无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 193-200.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180132 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20180132
隋丽丽1,王润1,赵丹2,申书昌1,孙立1,徐英明2,程晓丽2,霍丽华2
收稿日期:2018-03-30
修回日期:2018-06-05
出版日期:2019-02-20
网络出版日期:2019-01-24
作者简介:隋丽丽(1980-),女,副教授. E-mail: sui_leelee@126.com
基金资助:SUI Li-Li1, WANG Run1, ZHAO Dan2, SHEN Shu-Chang1, SUN Li1, XU Ying-Ming2, CHENG Xiao-Li2, HUO Li-Hua2
Received:2018-03-30
Revised:2018-06-05
Published:2019-02-20
Online:2019-01-24
About author:SUI Li-Li. E-mail: sui_leelee@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
具有多级结构的半导体金属氧化物, 其特有的立体空间结构使材料具有超高活性, 在吸附领域具有应用潜力。研究采用简单的一步溶剂热法制备了空心球状的MoO2前驱体, 400 ℃热处理后得到多级结构α-MoO3空心微球。空心球的直径为600~800 nm, 由宽度约70 nm的纳米棒构筑而成。该球状α-MoO3纳米材料对亚甲基蓝(MB)染料具有优良的吸附性能。当α-MoO3吸附剂用量为0.5 g/L、MB染料浓度为20 mg/L、吸附时间为5 min时, 移除率可达到73.40%。吸附60 min时, 吸附达到平衡, 此后移除率为97.53%~99.65%。该吸附动力学过程符合拟二级动力学模型, 吸附等温线符合 Langmuir 模型拟合, 最大吸附量为 1543.2 mg/g。α-MoO3微球由于多级且中空的纳米结构, 对MB染料具有用量少、吸附速率快和吸附完全等特点。该材料可以用于吸附废水中其他有机染料。
中图分类号:
隋丽丽,王润,赵丹,申书昌,孙立,徐英明,程晓丽,霍丽华. 多级结构α-MoO3空心微球的构筑及其对有机染料的吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(2): 193-200.
SUI Li-Li, WANG Run, ZHAO Dan, SHEN Shu-Chang, SUN Li, XU Ying-Ming, CHENG Xiao-Li, HUO Li-Hua. Construction of Hierarchical α-MoO3 Hollow Microspheres and Its High Adsorption Performance towards Organic Dyes[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 193-200.
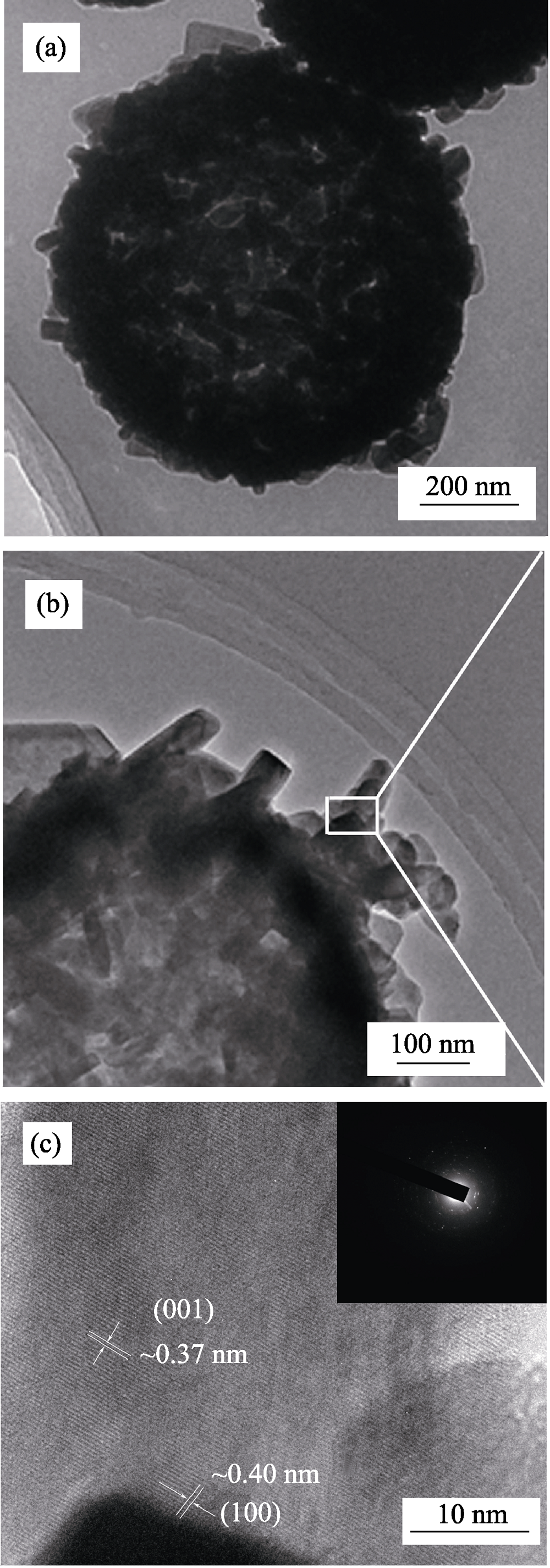
图4 α-MoO3空心微球的TEM照片(a)~(b), HRTEM照片(c)和SAED照片((c)中插图)
Fig. 4 Typical TEM (a, b), HRTEM (c) images and SAED pattern (inset in (c)) of α-MoO3 hollow microspheres

图5 α-MoO3空心微球的的N2脱附-吸附等温曲线及其孔径分布图(插图)
Fig. 5 Nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms and pore size distribution plot (inset) of α-MoO3 hollow microspheres
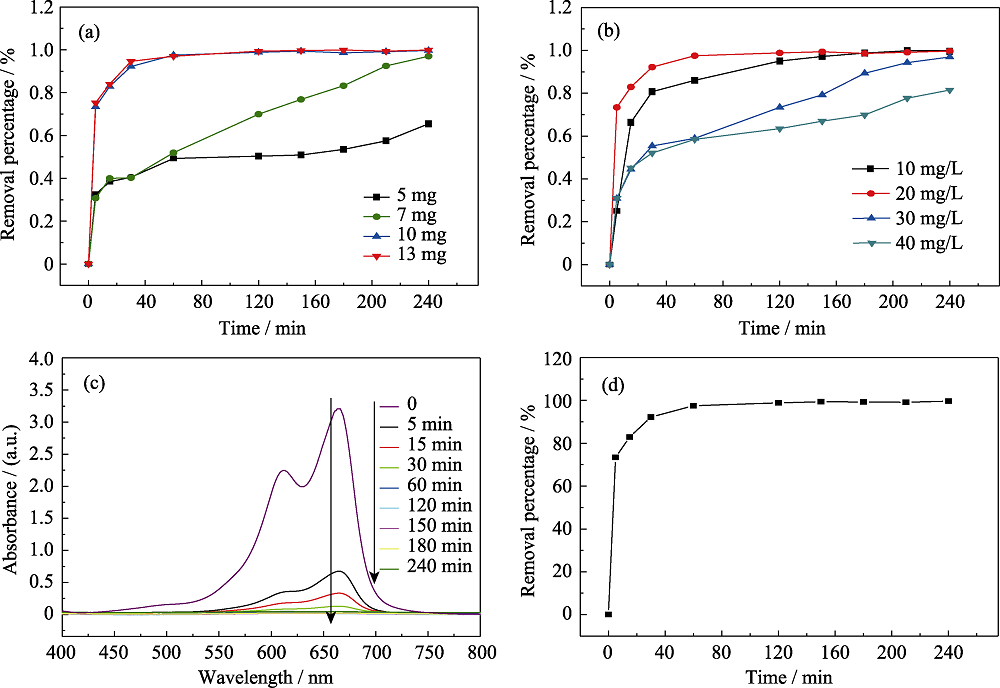
图6 吸附剂用量(a)和MB染料浓度(b)对α-MoO3微球吸附性能影响曲线, 不同吸附时间α-MoO3微球对MB染料的紫外-可见光谱图(c)和移除率曲线(d)
Fig. 6 Effect of adsorbent dosage (a) and concentration of MB (b) on the adsorption performances of α-MoO3 hollow microspheres, UV-Vis spectra (c) and removal percentage curves (d) of α-MoO3 to MB for different contact times
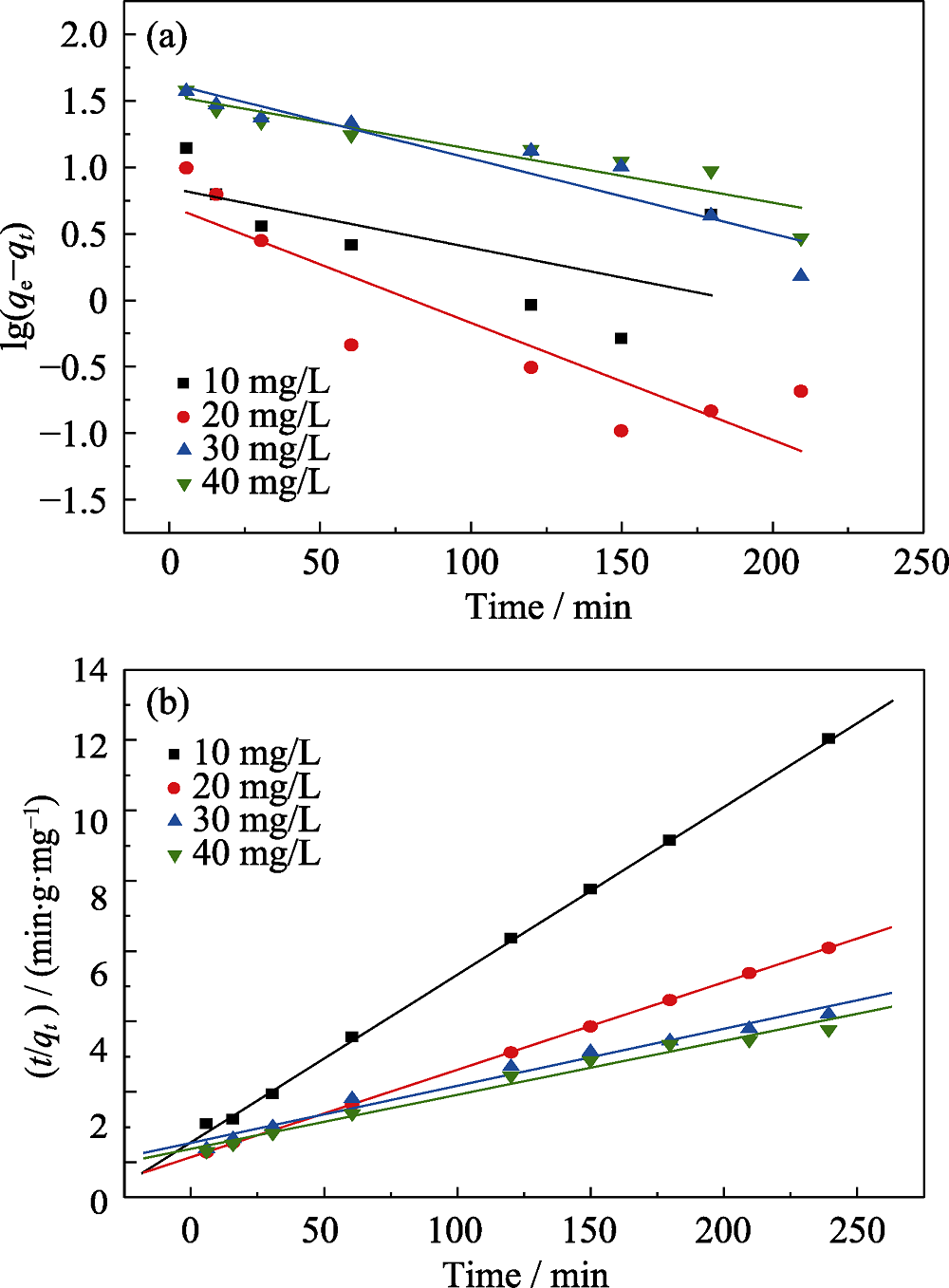
