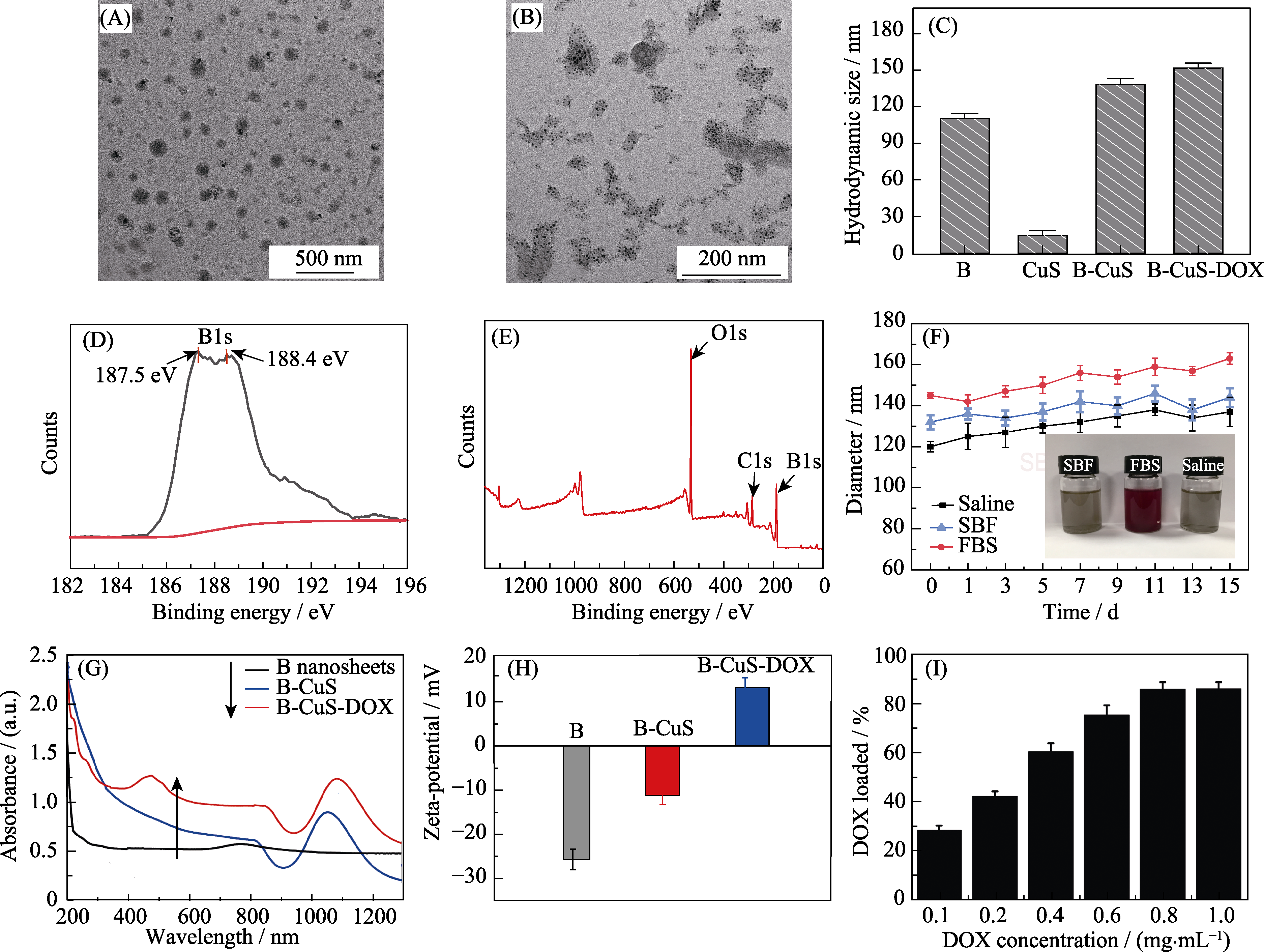
Fig. 1 Characterization of B nanosheets, B-CuS and B-CuS-DOX TEM images of (A) B-CuS and (B) B-CuS; (C) Diameter of B-CuS-DOX; (D) XPS survey spectra of B nanosheets; (E) The selective XPS survey spectra corresponding to B1s spectra; (F) Hydrodynamic size change of B-CuS-DOX dispersed in saline, medium containing fetal bovine serum (FBS), human simulated body fluid (SBF) for 15 d; (G) UV-Vis-NIR spectra and (H) Zeta potential of B nanosheets, B-CuS and B-CuS-DOX; (I) Histogram of the relationship between DOX drug loading and DOX concentration. DOX: doxorubicin
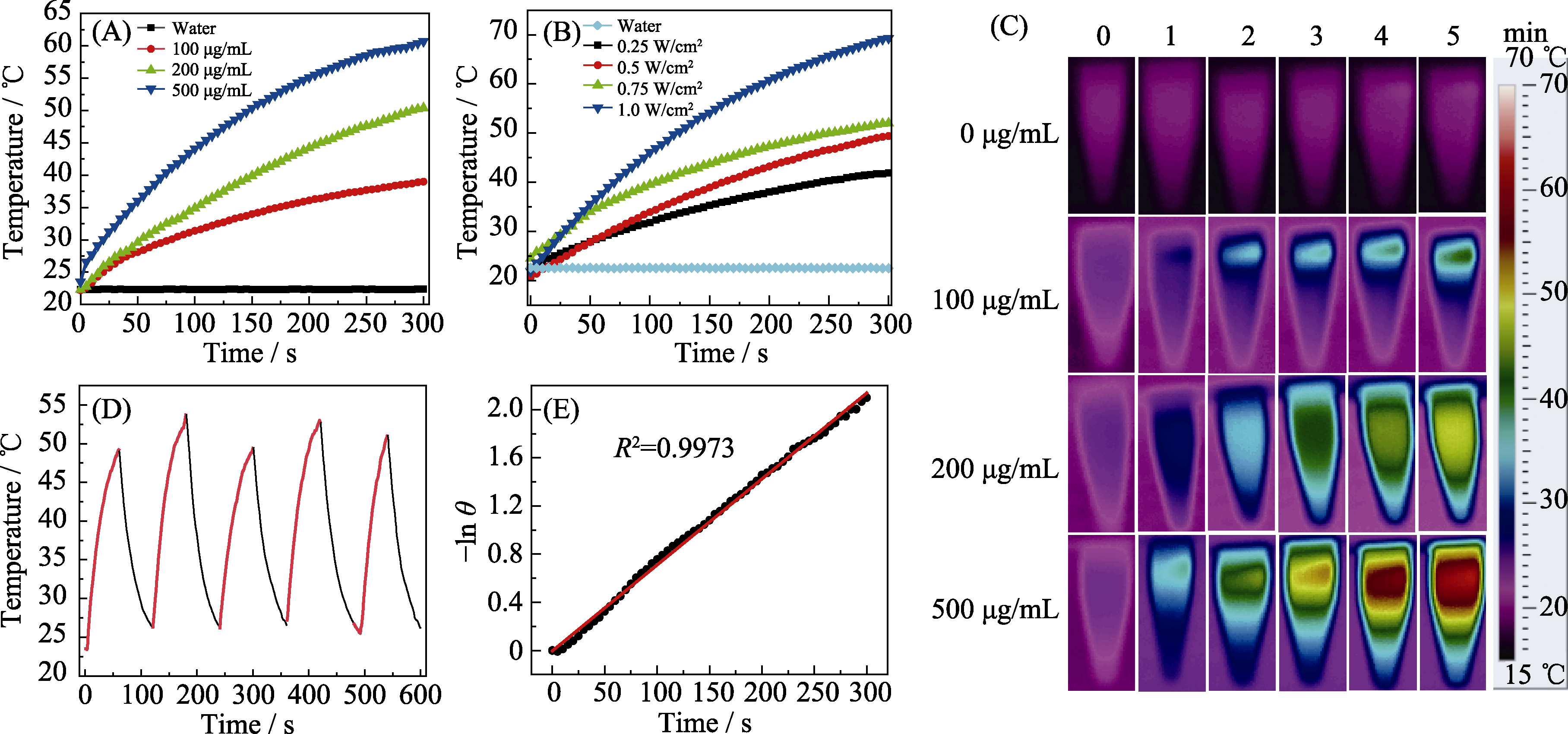
Fig. 2 Photothermal performance of B-CuS (A) The temperature change of B-CuS dispersion with different concentrations within 5 min of laser irradiation with a power density of 0.5 W/cm2; (B) The temperature change of B-CuS (200 μg/mL) dispersion under different laser power densities for 5 min; (C) Thermal images of B-CuS dispersions with different concentrations after irradiation within 5 min with a laser power density of 0.5 W/cm2; (D) B-CuS photothermal curve under five laser “on-off” cycles; (E) The linear regression equation of the negative natural logarithm of B-CuS heating and cooling time and temperature, θ=ΔT/ΔTmax
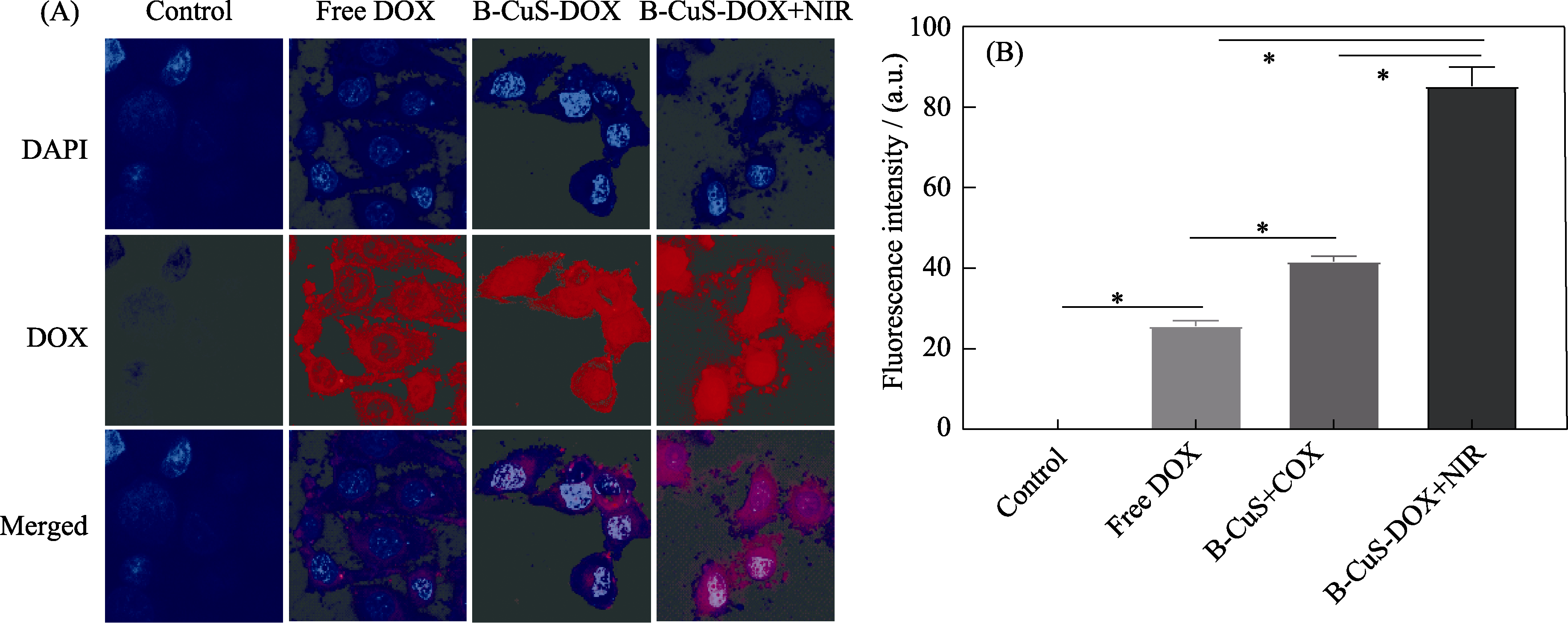
Fig. 4 In vitro cellular uptake of B-CuS-DOX (A) CLSM images of 4T1 cells treated with free DOX and B-CuS-DOX with or without laser irradiation; (B) Quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity of DOX uptake by 4T1 cells in each treatment. Scale bar: 15 μm; *: p < 0.05. DOX: doxorubicin
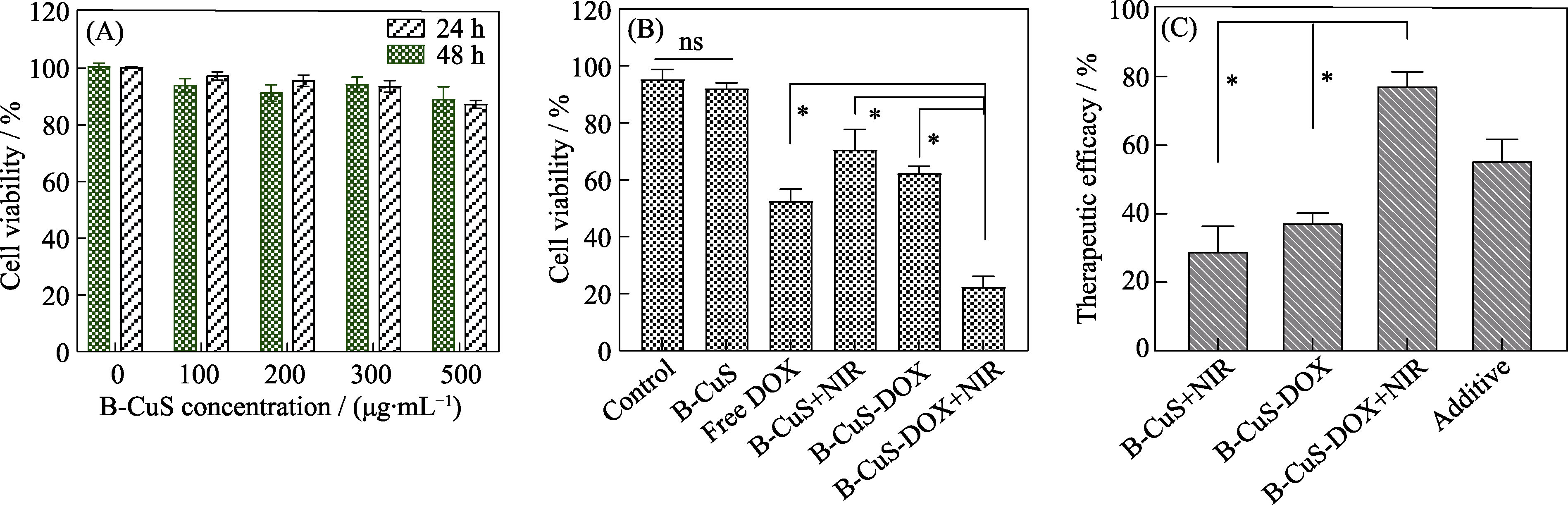
Fig. 5 Evaluation of B-CuS-DOX on cell chemotherapy-PTT synergistic therapy (DOX: doxorubicin) (A) Cell survival rate of 4T1 cells incubated with different concentrations of B-CuS for 24 and 48 h; (B) Cell survival rate of 4T1 cells treated with different experimental groups; (C) Therapeutic efficacy of PTT, chemotherapy, chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy and additive therapy. *: p<0.05
