
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 1306-1312.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140099
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Xiang-Rong1, LIU Zong-Huai2
Received:2014-03-05
Revised:2014-06-18
Published:2014-12-20
Online:2014-11-20
Supported by:CLC Number:
MA Xiang-Rong, LIU Zong-Huai. Effect of Sodium Citrate Amount on Morphology and Anion Exchange Property of Co2+-Ni2+-Fe3+-CO32- LDHs[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(12): 1306-1312.
| TSC amounts/(mmol·L-1) | Samples | Co2+/Ni2+/Fe3+ molar ratio | C/wt% | Samples | C/wt% | Cl/wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | S1-LDHs | 1.00/6.01/2.01 | 1.169 | D1-LDHs | 0.001 | 6.841 |
| 1.0 | S2-LDHs | 1.00/5.85/2.00 | 1.188 | D2-LDHs | 0.002 | 6.953 |
| 1.5 | S3-LDHs | 1.00/5.53/1.98 | 1.217 | D3-LDHs | 0.727 | 2.868 |
| 3.0 | S4-LDHs | 1.00/5.04/2.03 | 1.392 | D4-LDHs | 1.345 | 0.274 |
Table 1 Co2+/Ni2+/ Fe3 molar ratios in samples prepared with different TSC amounts and analysis on C and Cl elements in samples treated with a NaCl-HCl mixed solution
| TSC amounts/(mmol·L-1) | Samples | Co2+/Ni2+/Fe3+ molar ratio | C/wt% | Samples | C/wt% | Cl/wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | S1-LDHs | 1.00/6.01/2.01 | 1.169 | D1-LDHs | 0.001 | 6.841 |
| 1.0 | S2-LDHs | 1.00/5.85/2.00 | 1.188 | D2-LDHs | 0.002 | 6.953 |
| 1.5 | S3-LDHs | 1.00/5.53/1.98 | 1.217 | D3-LDHs | 0.727 | 2.868 |
| 3.0 | S4-LDHs | 1.00/5.04/2.03 | 1.392 | D4-LDHs | 1.345 | 0.274 |
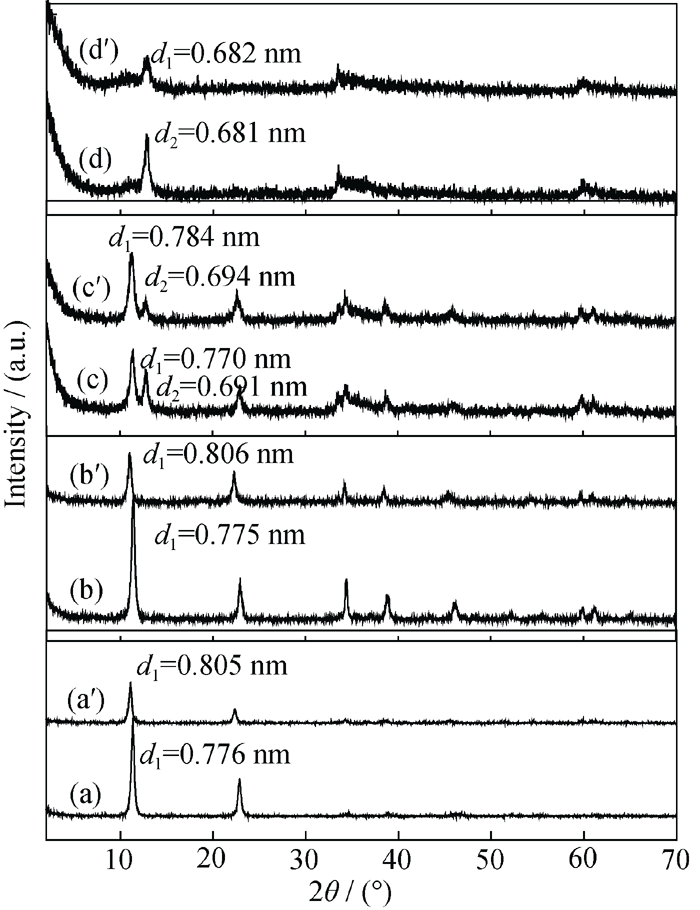
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of the products prepared with various TSC amounts and their corresponding products by treatment with a mixture solution of HCl-NaCl (a) S1-LDHs; (a°) D1-LDHs; (b) S2-LDHs; (b°) D2-LDHs; (c) S3-LDHs; (c°) D3-LDHs; (d) S4-LDHs; (d°) D4-LDHs
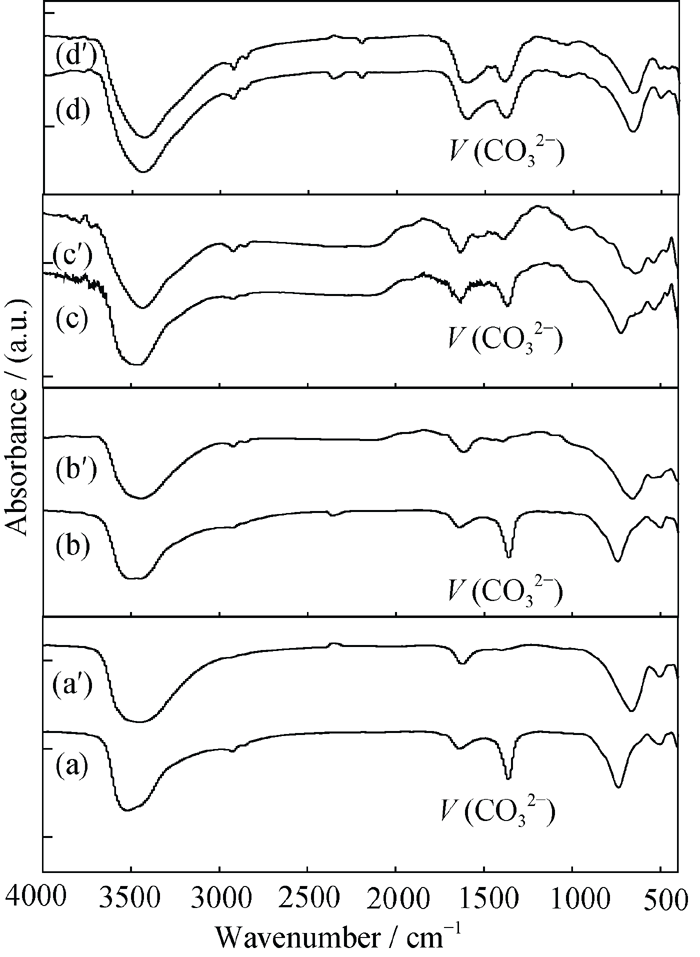
Fig. 4 FT-IR spectra of the obtained products in various TSC amounts and their corresponding products after treatment with a mixture of HCl-NaCl (a) S1-LDHs; (a°) D1-LDHs; (b) S2-LDHs; (b°) D2-LDHs; (c) S3- LDHs; (c°) D3-LDHs; (d) S4-LDHs; (d°) D4-LDHs
| [1] | TAYLOR H F.Crystal structure of some double hydroxide minerals. Mineral. Mag., 1973, 39(304): 377-389. |
| [2] | MIYATA S.Anion-exchange properties of hydrotalcite-like conpounds. Clay Clay Miner., 1983, 31(4): 305-311. |
