
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (8): 807-813.DOI: 10.15541/jim20130568
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Min1, NIU Chao1, DONG Zhan-Jun2, CHE Yin-Sheng1, DONG Duo1, ZHENG Hao-Yan1, YANG Chang-Xiu1
Received:2013-10-31
Revised:2013-12-23
Published:2014-08-20
Online:2014-07-15
CLC Number:
WANG Min, NIU Chao, DONG Zhan-Jun, CHE Yin-Sheng, DONG Duo, ZHENG Hao-Yan, YANG Chang-Xiu. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Property of N-doped BiVO4 via Sol-Gel Method Using Corn Stem as Template[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(8): 807-813.
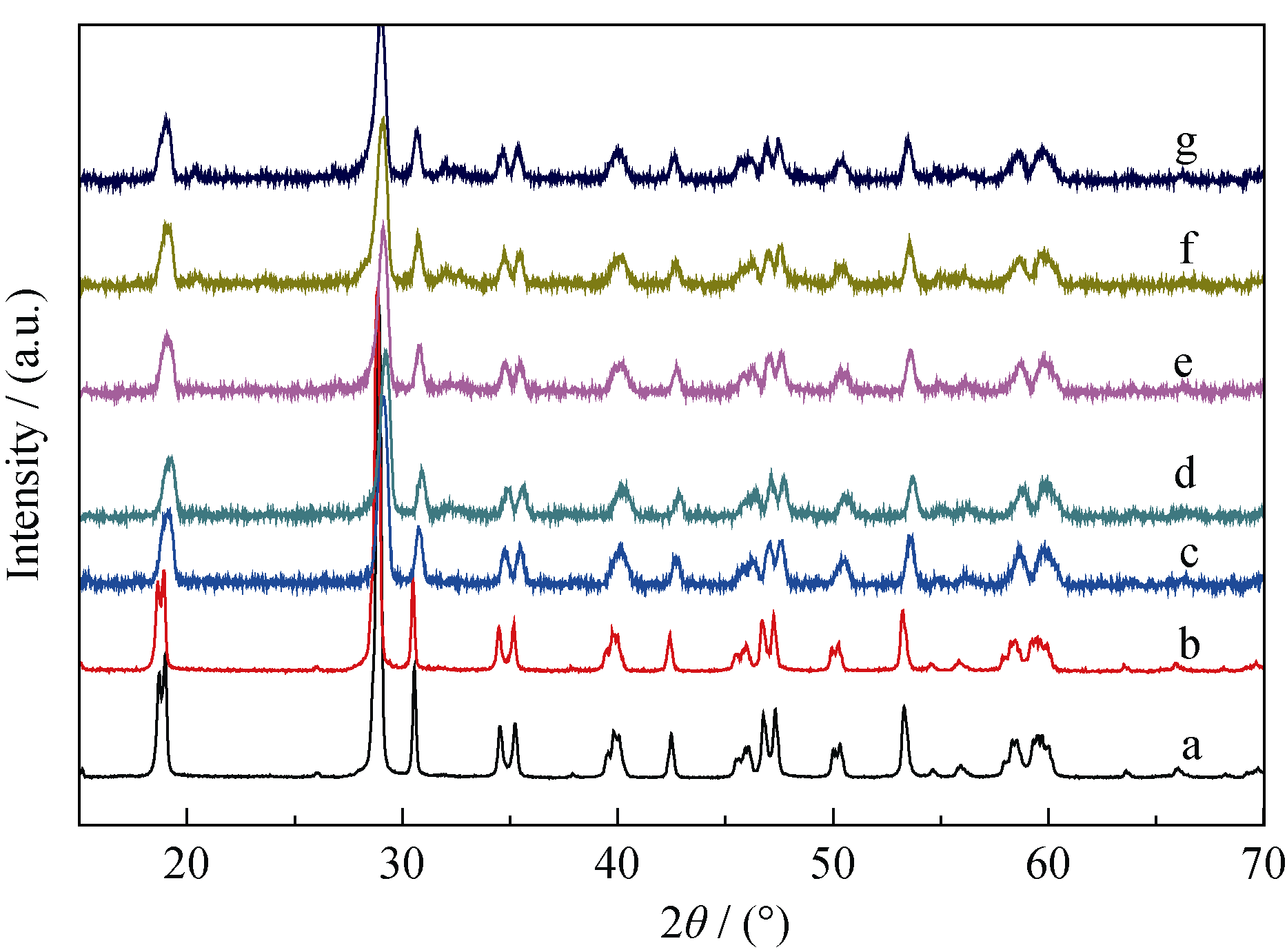
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of different BiVO4 samples (a) BiVO4; (b) BiVO4-12N; (c) CS-BiVO4; (d) CS- BiVO4-8N; (e) CS- BiVO4-10N; (f) CS- BiVO4-12N; (g) CS- BiVO4-14N
| Sample | D/nm | MO absorption amount | Band<br/>gap /eV |
|---|---|---|---|
| BiVO4 | 49 | 0.6% | 2.36 |
| CS-BiVO4 | 25 | 3.2% | 2.19 |
| CS-BiVO4-8N | 25 | 4.0% | 2.18 |
| CS-BiVO4-10N | 24 | 5.5% | 2.16 |
| CS-BiVO4-12N | 23 | 6.6% | 2.14 |
| CS-BiVO4-14N | 24 | 6.0% | 2.10 |
| BiVO4-12N | 27 | 1.2% | 2.23 |
Table 1 Structure and properties of samples
| Sample | D/nm | MO absorption amount | Band<br/>gap /eV |
|---|---|---|---|
| BiVO4 | 49 | 0.6% | 2.36 |
| CS-BiVO4 | 25 | 3.2% | 2.19 |
| CS-BiVO4-8N | 25 | 4.0% | 2.18 |
| CS-BiVO4-10N | 24 | 5.5% | 2.16 |
| CS-BiVO4-12N | 23 | 6.6% | 2.14 |
| CS-BiVO4-14N | 24 | 6.0% | 2.10 |
| BiVO4-12N | 27 | 1.2% | 2.23 |

Fig. 2 SEM images of different BiVO4 samples (a) Corn stem; (b) CS-BiVO4; (c) CS-BiVO4-8N; (d) CS- BiVO4-10N; (e) CS-BiVO4-12N; (f) CS-BiVO4-14N; (g) BiVO4; (h) BiVO4-12N
