
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 1321-1328.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220080
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIAO Zhixiang1( ), JIA Fanhao1,2(
), JIA Fanhao1,2( ), WANG Yongchen1, CHEN Jianguo1, REN Wei2, CHENG Jinrong1(
), WANG Yongchen1, CHEN Jianguo1, REN Wei2, CHENG Jinrong1( )
)
Received:2022-02-17
Revised:2022-03-29
Published:2022-12-20
Online:2022-08-04
Contact:
CHENG Jinrong, professor. E-mail: jrcheng@shu.edu.cn;About author:JIAO Zhixiang (1996-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: jzxxxzj@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
JIAO Zhixiang, JIA Fanhao, WANG Yongchen, CHEN Jianguo, REN Wei, CHENG Jinrong. Curie Temperature Prediction of BiFeO3-PbTiO3-BaTiO3 Solid Solution Based on Machine Learning[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1321-1328.
| Feature | Name | Physical attributes |
|---|---|---|
| μ | Reduced mass | Reduced mass of atoms |
| A/B | Ionic radius | Shannon ion radius |
| A/B_C | Covalent radius | The covalent bond radius of an atom |
| A/B_E | Electronegativity | Electronegativity of atoms |
| A/B_NV | NValence | The number of electrons of unfilled orbitals |
| A/B_NU | NUfilled | The number of electrons of unfilled orbitals |
| A/B_S | Space group numbering | The serial number of the element's space group in the space group table |
| Ti,Fe,Ba,Pb,Bi | Element content | Element content ratio of metal ions |
Table 1 Basic descriptor and related physical meaning
| Feature | Name | Physical attributes |
|---|---|---|
| μ | Reduced mass | Reduced mass of atoms |
| A/B | Ionic radius | Shannon ion radius |
| A/B_C | Covalent radius | The covalent bond radius of an atom |
| A/B_E | Electronegativity | Electronegativity of atoms |
| A/B_NV | NValence | The number of electrons of unfilled orbitals |
| A/B_NU | NUfilled | The number of electrons of unfilled orbitals |
| A/B_S | Space group numbering | The serial number of the element's space group in the space group table |
| Ti,Fe,Ba,Pb,Bi | Element content | Element content ratio of metal ions |
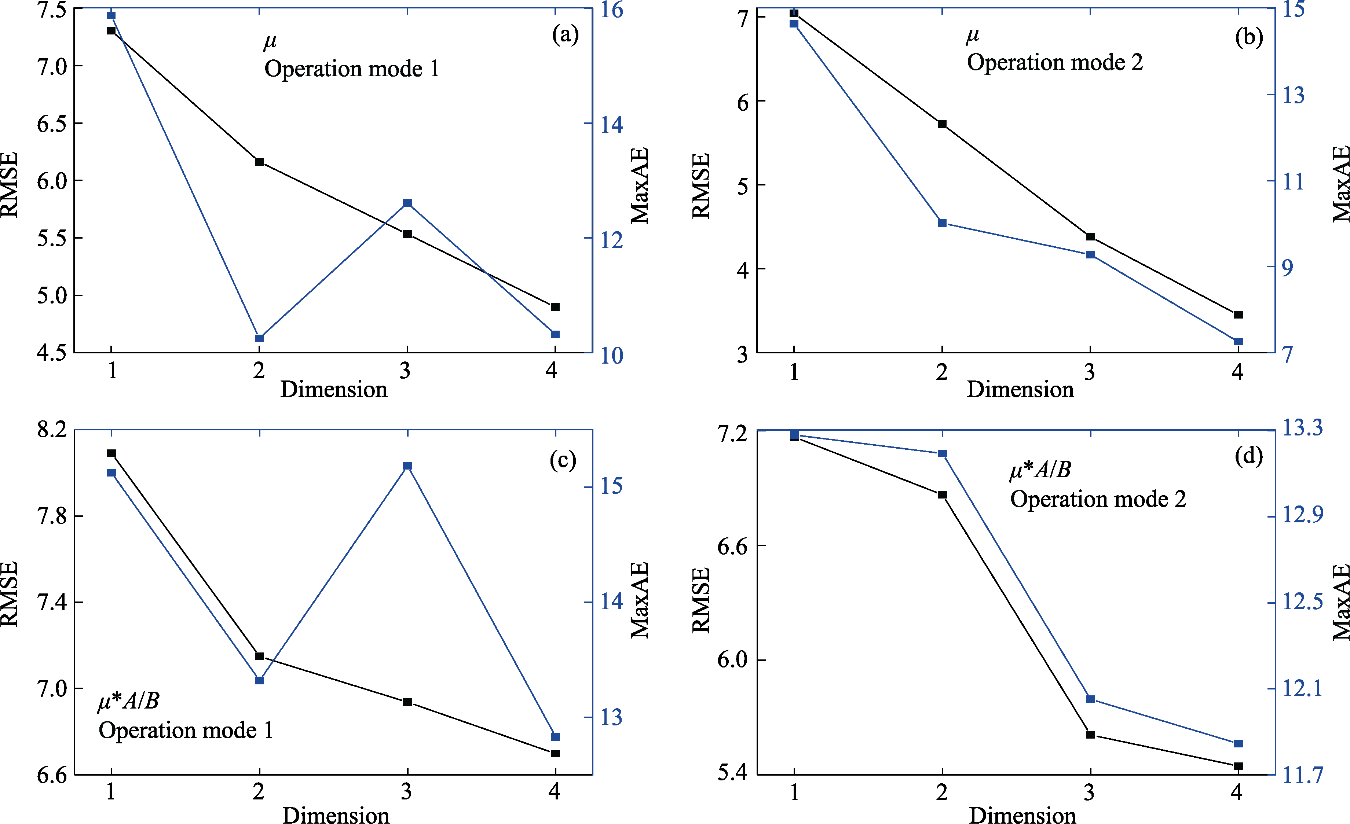
Fig. 4 RMSE and MaxAE of μ and μ*A/B varied with dimension under different operation modes (a, c) use operation mode 1; (b, d) use operation mode 2; (a, b) use the descriptor μ; (c, d) use the descriptor μ*A/B
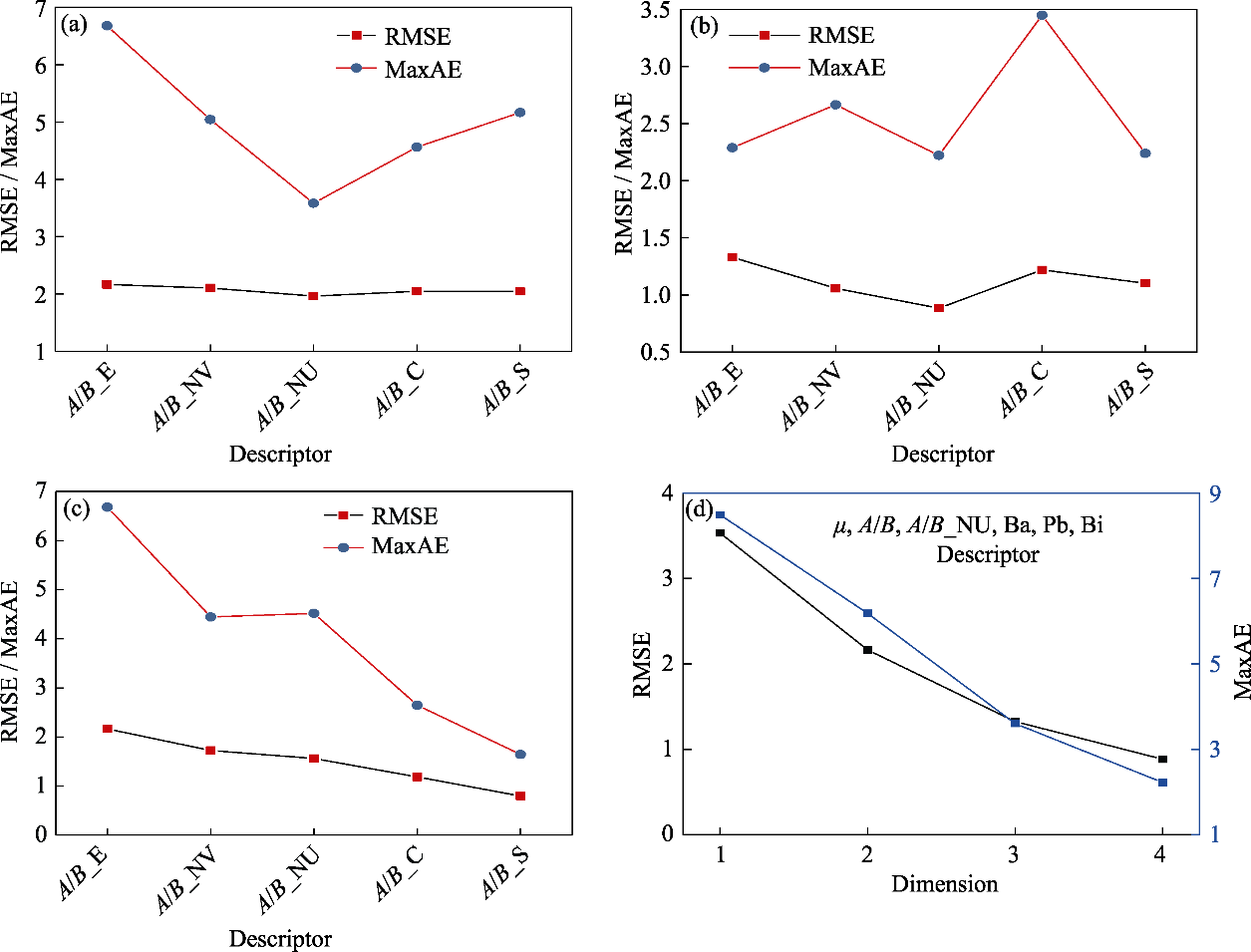
