无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (12): 1405-1413.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250012 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20250012
于泽龙1( ), 唐春1,2,3(
), 唐春1,2,3( ), 饶家豪1, 郭恒1,2,3, 周莹1,2(
), 饶家豪1, 郭恒1,2,3, 周莹1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-08
修回日期:2025-04-06
出版日期:2025-12-20
网络出版日期:2025-04-27
通讯作者:
唐 春, 副研究员. E-mail: tangchun@swpu.edu.cn;作者简介:于泽龙(2000-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 18535069947@163.com
基金资助:
YU Zelong1( ), TANG Chun1,2,3(
), TANG Chun1,2,3( ), RAO Jiahao1, GUO Heng1,2,3, ZHOU Ying1,2(
), RAO Jiahao1, GUO Heng1,2,3, ZHOU Ying1,2( )
)
Received:2025-01-08
Revised:2025-04-06
Published:2025-12-20
Online:2025-04-27
Contact:
TANG Chun, associate professor. E-mail: tangchun@swpu.edu.cn;About author:YU Zelong (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 18535069947@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
碱性电解水(Alkaline Water Electrolysis, AWE)制氢由于其较低的电流密度而面临效率低和成本高的挑战, 需要开发大电流密度下稳定的高效非贵金属电催化剂。本研究在泡沫镍(Nickel Foam, NF)骨架上采用水热法结合磷化技术制备了非晶NiMoOP/NF电催化材料, 非晶针状形貌可以有效增加活性位点数量并提升电解水制氢稳定性, 在10和1000 mA·cm-2的电流密度下, 析氢过电位达到31和370 mV, 并且在1 A·cm-2的大电流密度下可以稳定运行1100 h。将NiMoOP/NF材料应用于全水解与晶硅异质结太阳能电池耦合, 太阳能到氢能的理论转换效率高达18.60%。在工业模拟条件(温度60 ℃, 30%(质量分数) KOH电解液)下, 电解电压在1.77 V可实现400 mA·cm-2的电流密度, 其制氢能耗为4.19 kWh·Nm-3(Nm3: 标准立方米)。结合光伏电解制氢经济性研究表明, 光伏离网非储能制氢系统的最低制氢成本为¥28.52 kg-1。本研究开发的非晶纳米针状结构材料有效提高了电解水制氢活性和稳定性, 为设计大电流密度下制氢催化材料提供了思路, 结合光伏电解水制绿氢经济性分析为绿氢产业发展提供了支撑。