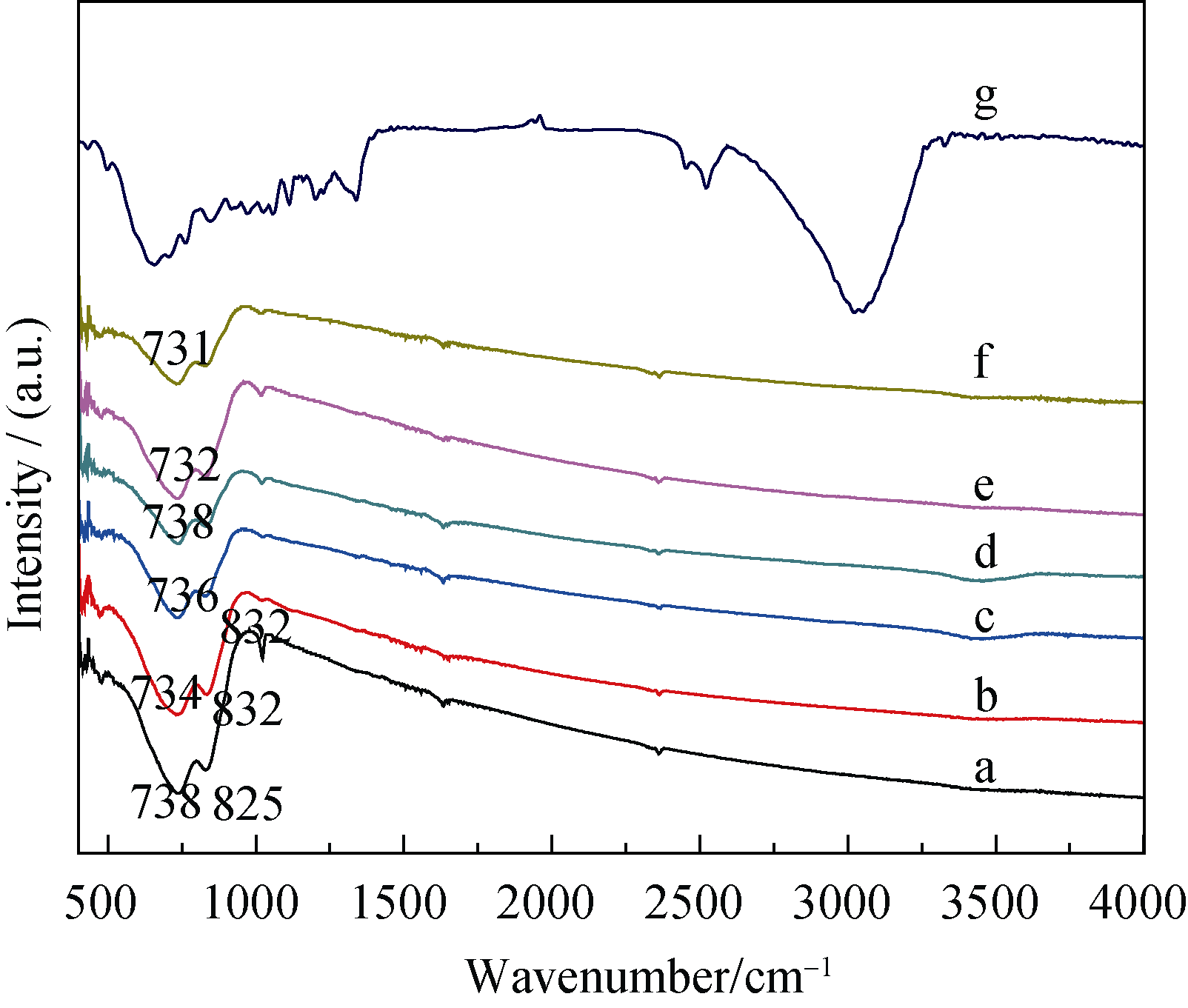
Fig. 4 FT-IR absorption spectra of different BiVO4 samples (a) BiVO4; (b)CS-BiVO4; (c) CS-BiVO4-8N; (d)CS-BiVO4-10N; (e) CS-BiVO4-12N; (f) CS- BiVO4-14N; (g) Corn-stem
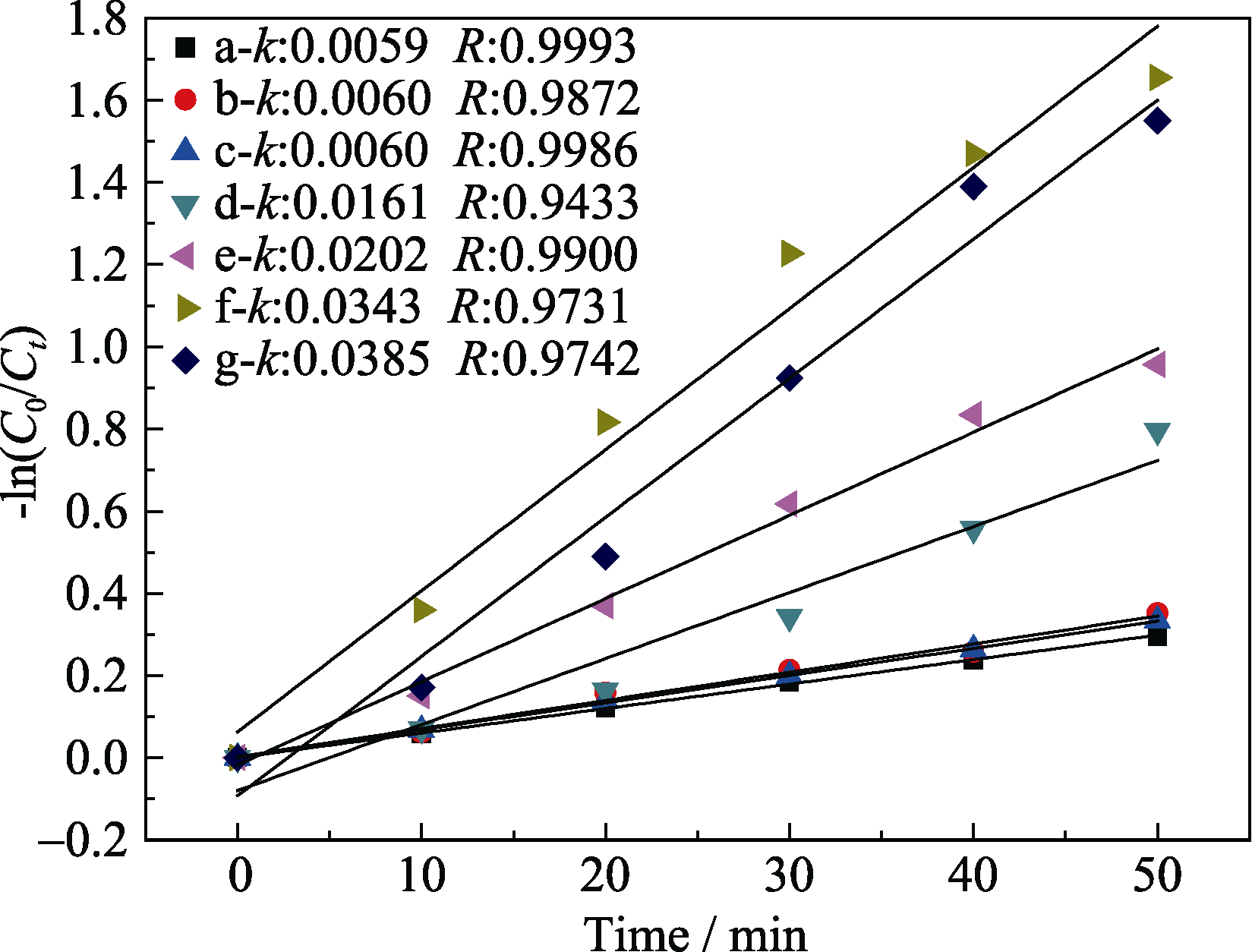
Fig. 7 -ln(Ct/C0) as a function of t on the catalysts by visible light irradiation (a) BiVO4; (b) CS-BiVO4; (c)BiVO4-12N; (d)CS-BiVO4-8N; (e) CS- BiVO4-10N; (f) CS- BiVO4-12N; (g) CS- BiVO4-14N
| [1] | LAI H F, CHEN C C, CHANG Y K, et al. Efficient photocatalytic degradation of thiobencarb over BiVO4 driven by visible light: Parameter and reaction pathway investigations .Separ. Purif. Tech., 2013, 122: 78-86. |
| [2] | XIAO Q, GAO L, ZHANG X. Synthesis and characterization of highly visible-light active monoclinic mesoporous BiVO4 .Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(12): 1256-1260. |
| [3] | GAO X M, FU F, WU Y F, et al. Preparation of Co-BiVO4 photocatalyst and its application in the photocatalytic oxidative thiophene. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(10): 1073-1078. |
| [4] | LIU G C, JIN Z, ZHANG X B, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis and photocatalytic properties of Cu-doped BiVO4 microsheets .Journal of Inorganic Materials. 2013, 28(3): 287-294. |
| [5] | LAI K R, ZHU Y T, LU J B, et al. Synergistic effects of codopants on photocatalytic O2 evolution in BiVO4. Solid State Sciences, 2013, 24: 79-84. |
| [6] | CASTILLO, NIKOLA C. HEEL ANDRE, GRAULE THOMAS, et al. Flame-assisted synthesis of nanoscale, amorphous and crystalline, spherical BiVO4 with visible-light photocatalytic activity .Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2010, 95: 335-347. |