Fig. 6 Effects of the changes of descriptor and model dimension on the RMSE and MaxAE (a) μ and A/B are the first two descriptors, and the third descriptor changes; (b) μ, A/B, Ba, Pb, and Bi are the first five descriptors, and the sixth descriptor changes; (c) μ and A/B are the first two descriptors and the third to seventh descriptors are introduced one by one. (d) Effect of the change of the dimension of the model fitted by six finally selected descriptors (μ, A/B, A/B_NU, Ba, Pb, and Bi) on RMSE and MaxAE
| Sample | Tc/℃ (y) | μʹ (x1) | A/Bʹ (x2) | A/B_NU (x3) | Ba (x4) | Pb (x5) | Bi (x6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi0.62Pb0.23Ba0.15Fe0.62Ti0.38O3 | 547 | 0.2821 | 0.3882 | 0.5036 | 0.0750 | 0.1150 | 0.3100 |
| Bi0.6Pb0.25Ba0.15Fe0.6Ti0.4O3 | 540 | 0.2690 | 0.4606 | 0.5000 | 0.0750 | 0.1250 | 0.3000 |
| Bi0.54Pb0.31Ba0.15Fe0.54Ti0.46O3 | 502 | 0.2295 | 0.6789 | 0.4897 | 0.0750 | 0.1550 | 0.2700 |
Table 2 The test sets after adjusting descriptor parameters
| Sample | Tc/℃ (y) | μʹ (x1) | A/Bʹ (x2) | A/B_NU (x3) | Ba (x4) | Pb (x5) | Bi (x6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi0.62Pb0.23Ba0.15Fe0.62Ti0.38O3 | 547 | 0.2821 | 0.3882 | 0.5036 | 0.0750 | 0.1150 | 0.3100 |
| Bi0.6Pb0.25Ba0.15Fe0.6Ti0.4O3 | 540 | 0.2690 | 0.4606 | 0.5000 | 0.0750 | 0.1250 | 0.3000 |
| Bi0.54Pb0.31Ba0.15Fe0.54Ti0.46O3 | 502 | 0.2295 | 0.6789 | 0.4897 | 0.0750 | 0.1550 | 0.2700 |
| Sample | Experim- ental Tc/℃ | Predi- ction Tc/℃ | Abso- lute error/℃ | Rela- tive- error/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi0.62Pb0.23Ba0.15Fe0.62Ti0.38O3 | 547 | 544.91 | 2.09 | 0.38 |
| Bi0.6Pb0.25Ba0.15Fe0.6Ti0.4O3 | 540 | 536.12 | 3.88 | 0.72 |
| Bi0.54Pb0.31Ba0.15Fe0.54Ti0.46O3 | 502 | 492.52 | 9.48 | 1.89 |
Table 3 Results of external verification set
| Sample | Experim- ental Tc/℃ | Predi- ction Tc/℃ | Abso- lute error/℃ | Rela- tive- error/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi0.62Pb0.23Ba0.15Fe0.62Ti0.38O3 | 547 | 544.91 | 2.09 | 0.38 |
| Bi0.6Pb0.25Ba0.15Fe0.6Ti0.4O3 | 540 | 536.12 | 3.88 | 0.72 |
| Bi0.54Pb0.31Ba0.15Fe0.54Ti0.46O3 | 502 | 492.52 | 9.48 | 1.89 |
| [1] |
