
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 570-576.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170253
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Shu-Jiang, YANG Yong-Heng, WEN Chun-Yang, ZHANG Guo-Kui, YUAN Chun-Hui
Received:2017-05-19
Revised:2017-06-29
Published:2018-05-20
Online:2018-04-26
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Shu-Jiang, YANG Yong-Heng, WEN Chun-Yang, ZHANG Guo-Kui, YUAN Chun-Hui. Preparation and Property of Nano-Ag/illite Composite Material[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(5): 570-576.
| No. | Sample | Average particle size/nm | D50/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | I | 1068.3 | 877.7 |
| 2 | N | 884.8 | 630.7 |
| 3 | Ag-I | 1043.6 | 851.1 |
| 4 | Ag-N | 875.7 | 642.7 |
| 5 | Ag-P-N | 873.2 | 649.3 |
| 6 | Ag-C-N | 857.8 | 648.3 |
Table 1 Particle size of the composite
| No. | Sample | Average particle size/nm | D50/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | I | 1068.3 | 877.7 |
| 2 | N | 884.8 | 630.7 |
| 3 | Ag-I | 1043.6 | 851.1 |
| 4 | Ag-N | 875.7 | 642.7 |
| 5 | Ag-P-N | 873.2 | 649.3 |
| 6 | Ag-C-N | 857.8 | 648.3 |
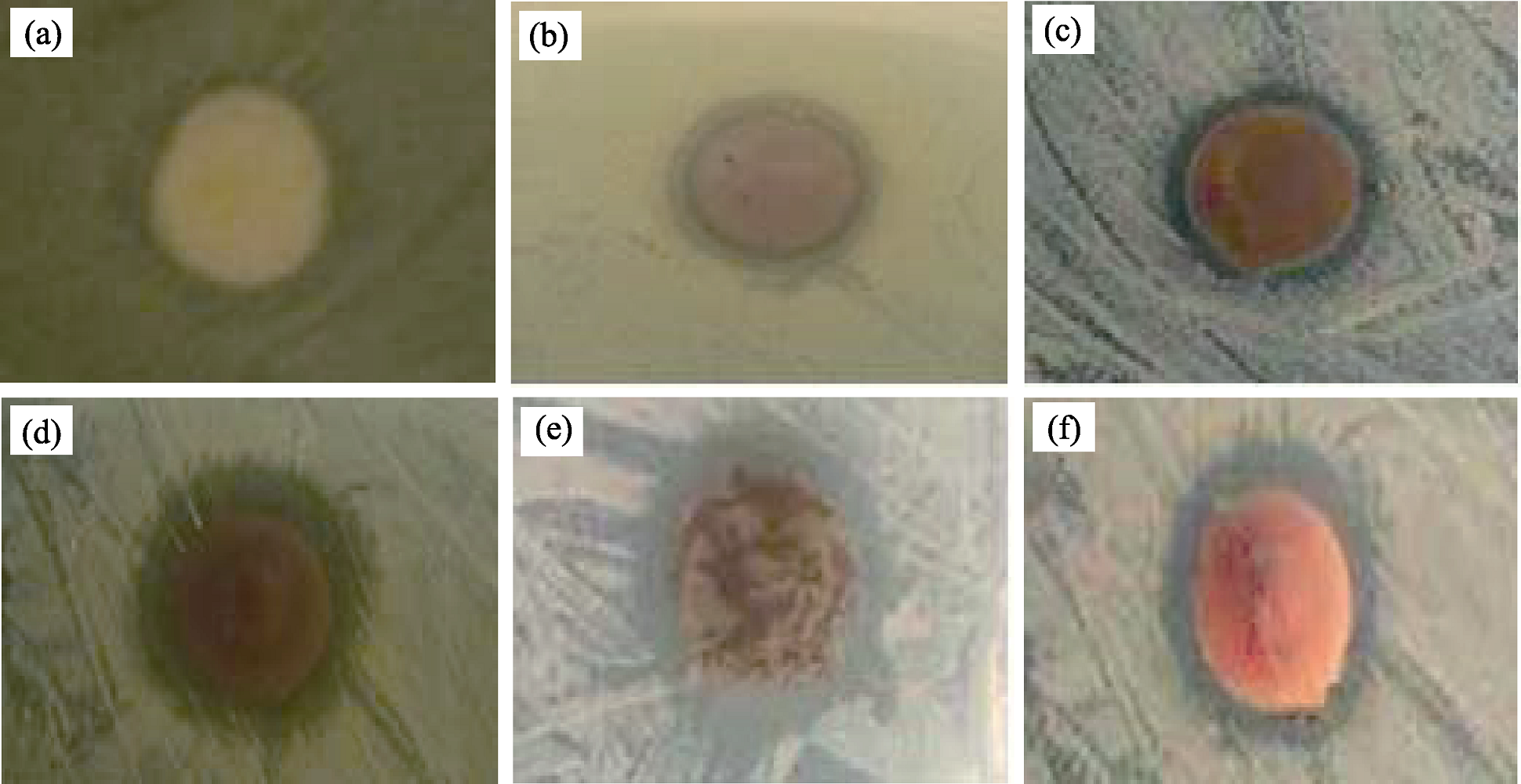
Fig. 7 Typical photographs of nano-Ag/illite composite re-cultivated Staphylococcus aureus colonies on agar(a) I; (b) Ag-I; (c) Ag-N; (d) Ag-P-N; (e) Ag-C-N; (f) AgNO3
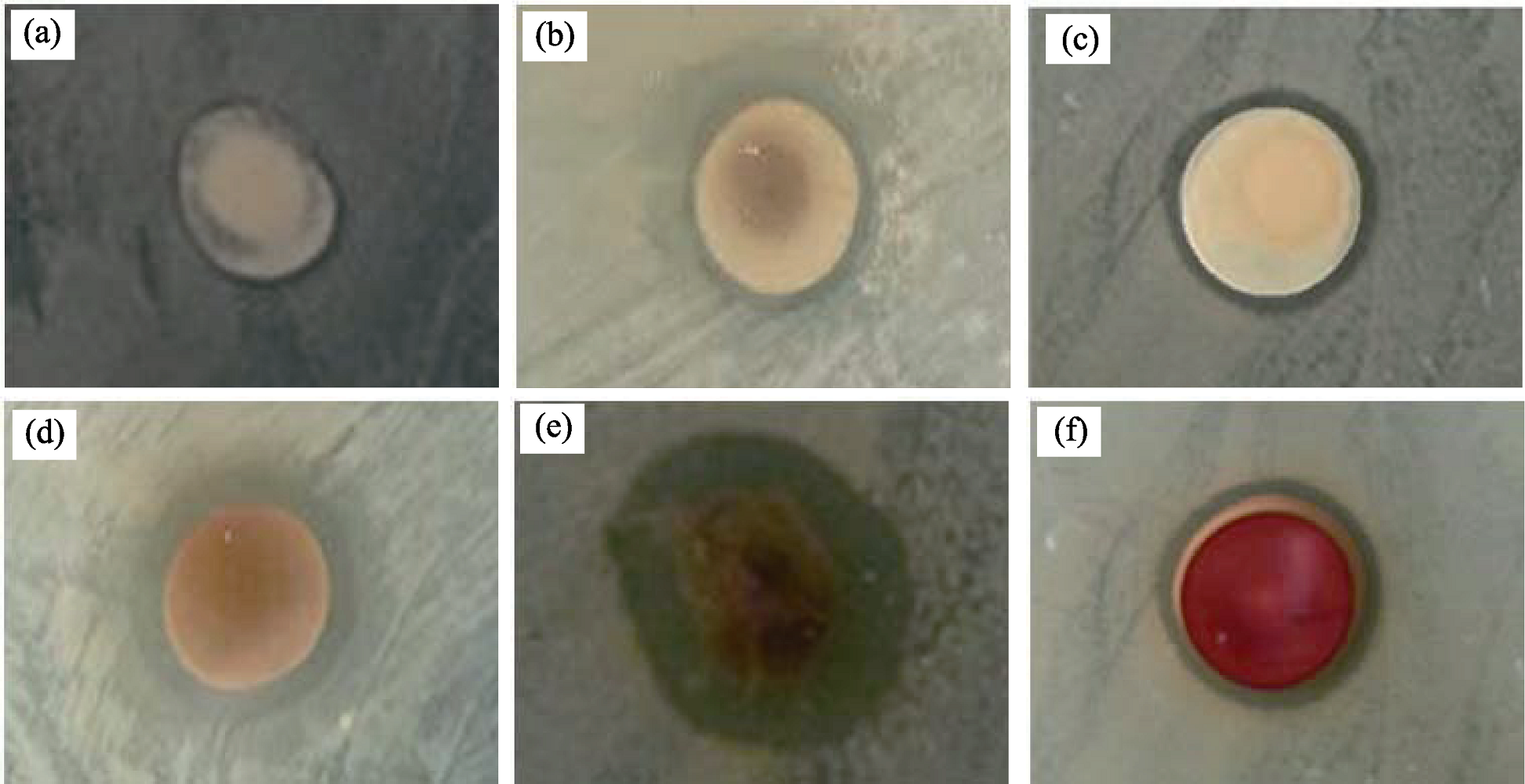
Fig. 8 Typical photographs of nano-Ag/illite composite re-cultivated Escherichia coli colonies on agar(a) I; (b) Ag-I; (c) Ag-N; (d) Ag-P-N; (e) Ag-C-N; (f) AgNO3
| No. | Sample | Staphylococcus aureus | Escherichia coli | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1/mm | D2/mm | D3/mm | D1/mm | D2/mm | D3/mm | ||
| 1 | I | 8.00 | 8.32 | 0.32 | 8.00 | 8.52 | 0.52 |
| 2 | Ag-I | 8.00 | 10.14 | 2.14 | 8.00 | 10.06 | 2.06 |
| 3 | Ag-N | 8.00 | 11.44 | 3.44 | 8.00 | 11.28 | 3.28 |
| 4 | Ag-P-N | 8.00 | 12.48 | 4.48 | 8.00 | 12.38 | 4.38 |
| 5 | Ag-C-N | 8.00 | 13.68 | 5.68 | 8.00 | 14.84 | 6.84 |
| 6 | AgNO3 | 8.00 | 12.80 | 4.80 | 8.00 | 11.48 | 3.48 |
Table 2 Result of inhibition zone test
| No. | Sample | Staphylococcus aureus | Escherichia coli | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1/mm | D2/mm | D3/mm | D1/mm | D2/mm | D3/mm | ||
| 1 | I | 8.00 | 8.32 | 0.32 | 8.00 | 8.52 | 0.52 |