| [1] | FU F F, WU Y L, ZHU J Y , et al. Multifunctional lactobionic acid-modified dendrimers for targeted drug delivery to liver cancer cells: investigating the role played by PEG spacer. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014,6(18):16416-16425. |
| [2] | SCHILLER J H, HARRINGTON D, BELANI C P ,et al. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 2002,346(2):92-98. |
| [3] | SHAO T P, WEN J, ZHANG Q ,et al. NIR photo-responsive drug delivery and synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy by monodispersed MoS2 nanosheets wrapped periodic mesoporous organosilicas. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2016,4(47):1-26. |
| [4] | GOLDMAN B . Multidrug resistance: can new drugs help chemotherapy score against cancer? J. Natl. Cancer I, 2003,95(4):255-257. |
| [5] | KANG H, TRONDOLI A C, ZHU G , et al. Near-infrared light- responsive core-shell nanogels for targeted drug delivery. ACS Nano, 2011,5(6):5094-5099. |
| [6] | CHEN Q, LIANG C, WANG C ,et al. An imagable and photothermal ‘abraxane-like’ nanodrug for combination cancer therapy to treat subcutaneous and metastatic breast tumors. Advanced Materials, 2015,27(5):903-910. |
| [7] | LI Z L, FAN X L, LIU J ,et al. Mesoporous silica-coated bismuth nanohybrids as a new platform for photoacoustic/computed tomography imaging and synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. Nanomedicine, 2018,13(18):2283-2300. |
| [8] | GAO J B, WANG F, WANG S H ,et al. Hyperthermia-triggered on-demand biomimetic nanocarriers for synergetic photothermal and chemotherapy. Advanced Science, 2020,7(11):1903642. |
| [9] | ZOU Y, LI M L, XIONG T , et al. A single molecule drug targeting photosensitizer for enhanced breast cancer photothermal therapy. Small, 2020,16(18):1907677. |
| [10] | SUN H, CHANG R, ZOU Q , et al. Supramolecular protein nanodrugs with coordination and heating-enhanced photothermal effects for antitumor therapy. Small, 2019,15(52):1905326. |
