无机材料学报 ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 299-304.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140421 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20140421
万 勇, 张 泉, 李 杨
收稿日期:2014-08-15
修回日期:2014-11-04
出版日期:2015-03-20
网络出版日期:2015-03-06
基金资助:WAN Yong, ZHANG Quan, LI Yang
Received:2014-08-15
Revised:2014-11-04
Published:2015-03-20
Online:2015-03-06
摘要:
采用溶胶-凝胶技术在铝表面涂覆氧化铝薄膜, 再利用长链脂肪酸对氧化铝薄膜进行疏水改性, 在金属铝表面构筑了具有较强减摩性能的超疏水薄膜。研究了沸水及水合肼溶液处理对氧化铝薄膜表面微纳织构的影响; 探讨了脂肪酸分子结构对薄膜静态和动态润湿性的影响, 利用球盘式微纳米摩擦磨损试验机评价了薄膜的摩擦学性能。结果显示, 水合肼溶液处理后的氧化铝薄膜经硬脂酸改性后不仅表现出超疏水性能, 而且具有较强的减摩性能。
中图分类号:
万 勇, 张 泉, 李 杨. 溶胶-凝胶法制备超疏水性薄膜摩擦学性能的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(3): 299-304.
WAN Yong, ZHANG Quan, LI Yang. Tribological Performance of Sol-Gel Derived Superhydrophobic Film[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 299-304.
| Alumina film | Contact angle /(o) | Sliding angle /(o) |
|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 144 | >20.0 |
| Treated by boiling water | 148 | 4.5 |
| Treated by hydrazine hydrate | 150 | 3.0 |
表 1 硬脂酸改性不同氧化铝薄膜的润湿性
Table 1 Wetability of alumina films modified by stearic acid.
| Alumina film | Contact angle /(o) | Sliding angle /(o) |
|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 144 | >20.0 |
| Treated by boiling water | 148 | 4.5 |
| Treated by hydrazine hydrate | 150 | 3.0 |
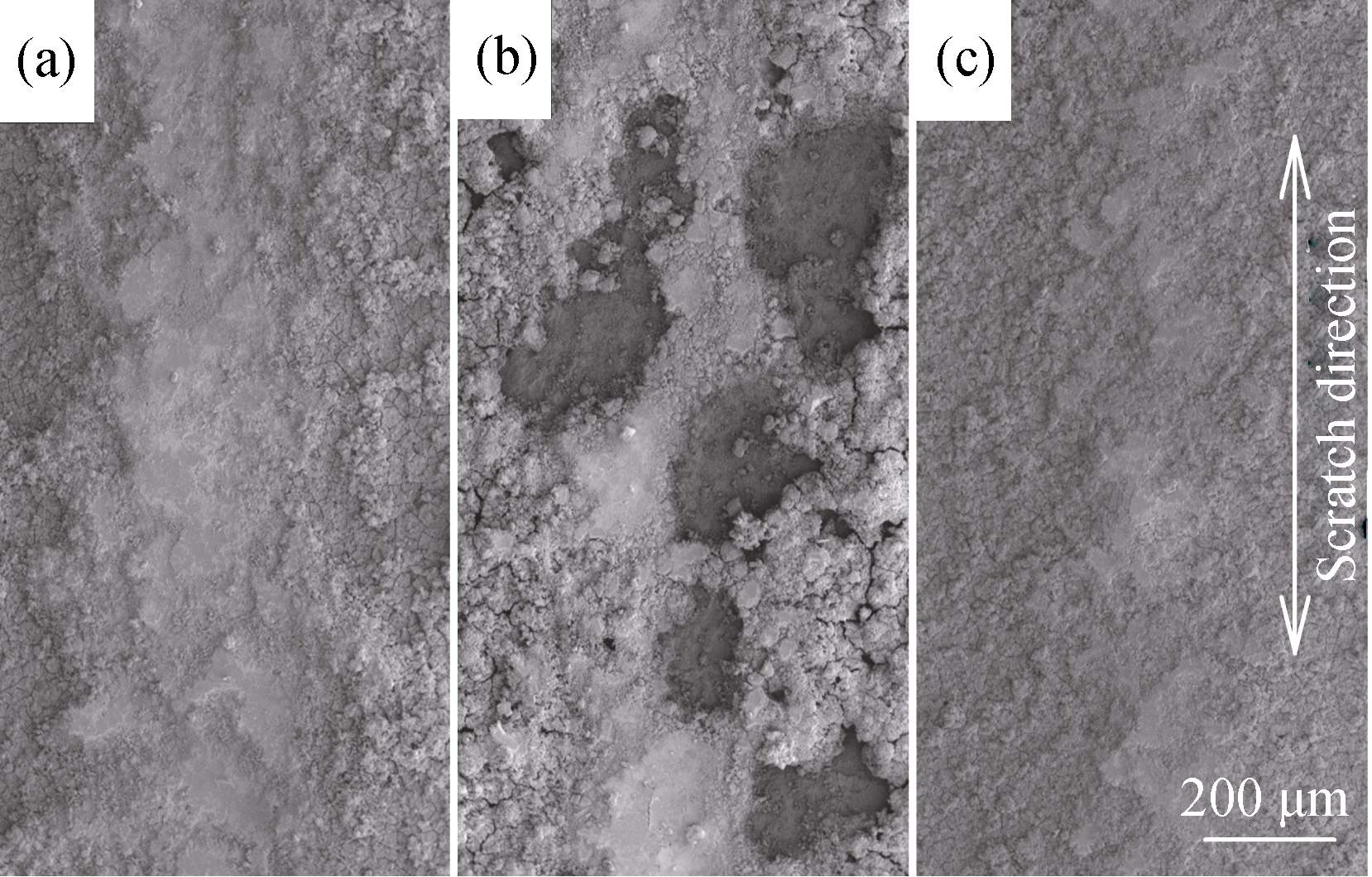
图7 硬脂酸改性氧化铝薄膜的磨痕SEM照片
Fig. 7 SEM images for alumina films modified by stearic acid (a) Untreated alumina film; (b) Alumina film treated by boiling water; (c) Alumina film treated by hydrazine
| Alumina film | Hydrophobic agent | Contact angle /(o) | Sliding angle /(o) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stearic acid | 144 | >20 | |
| Untreated | Lauric acid | 141 | >90 |
| Oleic acid | 134 | >90 | |
| Stearic acid | 150 | 3 | |
| Treated by hydrazine hydrate | Lauric acid | 146 | 5 |
| Oleic acid | 143 | 9 |
表 2 不同样品的表面润湿性
Table 2 Wetability of various alumina films
| Alumina film | Hydrophobic agent | Contact angle /(o) | Sliding angle /(o) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stearic acid | 144 | >20 | |
| Untreated | Lauric acid | 141 | >90 |
| Oleic acid | 134 | >90 | |
| Stearic acid | 150 | 3 | |
| Treated by hydrazine hydrate | Lauric acid | 146 | 5 |
| Oleic acid | 143 | 9 |
| [1] | LIU W, XIA Y, XUE Q.Effect of P-N type extreme pressure and anti wear additive on the friction and wear behaviour of aluminum steel sliding pair.Tribology, 2000, 20(5): 331-335. |
| [2] | HUANG W, YU Y, ZHANG X, et al.Effects of phosphorus additives on tribological performance of 7050 aluminum alloy.Chin. J. Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(3): 652-657. |
| [3] | KONISHI T, PEREZ J M.Properties of polyol esters--lubrication of an aluminum silicon alloy.Tribol. Trans. 1997, 40(3): 500-506. |
| [4] | SARMISTHA D, BISWAS S K.Boundary lubricated tribology of an aluminum-silicon alloy sliding against steel.Tribol. Lett., 2004, 17(3): 623-628. |
| [5] | BHUSHAN B.Handbook of Nanotechnology. Springer: Heidelberg, 2010. |