中图分类号:
于泽龙, 唐春, 饶家豪, 郭恒, 周莹. 碱性电解水大电流密度电催化剂的制备及经济性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1405-1413.
YU Zelong, TANG Chun, RAO Jiahao, GUO Heng, ZHOU Ying. Preparation and Economic Analysis of High-current-density Electrocatalysts for Alkaline Water Electrolysis[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1405-1413.
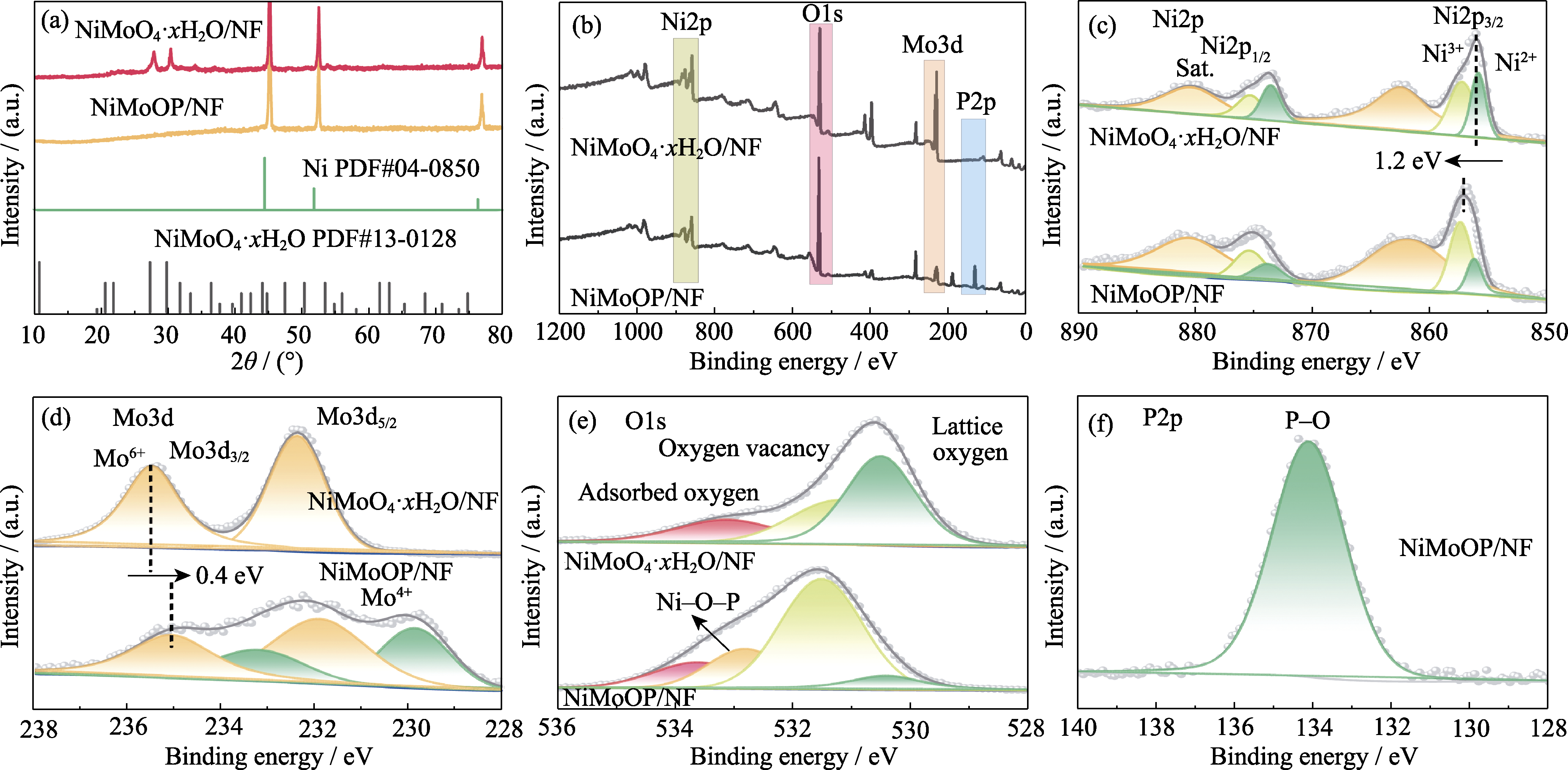
图2 NiMoO4·xH2O/NF和NiMoOP/NF的XRD图谱和XPS图谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns and XPS spectra of NiMoO4·xH2O/NF and NiMoOP/NF (a) XRD patterns; (b) Full XPS spectra; (c) Ni2p XPS spectra; (d) Mo3d XPS spectra; (e) O1s XPS spectra; (f) P2p XPS spectrum
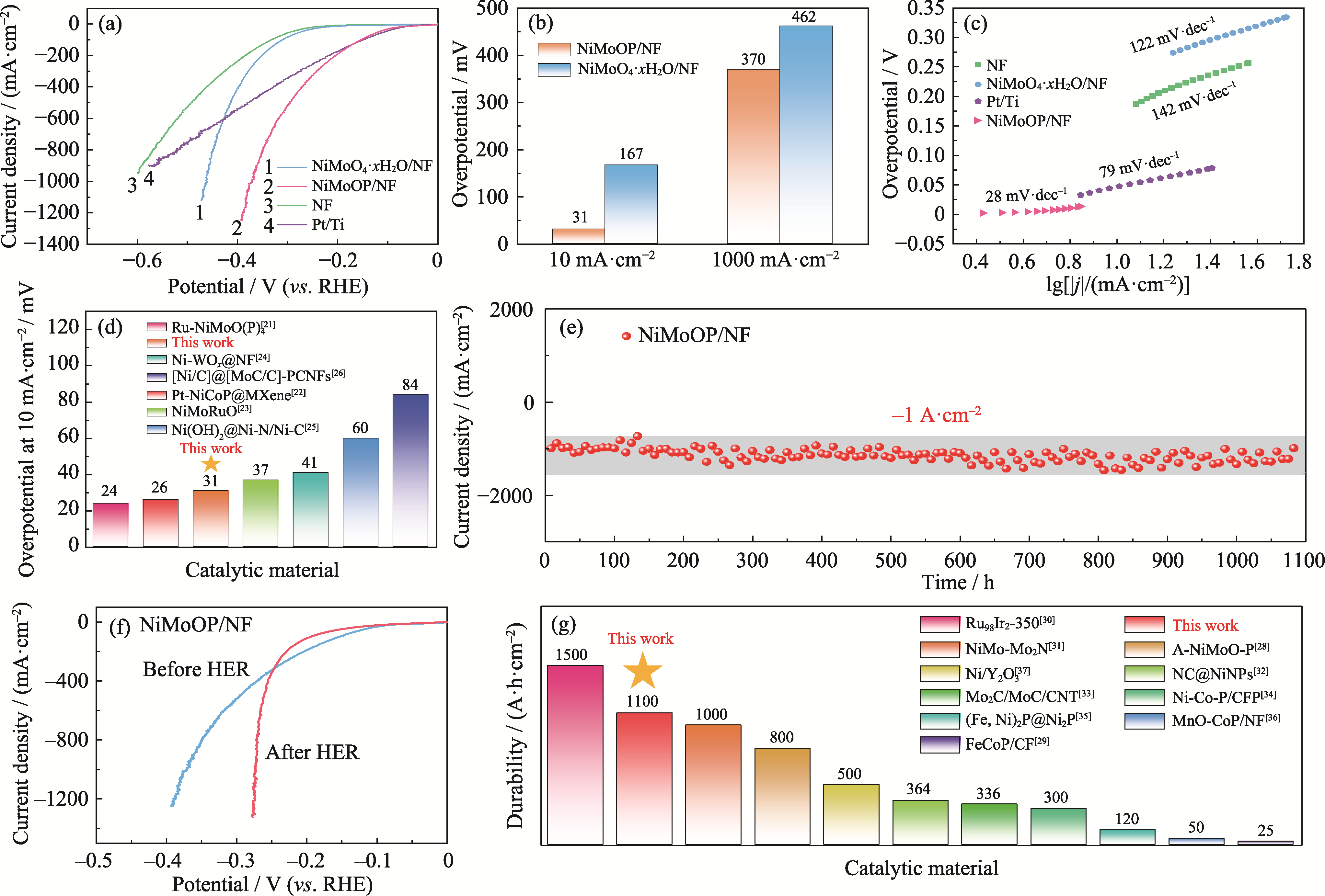
图3 NiMoOP/NF的电化学性能测试以及与其他催化材料性能对比
Fig. 3 Electrochemical performance tests of NiMoOP/NF and comparison with other catalytic materials (a) LSV curves; (b) Overpotentials; (c) Tafel plots; (d) Comparison of overpotentials for Ni-based catalysts; (e) I-t curve at -0.9 V (vs. RHE) without IR correction; (f) LSV curves of the catalyst before and after the 1100 h stability test; (g) Comparison of catalysts durability. Colorful figures are available on website
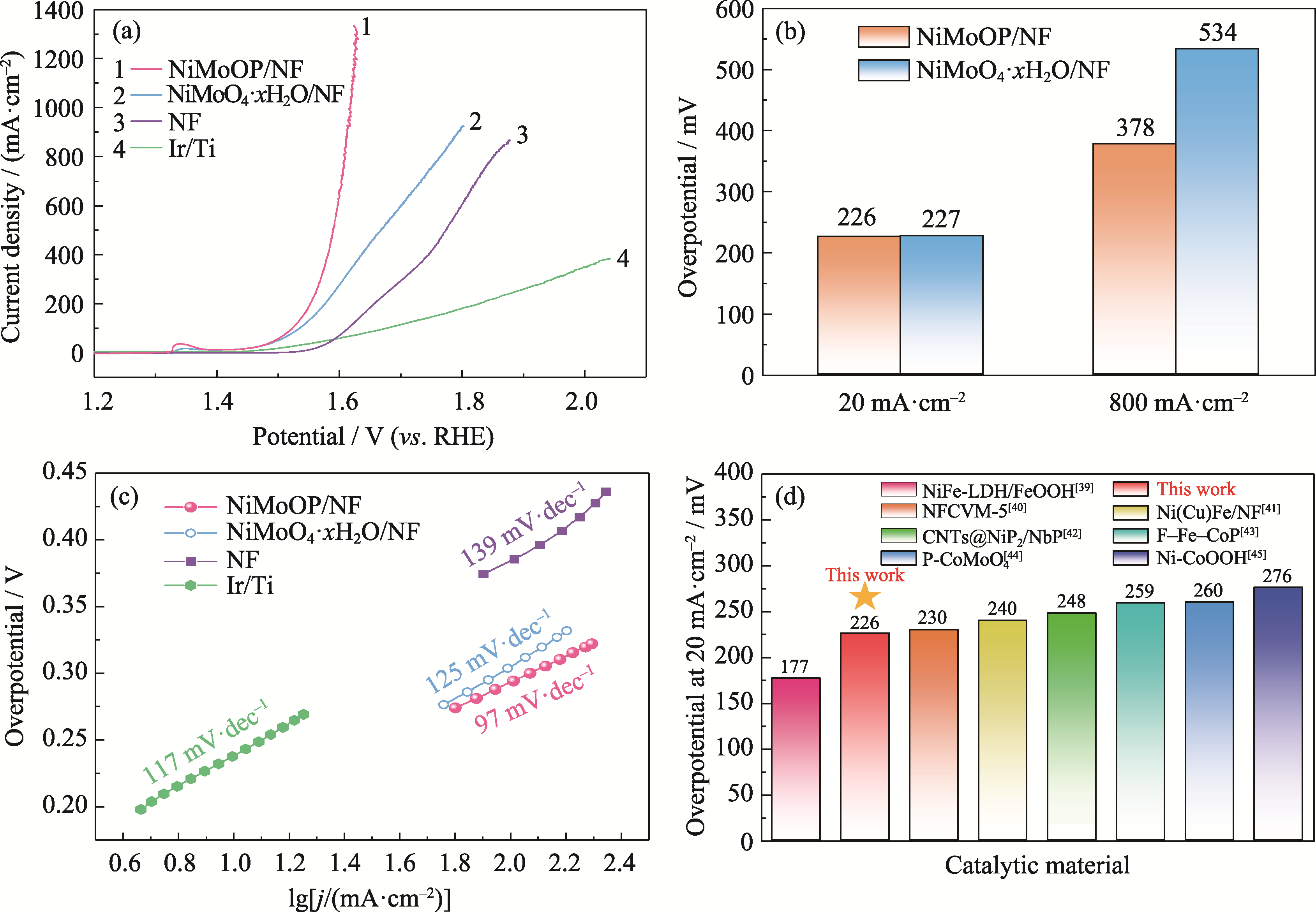
图4 NiMoOP/NF和其他材料的OER活性