| [11] | ZHANG Q H, GUO Q B, CHEN Q , et al. Highly efficient 2D NIR-II photothermal agent with Fenton catalytic activity for cancer synergistic photothermal-chemodynamic therapy. Advanced Science, 2020,7(7):1902576. |
| [12] | WENG Y Z W, GUAN S Y, LI W , et al. Defective porous carbon polyhedra decorated with copper nanoparticles for enhanced NIR‐ driven photothermal cancer therapy. Small, 2019,16(1):1905184. |
| [13] | MU X, LU Y, WU F , et al. Supramolecular nanodiscs self-assembled from non-ionic heptamethine cyanine for imaging-guided cancer photothermal therapy. Advanced Materials, 2020,32(2):1906711. |
| [14] | SARAH P.S, SCOTT M. T, XIE L M, et al. Photothermally enhanced drug delivery by ultrasmall multifunctional Fe-Co/graphitic shell nanocrystals. ACS Nano, 2011,5(2):1505-1512. |
| [15] | ZHENG M B, YUE C X, MA Y F , et al. Single-step assembly of DOX/ICG loaded lipid polymer nanoparticles for highly effective chemo-photothermal combination therapy. ACS Nano, 2013,7(3):2056-2067. |
| [16] | XIA Y N, LI W Y, COBLEY C M , et al. Gold nanocages: from synthesis to theranostic applications. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2011,44(10):914-924. |
| [17] | SKRABALAK S E, CHEN J, SUN Y , et al. Gold nanocages: synthesis, properties, and applications. Accounts Chem. Res., 2008,40(14):1587-1595. |
| [18] | HUANG X H, EI-SAYED M A. Gold nanoparticles: optical properties and implementations in cancer diagnosis and photothermal therapy. Journal of Advanced Research, 2010,1(1):13-28. |
| [19] | LIU Z, ROBINSON J T, SUN X , et al. PEGylated nano-graphene oxide for delivery of water insoluble cancer drugs. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008,130(33):10876-10877. |
| [20] | LIU X, TAO H, YANG K , et al. Optimization of surface chemistry on single-walled carbon nanotubes for in vivo photothermal ablation of tumors. Biomaterials, 2011,32(1):144-151. |
