无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (10): 1135-1142.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230580 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20230580
所属专题: 【能源环境】光催化(202412); 【能源环境】污染物催化去除(202506)
收稿日期:2023-12-18
修回日期:2024-05-06
出版日期:2024-10-20
网络出版日期:2024-05-16
通讯作者:
吴 昊, 讲师. E-mail: hwu@ysu.edu.cn作者简介:蔡梦宇(1998-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: c18503338109@163.com
基金资助:
CAI Mengyu( ), LI-YANG Hongmiao, YANG Caiyun, ZHOU Yuting, WU Hao(
), LI-YANG Hongmiao, YANG Caiyun, ZHOU Yuting, WU Hao( )
)
Received:2023-12-18
Revised:2024-05-06
Published:2024-10-20
Online:2024-05-16
Contact:
WU Hao, lecturer. E-mail: hwu@ysu.edu.cnAbout author:CAI Mengyu (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: c18503338109@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
载铁沸石因其来源广泛、制备简便及环境毒性低等特点, 被广泛用于催化类Fenton反应产生·OH, 以高效处理有机污染物。然而, 传统载铁沸石的制备成本高且Fe2+再生困难, 限制了其在催化类Fenton反应中的工业化应用。基于此, 本研究以污水处理厂活性污泥焚烧处理后的灰分为原料, 选择性回收其中的硅、铝和铁等元素。制备的Fe2+-方钠石(FSD)可用于类Fenton反应活化过氧乙酸(PAA), 以高效降解水溶液中的亚甲基蓝(MB)。 结果表明:FSD可在较宽的pH范围内催化PAA生成·OH、1O2和R-O·等多种活性氧物种, 进而通过羟基化或亚砜化途径催化降解MB。以0.5 mol/L Fe2+制备的FSD用量为0.3 g/L, PAA浓度为0.3 mmol/L时, FSD/PAA体系可在20 min内完全降解40 mg/L MB。此外, FSD中的还原性硫组分可促进Fe2+再生, 维持其催化活性。且FSD/PAA体系可在不同水质和生活污水中高效降解多种污染物, 具有性能优良和适用性广的优点。
中图分类号:
蔡梦宇, 李杨虹淼, 杨彩云, 周雨婷, 吴昊. 基于活性污泥焚灰的类Fenton催化剂的制备及其对亚甲基蓝的降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1135-1142.
CAI Mengyu, LI-YANG Hongmiao, YANG Caiyun, ZHOU Yuting, WU Hao. Activated Sludge Incineration Ash Derived Fenton-like Catalyst: Preparation and Degradation Performance on Methylene Blue[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1135-1142.
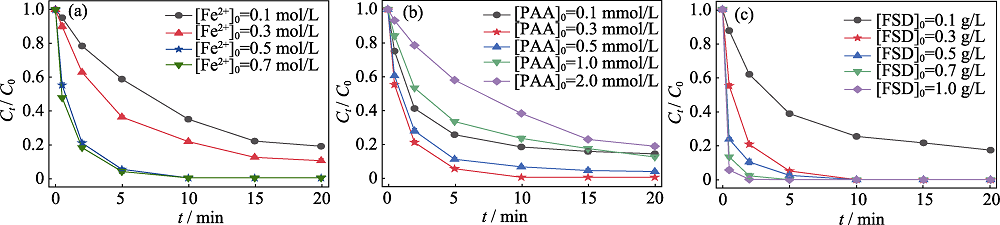
图4 (a)催化剂负载液Fe2+浓度、(b)氧化剂用量及(c)催化剂用量对FSD/PAA体系降解MB的影响
Fig. 4 Effects of (a) concentration of Fe2+ loading solution, (b) oxidant dosage and (c) catalyst dosage on degradation of MB by FSD/PAA system

图6 催化反应前后(a, c)FSD与(b, d)RFSD的(a, b)XPS总谱图和(c, d) Fe2p XPS谱图
Fig. 6 (a, b) Total and (c, d) Fe2p XPS spectra of (a, c) FSD and (b, d) RFSD before and after catalytical reaction
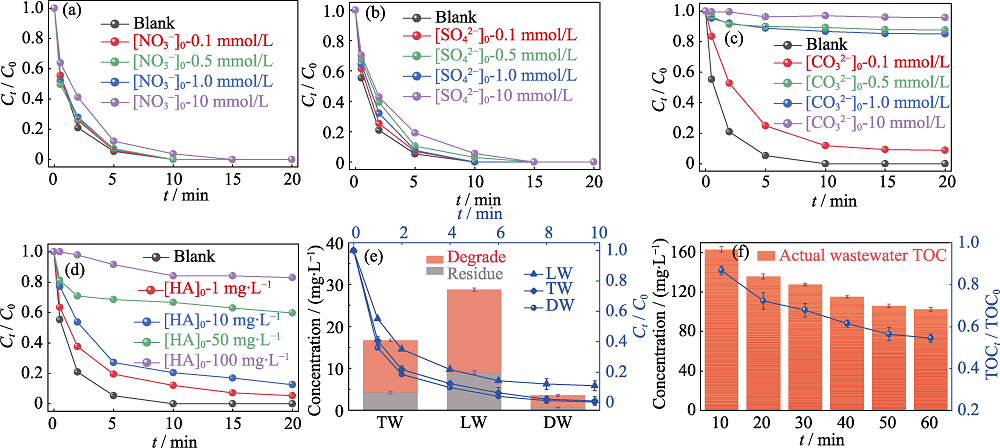
图8 水中共存物种、水质条件对最优FSD/PAA体系降解MB的影响
Fig. 8 Effects of co-existed substrates and water conditions on the degradation of MB by the optimized FSD/PAA system (a-d) Effects of (a) NO3-, (b) SO42-, (c) CO32-, and (d) HA on MB degradation by the optimized FSD/PAA system; (e) Effect of deionic water (DW), tap water (TW) and lake water (LW) on the degradation performance of MB by the optimized FSD/PAA system; (f) Performance of the optimized FSD/PAA system in actual wastewater; Colorful figures are available on website
| Item | TW | LW | Wastewater |
|---|---|---|---|
| TOC/(mg·L-1) | 16.7 | 28.8 | 188.1 |
| F-/(mg·L-1) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Cl-/(mg·L-1) | 23.2 | 24.3 | 51.1 |
| K+/(mg·L-1) | 30.9 | 35.6 | 64.4 |
| Mg2+/(mg·L-1) | 16.7 | 21.4 | 96.5 |
表S1 不同水样水质条件
Table S1 Characterizations of different water samples
| Item | TW | LW | Wastewater |
|---|---|---|---|
| TOC/(mg·L-1) | 16.7 | 28.8 | 188.1 |
| F-/(mg·L-1) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Cl-/(mg·L-1) | 23.2 | 24.3 | 51.1 |