| [3] | CHIBWE K, JONES W.Intercalation of organic and inorganic anions into layered double hydroxides. Chem. Commun., 1989, 926-927. |
| [4] | XIANG X, HIMA H I, WANG H, et al.Facile synthesis and catalytic properties of nickel-based mixed-metal oxides with mesopore networks from a novel hybrid composite precursor. Chem. Mater., 2008, 20(3): 1173-1182. |
| [5] | PRINETTO F, GHIOTTI G, DURAND R, et al.Investigation of acid-base properties of catalysts obtained from layered double hydroxides. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104(47): 11117-11126. |
| [6] | YU J, WANG X, TAO Y, et al.Effective NOx decomposition and storage/reduction over mixed oxides derived from layered double hydroxides. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2007, 46(17): 5794-5797. |
| [7] | KHAN A I, O’HARE D J. Intercalation chemistry of layered double hydroxides: recent developments and applications. J. Mater. Chem., 2002, 12(11): 3191-3198. |
| [8] | TZOU Y M, WANG S L, HSU L C, et al.Deintercalation of Li/Al LDH and its application to recover adsorbed chromate from used adsorbent. Appl. Clay. Sci., 2007, 37(1/2): 107-114. |
| [9] | WANG Y, YANG W, ZHANG S, et al.Synthesis and electeochemical characterization of Co-Al layered double hydrox-ides. J. Electrochem. Soc., 2005, 152(11): A2130-A2137. |
| [10] | LI F, LIU J, LI F, et al.Stoichiometric synthesis of pure MFe2O4(M=Mg, Co and Ni) spinel ferrites from tailored layered double hydroxide (hydro-talcite-like) precursors. Chem. Mater., 2004, 16(88): 1597-1602. |
| [11] | MEYN M, BENEKE K, LAGALY G.Anion-exchange reactions of layered double hydroxides. Adv. Inorg. Chem., 1990, 29(26): 5201-5207. |
| [12] | LI X, YANG W, LI F, et al.Stoichiometric synthesis of pure NiFe2O4 spinel from layered double hydroxide precurors for use as the anode material in lithium-ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. Solids., 2006, 67(6): 1286-1290. |
| [13] | LIU Z, MA R, OSADA M, et al.Synthesis, anion exchange, and delamination of Co-Al layered double hydroxide: assembly of the exfoliated nanosheet/polyanion composite films and magneto- optical studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(14): 4872-4880. |
| [14] | LIU Z, MA R, EBINA Y, et al.General synthesis and delamination of highly crystalline transition-metal-bearing layered double hydroxides. Langmuir, 2007, 23(2): 861-867. |