| [21] | CHEN Q, LIANG C, WANG X , et al. An albumin-based theranostic nano-agent for dual-modal imaging guided photothermal therapy to inhibit lymphatic metastasis of cancer post-surgery. Biomaterials, 2014,35(34):9355-9362. |
| [22] | CHENG L, HE W W, GONG H , et al. PEGylated micelle nanoparticles encapsulating a non-fluorescent near-infrared organic dye as a safe and highly effective photothermal agent for. in vivo cancer therapy Advanced Functional Materials, 2013,23(47):5893-5902. |
| [23] | JI X Y, KONG N, WANG J Q , et al. A novel top-down synthesis of ultrathin 2D boron nanosheets for multimodal imaging-guided cancer therapy. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(31): 1803031-1-11. |
| [24] | YANG J, DAI D, LOU X , et al. Supramolecular nanomaterials based on hollow mesoporous drug carriers and macrocycle-capped CuS nanogates for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. Theranostics, 2020, 10(2):615-629. |
| [25] | FENG L Z, DONG Z L, LIU Z , et al. The acidic tumor microenvironment: a target for smart cancer nano-theranostics. National Science Review, 2018,5(2):269-286. |
| [26] | ZHANG X Y, WU J R, WILLIAMS G R , et al. Dual-responsive molybdenum disulfide/copper sulfide-based delivery systems for enhanced chemo-photothermal therapy. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018,539:433-441. |
| [27] | KANG H, TRONDOLI A C, ZHU G , et al. Near-infrared light-responsive core-shell nanogels for targeted drug delivery. ACS Nano, 2011,5(6):5094-5099. |
| [28] | ZHENG M, YUE C, MA Y , et al. Single-step assembly of DOX/ICG loaded lipid-polymer nanoparticles for highly effective chemo-photothermal combination therapy.. ACS Nano, 2013,7(3):2056-2067. |
| [29] | LIU J J, WANG C, WANG X J , et al. Mesoporous silica coated single-walled carbon nanotubes as a multifunctional light-responsive platform for cancer combination therapy.. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015,25(3):384-392. |