| K+/(mg·L-1) | 30.9 | 35.6 | 64.4 |
| Mg2+/(mg·L-1) | 16.7 | 21.4 | 96.5 |
| Compound | Column temperature/℃ | Flow rate/ (mL·min-1) | Wavelength/ nm | Phase mobile phase | Phase elution gradient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MB | 40 | 0.2 | 254 | Ammonium acetate (A)+ acetonitrile (B) | 0-1-9-14 min, 10%B-10%B-90%B-90%B |
| SMX | 40 | 0.3 | 275 | 0.1% Formic acid solution (A)+ methanol (B) | 0-1-1-3.5-5 min, 20%B-20%B-51.25%B-51.25%B |
| GM | 40 | 0.3 | 278 | 0.1% Formic acid solution (A)+ acetonitrile (B) | 0-0.5-1-4-6 min, 5%B-5%B-30%B-30%B |
| MDZ | 40 | 0.8 | 318 | Ultrapure water (A)+ acetonitrile (B) | 0-0.5-3-5 min, 6%B-5%B-20%B-90%B |
| CIP | 40 | 0.3 | 278 | Ultrapure water (A)+ acetonitrile (B) | 0-0.5-3-5 min, 6%B-5%B-20%B-90%B |
| RHB | 40 | 0.2 | 554 | 0.1% Formic acid solution (A)+ acetonitrile (B) | 0-5-8 min, 5%B-95%B-95%B |
| TC | 40 | 0.3 | 360 | Ultrapure water (A)+ acetonitrile (B) | 0-0.5-3-5 min, 6%B-5%B-20%B-90%B |
表S2 梯度洗脱测量有机污染物的HPLC条件
Table S2 HPLC conditions for phase gradient elution measuring concentrations of organic contaminants
| Compound | Column temperature/℃ | Flow rate/ (mL·min-1) | Wavelength/ nm | Phase mobile phase | Phase elution gradient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MB | 40 | 0.2 | 254 | Ammonium acetate (A)+ acetonitrile (B) | 0-1-9-14 min, 10%B-10%B-90%B-90%B |
| SMX | 40 | 0.3 | 275 | 0.1% Formic acid solution (A)+ methanol (B) | 0-1-1-3.5-5 min, 20%B-20%B-51.25%B-51.25%B |
| GM | 40 | 0.3 | 278 | 0.1% Formic acid solution (A)+ acetonitrile (B) | 0-0.5-1-4-6 min, 5%B-5%B-30%B-30%B |
| MDZ | 40 | 0.8 | 318 | Ultrapure water (A)+ acetonitrile (B) | 0-0.5-3-5 min, 6%B-5%B-20%B-90%B |
| CIP | 40 | 0.3 | 278 | Ultrapure water (A)+ acetonitrile (B) | 0-0.5-3-5 min, 6%B-5%B-20%B-90%B |
| RHB | 40 | 0.2 | 554 | 0.1% Formic acid solution (A)+ acetonitrile (B) | 0-5-8 min, 5%B-95%B-95%B |
| TC | 40 | 0.3 | 360 | Ultrapure water (A)+ acetonitrile (B) | 0-0.5-3-5 min, 6%B-5%B-20%B-90%B |
| [1] | XIANG Y, YANG K, ZHAI Z, et al. Molybdenum co-catalytic promotion for Fe3+/peroxydisulfate process: performance, mechanism, and immobilization. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 438: 135656. |
| [2] | LI L, YIN Z, CHENG M, et al. Insights into reactive species generation and organics selective degradation in Fe-based heterogeneous Fenton-like systems: a critical review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 454: 140126. |
| [3] | LIU L, YU R H, ZHAO S X, et al. Heterogeneous Fenton system driven by iron-loaded sludge biochar for sulfamethoxazole- containing wastewater treatment. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 335: 117576. |
| [4] | YANG C Y, WU H, CAI M, et al. Valorization of biomass-derived polymers to functional biochar materials for supercapacitor applications via pyrolysis: advances and perspectives. Polymers, 2023, 15: 2741. |
| [5] | WANG J, TANG J. Fe-based Fenton-like catalysts for water treatment: preparation, characterization and modification. Chemosphere, 2021, 276: 130177. |
| [6] | AROCKIARAJ M, CLEMENT J, et al. Quantitative structural descriptors of sodalite materials. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2021, 1223: 128766. |