| [15] | MA R, LIU Z, TAKADA K, et al.Synthesis and exfoliation of Co2+-Fe3+ layered double hydroxides: an innovative topochemical approach. J. Mater. Chem., 2007, 129(16): 5257-5263. |
| [16] | NOBUO I, TAKI M, YOSHIRO K, et al.Deintercalation of carbonate ions from a hydrotalcite-like compound: enhanced decarbonation using acid-salt mixed solution. Chem. Mater., 2004, 16(15): 2926-2932. |
| [17] | HAN Y F, LIU Z H, YANG Z P, et al.Preparation of Ni2+-Fe3+ layered double hydroxide material with high crystallinity and well-defined hexagonal shapes. Chem. Mater., 2008, 20(2): 360-363. |
| [18] | OKAMOTO K, SASAKI T, FUJITA T, et al.Preparation of highly oriented organic-LDH hybrid films by combining the decarbon-ation, anion-exchange, and delamination processes. J. Mater. Chem., 2006, 16(17): 1608-1616. |
| [19] | MENG W, LI F, EVANS D G, et al.Preparation and intercalation chemistry of magnesium-iron (III) layered double hydroxides con-tai-ning exchangeable interlayer chloride and nitrate ions. Mater. Res. Bull., 2004, 39(9): 1185-1193. |
| [20] | LI H J, ZHU G, YANG Z P, et al.Preparation and capacitance property of MnO2-pillared Ni2+-Fe3+ layered double hydroxides nanocomposite. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci., 2010, 345(2): 228-233. |
| [1] | LI Qiaolei, GU Yue, YU Xuehua, ZHANG Chaowei, ZOU Mingke, LIANG Jingjing, LI Jinguo. Effect of Sintering Temperature on Surface Morphology and Roughness of 3D-printed Silicon Ceramic Cores [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(3): 325-332. |
| [2] | SUN Peng, ZHANG Shaoning, BI Hui, DONG Wujie, HUANG Fuqiang. Tuning Nitrogen Species and Content in Carbon Materials through Constructing Variable Structures for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 766-772. |
| [3] | XIAO Yumin, Li Bin, QIN Lizhao, LIN Hua, LI Qing, LIAO Bin. Efficient Preparation of CuGeO3 with Controllable Morphology Using CuCl2 as Copper Source [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 69-74. |
| [4] | XU Jingwei,LI Zheng,WANG Zepu,YU Han,HE Qi,FU Nian,DING Bangfu,ZHENG Shukai,YAN Xiaobing. Morphology and Photocatalytic Performance Regulation of Nd3+-doped BiVO4 with Staggered Band Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 789-795. |
| [5] | GENG Rui-Wen, YANG Xiao-Jing, XIE Qi-Ming, LI Rui, LUO Liang. Material Removal Mechanism of Monocrystalline Germanium Based on Nano-scratch Experiment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(8): 867-872. |