| [30] | CAI X J, JIA X Q, CHEN H R , et al. A versatile nanotheranostic agent for efficient dual-mode imaging guided synergistic chemo- thermal tumor therapy. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015,25(17):2520-2529. |
| [1] | HE Qian, TANG Wanlan, HAN Bingkun, WEI Jiayuan, LÜ Wenxuan, TANG Zhaomin. pH Responsive Copper-Doped Mesoporous Silica Nanocatalyst for Enhanced Chemo-Chemodynamic Tumor Therapy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 90-98. |
| [2] | BAI Zhiqiang, ZHAO Lu, BAI Yunfeng, FENG Feng. Research Progress on MXenes: Preparation, Property and Application in Tumor Theranostics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 361-375. |
| [3] | ZHANG Wenjun, ZHAO Xueying, LÜ Jiangwei, QU Youpeng. Progresses on Hollow Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas: Preparation and Application in Tumor Therapy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1192-1202. |
| [4] | WANG Yuwei, CHEN Jiajie, TIAN Zhengfang, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Potassium Ferrate-loaded Porphyrin-based (VI) Metal-organic Frameworks for Combined Photodymanic and Chemodynamic Tumor Therapy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1305-1315. |
| [5] | WEI Chengxiong, JIN Xin, YIN Peinan, WU Chengwei, ZHANG Wei. Carbon Spheres for Photothermal Therapy of Tumor Cells: Rapid Preparation and High Photothermal Effect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1208-1216. |
| [6] | CHENG Xiaokun, ZHANG Yue, Lü Haijun, LIU Xinying, HOU Senlin, CHEN Aibing. Porous Carbon Nanomaterials Based Tumor Targeting Drug Delivery System: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 9-24. |
| [7] | DONG Shaojie,WANG Xudong,SHEN Steve Guofang,WANG Xiaohong,LIN Kaili. Research Progress on Functional Modifications and Applications of Bioceramic Scaffolds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 867-881. |
