无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 536-544.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240494 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240494
所属专题: 【信息功能】介电、铁电、压电材料(202506)
熊思宇1( ), 莫尘1, 朱肖伟1, 朱国斌1, 陈德钦1, 刘来君1, 施晓东2, 李纯纯1(
), 莫尘1, 朱肖伟1, 朱国斌1, 陈德钦1, 刘来君1, 施晓东2, 李纯纯1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-27
修回日期:2024-12-19
出版日期:2025-05-20
网络出版日期:2025-01-09
通讯作者:
李纯纯, 副研究员. E-mail: lichunchun2003@126.com作者简介:熊思宇(2000-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: xiongsiyu0927@163.com
基金资助:
XIONG Siyu1( ), MO Chen1, ZHU Xiaowei1, ZHU Guobin1, CHEN Deqin1, LIU Laijun1, SHI Xiaodong2, LI Chunchun1(
), MO Chen1, ZHU Xiaowei1, ZHU Guobin1, CHEN Deqin1, LIU Laijun1, SHI Xiaodong2, LI Chunchun1( )
)
Received:2024-11-27
Revised:2024-12-19
Published:2025-05-20
Online:2025-01-09
Contact:
LI Chunchun, associate professor. E-mail: lichunchun2003@126.comAbout author:XIONG Siyu (2000-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: xiongsiyu0927@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
超低介电常数锂基硅酸盐微波介质陶瓷材料作为介质基板在第五代无线通信技术中显示出极大的潜力。然而, 较高的烧结温度带来的残余应力会导致材料的介电损耗增加, 微波介电性能变差。本工作通过在LiAlSi2O6陶瓷中引入B3+来减少Al3+含量, 从而改善LiAlSi2O6陶瓷的烧结温度和微波介电性能。采用固相反应法与冷等静压技术相结合的方式制备了LiBxAl1-xSi2O6(0≤x≤0.20)微波介质陶瓷, 并研究了B3+掺杂对该材料的烧结特性、相结构、微观形貌以及微波介电性能的影响。研究结果表明, 随着掺杂量的增加, 陶瓷的烧结温度由1400 ℃大幅降低至1000 ℃。同时, 相对介电常数(εr)从3.95降低至3.69, 品质因数(Q×f)从24300 GHz显著提升至30560 GHz, 谐振频率温度系数(τf)从-45.9×10-6 ℃-1升高至-20.9×10-6 ℃-1。具体而言, εr的变化主要受材料本征极化率、晶格振动以及共价键强度的共同影响; Q×f提升则与填充分数(PF)增加和阻尼系数减小密切相关; τf增大与氧的键价(VO)存在较强的关联性。此外, x = 0.20组分展现出最佳的微波介电性能, 具体表现为εr = 3.69, Q×f = 30560 GHz, τf = -20.9×10-6 ℃-1。本研究制备的LiBxAl1-xSi2O6为未来高性能微波介质陶瓷材料的开发与应用提供了重要的理论依据和实践指导。
中图分类号:
熊思宇, 莫尘, 朱肖伟, 朱国斌, 陈德钦, 刘来君, 施晓东, 李纯纯. 超低介电常数LiBxAl1-xSi2O6微波介质陶瓷的低温烧结[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 536-544.
XIONG Siyu, MO Chen, ZHU Xiaowei, ZHU Guobin, CHEN Deqin, LIU Laijun, SHI Xiaodong, LI Chunchun. Low-temperature Sintering of LiBxAl1-xSi2O6 Microwave Dielectric Ceramics with Ultra-low Permittivity[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 536-544.