| [6] | LIU Xiao-Yuan, LIU Bao-Dan, JIANG Ya-Nan, WANG Ke, ZHOU Yang, YANG Bing, ZHANG Xing-Lai, JIANG Xin. In-situ Synthesis of Perovskite SrTiO3 Nanostructures with Modified Morphology and Tunable Optical Absorption Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(1): 65-71. |
| [7] | JIANG Qing-Song, CHEN Ruo-Ting, LI Wen-Bo, CHENG Wen-Jie, HUANG Ye-Xiao, HU Guang. Application of Transparent Cobalt Sulfide Counter Electrodes in Dye-sensitized Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(8): 832-838. |
| [8] | QI Mei-Li, QI Jia, XIAO Gui-Yong, LV Yu-Peng. Effect of Surfactants on the Morphology of Hydroxyapatite Fibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(7): 726-730. |
| [9] | ZHU Yu-Chan, YUAN Min, ZHANG Huan, WANG Le, QUAN Shan-Shan, CHAI Bo, REN Zhan-Dong. Preparation of Pt/Ti Electrodes Preferred Growth along the [111] Direction and Its Electrocatalytic Activity for Chlorine Evolution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(5): 510-516. |
| [10] | LIU Jing-Jing, HEULENS Jeroen, GUO Mu-Xing, MOELANS Nele. Isothermal Crystal Growth Behavior of CaSiO3 in Ternary Oxide Melts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(5): 547-554. |
| [11] | SUN Xiao-Dan, LIU Zhong-Qun, YAN Hao. Preparation and Biological Application of Graphene Quantum Dots [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(4): 337-344. |
| [12] | ZHAI Ying-Jiao, LI Jin-Hua, CHU Xue-Ying, XU Ming-Ze, LI Xue, FANG Xuan, WEI Zhi-Peng, WANG Xiao-Hua. Preparation and Application of Molybdenum Disulfide Nanostructures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(9): 897-905. |
| [13] | ZHANG Chuan, WANG Ji-Tong, LI Xu, LONG Dong-Hui, QIAO Wen-Ming, LING Li-Cheng. Facile Preparation, Structural Control and Spheroidization of Mesoporous Carbons Using Hydrolyzed Water Glass as a Template [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(8): 848-854. |
| [14] | WEN Hai-Meng, SONG Jun, WANG Chong-Qing, ZHOU Yu, WANG Jun. Directly Synthesis of ZSM-22 Particles by Adding Polyurethane Foam in Ionic Liquid-directed Dry-gel-conversion [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(6): 615-620. |
| [15] | CHEN Jun-Jun, WANG Jing, HUI Xiang. Preparation and Characterization of Sodium Zirconium Phosphate Powder with Peculiar Morphology [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(8): 839-844. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||