| [7] | LI S H, EIJI YAMASUE, HIDEYUKI OKUMURA, et al. Effect of oxygen and nitrogen concentration of nitrogen doped TiOx film as photocatalyst prepared by reactive sputtering.Appl.Catal. A: Gener., 2009, 371: 179-190. |
| [8] | RAO Z P, WAN J, FENG J H, et al. Preparation of nano-scaled TiO2-xNx photocatalyst by PEALD in-situ doping . Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(7): 691-695. |
| [9] | LU Y G, YANG Y C, YE Z X, et al. Preparation and visible light responsive photocatalytic activity of nitrogen-doped Bi2O3 photocatalyst. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(6): 643-648. |
| [10] | Sun J H, Qiao L P, Sun S P, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of Orange G on nitrogen-doped TiO2 catalysts under visible light and sunlight irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 155: 312-319. |
| [11] | CHEN S F, LIU X Q, LIU Y Z, et al. The preparation of nitrogen-doped TiO2-xNx photocatalyst coated on hollow glass microbeads. Appl. Surface Sci., 2007, 253: 3077-3082. |
| [12] | Wang M, Liu Q, Che Y S.et al. Characterization and photocatalytic properties of N-doped BiVO4 synthesized via a Sol-Gel method. J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 548: 70-76. |
| [13] | WANG M, LUAN H Y, TONG Y, et al. Synthesis and photocatalytic property of FeVO4 photocatalyst by corn stalk template method .Journal of Shenyang Ligong University, 2012, 31(6): 1-5. |
| [14] | LI J Q, LI Q L, ZHAO J, et al. Preparation and photocatalytic properties of reticular TiO2 by leaf template Method. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 68(18): 1845-1849. |