| 2 | Ag-I | 8.00 | 10.14 | 2.14 | 8.00 | 10.06 | 2.06 |
| 3 | Ag-N | 8.00 | 11.44 | 3.44 | 8.00 | 11.28 | 3.28 |
| 4 | Ag-P-N | 8.00 | 12.48 | 4.48 | 8.00 | 12.38 | 4.38 |
| 5 | Ag-C-N | 8.00 | 13.68 | 5.68 | 8.00 | 14.84 | 6.84 |
| 6 | AgNO3 | 8.00 | 12.80 | 4.80 | 8.00 | 11.48 | 3.48 |
| [1] | LIU XIN-HAI, LI YI-BO.Study on surface modification of illite. Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2004, 33(2): 8-10. |
| [2] | SHI JUN, YU ZHI-WEI, ZHENG JU-GONG,et al. Research of the modified illite on reinforcing mechanical properties of flexible PVC. Journal of East China Institute of Technology (Natural Science), 2014, 37(1): 84-87. |
| [3] | HUANG JI-TAI, DAI JIN-CAO, BEI YI-LING,et al. Modification of illite fines and its application to rubber. China Mining Magazine, 1995, 4(6): 52-55. |
| [4] | ÖZTOP B, SHAHWAN T.Modification of a montmorillonite-illite clay using alkaline hydrothermal treatment and its application for the removal of aqueous Cs+ ions.Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2006, 295(2): 303-309. |
| [5] | WANG L, LI L.Illite spatial distribution patterns dictate Cr(VI) sorption macrocapacity and macrokinetics.Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(3): 1374-1383. |
| [6] | BANIK N, MARSAC R, Lützenkirchen J,et al. Sorption and redox speciation of plutonium at the illite surface. Environmental Science&Technology, 2016, 50(4): 2092-2098. |
| [7] | LI XIAO-MIN, KOU XIAO-WEI.Illite: a new potential clay mineral material.World Geology, 2000, 19(4): 346-349. |
| [8] | RAI M, YADAV A, GADE A.Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnology Advances, 2009, 27(1): 76-83. |
| [9] | WANG HUI-LEI, LIU XIAO-HENG.Preparation of silver nanoparticle loaded mesoporous TiO2 and its photocatalytic property.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(5): 555-560. |
| [10] | TAN YING, TAN GUO-XIN, NING CHENG-YUN,et al. Bioinspired polydopamine functionalization of titanium surface for silver nanoparticles immobilization with antibacterial property. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(12): 1320-1326. |
| [11] | LI F, WEIR M D, CHEN J,et al. Comparison of quaternary ammonium-containing with nano-silver-containing adhesive in antibacterial properties and cytotoxicity. Dental Materials, 2013, 29(4): 450-461. |