| [6] | MABOUDIAN R, CARRARO C.Surface chemistry and tribology of MEMS.Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2005, 55(3): 35-54. |
| [7] | WILLIAMS J A, LE H R.Tribology and MEMS.J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys., 2006, 39(12): R201-R214. |
| [8] | LIU L, SONG S Y, ZHANG P Y.Preparation and micro- tribological study on dually mixed self-assembled monolayers.Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2012, 28(2): 427-432. |
| [9] | HOQUE E, DEROSE J A, HOFFMANN P, et al.Alkylperfluorosilane self-assembled monolayers on aluminum: a comparison with alkylphosphonate self-assembled monolayers.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(10): 3956-3962. |
| [10] | KHATRI O P, BAIN C D, BISWAS S K.Effects of chain length and heat treatment on the nanotribology of alkylsilane monolayers self-assembled on a rough aluminum surface.J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109(49): 23405-23414. |
| [11] | BARTHLOTT W, NEINHUIS C.Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces.Planta, 1997, 202(1): 1-8. |
| [12] | CHU Z, SEEGER S.Superamphiphobic surfaces.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43(8): 2784-2798. |
| [13] | LIU X, LIANG Y, ZHOU F, et al.Extreme wettability and tunable adhesion: biomimicking beyond nature?Soft Matter, 2012, 8(7): 2070-2086. |
| [14] | LIU K, JIANG L.Metallic surfaces with special wettability.Nanoscale, 2011, 3(3): 825-838. |
| [15] | GUO Z, LIU W, SU B L.Superhydrophobic surfaces: from natural to biomimetic to functional.J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 353(2): 335-355. |
| [16] | ZHANG Y L, XIA H, KIM E, et al.Recent developments in superhydrophobic surfaces with unique structural and functional properties.Soft Matter, 2012, 8(44): 11217-11231. |
| [17] | DI Z Y, HE J P, ZHOU J H, et al.Fabrication and anticorrosion property of superhydrophobic surfaces with hierarchical structure through an organic-inorganic self-assemble process.J. Inorg. Mater., 2010, 25(7): 765-769. |
| [18] | RUAN M, LI W, WANG B, et al.Preparation and anti-icing behavior of superhydrophobic surfaces on aluminum alloy substrates.Langmuir, 2013, 29(27): 8482-8491. |
| [19] | GHALMI Z, FARZANEH M.Durability of nanostructured coatings based on PTFE nanoparticles deposited on porous aluminum alloy.Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 314: 564-569. |
| [20] | MENINI R, GHALMI Z, FARZANEH M.Highly resistant icephobic coatings on aluminum alloys.Cold Reg. Sci. Technol., 2011, 65(1): 65-69. |
| [21] | ZHANG F, ZHAO L, CHEN H, et al.Corrosion resistance of superhydrophobic layered double hydroxide films on aluminium.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Eng., 2008, 47(13): 2466-2469. |
| [22] | HUBERT T, SCHWARZ J, OERTEL B.Sol-Gel alumina coatings on stainless steel for wear protection.J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techn. 2006, 38(2): 179-184. |
| [23] | ZHELUDKEVICH M L, MIRANDA SALVADO I, FERREIRAG M G S. Sol-Gel coatings for corrosion protection of metals.J. Mater. Chem., 2005, 15(4): 5099-5111. |