图7 α-MoO3空心球对不同浓度MB吸附过程的拟一级动力学方程(a)和拟二级动力学方程(b)拟合曲线
Fig. 7 Pseudo-first-order (a) and pseudo-second-order (b) sorption kinetics for different concentrations of MB onto α-MoO3 hollow microspheres
| C0/(mg·L-1) | qe.exp/(mg·g-1) | Pseudo-second-order | Pseudo-first-order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe.cal/(mg·g-1) | k2/(×10-3, g·mg-1·min-1) | R2 | qe.cal/(mg·g-1) | k1 /(×10-3, min-1) | R2 | |||
| 10 | 19.97 | 20.83 | 4.10 | 0.9996 | 6.98 | 10.13 | 0.6385 | |
| 20 | 39.86 | 40.16 | 10.90 | 0.9999 | 5.34 | 20.45 | 0.8994 | |
| 30 | 58.16 | 59.85 | 0.63 | 0.9907 | 44.67 | 13.04 | 0.9456 | |
| 40 | 65.22 | 65.10 | 0.82 | 0.9903 | 36.89 | 9.30 | 0.9308 | |
表1 α-MoO3空心微球对MB的吸附动力学参数
Table 1 Kinetic parameters for adsorption of MB on the samples of α-MoO3 hollow microspheres
| C0/(mg·L-1) | qe.exp/(mg·g-1) | Pseudo-second-order | Pseudo-first-order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe.cal/(mg·g-1) | k2/(×10-3, g·mg-1·min-1) | R2 | qe.cal/(mg·g-1) | k1 /(×10-3, min-1) | R2 | |||
| 10 | 19.97 | 20.83 | 4.10 | 0.9996 | 6.98 | 10.13 | 0.6385 | |
| 20 | 39.86 | 40.16 | 10.90 | 0.9999 | 5.34 | 20.45 | 0.8994 | |
| 30 | 58.16 | 59.85 | 0.63 | 0.9907 | 44.67 | 13.04 | 0.9456 | |
| 40 | 65.22 | 65.10 | 0.82 | 0.9903 | 36.89 | 9.30 | 0.9308 | |

图8 α-MoO3空心微球吸附MB的Langmuir (a)和Freundlich (b)吸附等温线
Fig. 8 Langmuir (a) and Freundlich (b) adsorption isotherm curves for adsorption of MB by α-MoO3 hollow microspheres
| Adsorption | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/(mg·g-1) | KL/(L·mg-1) | RL | R2 | KF/(L·g-1) | n | R2 | |
| MB | 1543.2 | 1.19 | 0.0014 | 0.9978 | 724.44 | 1.82 | 0.9035 |
表2 α-MoO3空心微球对MB的吸附热力学参数
Table 2 Adsorption isotherm parameters of α-MoO3 hollow microspheres to MB
| Adsorption | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/(mg·g-1) | KL/(L·mg-1) | RL | R2 | KF/(L·g-1) | n | R2 | |
| MB | 1543.2 | 1.19 | 0.0014 | 0.9978 | 724.44 | 1.82 | 0.9035 |
| Adsorbent | Maximum adsorption capacity, qm/(mg·g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical α-MoO3 hollow microspheres | 1543.2 | This work |
| WO3 nanotube | 75.0 | [26] |
| WO3 nanorods | 73.0 | [27] |