Fig. 4 OER performance of NiMoOP/NF and other catalytic materials (a) LSV curves; (b) Overpotentials; (c) Tafel plots; (d) Comparison of overpotentials with different catalysts. Colorful figures are available on website
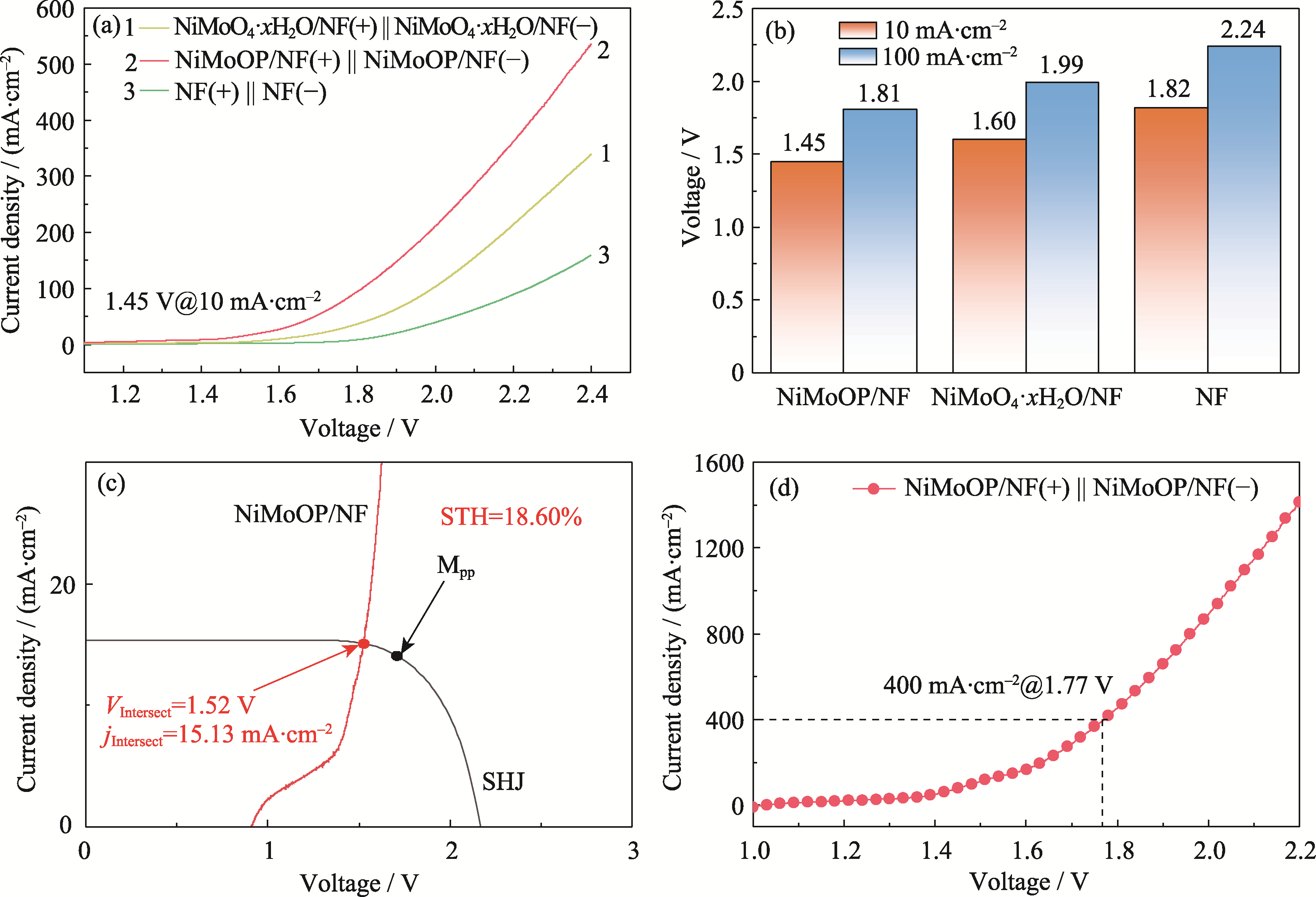
图5 NiMoOP/NF的全水解性能测试及STH计算
Fig. 5 Performance and STH calculation of overall water splitting for NiMoOP/NF (a) LSV curves for overall water splitting; (b) Comparison of cell voltages at 10 and 100 mA·cm-2; (c) J-V curves of crystalline silicon heterojunction solar cells and polarization curves of the overall water splitting system; (d) Overall water splitting performance test under industrial simulation conditions (30% (in mass) KOH, 60 ℃). Colorful figures are available on website
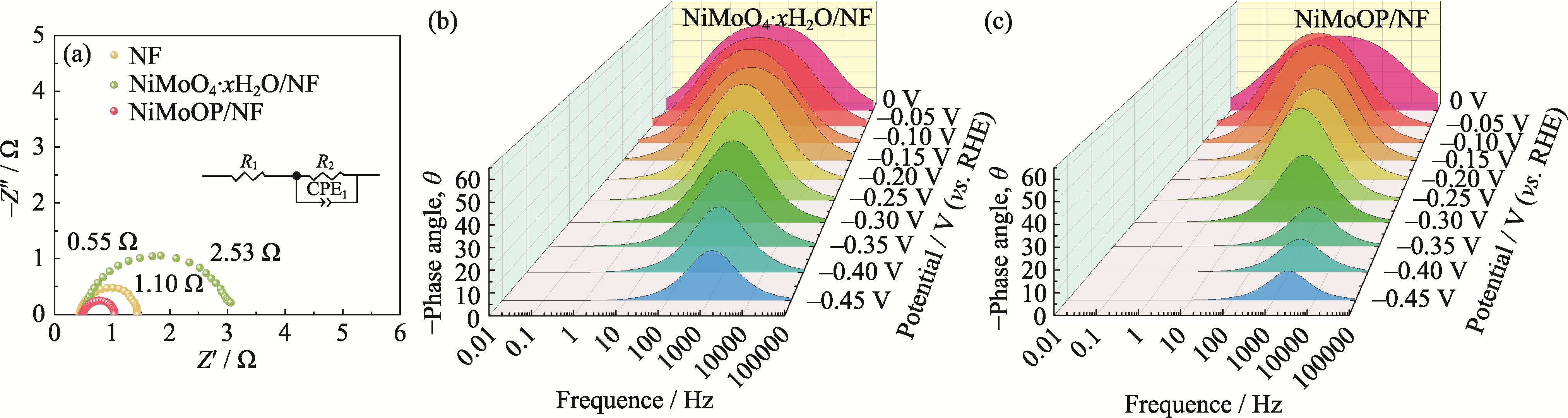
图S3 (a) NiMoO4·xH2O/NF、NiMoOP/NF和NF的奈奎斯特谱图; (b) NiMoO4·xH2O/NF和(c) NiMoOP/NF的伯德谱图
Fig. S3 (a) Nyquist plots of NiMoO4·xH2O/NF, NiMoOP/NF, and NF; (b, c) Bode plots of (b) NiMoO4·xH2O/NF and (c) NiMoOP/NF
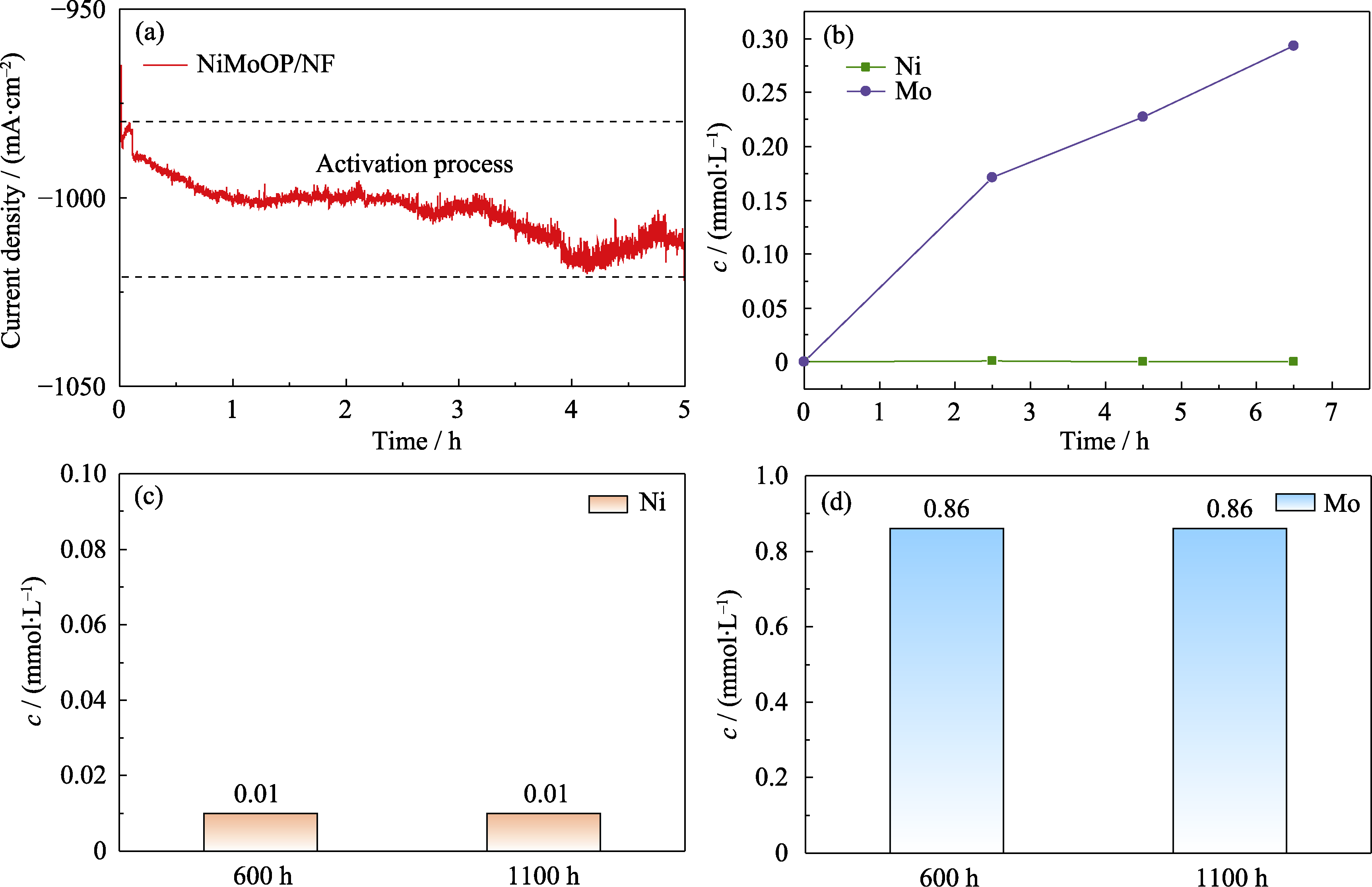
图S5 NiMoOP/NF的电化学活化现象和离子溶出数据
Fig. S5 Electrochemical activation phenomenon and ion dissolution data of NiMoOP/NF (a) I-t curve during initial 5 h of reaction; (b) Ni and Mo elemental concentrations in the electrolyte at initial stage of the reaction; (c) Ni and (d) Mo elemental concentrations in the electrolyte after 600 and 1100 h reaction