| [7] | ZHAO D, ARMUTLULU A, CHEN Y, et al. Highly efficient removal of Cu(II) using mesoporous sodalite zeolite produced from industrial waste lithium-silicon-fume via reactive oxidation species route. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 319: 128682. |
| [8] | SCHNELL M, HORST T, QUICKER P. Thermal treatment of sewage sludge in Germany: a review. Journal of Environmental Management. 2020, 263: 110367. |
| [9] | ZHAO S, YAN K, WANG Z, et al. Does anaerobic digestion improve environmental and economic benefits of sludge incineration in China? Insight from life-cycle perspective. Resources, Conservation & Recycling, 2023, 188: 106688. |
| [10] | 蔡梦宇, 杨彩云, 吴昊, 等. 厌氧消化沼渣的生物电化学深度稳定化及能源回收. 燕山大学学报, 2023, 47(6): 519. |
| [11] | GUO X L, YUAN S T, XU Y, et al. Effects of phosphorus and iron on the composition and property of Portland cement clinker utilized incinerated sewage sludge ash. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 341: 127754. |
| [12] | BUTA M, HUBENY J, ZIELINSKI W, et al. Sewage sludge in agriculture-the effects of selected chemical pollutants and emerging genetic resistance determinants on the quality of soil and crops--a review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 214: 112070. |
| [13] | LIU Z Z, MAYER B, VENKITRSHWARAN K, et al. The state of technologies and research for energy recovery from municipal wastewater sludge and biosolids. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 2020, 14: 31. |
| [14] | LIU Y, HE X, DUAN X, et al. Photochemical degradation of oxytetracycline: influence of pH and role of carbonate radical. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 276(15): 113. |
| [15] | KIM J, ZHANG T Q, LIU W, et al. Advanced oxidation process with peracetic acid and Fe(II) for contaminant degradation. Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 53(22): 13312. |
| [16] | WANG L, YAN T, TANG R, et al. Motivation of reactive oxidation species in peracetic acid by adding nanoscale zero-valent iron to synergic removal of spiramycin under ultraviolet irradiation: mechanism and N-nitrosodimethylamine formation potential assessment. Water Research, 2021, 205: 117684. |
| [17] | CHEN S, CAI M, LIU Y, et al. Effects of water matrices on the degradation of naproxen by reactive radicals in the UV/peracetic acid process. Water Research, 2019, 150(1): 153. |
| [18] | XIANG Y, YUAN D, ZHU E, et al. Efficacious reduction of ferric ions by molybdenum carbide in the peroxydisulfate Fenton-like reaction for dexamethasone degradation. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 3(3): 857. |
| [19] | AO X, ELORANTA J, HUANG C, et al. Peracetic acid-based advanced oxidation processes for decontamination and disinfection of water: a review. Water Research, 2021, 188: 116479. |
| [20] | WOLSKI L, ZIOLEK M. Insight into pathways of methylene blue degradation with H2O2 over mono and bimetallic Nb, Zn oxides. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 224: 634. |
| [21] | MONDAL S, REYES M E D A, PAL U. Plasmon induced enhanced photocatalytic activity of gold loaded hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for methylene blue degradation under visible light. RSC Advances, 2017, 7: 8633. |
