
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 1252-1260.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250045
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Mingxuan1,2( ), LI Junjie1,2(
), LI Junjie1,2( ), CHEN Shuo1,2, YAN Yonggao1,2, SU Xianli1,2(
), CHEN Shuo1,2, YAN Yonggao1,2, SU Xianli1,2( ), ZHANG Qingjie2, TANG Xinfeng1,2
), ZHANG Qingjie2, TANG Xinfeng1,2
Received:2025-02-07
Revised:2025-05-14
Published:2025-11-20
Online:2025-06-05
Contact:
SU Xianli, professor. E-mail: suxianli@whut.edu.cn;About author:WU Mingxuan (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: krenwu_u@whut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
WU Mingxuan, LI Junjie, CHEN Shuo, YAN Yonggao, SU Xianli, ZHANG Qingjie, TANG Xinfeng. Homogeneity of Zone-melted n-type Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.70Se0.30 Thermoelectric Material[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1252-1260.

Fig. 2 σ, S and PF of different regions in Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006 with zone melting temperatures of (a) 958, (b) 973, (c) 988, and (d) 1003 K

Fig. 5 Variation trends of Bi/Sb and Te/Se of different regions in Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006 samples prepared under different zone melting temperatures Colorful figures are available on website
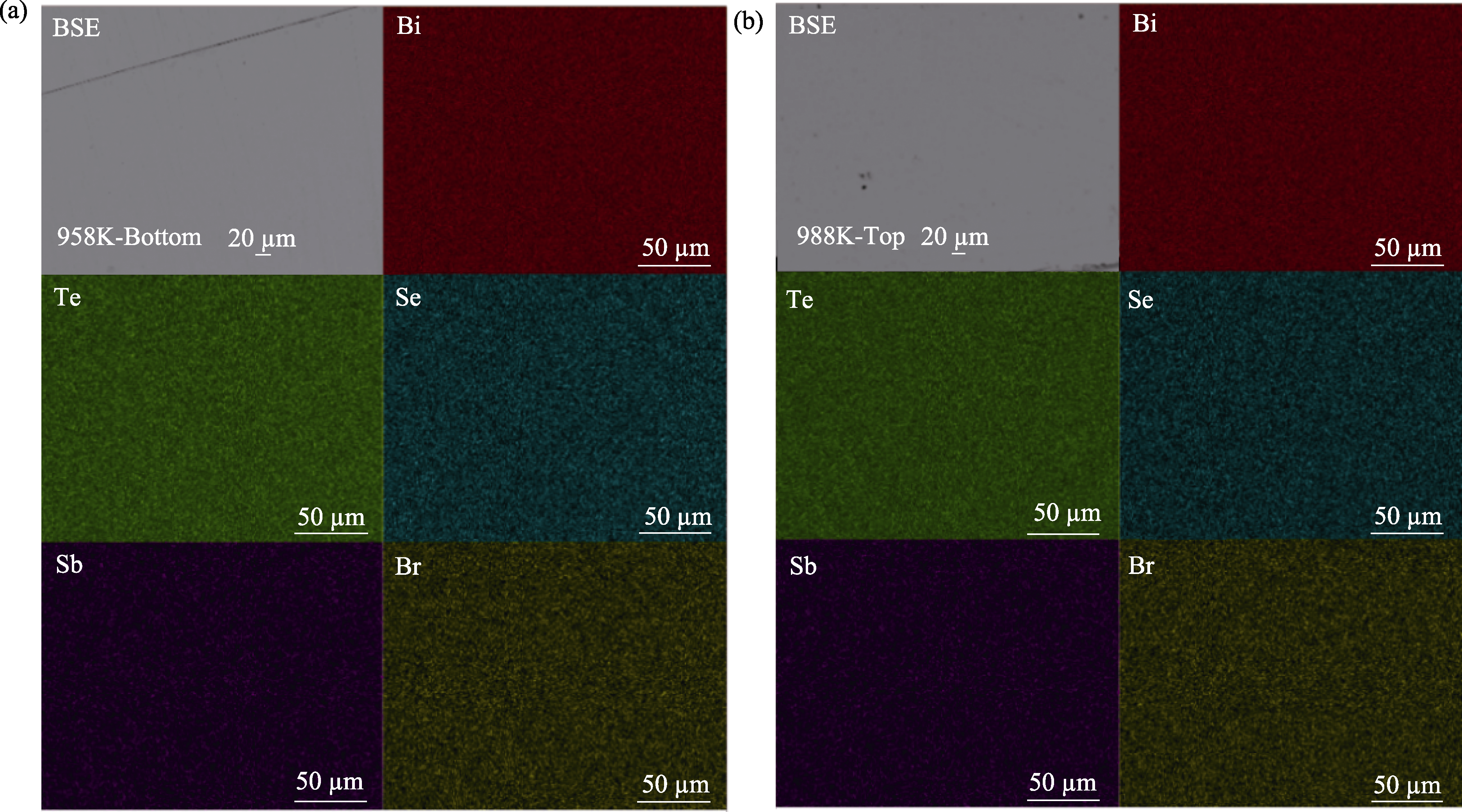
Fig. S2 BSE images of polished surface and surface distributions of Bi, Sb, Se, Te and Br elements in the corresponding regions for (a) 958 K-Bottom and (b) 988 K-Top
| Sample | σ/(×104, S·m−1) | S/(μV·K-1) | κ/(W·m-1·K-1) | ZT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 958 K-CB | 11.1 | -186 | 1.37 | 0.86 |
| 958 K-CT | 10.9 | -195 | 1.43 | 0.89 |
| 958 K-EB | 10.4 | -195 | 1.38 | 0.88 |
| 958 K-ET | 11.4 | -199 | 1.42 | 0.98 |
| 973 K-CB | 11.2 | -197 | 1.50 | 0.89 |
| 973 K-CT | 9.86 | -201 | 1.48 | 0.82 |
| 973 K-EB | 9.45 | -196 | 1.50 | 0.74 |
| 973 K -ET | 9.88 | -204 | 1.48 | 0.85 |