| [15] | ZHOU W J, HE W, MA J Y, et al. Biosynthesis of mesoporous organic-inorganic hybrid Fe2O3 with high photocatalytic activity. Mater. Sci. Engi. C, 2009, 29: 1893-1896. |
| [16] | DONG Q, SU H L, ZHANG D, et al. Synthesis of hierarchical mesoporous titania with interwoven networks by eggshell membrane directed sol-gel technique.Micro. Mesopo. Mater., 2007, 98: 344-351. |
| [17] | YAN Y, SUN S F, SONG Y, et al. Microwave-assisted in situ synthesis of reduced graphene oxide-BiVO4 composite photocatalysts and their enhanced photocatalytic performance for the degradation of ciprofloxacin. J. Hazar. Mater., 2013, 250-251: 106-114. |
| [18] | ZHANG A P, ZHANG J Z. Characterization of visible-light-driven BiVO4 photocatalysts synthesized via a surfactant-assisted hydrothermal method. Spectrochimica Acta Part A, 2009, 73: 336-341. |
| [19] | LIU S X, CHEN X Y, CHEN X. Preparation of N-doped visible-light response nanosize TiO2 photocatalyst using the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis method. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2006, 27(8): 697-702. |
| [20] | HAO D, JIANG C H, YANG Z M, et al. The preparation of N-doped TiO2 and its photocatalytic property. Chin. J. Mater. Reseach, 2013, 27(3): 247-251. |
| [21] | WANG J P, WANG Z Y, HUANG B B, et al. Oxygen vacancy induced band-gap narrowing and enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity of ZnO. Appl. Mater. Interf., 2012, 4: 4024-4030. |
| [1] | WANG Xinling, ZHOU Na, TIAN Yawen, ZHOU Mingran, HAN Jingru, SHEN Yuansheng, HU Zhiyi, LI Yu. SnS2/ZIF-8 Derived Two-dimensional Porous Nitrogen-doped Carbon Nanosheets for Lithium-sulfur Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 938-946. |