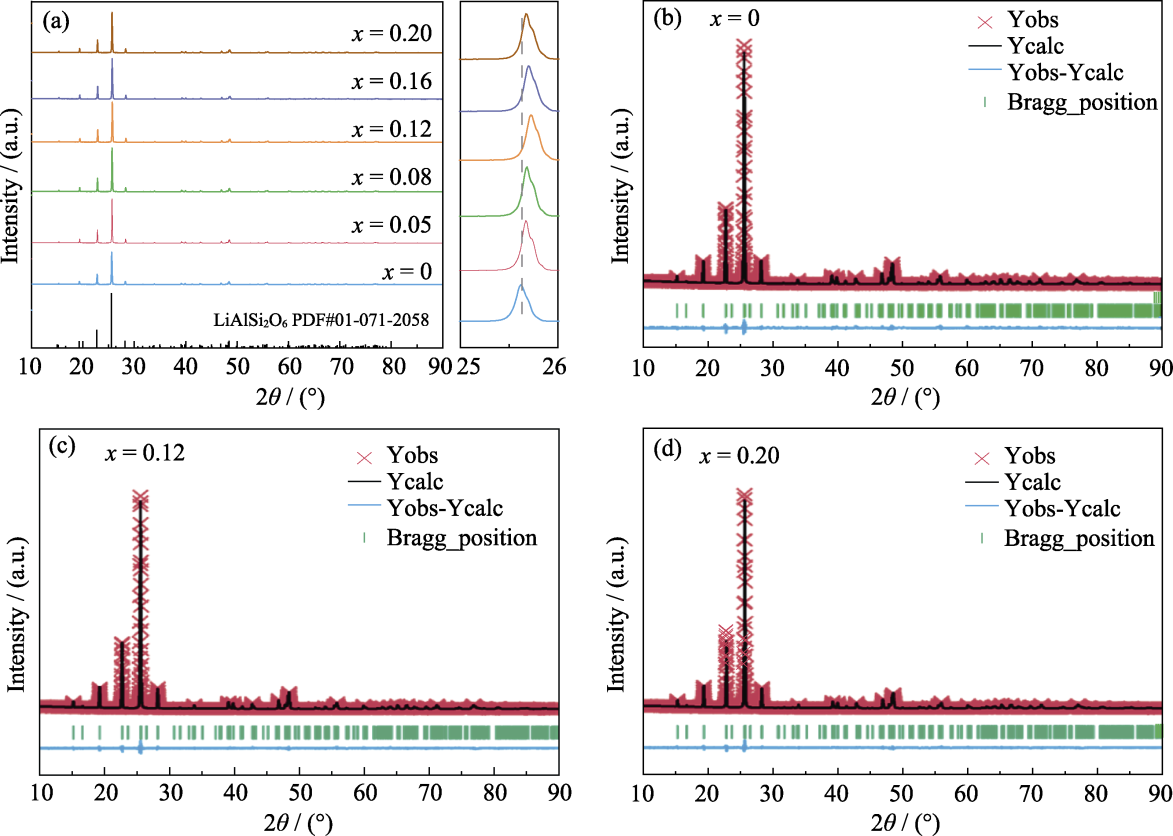
图2 LiBxAl1-xSi2O6陶瓷的XRD图谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of LiBxAl1-xSi2O6 ceramics (a) At the optimum sintering temperature; (b-d) Rietveld refinement fitting patterns at (b) x = 0, (c) x = 0.12, and (d) x = 0.20
| x | Lattice parameter | χ2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 | ||||
| 0 | 0.75380(5) | 0.75380(5) | 0.91556(4) | 0.52024(4) | 7.69 | 10.8 | 1.84 |
| 0.05 | 0.75346(3) | 0.75346(3) | 0.91533(1) | 0.51963(9) | 7.32 | 10.1 | 1.83 |
| 0.08 | 0.75320(5) | 0.75320(5) | 0.91494(0) | 0.51906(2) | 7.24 | 10.2 | 1.89 |
| 0.12 | 0.75286(8) | 0.75286(8) | 0.91434(9) | 0.51826(2) | 7.24 | 10.2 | 1.87 |
| 0.16 | 0.75246(2) | 0.75246(2) | 0.91332(8) | 0.51712(5) | 7.29 | 10.1 | 1.86 |
| 0.20 | 0.75206(4) | 0.75206(4) | 0.91257(9) | 0.51615(5) | 7.22 | 9.98 | 1.87 |
表1 LiBxAl1-xSi2O6陶瓷的Rietveld结构精修参数
Table 1 Rietveld refined structural parameters of LiBxAl1-xSi2O6 ceramics
| x | Lattice parameter | χ2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 | ||||
| 0 | 0.75380(5) | 0.75380(5) | 0.91556(4) | 0.52024(4) | 7.69 | 10.8 | 1.84 |
| 0.05 | 0.75346(3) | 0.75346(3) | 0.91533(1) | 0.51963(9) | 7.32 | 10.1 | 1.83 |
| 0.08 | 0.75320(5) | 0.75320(5) | 0.91494(0) | 0.51906(2) | 7.24 | 10.2 | 1.89 |
| 0.12 | 0.75286(8) | 0.75286(8) | 0.91434(9) | 0.51826(2) | 7.24 | 10.2 | 1.87 |
| 0.16 | 0.75246(2) | 0.75246(2) | 0.91332(8) | 0.51712(5) | 7.29 | 10.1 | 1.86 |
| 0.20 | 0.75206(4) | 0.75206(4) | 0.91257(9) | 0.51615(5) | 7.22 | 9.98 | 1.87 |
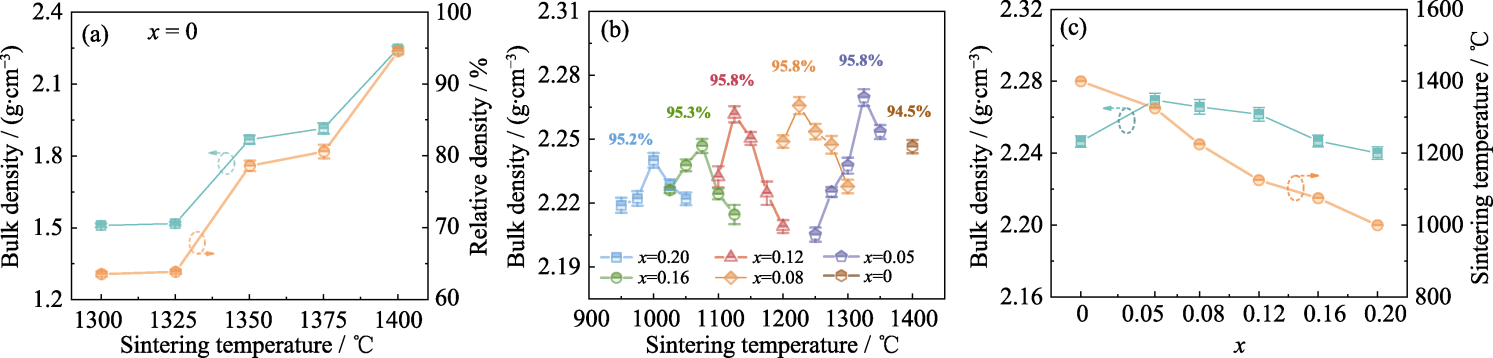
图3 LiBxAl1-xSi2O6陶瓷的密度与烧结温度的关系
Fig. 3 Relationship between bulk density and sintering temperature of LiBxAl1-xSi2O6 ceramics (a) LiAlSi2O6 ceramic; (b) LiBxAl1-xSi2O6 ceramic; (c) Bulk density and sintering temperature varied with x
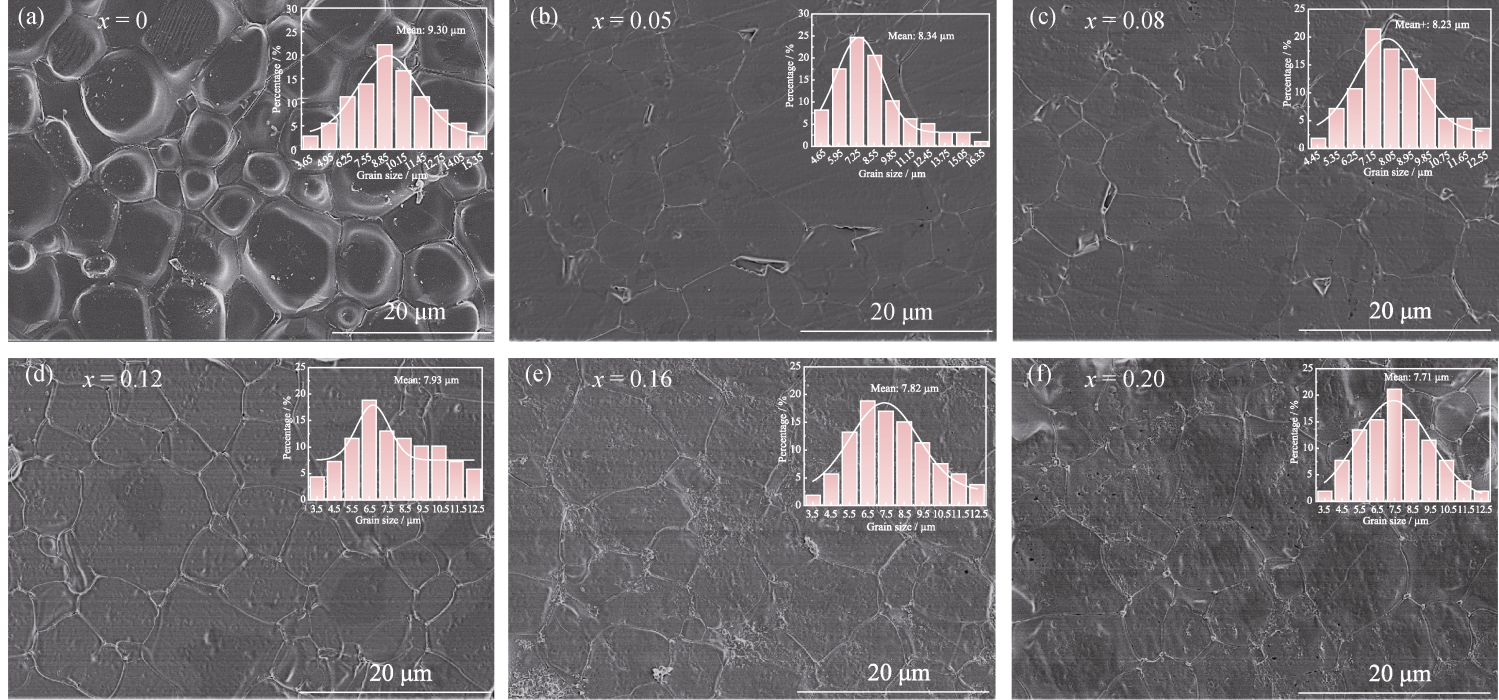
图4 LiBxAl1-xSi2O6陶瓷的SEM照片和晶粒尺寸分布
Fig. 4 SEM images and grain size distributions of LiBxAl1-xSi2O6 ceramics (a) x = 0; (b) x = 0.05; (c) x = 0.08; (d) x = 0.12; (e) x = 0.16; (f) x = 0.20
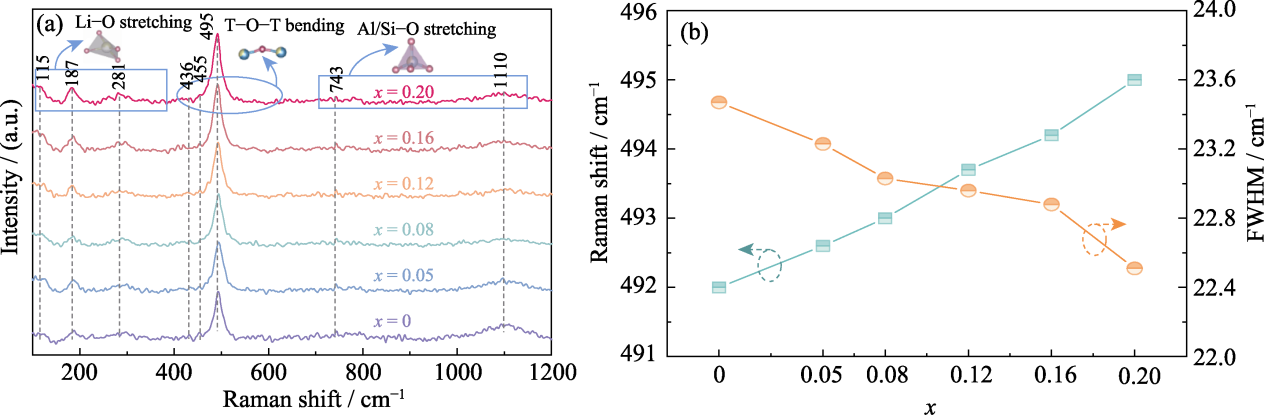
图5 LiBxAl1-xSi2O6陶瓷的拉曼光谱图及性能参数
Fig. 5 Raman spectra and corresponding parameters of LiBxAl1-xSi2O6 ceramics (a) Raman spectra at different compositions; (b) Raman shift and FWHM at 493 cm-1 changed with composition
| x | Vm / nm3 | α / nm3 | εtheo | εr | α·Vm-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.1300610 | 0.0157900 | 4.1042 | 3.95 | 0.121405 |
| 0.05 | 0.1299098 | 0.0157530 | 4.0968 | 3.90 | 0.121261 |
| 0.08 | 0.1297655 | 0.0157308 | 4.0949 | 3.85 | 0.121225 |