| [8] | LI Xia,SHENASHEN Mohamed A,MEKAWY Moataz,TANIGUCHI Akiyoshi,EI-SAFTY Sherif A. Aluminum Hydroxide Nanosheets with Structure-dependent Storage and Transportation toward Cancer Chemotherapy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 250-256. |
| [9] | ZENG Yulin, CHEN Jiajie, TIAN Zhengfang, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Preparation of Mesoporous Organosilica-based Nanosystem for in vitro Synergistic Chemo- and Photothermal Therapy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12): 1365-1372. |
| [10] | HE Qian-Jun, CHEN Dan-Yang, FAN Ming-Jian. Progress of Precision Nanomedicine-mediated Gas Therapy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(8): 811-824. |
| [11] | PAN Shan, LI Yong-Sheng, SHI Jian-Lin. Facile Synthesis of Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Co-loading of Doxorubicin and Hemoglobin [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1097-1102. |
| [12] | ZHAI Yun-Gang, DONG Wen-Jie, GAO Yong-Ping, NIU De-Chao, CHEN Jian-Zhuang, GU Jin-Lou, LI Yong-Sheng, SHI Jian-Lin. Preparation of Superparamagnetic Gold Nanocomposites with Different Diameters and Their Imaging and Therapy Applications [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(9): 950-956. |
| [13] | YAO Ai-Hua, XU Wei, AI Fan-Rong, CHEN Qi, WANG De-Ping, HUANG Wen-Hai, Xu Jun. Study on Hollow Hydroxyapatite Microspheres as Delivery System for Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(9): 974-978. |
| [14] | LIU Hao-Huai, ZHANG Jian-Hua, XU Qing-Ling, ZHANG Li, LI Yu-Bao. Studies on Hydroxyapatite/Polyurethane Scaffold Containing Drug-loaded Microspheres for Bone Tissue Engineering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(10): 1073-1077. |
| [15] | ZHOU Yan-Ling, FENG Xin-Xing, ZHAI Wan-Yin, CHANG Jiang. Study on the Loading and Releasing Behavior of EpirubicinHydrochloride from Mesoporous Bioactive Glasses (MBGs) [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(1): 68-72. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||