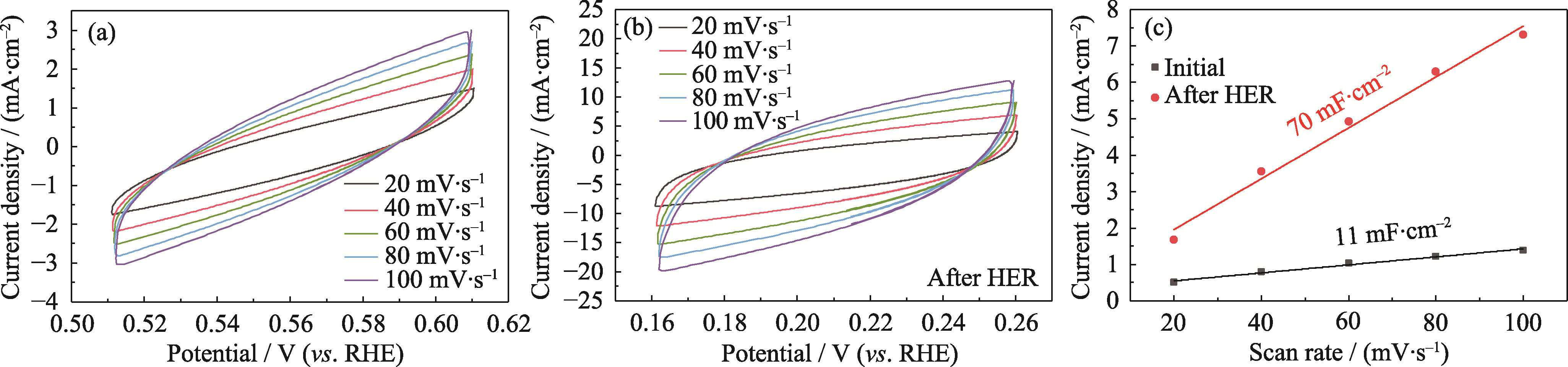
图S7 NiMoOP/NF在10 h HER前后的CV曲线和双电层电容
Fig. S7 CV curves and double-layer capacitance of NiMoOP/NF before and after 10 h of HER (a) Initial NiMoOP/NF; (b) NiMoOP/NF after 10 h of HER; (c) Double-layer capacitance before and after HER

图S9 NiMoOP/NF的法拉第效率测试
Fig. S9 Faraday efficiency testing of NiMoOP/NF (a) Faraday efficiency results; (b) Photo of liquid level before reaction; (c) Photo of liquid level after reaction
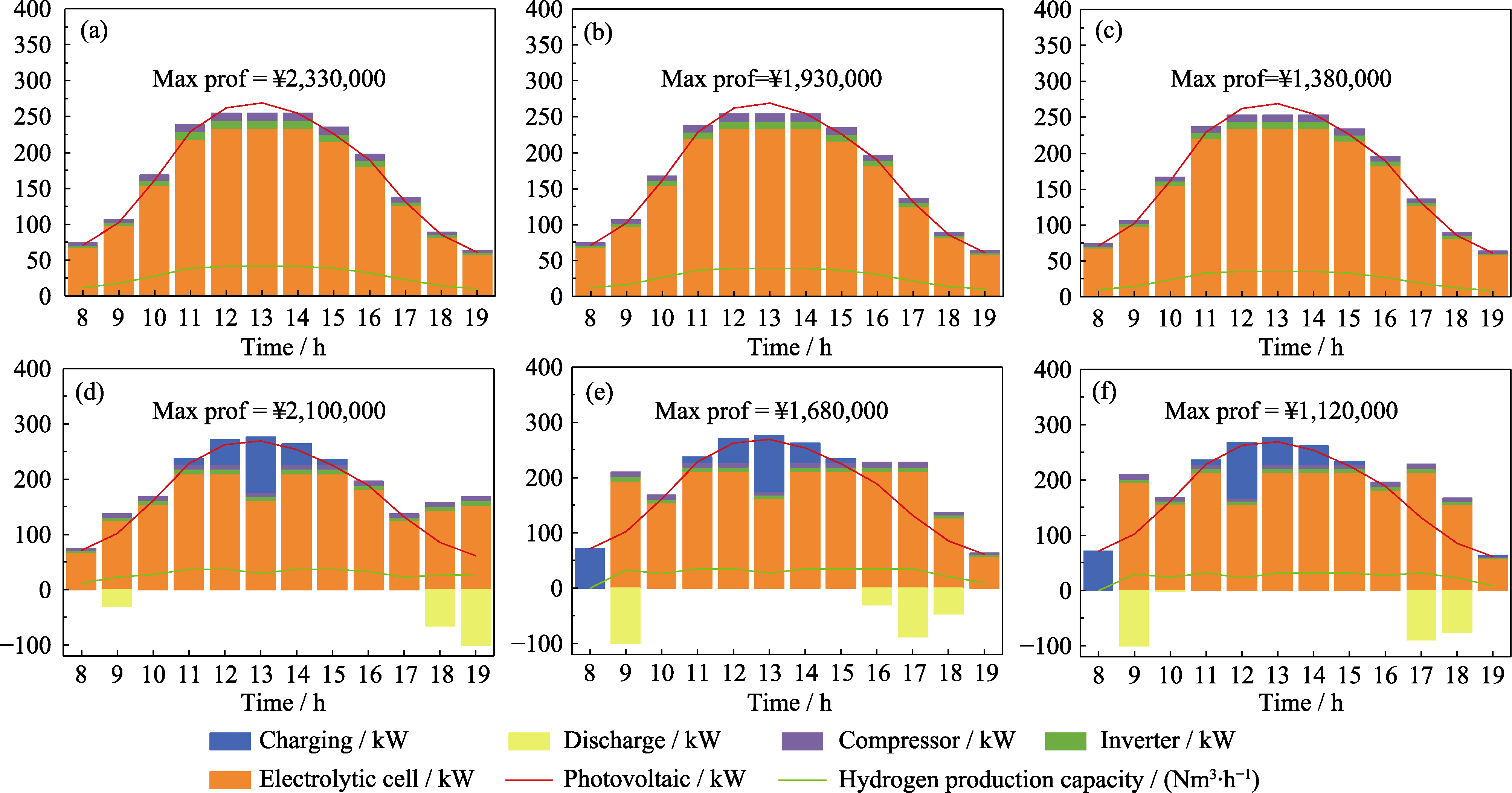
图S10 在(a~c)非储能和(d~f)储能模式, (a, d) 4.19、(b, e) 4.5、(c, f) 5 kWh·Nm-3条件下系统各模块运行情况
Fig. S10 Operation of each system module at (a, d) 4.19, (b, e) 4.5 and (c, f) 5 kWh·Nm-3 under (a-c) non-storage and (d-f) storage modes
| [1] |
DONG B, YU N, WANG Q Y, et al. Double active sites promoting hydrogen evolution activity and stability of CoRuOH/Co2P by rapid hydrolysis. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2024, 35(7): 109221.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ZHU Y, CHEN B, CHENG T, et al. Amorphous Nd-Ni-B/NF rare earth composites: preparation and HER electrocatalytic performance. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 637.
DOI |
| [3] |
SUN W, WANG Y, XIANG K, et al. CoP decorated on Ti3C2Tx MXene nanocomposites as robust electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2024, 40(8): 2308015.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