CHEN J, QI Y, SHI G, et al. A high temperature piezoelectric ceramic: (1-x)(Bi0.9La0.1)FeO3-xPbTiO3 crystalline solutions. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control., 2009, 56(9): 1820-1825.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN J, JIN D, CHENG J. Impedance spectroscopy studies of 0.7Bi(Fe1-xGax)O3-0.3PbTiO3 high temperature piezoelectric ceramics. J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 580: 67-71.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHENG J, YU S, CHEN J, et al. Dielectric and magnetic enhancements in BiFeO3-PbTiO3 solid solutions with La doping. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, 89(12): 122911.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHEN J, CHENG J. Enhanced high-field strain and reduced high- temperature dielectric loss in 0.6(Bi0.9La0.1)(Fe1-xTix)O3-0.4PbTiO3 piezoelectric. Ceram. Int., 2015, 41(1): 1617-1621.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 谢颖. ABO3型钙钛矿的相变机理表面稳定性和电子结构的理论研究. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江大学出版社, 2015. |
| [6] | MURPHY K. Machine learning:a probabilistic perspective. Cambridge: The MIT Press, 2012, 58(8): 27-71. |
| [7] | PEDREGOSA F, VAROQUAUX G, GRAMFORT A, et al. Scikit- learn: machine learning in python. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12(10): 2825-2830. |
| [8] |
RUPP M, TKATCHENKO A, MÜLLER K, et al. Fast and accurate modeling of molecular atomization energies with machine learning. Phy. Rev. Lett., 2012, 108(5): 058301.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
JORDAN M, MITCHELL T. Machine learning: trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science, 2015, 349(6245): 255-260.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
ZHONG M, TRAN K, MIN Y, et al. Accelerated discovery of CO2 electrocatalysts using active machine learning. Nature, 2020, 581(7807): 178-183.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
BATRA R. Accurate machine learning in materials science facilitated by using diverse data sources. Nature, 2021, 589(7843): 524-525.
DOI URL |
| [12] | RANDHAWA G, HILL K, KARI L. ML-DSP: Machine learning with digital signal processing for ultrafast, accurate, and scalable genome classification at all taxonomic levels. BioMed Central, 2019, 20(1): 267-23. |
| [13] |
CHENG Z, ZHU E, CHEN N. Application of orthogonal expansion to mapping and modelling. Chemometr., 1993, 7(4): 243-253.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
CHEN N, LI C, QIN P. Chemical pattern recognition applied to materials optimal design and industry optimization. Chin. Sci. Bull., 1997, 42(10): 793-799.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