| 0.12 | 0.1295655 | 0.0157012 | 4.0928 | 3.81 | 0.121184 |
| 0.16 | 0.1292813 | 0.0156716 | 4.0947 | 3.76 | 0.121221 |
| 0.20 | 0.1290388 | 0.0156420 | 4.0946 | 3.69 | 0.121219 |
表2 LiBxAl1-xSi2O6陶瓷样品的Vm、α、εtheo、εr和α/Vm
Table 2 Vm, α, εtheo, εr, and α/Vm of LiBxAl1-xSi2O6 ceramics
| x | Vm / nm3 | α / nm3 | εtheo | εr | α·Vm-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.1300610 | 0.0157900 | 4.1042 | 3.95 | 0.121405 |
| 0.05 | 0.1299098 | 0.0157530 | 4.0968 | 3.90 | 0.121261 |
| 0.08 | 0.1297655 | 0.0157308 | 4.0949 | 3.85 | 0.121225 |
| 0.12 | 0.1295655 | 0.0157012 | 4.0928 | 3.81 | 0.121184 |
| 0.16 | 0.1292813 | 0.0156716 | 4.0947 | 3.76 | 0.121221 |
| 0.20 | 0.1290388 | 0.0156420 | 4.0946 | 3.69 | 0.121219 |
| x | VLi | VSi/Al | VO | CLi-O/% | CSi/Al-O/% | Average/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.820 | 3.906 | 1.912 | 18.87 | 53.18 | 36.03 |
| 0.05 | 0.821 | 3.935 | 1.924 | 18.89 | 53.44 | 36.16 |
| 0.08 | 0.823 | 3.947 | 1.930 | 18.92 | 53.54 | 36.23 |
| 0.12 | 0.824 | 3.978 | 1.943 | 18.94 | 53.81 | 36.37 |
| 0.16 | 0.825 | 4.036 | 1.968 | 18.95 | 54.31 | 36.63 |
| 0.20 | 0.829 | 4.075 | 1.986 | 19.02 | 54.65 | 36.83 |
表3 LiBxAl1-xSi2O6陶瓷的键价、共价键强度和平均共价键强度
Table 3 Bond valence, covalence and average covalence of LiBxAl1-xSi2O6 ceramics
| x | VLi | VSi/Al | VO | CLi-O/% | CSi/Al-O/% | Average/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.820 | 3.906 | 1.912 | 18.87 | 53.18 | 36.03 |
| 0.05 | 0.821 | 3.935 | 1.924 | 18.89 | 53.44 | 36.16 |
| 0.08 | 0.823 | 3.947 | 1.930 | 18.92 | 53.54 | 36.23 |
| 0.12 | 0.824 | 3.978 | 1.943 | 18.94 | 53.81 | 36.37 |
| 0.16 | 0.825 | 4.036 | 1.968 | 18.95 | 54.31 | 36.63 |
| 0.20 | 0.829 | 4.075 | 1.986 | 19.02 | 54.65 | 36.83 |
| Component | ST/℃ | εr | Q×f/GHz | τf/(×10-6, ℃-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiAlSiO4 | 1350 | 4.9 | 36000 | -57.3 | [ |
| Li(Al0.99Li0.01)SiO3.99 | 1250 | 3.49 | 51358 | -51.48 | [ |
| Ca2SiO4 | 1450 | 8.6 | 26100 | -89 | [ |
| Sr2SiO4 | 1575 | 9.5 | 19100 | -205 | [ |
| Ba2SiO4 | 1525 | 13.1 | 17900 | -17 | [ |
| Zn2SiO4 | 1340 | 5.7 | 53000 | -16 | [ |
| Ba2ZnSi2O7 | 1200 | 8.09 | 26600 | -51.4 | [ |
| Sr2MgSi2O7 | 1280 | 6.85 | 22530 | -32 | [ |
| Sr3MgSi2O8 | 1450 | 11.6 | 25375 | -57.41 | [ |
| Li2SiO3 | 1025 | 6.19 | 30550 | -40.95 | [ |
| Li2ZnSiO4 | 1250 | 5.8 | 14700 | -96.6 | [ |
| Li2MgSiO4 | 1100 | 5.73 | 13570 | -16.7 | [ |
| LiBxAl1-xSiO4(0.02≤x≤0.1) | 875-1100 | 3.34-3.73 | 25770-27540 | -22.85--16.5 | [ |