| 988 K-CB | 11.1 | -205 | 1.47 | 0.96 |
| 988 K-CT | 8.54 | -202 | 1.44 | 0.73 |
| 988 K-EB | 9.98 | -200 | 1.48 | 0.76 |
| 988 K-ET | 9.05 | -201 | 1.43 | 0.86 |
| 1003 K-CB | 9.00 | -206 | 1.47 | 0.80 |
| 1003 K-CT | 7.27 | -216 | 1.39 | 0.74 |
| 1003 K-EB | 7.34 | -202 | 1.47 | 0.63 |
| 1003 K-ET | 7.51 | -214 | 1.39 | 0.76 |
Table S1 σ, S, κ and ZT of Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006 samples at room temperature
| Sample | σ/(×104, S·m−1) | S/(μV·K-1) | κ/(W·m-1·K-1) | ZT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 958 K-CB | 11.1 | -186 | 1.37 | 0.86 |
| 958 K-CT | 10.9 | -195 | 1.43 | 0.89 |
| 958 K-EB | 10.4 | -195 | 1.38 | 0.88 |
| 958 K-ET | 11.4 | -199 | 1.42 | 0.98 |
| 973 K-CB | 11.2 | -197 | 1.50 | 0.89 |
| 973 K-CT | 9.86 | -201 | 1.48 | 0.82 |
| 973 K-EB | 9.45 | -196 | 1.50 | 0.74 |
| 973 K -ET | 9.88 | -204 | 1.48 | 0.85 |
| 988 K-CB | 11.1 | -205 | 1.47 | 0.96 |
| 988 K-CT | 8.54 | -202 | 1.44 | 0.73 |
| 988 K-EB | 9.98 | -200 | 1.48 | 0.76 |
| 988 K-ET | 9.05 | -201 | 1.43 | 0.86 |
| 1003 K-CB | 9.00 | -206 | 1.47 | 0.80 |
| 1003 K-CT | 7.27 | -216 | 1.39 | 0.74 |
| 1003 K-EB | 7.34 | -202 | 1.47 | 0.63 |
| 1003 K-ET | 7.51 | -214 | 1.39 | 0.76 |
| [1] |
YANG D, XING Y, WANG J, et al. Multifactor roadmap for designing low-power-consumed micro thermoelectric thermostats in a closed-loop integrated 5G optical module. Interdisciplinary Materials, 2024, 3(2): 326.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 范人杰, 江先燕, 陶奇睿, 等. In1+xTe化合物的结构及热电性能研究. 物理学报, 2021, 70(13): 393. |
| [3] |
LIU Z, HONG T, XU L, et al. Lattice expansion enables interstitial doping to achieve a high average ZT in n-type PbS. Interdisciplinary Materials, 2023, 2(1): 161.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
QIU J, YAN Y, XIE H, et al. Achieving superior performance in thermoelectric Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3.72 by enhancing texture and inducing high-density line defects. Science China Materials, 2021, 64: 1507.