SUN Q, CHEN Z, YANG Z, et al. Amorphous vanadium oxide loaded by metallic nickel-copper towards high-efficiency electrocatalyzing hydrogen production. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 38(6): 647.
DOI URL |
| [5] | XU S, WU Q, LU B A, et al. Recent advances and future prospects on industrial catalysts for green hydrogen production in alkaline media. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2023, 39(2): 2209001. |
| [6] | 周莹, 饶家豪, 唐春, 等. 光伏电催化硫化氢分解制氢脱硫经济性分析. 天然气工业, 2024, 44(11): 178. |
| [7] |
徐进, 丁显, 宫永立, 等. 电解水制氢厂站经济性分析. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(7): 2374.
DOI |
| [8] |
LAGADEC M F, GRIMAUD A. Water electrolysers with closed and open electrochemical systems. Nature Materials, 2020, 19(11): 1140.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | 夏杨红, 胡致远, 韦巍, 等. 可再生能源电解制氢宽范围运行控制策略. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45(8): 34. |
| [10] |
BLEEKER J, VAN KASTEREN C, VAN OMMEN J R, et al. Gas bubble removal from a zero-gap alkaline electrolyser with a pressure swing and why foam electrodes might not be suitable at high current densities. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 57: 1398.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WANG X, TIAN H, YU X, et al. Advances and insights in amorphous electrocatalyst towards water splitting. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2023, 51: 5.