| LiBxAl1-xSi2O6(0≤x≤0.20) | 1000-1400 | 3.69-3.95 | 24300-30500 | -45.9--20.9 | This work |
表4
Table 4 Sintering temperatures (ST) and microwave dielectric properties of several silicates compared with LiBxAl1-xSi2O6[17,19,26,28,38,41 -45]
| Component | ST/℃ | εr | Q×f/GHz | τf/(×10-6, ℃-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiAlSiO4 | 1350 | 4.9 | 36000 | -57.3 | [ |
| Li(Al0.99Li0.01)SiO3.99 | 1250 | 3.49 | 51358 | -51.48 | [ |
| Ca2SiO4 | 1450 | 8.6 | 26100 | -89 | [ |
| Sr2SiO4 | 1575 | 9.5 | 19100 | -205 | [ |
| Ba2SiO4 | 1525 | 13.1 | 17900 | -17 | [ |
| Zn2SiO4 | 1340 | 5.7 | 53000 | -16 | [ |
| Ba2ZnSi2O7 | 1200 | 8.09 | 26600 | -51.4 | [ |
| Sr2MgSi2O7 | 1280 | 6.85 | 22530 | -32 | [ |
| Sr3MgSi2O8 | 1450 | 11.6 | 25375 | -57.41 | [ |
| Li2SiO3 | 1025 | 6.19 | 30550 | -40.95 | [ |
| Li2ZnSiO4 | 1250 | 5.8 | 14700 | -96.6 | [ |
| Li2MgSiO4 | 1100 | 5.73 | 13570 | -16.7 | [ |
| LiBxAl1-xSiO4(0.02≤x≤0.1) | 875-1100 | 3.34-3.73 | 25770-27540 | -22.85--16.5 | [ |
| LiBxAl1-xSi2O6(0≤x≤0.20) | 1000-1400 | 3.69-3.95 | 24300-30500 | -45.9--20.9 | This work |
| [1] | ZHOU D, PANG L X, WANG D W, et al. High permittivity and low loss microwave dielectrics suitable for 5G resonators and low temperature co-fired ceramic architecture. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(38): 10094. |
| [2] | XIONG Y, XIE H Y, RAO Z G, et al. Compositional modulation in ZnGa2O4 via Zn2+/Ge4+ co-doping to simultaneously lower sintering temperature and improve microwave dielectric properties. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10(6): 1360. |
| [3] | LIN Q B, SONG K X, LIU B, et al. Vibrational spectroscopy and microwave dielectric properties of AY2Si3O10 (A = Sr, Ba) ceramics for 5G applications. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(1): 1171. |
| [4] | CHEN D Q, YAN N, CAO X F, et al. Entropy regulation in LaNbO4-based fergusonite to implement high-temperature phase transition and promising dielectric properties. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2023, 12(5): 1067. |
| [5] | ZHANG P, ZHAO Y G. Influence of Sm3+ substitutions for Nd3+ on the microwave dielectric properties of (Nd1-xSmx)NbO4 (x = 0.02-0.15) ceramics. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 654: 240. |
| [6] | JABEEN S, KHAN Q U. An integrated MIMO antenna design for Sub-6 GHz & millimeter-wave applications with high isolation. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2022, 153: 154247. |