DOI |
| [5] | 唐新峰, 柳伟, 谭刚健, 等. 热电材料物理化学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2024: 1-30. |
| [6] | 陈立东, 刘睿恒, 史迅. 热电材料与器件. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018: 1-18. |
| [7] | 张建中. 温差电技术. 电源技术, 2016(3): 754. |
| [8] |
LIN L, ZHANG Y F, LIU H B, et al. A new configuration design of thermoelectric cooler driven by thermoelectric generator. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 160: 114087.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIU W D, WANG D Z, LIU Q, et al. High-performance GeTe- based thermoelectrics: from materials to devices. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(19): 2000367.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
TAN G, ZHAO L D, KANATZIDIS M G. Rationally designing high-performance bulk thermoelectric materials. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(19): 12123.
PMID |
| [11] |
HE J, TRITT T M. Advances in thermoelectric materials research: looking back and moving forward. Science, 2017, 357(6358): eaak9997.
DOI URL |
| [12] | ROWE D M. Thermoelectrics handbook:macro to nano. Boston: CRC press, 2018: 1008. |
| [13] | 訾鹏, 白辉, 汪聪, 等. AgyIn3.33-y/3Se5化合物结构和热电性能. 物理学报, 2022, 71(11): 326. |
| [14] |
XIE H, ZHAO L D, KANATZIDIS M G. Lattice dynamics and thermoelectric properties of diamondoid materials. Interdisciplinary Materials, 2024, 3(1): 5.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
HUANG Y, LYU T, ZENG M, et al. Manipulation of metavalent bonding to stabilize metastable phase: a strategy for enhancing ZT in GeSe. Interdisciplinary Materials, 2024: 3(4): 607.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
YANG D, LUO T, SU X, et al. Unveiling the intrinsic low thermal conductivity of BiAgSeS through entropy engineering in SHS kinetic process. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 991.
DOI |
| [17] |
GONG H, SU X L, YAN Y G, et al. Ultra-fast synthesis of Cu2S thermoelectric materials under pulsed electric field. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(12): 1295.
DOI |
| [18] |
PEIAN R, CONG W, PENG Z, et al. Effect of Te and In co-doping on thermoelectric properties of Cu2SnSe3 compounds. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1079.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
YANG J, CAILLAT T. Thermoelectric materials for space and automotive power generation. MRS Bulletin, 2006, 31(3): 224.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WANG W C, CHANG Y L. Experimental investigation of thermal deformation in thermoelectric coolers. Strain, 2011, 47: 232.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SNYDER G J, URSELL T S. Thermoelectric efficiency and compatibility. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 91(14): 148301.
DOI URL |
| [22] | SNYDER G J, SNYDER A H. Figure of merit ZT of a thermoelectric device defined from materials properties. Energy & Environmental Science, 2017, 10(11): 2280. |
| [23] |
郭凯, 骆军, 赵景泰. 热电材料的基本原理, 关键问题及研究进展. 自然杂志, 2015, 37(3): 175.
DOI |
| [24] | 唐昊, 白辉, 吕嘉南, 等. 表面修饰工程协同优化Bi2Te3基微型热电器件的界面性能. 物理学报, 2022, 71(16): 330. |
| [25] |
YANG X, SU X L, YAN Y G, et al. Structures and thermoelectric properties of (GeTe)(n)Bi2Te3. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 75.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
CHEN Y, SHI Q, ZHONG Y, et al. Ga intercalation in van der Waals layers for advancing p-type Bi2Te3-based thermoelectrics. Chinese Physics B, 2023, 32(6): 067201.
DOI |
| [27] |
CHI H, LIU W, SUN K, et al. Low-temperature transport properties of Tl-doped Bi2Te3 single crystals. Physical Review B—Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2013, 88(4): 045202.
DOI URL |
| [28] | LIU F, ZHANG M, NAN P, et al. Unraveling the origin of donor- like effect in bismuth-telluride-based thermoelectric materials. Small Science, 2023, 3(8): 2300082. |
| [29] |
LIU D, BAI S, WEN Y, et al. Lattice plainification and band engineering lead to high thermoelectric cooling and power generation in n-type Bi2Te3 with mass production. National Science Review, 2025, 12(2): nwae448.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZHANG Z, SUN M, LIU J, et al. Ultra-fast fabrication of Bi2Te3 based thermoelectric materials by flash-sintering at room temperature combining with spark plasma sintering. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12: 10045.