| WO3 hollow spheres | 138.9 | [28] |
| Hierarchical WO3 hydrates | 274.3 | [8] |
| SiO2 nanoparticles | 679.9 | [29] |
| Fe3O4@Ag/SiO2 nanospheres | 128.5 | [30] |
表3 不同金属氧化物吸附剂材料对MB染料的最大吸附容量比较
Table 3 Comparison of the maximum adsorption capacities for MB on adsorbents of different metal oxides
| Adsorbent | Maximum adsorption capacity, qm/(mg·g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Hierarchical α-MoO3 hollow microspheres | 1543.2 | This work |
| WO3 nanotube | 75.0 | [26] |
| WO3 nanorods | 73.0 | [27] |
| WO3 hollow spheres | 138.9 | [28] |
| Hierarchical WO3 hydrates | 274.3 | [8] |
| SiO2 nanoparticles | 679.9 | [29] |
| Fe3O4@Ag/SiO2 nanospheres | 128.5 | [30] |
| [1] | KUMAR K Y, ARCHANAr S, VINUTH T N,et al. Superb adsorption capacity of hydrothermally synthesized copper oxide and nickel oxide nanoflakes towards anionic and cationic dyes. J. Sci.: Adv. Mater. Devices, 2017, 2(2): 183-191. |
| [2] | JIN Y J, LI N, LIU H Q,et al. Highly efficient degradation of dye pollutants by Ce-doped MoO3 catalyst at room temperature. Dalton Trans., 2014, 43(34): 12860-12870. |
| [3] | HOKKANEN S, BHATNAGAR A, SILLANPAA M.A review on modification methods to cellulose-based adsorbents to improve adsorption capacity.Water Res., 2016, 91: 156-173. |
| [4] | TIAN P, HAN X Y, NING G L,et al. Synthesis of porous hierarchical MgO and its superb adsorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5(23): 12411-12418. |
| [5] | RONG X S, QIU F X, QIN J,et al. A facile hydrothermal synthesis, adsorption kinetics and isotherms to Congo Red azo-dye from aqueous solution of NiO/grapheme nanosheets adsorbent. J. Indust. Eng. Chem., 2015, 26: 354-363. |
| [6] | SONG L X, YANG Z K, TENG Y,et al. Nickel oxide nanoflowers: formation, structure, magnetic property and adsorptive performance towards organic dyes and heavy metal ions. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(31): 8731-8736. |
| [7] | ZHU D Z, ZHANG J, SONG J M,et al. Efficient one-pot synthesis of hierarchical flower-like α-Fe2O3 hollow sphereswith excellent adsorption performance for water treatment. Appl Surf. Sci., 2013, 284: 855-861. |