CHEN N, LU W, CHEN R, et al. Chemometric methods applied to industrial optimization and materials optimal design. Chemom. Intel. Lab. Syst., 1999, 45(1): 329-333.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
CHEN N, ZHU D, WANG W. Intelligent materials processing by hyperspace data mining. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intel., 2000, 13(5): 527-532.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
RESTA R. Macroscopic polarization in crystalline dielectrics: the geometric phase approach. Review Modern Physics, 1994, 66(3): 899-916.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ARMIENTO R, KOZINSKY B, FORNARI M, et al. Screening for high-performance piezoelectrics using high-throughput density functional theory. Physics Review B, 2011, 84(1): 014103.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
PRASANNA V, BENJAMIN K, ALP S, et al. Experimental search for high-temperature ferroelectric perovskites guided by two-step machine learning. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1668.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
EVAN M, SUHAS Y, ILYA G. Prediction of the Curie temperatures of ferroelectric solid solutions using machine learning methods. Computational Materials Science, 2021, 199(7061): 110730.
DOI URL |
| [21] | OUYANG R, CURTAROLO S, AHMETCIK E, et al. SISSO: A compressed-sensing method for identifying the best low-dimensional descriptor in an immensity of offered candidates. Phys. Rev. Mater., 2018, 2(8): 083802. |
| [22] |
OUYANG R, AHMETCIK E, CARBOGNO C, et al. Simultaneous learning of several materials properties from incomplete databases with multi-task SISSO. J. Phys.: Mater., 2019, 2(2): 024002.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
OUYANG R. Exploiting ionic radii for rational design of halide perovskites. Chem. Mater., 2020, 32(1): 595-604.
DOI URL |
| [24] | NING Z. Dielectric, ferroelectric, piezoelectric and aging properties of BiFeO3-PbTiO3-BaTiO3 high temperature piezoelectric ceramics. Shanghai: Master Thesis, Shanghai University, 2020. |
| [25] | TU T. Fabrication of BF-PT-BT high temperature piezoelectric ceramics and sensors. Shanghai: Master Thesis, Shanghai University, 2017. |
| [26] |
CHRISTOPHER J, CHRISTOPHER S, BRYAN R, et al. New tolerance factor to predict the stability of perovskite oxides and halides. Science Advances, 2019, 5(2): eaav0693.