DOI |
| [31] |
CHEN C, WANG B, YING P, et al. Microstructure engineered Bi2Te3-based materials with outstanding mechanical and thermoelectric properties. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2025, 1020: 179543.
DOI URL |
| [32] | SHI Q, LI J, ZHAO X, et al. Comprehensive insight into p-type Bi2Te3-based thermoelectrics near room temperature. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(44): 49425. |
| [33] |
LU Z Q, LIU K K, LI Q, et al. Donor-like effect and thermoelectric performance in p-type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 alloy. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1331.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 李强, 陈硕, 刘可可, 等. n型Bi2Te3基化合物的类施主效应和热电性能. 物理学报, 2023, 72(9): 135. |
| [35] |
ZHANG Q, FANG T, LIU F, et al. Tuning optimum temperature range of Bi2Te3-based thermoelectric materials by defect engineering. Chemistry-An Asian Journal, 2020, 15(18): 2775.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
HUANG W, TAN X, CAI J, et al. Synergistic effects improve thermoelectric properties of zone-melted n-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3. Materials Today Physics, 2023, 32: 101022.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 田源, 汪波, 李存成, 等. 区熔n型碲化铋材料的制备及性能优化. 材料科学与工程学报, 2024, 42(2): 186. |
| [38] |
LIU D, STÖTZEL J, SEYRING M, et al. Anisotropic n-type Bi2Te3-In2Te3 thermoelectric material produced by seeding zone melting and solid state transformation. Crystal Growth & Design, 2016, 16(2): 617.
DOI URL |
| [39] | WANG T, ZHOU C, HUANG W, et al. Synergistic improvement of BiI3 and In on thermoelectric properties of zone-melted n-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(31): 41080. |
| [40] |
LIU D, LI X, BORLIDO P M D C, et al. Anisotropic layered Bi2Te3-In2Te3 composites: control of interface density for tuning of thermoelectric properties. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 43611.
DOI |
| [41] |
HA H P, HYUN D B, BYUN J Y, et al. Enhancement of the yield of high-quality ingots in the zone-melting growth of p-type bismuth telluride alloys. Journal of Materials Science, 2002, 37(21): 4691.
DOI |
| [42] |
KIM H S, HEINZ N A, GIBBS Z M, et al. High thermoelectric performance in (Bi0.25Sb0.75)2Te3 due to band convergence and improved by carrier concentration control. Materials Today, 2017, 20(8): 452.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
PERRIN D, CHITROUB M, SCHERRER S, et al. Study of the n-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 doped with bromine impurity. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2000, 61(10): 1687.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
KAVEI G, KARAMI M. Thermoelectric crystals Bi2Te2.88Se0.12 undoped and doped by CdCl2 or CdBr2 impurities, fabricated and characterized by XRD and Hall effect. Materials Research Bulletin, 2008, 43(2): 239.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
CHEN Y R, HWANG W S, HSIEH H L, et al. Thermal and microstructure simulation of thermoelectric material Bi2Te3 grown by zone- melting technique. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2014, 402: 273.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
KAVEI G, AHMADI K, KAVEI A. Electrical conductivity variation of (Bi2Te3)0.25(Sb2Te3)0.75 crystal grown using the zone melting method. International Journal of Materials Research, 2013, 104(3): 314.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
XIA H, LI X, XU Q. Macro-micro-coupling simulation and space experiment study on zone melting process of bismuth telluride-based crystal materials. Metals, 2022, 12(5): 886.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
GUO X, QIN J, JIA X, et al. Quaternary thermoelectric materials: synthesis, microstructure and thermoelectric properties of the (Bi,Sb)2(Te,Se)3 alloys. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 705: 363.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
CHAUHAN N S, PYRLIN S V, LEBEDEV O I, et al. Compositional fluctuations mediated by excess tellurium in bismuth antimony telluride nanocomposites yield high thermoelectric performance. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(37): 20184.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
LIU Y, ZHANG Y, LIM K H, et al. High thermoelectric performance in crystallographically textured n-type Bi2Te3-xSex produced from asymmetric colloidal nanocrystals. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(7): 7174.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
VASIL’EV A, IVANOV O, YAPRYNTSEV M, et al. Aspects of the microstructure and thermoelectric properties of a two-phase ceramic material based on the high-entropy system Bi-Sb-Te-Se-S. Glass and Ceramics, 2023, 80(1): 52.