| [7] | LOU W C, MAO M M, SONG K X, et al. Low permittivity cordierite-based microwave dielectric ceramics for 5G/6G telecommunications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(6): 2820. |
| [8] | XIONG S Y, CHEN D Q, ZHU X W, et al. Processing strategy and composite regulation on dielectric performance in Li2O-Al2O3-B2O3 dielectric systems using SrTiO3. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2024, 107(9): 6080. |
| [9] | WU F F, ZHOU D, DU C, et al. Design of a Sub-6 GHz dielectric resonator antenna with novel temperature-stabilized (Sm1-xBix)NbO4 (x = 0-0.15) microwave dielectric ceramics. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(5): 7030. |
| [10] | LIU B, HU C C, HUANG Y H, et al. Crystal structure, infrared reflectivity spectra and microwave dielectric properties of CaAl2O4 ceramics with low permittivity. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 791: 1033. |
| [11] | LIU B, LIU X Q, CHEN X M. Sr2LaAlTiO7: a new Ruddlesden- Popper compound with excellent microwave dielectric properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(8): 1720. |
| [12] | JIANG C, WU S P, MA Q, et al. Synthesis and microwave dielectric properties of Nd2SiO5 ceramics. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 544: 141. |
| [13] | ZOU Z Y, CHEN Z H, LAN X K, et al. Weak ferroelectricity and low-permittivity microwave dielectric properties of Ba2Zn(1+x)Si2O(7+x) ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(9): 3065. |
| [14] | KRZMANC M M, VALANT M, JANCAR B, et al. Sub-solidus synthesis and microwave dielectric characterization of plagioclase feldspars. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2005, 88(9): 2472. |
| [15] | SONG X Q, LEI W, ZHOU Y Y, et al. Ultra-low fired fluoride composite microwave dielectric ceramics and their application for BaCuSi2O6-based LTCC. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(2): 1140. |
| [16] | HUANG L, DING S H, YAN X K, et al. Structure and microwave dielectric properties of BaAl2Si2O8 ceramic with Li2O-B2O3 sintering additive. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 820: 153100. |
| [17] | WANG Y R, DING S H, HOU Z P, et al. Structure and microwave dielectric properties of Li(Al1-xLix)SiO4-x ceramics. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(3): 4290. |
| [18] | KWEON S H, JOUNG M R, KIM J S, et al. Low temperature sintering and microwave dielectric properties of B2O3-added LiAlSiO4 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2011, 94(7): 1995. |
| [19] | JOSEPH T, SEBASTIAN M T. Microwave dielectric properties of alkaline earth orthosilicates M2SiO4 (M = Ba, Sr, Ca). Materials Letters, 2011, 65(5): 891. |