| [8] | LIU B X, WANG J S, WU J S,et al. Controlled fabrication of hierarchical WO3 hydrates with excellent adsorption performance. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(6): 1947-1954. |
| [9] | LEE J H.Gas sensors using hierarchical and hollow oxide nanostructures: overview. Sens. Actuators, B, 2009, 140(1): 319-336. |
| [10] | LIU Y, FENG P Z, WANG Z,et al. Novel fabrication and enhanced photocatalytic MB degradation of hierarchical porous monoliths of MoO3 nanoplates. Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1): 1845-1854. |
| [11] | WANG M, SONG X X, CHENG X L,et al. Highly selective and efficient adsorption dyes selfassembled by 3D hierarchical architecture of molybdenum oxide. RSC Adv., 2015, 5(104): 85248-85255. |
| [12] | SUI L L, ZHANG X F, CHENG X L,et al.Au-Loaded hierachical MoO3 hollow spheres with enhanced gas sensing performance for the detection of BTX (benzene, toluene, and xylene) and the sensing mechanism. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(2): 1661-1670. |
| [13] | ZHANG J, SONG P, LI J,et al. Template-assisted synthesis of hierarchical MoO3 microboxes and their high gas-sensing performance. Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 249: 458-466. |
| [14] | XIA Y C, WU C S, ZHAO N Y,et al. hierarchical nanostructures for excellent performance ethanol sensor. Mater. Lett., 2016, 171: 117-120. |
| [15] | YAN H H, SONG P, ZHANG S,et al. Facile fabrication and enhanced gas sensing properties of hierarchical MoO3 nanostructures. RSC Adv., 2015, 5(89): 72728-72735. |
| [16] | WANG S T, ZHANG Y G, MA X C,et al. Hydrothermal route to single crystalline α-MoO3 nanobelts and hierarchical structures. Solid State Commun., 2005, 136(5): 283-287. |
| [17] | YU X Y, ZHANG G X, LU Z Y,et al. Green sacrificial template fabrication of hierarchical MoO3 nanostructures. CrystEngComm, 2014, 16(19): 3935-3939. |
| [18] | LIANG R L, CAO H Q, QIAN D,et al. MoO3 nanowires as electrochemical pseudocapacitor materials. Chem. Commun., 2011, 47(37): 10305-10307. |
| [19] | JIAN J B, LIU J L, PENG S J,et al. Facile synthesis of α-MoO3 nanobelts and their pseudocapacitive behavior in an aqueous Li2SO4 solution. J. Mater. Chem. A., 2013, 1(7): 2588-2594. |