DOI |
| [52] |
CHEN H W, CHEN B C, WU H J. Dilute Sb doping yields softer p-type Bi2Te3 thermoelectrics. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2024, 10(6): 2300793.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
GUAN X, LIU Z, MA N, et al. High-performance p-type Bi2Te3- based thermoelectric materials with a wide temperature range obtained by direct Sb doping. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2025, 38: 849.
DOI |
| [54] | WITTING I T, RICCI F, CHASAPIS T C, et al. The thermoelectric properties of n-type bismuth telluride: bismuth selenide alloys Bi2Te3-xSex. Research, 2020, 2020: 4361703. |
| [55] |
LI Y, BAI S, WEN Y, et al. Realizing high-efficiency thermoelectric module by suppressing donor-like effect and improving preferred orientation in n-type Bi2(Te,Se)3. Science Bulletin, 2024, 69(11): 1728.
DOI URL |
| [1] | MIAO Pengcheng, WANG Lijun, SHEN Ziyi, HUANG Li, YUAN Ningyi, DING Jianning. Micro-spherical Ag2Se: Solvothermal Synthesis and Thermoelectric Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1373-1378. |
| [2] | LIN Siqi, LI Airan, FU Chenguang, LI Rongbing, JIN Min. Crystal Growth and Thermoelectric Properties of Zintl Phase Mg3X2 (X=Sb, Bi) Based Materials: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [3] | LU Zhiqiang, LIU Keke, LI Qiang, HU Qin, FENG Liping, ZHANG Qingjie, WU Jinsong, SU Xianli, TANG Xinfeng. Donor-like Effect and Thermoelectric Performance in p-Type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 Alloy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1331-1337. |
| [4] | JIANG Runlu, WU Xin, GUO Haocheng, ZHENG Qi, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. UiO-67 Based Conductive Composites: Preparation and Thermoelectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1338-1344. |
| [5] | CHENG Cheng, LI Jianbo, TIAN Zhen, WANG Pengjiang, KANG Huijun, WANG Tongmin. Thermoelectric Property of In2O3/InNbO4 Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 724-730. |
| [6] | LIU Dan, ZHAO Yaxin, GUO Rui, LIU Yantao, ZHANG Zhidong, ZHANG Zengxing, XUE Chenyang. Effect of Annealing Conditions on Thermoelectric Properties of Magnetron Sputtered MgO-Ag3Sb-Sb2O4 Flexible Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1302-1310. |
| [7] | REN PeiAn, WANG Cong, ZI Peng, TAO Qirui, SU Xianli, TANG Xinfeng. Effect of Te and In Co-doping on Thermoelectric Properties of Cu2SnSe3 Compounds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1079-1086. |
| [8] | LU Xu, HOU Jichong, ZHANG Qiang, FAN Jianfeng, CHEN Shaoping, WANG Xiaomin. Effect of Mg Content on Thermoelectric Property of Mg3(1+z)Sb2 Compounds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 835-840. |
| [9] | YANG Xiao, SU Xianli, YAN Yonggao, TANG Xinfeng. Structures and Thermoelectric Properties of (GeTe)nBi2Te3 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 75-80. |
| [10] | LI Zhou, XIAO Chong. Optimizing Electrical and Thermal Transport Property in BiCuSeO Superlattice via Heterolayer-isovalent Dual-doping Approach [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 294-300. |
| [11] | LI Song-Hao, ZHANG Xin, LIU Hong-Liang, ZHENG Liang, ZHANG Jiu-Xing. Synthesis and Thermoelectric Properties of Ag-doped SnSe [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(7): 751-755. |
| [12] | WU Zi-Hua, XIE Hua-Qing, WANG Yuan-Yuan, MAO Jian-Hui, XING Jiao-Jiao, LI Yi-Huai. PPP Addition to Improve Thermoelectric Properties of ZnO-based Thermoelectric Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(11): 1249-1254. |
| [13] | LOU Feng-Guang, WANG Shi-Kai, WANG-Meng, Feng Su-Ya, YU Chun-Lei, HU Li-Li. Sol-Gel Derived Al3+,Yb3+ Co-doped Silica Fiber Core [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(4): 393-398. |
| [14] | ZHAN Bin, LAN Jin-Le, LIU Yao-Chun, DING Jing-Xuan, LIN Yuan-Hua, NAN Ce-Wen. Research Progress of Oxides Thermoelectric Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(3): 237-244. |
| [15] | WU Zi-Hua, XIE Hua-Qing, ZENG Qing-Feng. Thermoelectric Properties of Ni-doped ZnO Synthesized by Sol-Gel Processing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(9): 921-924. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||