DOI |
| [12] |
SHI Y, ZHOU S, LIU J, et al. An integrated amorphous cobalt phosphoselenide electrocatalyst with high mass activity boosts alkaline overall water splitting. Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2023, 341: 123326.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
CHANG Y, KONG L, XU D, et al. Mo migration-induced crystalline to amorphous conversion and formation of RuMo/ NiMoO4 heterogeneous nanoarray for hydrazine-assisted water splitting at large current density. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2025, 64(2): e202414234.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LIU S, WANG Y, ZHAO H, et al. Amorphous W-doped iron phosphide with superhydrophilic surface to boost water-splitting under large current density. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 496: 153956.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
RAJA D S, CHUAH X F, LU S Y. In situ grown bimetallic MOF-based composite as highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting with ultrastability at high current densities. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(23): 1801065.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
JIN M, ZHANG X, NIU S, et al. Strategies for designing high- performance hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalysts at large current densities above 1000 mA cm-2. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(8): 11577.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WANG J, HU J, NIU S, et al. Crystalline-amorphous Ni2P4O12/ NiMoOx nanoarrays for alkaline water electrolysis: enhanced catalytic activity via in situ surface reconstruction. Small, 2022, 18(10): 2105972.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
YU L, ZHU Q, SONG S, et al. Non-noble metal-nitride based electrocatalysts for high-performance alkaline seawater electrolysis. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 5106.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
ZHANG Y, LIU J, PAN Y, et al. The evolution of MoS2 properties under oxygen plasma treatment and its application in MoS2 based devices. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30(19): 18185.
DOI |
| [20] | HU H, ZHANG Z, ZHANG Y, et al. An ultra-low Pt metal nitride electrocatalyst for sustainable seawater hydrogen production. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(10): 4584. |
| [21] |
WU S, CHEN D, LI S, et al. Ru cluster incorporated NiMoO(P)4 nanosheet arrays as high-efficient bifunctional catalyst for wind/ solar-to-hydrogen generation systems. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(35): 2304179.