| [12] | SPADARO D, BARLETTA E, BARRECA F,et al. Synthesis of PMA stabilized silver nanoparticles by chemical reduction process under a two-step UV irradiation. Applied Surface Science, 2010, 256(12): 3812-3816. |
| [13] | PAL A, SHAH S, DEVI S.Microwave-assisted synthesis of silver nanoparticles using ethanol as a reducing agent.Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2009, 114(2): 530-532. |
| [14] | HE B, TAN J J, KONG Y L,et al. Synthesis of size controlled Ag nanoparticles. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A Chemical, 2004, 221(1/2): 121-126. |
| [15] | YAO BAO-HUI, XU GUO-CAI, ZHANG HONG-YAN,et al. Synthesis of nanosilver with polyvinylpyrrolidone(PVP) by microwave method. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2010, 26(9): 1629-1632. |
| [16] | VODNIK V V, BOŽANIĆ D K, DŽUNUZOVIĆ E,et al. Thermal and optical properties of silver-poly(methylmethacrylate) nanocomposites prepared by in-situ radical polymerization. European Polymer Journal, 2010, 46(2): 137-144. |
| [17] | SHI ZHEN-WU, GUO SHAO-BO, XUE QUN-HU.Preparation, photocatalytic property and antibacterial property of Ag@TiO2@SiO2 composite nanomaterials.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(5): 466-472. |
| [18] | SÁNCHEZ F G, LOON L R V, GIMMI T,et al. Self-diffusion of water and its dependence on temperature and ionic strength in highly compacted montmorillonite, illite and kaolinite. Applied Geochemistry, 2008, 23(12): 3840-3851. |
| [19] | 季桂娟, 张培萍, 姜桂兰. 膨润土加工与应用, 2版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2013: 15-19. |
| [20] | HU XIAO-XIA, ZHAO LIN, ZHAO SHU-YU,et al. Microwave- assisted preparation of copper hydroxyphosphate and characterization of Photocatalysis under visible light. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(4): 421-426. |
| [21] | HUANG XIANG-DONG, LI JIAN-BAO, XIE ZHI-PENG,et al. Microwave interaction with inorganic nonmetallic substance, Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1998, 13(3): 282-290. |
| [22] | ZENG XIANG-FENG, ZHANG KAI, YU XIAO-MAN,et al. Adsorption behaviors of Cd on montmorillonite/illite in alkaline saline conditions. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2008, 27(6): 2251-2257. |