| [22] |
XIA S, ZHANG L, PAN G, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue with a nanocomposite system: synthesis, photocatalysis and degradation pathways. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015, 17: 5345.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | LIU Y, JIN W, ZHAO Y, et al. Enhanced catalytic degradation of methylene blue by α-Fe2O3/graphene oxide via heterogeneous photo-Fenton reactions. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 206: 642. |
| [24] | WANG S, WANG H, LIU Y, et al. Effective degradation of sulfamethoxazole with Fe2+-zeolite/peracetic acid. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 233: 115973. |
| [25] | WANG J, WANG Z, CHENG Y, et al. Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2): a novel activator of peracetic acid for the degradation of sulfonamide antibiotics. Water Research, 2021, 201: 117291. |
| [26] | WANG J, XIONG B, LEI M, et al. Applying a novel advanced oxidation process of activated peracetic acid by CoFe2O4 to efficiently degrade sulfamethoxazole. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 280: 119422. |
| [1] | 王梦桃, 索军, 方东, 易健宏, 刘意春, Olim RUZIMURADOV. ITO/TiO2纳米管阵列复合材料的可见光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1292-1300. |
| [2] | 迟聪聪, 屈盼盼, 任超男, 许馨, 白飞飞, 张丹洁. SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2核壳结构的制备及其光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [3] | 周帆, 毕辉, 黄富强. 用稻壳制备亚甲基蓝高吸附容量的超高比表面积活性炭[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 893-903. |
| [4] | 张晓锋,张冠华,孟跃,薛继龙,夏盛杰,倪哲明. 席夫碱钴改性CoCr-LDHs材料光催化降解亚甲基蓝研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 974-982. |
| [5] | 隋丽丽,王润,赵丹,申书昌,孙立,徐英明,程晓丽,霍丽华. 多级结构α-MoO3空心微球的构筑及其对有机染料的吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(2): 193-200. |
| [6] | 赵海兵, 徐海峰, 杨克伟, 林辰学, 冯苗, 于岩. Mg掺杂TiO2纳米晶光氧化还原染料的可逆颜色转变研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(10): 1124-1130. |
| [7] | 喻 洋, 佟明兴, 何玉兰, 陈 辉, 高 静, 李国华. 介孔TiO2/WO3空心球的制备及其可见光光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(4): 365-371. |
| [8] | 徐明丽, 段 奔, 张英杰, 杨国涛, 董 鹏, 夏书标, 杨显万. 碳纳米管载体改性条件对Pt纳米粒子电催化氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(9): 931-936. |
| [9] | 彭 丹, 郑学军, 谢澍梵, 罗晓菊, 王 丁. GaN/ZnO复合体的制备及光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(9): 956-960. |
| [10] | 陈 渊, 周科朝, 黄苏萍, 李志友, 刘国聪. 水热法制备Cu掺杂可见光催化剂BiVO4及其光催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(1): 19-25. |
| [11] | 刘国聪, 李海斌, 董 辉. La掺杂TiO2介孔微球的超声水热合成和光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(7): 739-746. |
| [12] | 舒火明, 谢吉民, 许 晖, 李华明, 徐远国, 顾 正. ZnO/AgNbO3光催化剂的表征及活性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(9): 935-941. |
| [13] | 陈 怡,施利毅,袁 帅,吴 钧,张美红,方建慧. TiO2纳米管阵列薄膜光电协同降解亚甲基蓝的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(4): 680-684. |
| [14] | 江芳,邵飞. SiO2柱层状钛酸的制备及光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(6): 1263-1266. |
| [15] | 传秀云,卢先春,卢先初. 负载TiO2的硅藻土对亚甲基蓝的光降解性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(4): 657-661. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||