DOI URL |
| [22] | NIU H J, HUANG C, SUN T, et al. Enhancing Ni/Co activity by neighboring Pt atoms in NiCoP/MXene electrocatalyst for alkaline hydrogen evolution. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(20): e202401819. |
| [23] |
ZHANG Z, WANG H, MA M, et al. Integrating NiMoO wafer as a heterogeneous ‘turbo’ for engineering robust Ru-based electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 420: 127686.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
LIANG W, ZHOU M, LIN X, et al. Nickel-doped tungsten oxide promotes stable and efficient hydrogen evolution in seawater. Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2023, 325: 122397.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LIN J, YIN D, HE W, et al. Self-supporting honeycomb coaxial carbon fibers: a new strategy to achieve an efficient hydrogen evolution reaction both in base and acid media. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 488: 151195.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
DASTAFKAN K, SHEN X, HOCKING R K, et al. Monometallic interphasic synergy via nano-hetero-interfacing for hydrogen evolution in alkaline electrolytes. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 547.
DOI |
| [27] |
LI J, TANG C, ZHANG H, et al. Mesoporous molybdenum carbide for greatly enhanced hydrogen evolution at high current density and its mechanism studies. Materials Reports: Energy, 2023, 3(3): 100215.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LI Q, CHEN C, LUO W, et al. In situ active site refreshing of electro-catalytic materials for ultra-durable hydrogen evolution at elevated current density. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(17): 2304099.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
XU Y, ZHAO Y, SUN M, et al. Reconstruction of Fe sacrifice protective layer enables highly effective CoP catalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction at high current density. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 490: 151697.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
YAN S, CHEN X, LI W, et al. Highly active and stable alkaline hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst based on Ir-incorporated partially oxidized Ru aerogel under industrial-level current density. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(7): 2307061.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
JIA H, WANG H, YAN F, et al. Unravelling electrocatalytic concerted diatomic-ensembles over superior hydrogen-evolution array structured by NiMo/Mo2N heteronanojunctions. Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2024, 343: 123362.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
TANG Y, LIU F, LIU W, et al. Multifunctional carbon-armored Ni electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution under high current density in alkaline electrolyte solution. Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2023, 321: 122081.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LI C, WANG Z, LIU M, et al. Ultrafast self-heating synthesis of robust heterogeneous nanocarbides for high current density hydrogen evolution reaction. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 3338.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
CHEN X, ZHAO X, WANG Y, et al. Layered Ni-Co-P electrode synthesized by CV electrodeposition for hydrogen evolution at large currents. ChemCatChem, 2021, 13(16): 3619.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
LI Y, YU X, GAO J, et al. Structural and electronic modulation of (Fe, Ni)2P@Ni2P heterostructure for efficient overall water splitting at high current density. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 470: 144373.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
DONG Y, DENG Z, ZHANG H, et al. A highly active and durable hierarchical electrocatalyst for large-current-density water splitting. Nano Letters, 2023, 23(19): 9087.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
SUN H, YAO B, HAN Y, et al. Multi-interface engineering of self- supported nickel/yttrium oxide electrode enables kinetically accelerated and ultra-stable alkaline hydrogen evolution at industrial-level current density. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(11): 2303563.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
DU W, SHI Y, ZHOU W, et al. Unveiling the in situ dissolution and polymerization of Mo in Ni4Mo alloy for promoting the hydrogen evolution reaction. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(13): 7051.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
WANG Y H, LI L, SHI J, et al. Oxygen defect engineering promotes synergy between adsorbate evolution and single lattice oxygen mechanisms of OER in transition metal-based (oxy)hydroxide. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(32): 2303321.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
KHATUN S, SHIMIZU K, PAL S, et al. Enthralling anodic protection by molybdate on high-entropy alloy-based electrocatalyst for sustainable seawater oxidation. Small, 2024, 20(43): 2402720.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
WANG H, LIU X, LIU G, et al. Copper doping-induced high- valence nickel-iron-based electrocatalyst toward enhanced and durable oxygen evolution reaction. Chem Catalysis, 2023, 3(3): 100552.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
SINGH S, NGUYEN D C, KIM N H, et al. Interface engineering induced electrocatalytic behavior in core-shelled CNTs@NiP2/NbP heterostructure for highly efficient overall water splitting. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 442: 136120.
DOI URL |
| [43] | XU D, LIU S, ZHANG M, et al. Manipulating the dynamic self- reconstruction of CoP electrocatalyst driven by charge transport and ion leaching. Small, 2023, 19(33): 2300201. |
| [44] |
WANG J, HU J, LIANG C, et al. Surface reconstruction of phosphorus-doped cobalt molybdate microarrays in electrochemical water splitting. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446: 137094.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
CHEN M, LIU D, FENG J, et al. In-situ generation of Ni-CoOOH through deep reconstruction for durable alkaline water electrolysis. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 443: 136432.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 岳全鑫, 郭瑞华, 王瑞芬, 安胜利, 张国芳, 关丽丽. 3D核壳结构NiMoO4@CoFe-LDH纳米棒的高效析氧及全解水性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1254-1264. |
| [2] | 张文宇, 郭瑞华, 岳全鑫, 黄雅荣, 张国芳, 关丽丽. 高熵磷化物双功能催化剂的制备及高效电解水性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1265-1274. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||