| [23] | FOX B S, BEYER M K, BONDYBEY V E.Coordination chemistry of silver cations.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2002, 124(45): 13613-13623. |
| [24] | PEARSON R G.Hard and soft acids and bases.Journal of The American Chemical Society. 1963, 85(22): 3533-3539. |
| [25] | SUN XIAO-FEI, WEI CHANG-PING, LI QI-YUAN,et al. Ag/SiO2 composite thin films: preparation by UV radiation deoxidation and optical properties. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2008, 24(11): 1895-1899. |
| [26] | SONDI I, SALOPEK-SONDI B.Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study onE. coli as a model for gram-negative bacteria. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2004, 275(1): 177-182. |
| [27] | GUZMAN M, DILLE J, GODET S.Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2012, 8(1): 37-45. |
| [28] | SADEGHI B, GARMAROUDI F S, HASHEMI M,et al. Comparison of the anti-bacterial activity on the nanosilver shapes: nanoparticles, nanorods and nanoplates. Advanced Powder Technology, 2012, 23(1): 22-26. |
| [1] | LIANG Ruihui, ZHONG Xin, HONG Du, HUANG Liping, NIU Yaran, ZHENG Xuebin. High-temperature Water Vapor Corrosion Behaviors of Environmental Barrier Coatings with Yb2O3-modified Silicon Bond Layer [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 425-432. |
| [2] | FENG Guanzheng, YANG Jian, ZHOU Du, CHEN Qiming, XU Wentao, ZHOU Youfu. Mechanism for Hydrothermal-carbothermal Synthesis of AlN Nanopowders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 104-110. |
| [3] | WANG Tingting, SHI Shumei, LIU Chenyuan, ZHU Wancheng, ZHANG Heng. Synthesis of Hierarchical Porous Nickel Phyllosilicate Microspheres as Efficient Adsorbents for Removal of Basic Fuchsin [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1330-1336. |
| [4] | SONG Keke, HUANG Hao, LU Mengjie, YANG Anchun, WENG Jie, DUAN Ke. Hydrothermal Preparation and Characterization of Zn, Si, Mg, Fe Doped Hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1091-1096. |
| [5] | DENG Min, JIANG Qi, DUAN Zhi-Hong, LIU Qing-Qing, JIANG Li, LU Xiao-Ying. Rice-like CuO Chemically Modified Electrode: Preparation and Detection for Glucose [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 152-158. |
| [6] | YAO Mei-Na, YANG Xian-Jin, CUI Zhen-Duo, ZHU Sheng-Li, LI Zhao-Yang, LIANG Yan-Qin. Detection of Cd2+ by Square Wave Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Using an Activated Bismuth-film Electrodes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(1): 91-95. |