| [2] | AN Lin, WU Hao, HAN Xin, LI Yaogang, WANG Hongzhi, ZHANG Qinghong. Non-precious Metals Co5.47N/Nitrogen-doped rGO Co-catalyst Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Performance of TiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(5): 534-540. |
| [3] | LIU Ziruo, LIU Wei, HAO Ce, HU Jinwen, SHI Yantao. Honeycomb-like Carbon-supported Fe Single Atom Catalyst: Preparation and Electrocatalytic Performance in Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 943-949. |
| [4] | CAI Miao, CHEN Zihang, ZENG Shi, DU Jianghui, XIONG Juan. CuS Nanosheet Decorated Bi5O7I Composite for the Enhanced Photocatalytic Reduction Activity of Aqueous Cr(VI) [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 665-672. |
| [5] | ZHENG Yanning, JI Junrong, LIANG Xueling, LAI Zhengjie, CHENG Qifan, LIAO Dankui. Performance of Nitrogen-doped Hollow Carbon Spheres as Oxidase Mimic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 527-534. |
| [6] | LIU Cai, LIU Fang, HUANG Fang, WANG Xiaojuan. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Alga-based CDs-Cu-TiO2 Composite Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1154-1162. |
| [7] | XU Shichao,ZHU Tianzhe,QIAO Yang,BAI Xuejian,TANG Nan,ZHENG Chunming. Fabrication of Z-scheme BiVO4/GO/g-C3N4 Photocatalyst with Efficient Visble-light Photocatalytic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 839-846. |
| [8] | ZHU Enquan,MA Yuhua,AINIWA· Munire,SU Zhi. Adsorption-enrichment and Localized-photodegradation of Bentonite-supported Red Phosphorus Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 803-808. |