| [20] | PELLETANT A, REVERON H, CHÊVALIER J, et al. Grain size dependence of pure β-eucryptite thermal expansion coefficient. Materials Letters, 2012, 66(1): 68. |
| [21] | FERRAZ R F, PEREIRA M D C, OLIVEIRA R A P. Synthesis and characterization of β-spodumene by a new Sol-Gel route assisted by whey protein. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2024, 111(3): 718. |
| [22] | WELSCH A M, MURAWSKI D, PREKAJSKI M, et al. Ionic conductivity in single-crystal LiAlSi2O6: influence of structure on lithium mobility. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 2015, 42(5): 413. |
| [23] | WELSCH A M, BEHRENS H, ROSS S, et al. Structural control of ionic conductivity in LiAlSi2O6 and LiAlSi4O10 glasses and single crystals. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 2012, 226(5/6): 491. |
| [24] | SHOU H W, DUAN Y H. Anisotropic elasticity and thermal conductivities of (α, β, γ)-LiAlSi2O6 from the first-principles calculation. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 756: 40. |
| [25] | LI C C, XIANG H C, YIN C Z, et al. Ultra-low loss microwave dielectric ceramic Li2Mg2TiO5 and low-temperature firing via B2O3 addition. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2018, 47(11): 6383. |
| [26] | PENG R, LI Y X, SU H, et al. Effect of cobalt-doping on the dielectric properties and densification temperature of Li2MgSiO4 ceramic: calculation and experiment. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 827: 154162. |
| [27] | PENG R, LI Y X, TANG X L, et al. Improved sintering and microwave dielectric properties of Li2CaSiO4 ceramic with magnesium atom substitution. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(7): 8869. |
| [28] | XIONG S Y, ZHU G B, ZHU X W, et al. Microstrip dielectric patch antenna fabrication and characterization using ultra low permittivity and low temperature Co-fired LiAlSiO4 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2025, 45(2): 116930. |
| [29] | LI C, DING S H, SONG T X, et al. Structure and microwave dielectric properties of BaAl2-2xLi2xSi2O8-2x ceramics. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(4): 4895. |
| [30] | SHANNON R D. Dielectric polarizabilities of ions in oxides and fluorides. Journal of Applied Physics, 1993, 73(1): 348. |
| [31] | YIN C Z, DU K, ZHANG M, et al. Novel low-εr and lightweight LiBO2 microwave dielectric ceramics with good chemical compatibility with silver. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(11): 4580. |