| [7] | JIA Si-Qi, JIANG Zheng, CHI Li-Na, YE Ying, HU Shuang-Shuang. Synthesis and Photoelectrocatalytic Performance of Sb2S3 Nanorods from Natural Stibnite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(11): 1213-1218. |
| [8] | DENG Min, JIANG Qi, FANG Yuan, LI Huan, QIU Jia-Xin, LU Xiao-Ying. Carbon Nanotubes/Polyaniline Chemically Modified Electrode: Preparation and Ascorbic Acid Detection [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(1): 53-59. |
| [9] | YANG Kun-Kun, YANG Shao-Hua, ZHAO Ping, ZHAO Yan-Long. Hydrothermal Synthesis of FeS2/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite with Enhanced Discharge Performance for Thermal Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 691-698. |
| [10] | GUO Yu, LI Dong-Xin, WU Hong-Mei, JIN Yu-Jia, ZHOU Li-Dai, CHEN Qiang-Qiang. Preparation, Characterization and Catalytic Performance of Supported Titanium Silicalite-1 Zeolite Membrane Catalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(6): 631-636. |
| [11] | ABUBAKER Abutartour, LOTFIA El-Majdoub, SHI Ya-Sai, LI Ni-Li, XU Qing-Hong. A New Porous Zirconium Phosphonate Hybride Material and Its Adsorption Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(3): 305-312. |
| [12] | LU Shu-Juan, WANG Chang, ZHAO Bo-Wen, WANG Hao, LIU Jing-Bing, YAN Hui. Electrochromic Properties of PEG-modified Tungsten Oxide Thin Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(2): 185-190. |
| [13] | YAN Hui, Qi Lu, ZHANG Ding, WANG Zheng-De, LIU Yun-Ying, WANG Xiao-Xia, ZHU Tie-Yong. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Spherical Li4Ti5O12 as Anode Material for Lithium-ion Secondary Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(11): 1242-1248. |
| [14] | XIE Hui-Dong, LI Fei, CHEN Chao, XI Hai-Hong, SHI Ling. Microwave Dielectric Properties of LaPO4 Ceramics Synthesized by a Hydrothermal Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(8): 882-886. |
| [15] | HUANG Chang-Bao, NI You-Bao, WU Hai-Xin, WANG Zhen-You, XIAO Rui-Chun, QI Ming. Growth and Characterization of Sulfur-doped GaSe Single Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(8): 887-890. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||