DOI URL |
| [27] | BUTLER K, FROST J, SKELTON J, et al. Computational materials design of crystalline solids. Che. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(22): 6138-6146. |
| [28] |
YU J, ITOH M. Physics-guided data-mining driven design of room- temperature multiferroic perovskite oxides. Phys. Status Solidi RRL, 2019, 13(6): 1900028.
DOI URL |
| [29] | UUSI E, MALM J, IMAMURA N, et al. Characterization of RMnO3 (R=Sc, Y, Dy-Lu): high-pressure synthesized metastable perovskites and their hexagonal precursor phases. Materials Chemistry & Physics, 2008, 112(3): 1029-1034. |
| [30] |
SCHOBER P, BOER C, SCHWARTE L. Correlation coefficients: appropriate use and interpretation. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 2018, 126(5): 1763-1768.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
YANG X, LI M, SU Q, et al. QSAR studies on pyrrolidine amides derivatives as DPP-IV inhibitors for type 2 diabetes. Medicinal Chemistry Research, 2013, 22(11): 5274-5283.
DOI URL |
| [1] | ZHANG Jiawei, CHEN Ning, CHENG Yuan, WANG Bo, ZHU Jianguo, JIN Cheng. Electrical Properties of Bismuth Layered Piezoelectric Bi4Ti3O12 Ceramics with A/B-site Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [2] | SHI Siqi, SUN Shiyu, MA Shuchang, ZOU Xinxin, QIAN Quan, LIU Yue. Detection Method on Data Accuracy Incorporating Materials Domain Knowledge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1311-1320. |
| [3] | ZHANG Ruihong, WEI Xin, LU Zhanhui, AI Yuejie. Training Model for Predicting Adsorption Energy of Metal Ions Based on Machine Learning [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1178-1184. |
| [4] | MENG Yanran, WANG Xinger, YANG Jian, XU Han, YUE Feng. Research on Machine Learning Based Model for Predicting the Impact Status of Laminated Glass [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 61-68. |
| [5] | GUO Lin, QIAO Xianji, LI Xiuzhi, LONG Xifa, HE Chao. Dielectric, Ferroelectric and Piezoelectric Properties of Pb(In1/2Nb1/2)O3-Pb(Ni1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 Ternary Ceramics Near Morphotropic Phase Boundary [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12): 1380-1384. |
| [6] | SHI Wei, LENG Sen-Lin, LONG Yu, ZHU Jian-Guo, XIAO Ding-Quan. Effect of BiYbO3 Solid Solution Limit on Electric Properties and Structure of BSPT Piezoceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(06): 623-628. |
| [7] | LI Qi-Shou,XIAO Ding-Quan, ZHU Jian-Guo. Effect of Y-doping on the Ferroelectric Properties of BSPTHigh-temperature Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(2): 185-190. |
| [8] | LI Yan-Yan,LI Guo-Rong,WANG Tian-Bao,ZHENG Liao-Ying,LENG Sen-Lin,YIN Qing-Rui. Effects of NiobiumDoping on the Structure and Electrical Properties of (Ba,Bi,Na)TiO3-based PTCR Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(2): 374-378. |
| [9] | FENG Ya-Jun,XU Zhuo,LI Zhen-Rong,ZHANG Lin,YAO Xi. High Temperature Piezoelectric Ceramics (1-x)BiScO3-xPbTiO3 Near the Morphotropic Phase Boundary (MPB) [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(5): 1127-1133. |
| [10] | WANG Sheng,ZHANG Shu-Ren,ZHOU Xiao-Hua,LI Bo,CHEN Zhu. Dielectric Properties of BaTiO3-Nb2O5-Ni2O3 Ternary System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(2): 369-374. |
| [11] | CAI Zhi-Rang,LIU Ning,TONG Wei,XU Su-Jun,ZHANG Yu-Heng. Magnetocaloric Effect of (La0.6Dy0.1)Sr0.3MnO3 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2005, 20(3): 618-622. |
| [12] | FENG Quan-Yuan,CHEN Wei,REN Lang. Phase Shifter Materials with Zn Ti Sn-subtituted Lithium Ferrites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2000, 15(3): 527-530. |
| [13] | YAN Hai-Xue,LI Cheng-En,ZHOU Jia-Guang,ZHU Wei-Min. Structures and Properties of Bismuth Layer-structured Piezoelectric Ceramics with High Tc [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2000, 15(2): 209-220. |
| [14] | HUANG Xuan-Wei,LI Cheng-En. Studies on Synthesis and Properties of High Temperature Piezoelectric Ceramic Materials: Ca-(Na, Ce)-Bi-Ti System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1998, 13(1): 59-64. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||