| [32] | XING Z, YIN C Z, YU Z Z, et al. Synthesis of LiBGeO4 using compositional design and its dielectric behaviors at RF and microwave frequencies. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(14): 22460. |
| [33] | SHANNON R D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallographica Section A, 1976, 32(5): 751. |
| [34] | YOON S H, KIM D W, CHO S Y, et al. Investigation of the relations between structure and microwave dielectric properties of divalent metal tungstate compounds. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26(10):2051. |
| [35] | SU C X, AO L Y, ZHANG Z W, et al. Crystal structure, Raman spectra and microwave dielectric properties of novel temperature- stable LiYbSiO4 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(12): 19996. |
| [36] | KIM E S, CHUN B S, FREER R, et al. Effects of packing fraction and bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of A2+B6+O4 (A2+: Ca, Pb, Ba; B6+: Mo, W) ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010, 30(7): 1731. |
| [37] | DU Q B, TANG Y, LI J, et al. A low-εr and high-Q microwave dielectric ceramic Li2SrSiO4 with abnormally low sintering temperature. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(15): 7678. |
| [38] | HUANG Y W, YANG X H, ZHANG Y C. Novel single-phase Li2SiO3 microwave dielectric ceramic with low permittivity. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2025, 45(2): 116940. |
| [39] | REANEY I M, IDDLES D. Microwave dielectric ceramics for resonators and filters in mobile phone networks. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(7):2063. |
| [40] | PARK H S, YOON K H, KIM E S. Effect of bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of complex perovskite ceramics. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2003, 79(2): 181. |
| [41] | GUO Y P, OHSATO H, KAKIMOTO K I. Characterization and dielectric behavior of willemite and TiO2-doped willemite ceramics at millimeter-wave frequency. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26(10): 1827. |
| [42] | ZOU Z Y, DU K, LAN X K, et al. Anti-reductive characteristics and dielectric loss mechanisms of Ba2ZnSi2O7 microwave dielectric ceramic. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(15): 19415. |
| [43] | XIAO M, WEI Y S, SUN H R, et al. Crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of low-permittivity Sr2MgSi2O7 ceramic. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2018, 29(23): 20339. |