| [9] | Shi-Qiang LUO, Chun-Man ZHENG, Wei-Wei SUN, Wei XIE, Jian-Huang KE, Shuang-Ke LIU, Xiao-Bin HONG, Yu-Jie LI, Jing XU. Controllable Preparation of Co-NC Nanoporous Carbon Derived from ZIF-67 for Advanced Lithium-sulfur Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(5): 502-508. |
| [10] | WANG Zhong, ZHA Xian-Hu, WU Ze, HUANG Qing, DU Shi-Yu. First-principles Study on Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Mn-doped Strontium Ferrite SrFe12O19 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(10): 1047-1054. |
| [11] | HE Wang-Tao, MA Ru-Guang, ZHU Yu-Fang, YANG Ming-Jie, WANG Jia-Cheng. Renewable Porous Carbons Prepared by KOH Activation as Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(10): 1115-1122. |
| [12] | LI Jian, ZHANG Gang-Hua, FAN Li-Kun, HUANG Guo-Quan, GAO Zhi-Peng, ZENG Tao. Enhanced Visible-light-driven Photocatalytic Activity of Multiferroic KBiFe2O5 by Adjusting pH Value [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(7): 805-810. |
| [13] | WANG Dan-Jun, WANG Chan, ZHAO Qiang, GUO Li, YANG Xiao, WU Jiao, FU Feng. Au Nanoparticles (NPs) Surface Plasmon Resonance Enhanced Photocatalytic Activities of Au/Bi2WO6 Heterogeneous Nanostructures [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(6): 659-666. |
| [14] | ZHAO Ning, LIU Chun-Jun, WANG Bo, PENG Tong-Hua. Stacking Faults in 4H-SiC Single Crystal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(5): 540-544. |
| [15] | YAN Shi-Sheng, PENG Hong-Yan, ZHAO Zhi-Bin, PAN Meng-Mei, YANG Da-Li, A Jin-Hua, YE Guo-Lin, WANG Chong-Tai, GUO Xin-Wei. Nitrogen-doped Diamond Electrode Property and Anodic Catalytic Degradation of Nitrobenzene [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(5): 565-569. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||