| [20] | CHEN D L, LIU M N, YIN L,et al. Single-crystalline MoO3 nanoplates: topochemical synthesis and enhanced ethanol-sensing performance. J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21(25): 9332-9342. |
| [21] | XU B Y, LI Y, WANG G F,et al. In situ synthesis and high adsorption performance of MoO2/Mo4O11 and MoO2/MoS2 composite nanorods by reduction of MoO3. Dalton Trans., 2015, 44(13): 6224-6228. |
| [22] | LEI C S, ZHU X F, ZHU B C,et al. Hierarchical NiO-SiO2 composite hollow microspheres with enhanced adsorption affinity towards Congo red in water. J. Colloid Inter. Sci., 2016, 466: 238-246. |
| [23] | ZHANG P P, MA X M, GUO Y M, et al. Size-controlled synthesis of hierarchical NiO hollow microspheres. Size-controlled synthesis of hierarchical NiO hollow microspheres and the adsorption for Congo red in water. Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 189-190(5): 188-195. |
| [24] | DHANAVEL S, NIVETHAA E A K, DHANAPA K,et al. α-MoO3/polyaniline composite for effective scavenging of Rhodamine B, Congo red and textile dye effluent. RSC Adv., 2016, 6(34): 28871-28886. |
| [25] | MA Y, JIA Y L, JIA Z B,et al. Facile synthesize α-MoO3 nanobelts with high adsorption property. Mater. Lett., 2015, 157: 53-56. |
| [26] | LI J, LIU X H, HAN Q F,et al. Formation of WO3 nanotube-based bundles directed by NaHSO4 and its application in water treatment. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(7): 1246-1253. |
| [27] | ZHU J, WANG S L, XIE S H,et al. Hexagonal single crystal growth of WO3 nanorods along a [110] axis with enhanced adsorption capacity. Chem. Commun., 2011, 47(15): 4403-4405. |
| [28] | JEON S, YONG K.Morphology-controlled synthesis of highly adsorptive tungsten oxide nanostructures and their application to water treatment.J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20(45): 10146-10151. |
| [29] | PERES E C, SLAVIERO J C, CUNHA A M,et al. Microwave synthesis of silica nanoparticles and its application for methylene blue adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2018, 6(1): 649-659. |