| [44] | HE Y H, WEI X L, HE G Q, et al. Sintering behavior, phase composition, microstructure, and dielectric properties of low- permittivity alkaline earth silicate Sr3MgSi2O8 ceramics. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2022, 33(35): 26263. |
| [45] | DOU G, ZHOU D X, GONG S P, et al. Low temperature sintering and microwave dielectric properties of Li2ZnSiO4 ceramics with ZB glass. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2013, 24(5): 1601. |
| [1] | 李文元, 徐佳楠, 邓瀚澳, 常爱民, 张博. 钒取代对LaTaO4陶瓷微观结构和微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 697-703. |
| [2] | 屈婧婧, 魏星, 刘飞, 袁昌来, 陈国华, 黄先培. 热处理对Mg-Al-Si-Ti-B系微晶玻璃析晶及介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(12): 1309-1315. |
| [3] | 刘 飞, 黄先培, 袁昌来, 陈国华. 烧结温度和CaTiO3添加对不稳定层状Can+1TinO3n+1 (n = 1)陶瓷体系结构与介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(5): 489-494. |
| [4] | 屈婧婧, 魏 星, 宋小辉, 袁昌来, 刘 飞. B位(Mg1/3Ta2/3)4+置换对新型Sr基(Sr, Nd, Ca)TiO3微波陶瓷结构及介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(3): 293-298. |
| [5] | 张 瑶, 丁士华, 刘杨琼, 段绍英, 肖 鹏, 韩林材. Ba1-xMgxAl2Si2O8晶体结构与微波介电性能的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(1): 91-95. |
| [6] | 张 康, 李 蔚, 林慧兴. MgO/Eu2O3共掺杂对Al2O3陶瓷微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(9): 984-988. |
| [7] | 苏静杰, 杨 梓, 李义锋, 唐伟忠, 安晓明, 郭 辉. 分体圆柱谐振腔法用于金刚石膜微波介电性能测试的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(7): 751-756. |
| [8] | 屈婧婧, 魏 星, 经本钦, 刘 飞, 袁昌来. 高Q值(1-x)(Sr0.2Nd0.208Ca0.488)TiO3-xNd(Ti0.5Mg0.5)O3微波陶瓷的微结构及介电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(11): 1213-1217. |
| [9] | 刘 林, 方有维, 邓新峰, 庄文东, 唐 斌, 张树人. (Ba1-xSrx)La4Ti4O15(x=0.8~0.95)陶瓷的微结构及微波介电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(3): 281-284. |
| [10] | 雷 文,吕文中,王晓川,梁 军,江建军. CaTiO3对(1-x)ZnAl2O4-xMg2TiO4(x=0.21)微波介质陶瓷结构和性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(5): 957-961. |
| [11] | 刘忠池,周东祥,龚树萍,胡云香. 铜钼复合添加ZnO-TiO2微波介质陶瓷的低温烧结及相转变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(4): 712-716. |
| [12] | 李月明,宋婷婷,胡元云,彭浩,刘维良. (1-x)CaTiO3-xLi1/2Sm1/2TiO3陶瓷的微波介电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(4): 695-699. |
| [13] | 王焕平,徐时清,张启龙,杨辉. 溶胶-凝胶制备(Ca0.7Mg0.3)SiO3陶瓷及其微波介电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(4): 691-694. |
| [14] | 吕文中,朱建华,Eric Rop Kipkoech. NdAlO3掺杂对Ba4.2Nd9.2Ti18O54陶瓷微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(1): 139-144. |
| [15] | 胡明哲,周东祥,姜胜林,蔡雪卿,黄静. Nd3+取代对(PbCa)(FeNb)O3介质陶瓷微波特性及晶体结构的影响研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2005, 20(1): 126-132. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||