| [30] | SAINI J, GARG V K, GUPTA R K.Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by Fe3O4@Ag/SiO2 nanospheres: synthesis, characterization and adsorption performance. J. Mol. Liq., 2018, 250: 413-422. |
| [1] | 蔡梦宇, 李杨虹淼, 杨彩云, 周雨婷, 吴昊. 基于活性污泥焚灰的类Fenton催化剂的制备及其对亚甲基蓝的降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1135-1142. |
| [2] | 王梦桃, 索军, 方东, 易健宏, 刘意春, Olim RUZIMURADOV. ITO/TiO2纳米管阵列复合材料的可见光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1292-1300. |
| [3] | 迟聪聪, 屈盼盼, 任超男, 许馨, 白飞飞, 张丹洁. SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2核壳结构的制备及其光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [4] | 周帆, 毕辉, 黄富强. 用稻壳制备亚甲基蓝高吸附容量的超高比表面积活性炭[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 893-903. |
| [5] | 程福强,吉田田,薛敏,孟子晖,吴玉凯. 巯基改性SBA-15的制备及其对Cr6+的吸附[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 193-198. |
| [6] | 张晓锋,张冠华,孟跃,薛继龙,夏盛杰,倪哲明. 席夫碱钴改性CoCr-LDHs材料光催化降解亚甲基蓝研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 974-982. |
| [7] | 柯剑煌, 谢凯, 韩喻, 孙巍巍, 罗世强, 刘锦锋. 基于不同共溶剂体系对于高电压正极材料LiCoPO4的形貌控制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 618-624. |
| [8] | 张翊青, 刘梨, 张淑娟, 万正睿, 刘红英, 周立群. NH2-UIO-66负载RuCuMo纳米催化剂的制备及其催化产氢[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(12): 1316-1324. |
| [9] | 赵海兵, 徐海峰, 杨克伟, 林辰学, 冯苗, 于岩. Mg掺杂TiO2纳米晶光氧化还原染料的可逆颜色转变研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(10): 1124-1130. |
| [10] | 喻 洋, 佟明兴, 何玉兰, 陈 辉, 高 静, 李国华. 介孔TiO2/WO3空心球的制备及其可见光光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(4): 365-371. |
| [11] | 武萱蓉, 杨巧珍, 赵永祥, 路艳罗. ZnS微球的水热/溶剂热法合成及其光催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(5): 473-478. |
| [12] | 李 斌, 李英莲, 莫淑一, 陈明光, 王东生, 龙 飞. In2Se3/CuSe核壳结构微纳粉的合成及其喷涂热处理制备CuInSe2薄膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(10): 1135-1140. |
| [13] | 徐明丽, 段 奔, 张英杰, 杨国涛, 董 鹏, 夏书标, 杨显万. 碳纳米管载体改性条件对Pt纳米粒子电催化氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(9): 931-936. |
| [14] | 卢 青, 华罗光, 陈亦琳, 高碧芬, 林碧洲. 氧缺陷Bi2WO6-x可见光催化剂的制备和性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(4): 413-419. |
| [15] | 彭 丹, 郑学军, 谢澍梵, 罗晓菊, 王 丁. GaN/ZnO复合体的制备及光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(9): 956-960. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||