| [24] | ZHENG S, LI J.Inorganic-organic Sol-Gel hybrid coatings for corrosion protection of metals.J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol, 2010, 54(2): 174-187. |
| [25] | LIU W, CHEN Y, LI B.Research progress on preparation and tribological investigation of Sol-Gel-derived ceramic-based ultra- thin films.Tribology. 2003, 23(2): 162-167. |
| [26] | FU Q, CAO C B, ZHU H S.Preparation of alumina films from a new Sol-Gel route.Thin Solid Films, 1999, 348(1/2): 99-102. |
| [27] | BOWDEN F P, GREGORY J N, TABOR D.Lubrication of metal surfaces by fatty acids.Nature 1945, 156(3952): 97-101. |
| [28] | SAHOO R R, BISWAS S K.Frictional response of fatty acids on steel.J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2009, 333(2): 707-718. |
| [29] | RUTHS M, LUNDGREN S, DANERLÖV K, et al. Friction of fatty acids in nanometer-sized contacts of different adhesive strength.Langmuir, 2008, 24(4): 1509-1516. |
| [30] | WU Y L, CHEN Z, ZENG X T.Nanoscale morphology for high hydrophobicity of a hard Sol-Gel thin film.Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254(21): 6952-6958. |
| [31] | YAMAGUCHI N, TADANAGA K, MATSUDA A, et al.Formation of anti-reflective alumina films on polymer substrates by the Sol-Gel process with hot water treatment.Surf. Coatings Technol. 2006, 201(6): 3653-3657. |
| [32] | MA W, WU H, HIGAKI Y, et al.A "non-sticky" superhydrophobic surface prepared by self-assembly of fluoroalkyl phosphonic acid on a hierarchically micro/nanostructured alumina gel film.Chem. Commun., 2012, 48: 6824-6826. |
| [33] | LAIBINIS P E, HICKMAN J J, WRIGHTON M S, et al.Orthogonal self-assembled monolayers: alkanethiols on gold and alkane carboxylic acids on alumina.Science, 1989, 245(4920): 845-847. |
| [34] | TAO Y T.Structural comparison of self-assembled monolayers of n-alkanoic acids on the surfaces of silver, copper, and aluminum.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115(10): 4350-4358. |
| [35] | DOWSON D.History of tribology. London: Professional Engineering Publishing, 1998. |
| [36] | JOHNSON K L, KENDALL K, ROBERTS A D.Surface energy and the contact of elastic solids.Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A. 1971, 324(1558): 301-313. |
| [37] | BEAKE B D, LEGGETT G I.Variation of frictional forces in air with the compositions of heterogeneous organic surfaces.Langmuir. 2000, 16(2): 735-739. |
| [38] | CHENG H,HU Y . Influence of chain ordering on frictional properties of self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) in nano-lubrication. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2012, 171-172: 53-65. |
| [1] | 江宗玉, 黄红花, 清江, 王红宁, 姚超, 陈若愚. 铝离子掺杂MIL-101(Cr)的制备及其VOCs吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 747-753. |
| [2] | 孙晶, 李翔, 毛小建, 章健, 王士维. 月桂酸改性剂对氮化铝粉体抗水解性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 826-832. |
| [3] | 熊思宇, 莫尘, 朱肖伟, 朱国斌, 陈德钦, 刘来君, 施晓东, 李纯纯. 超低介电常数LiBxAl1-xSi2O6微波介质陶瓷的低温烧结[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 536-544. |
| [4] | 冯关正, 杨健, 周渡, 陈啟明, 许文涛, 周有福. 水热-碳热合成AlN纳米粉体的机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 104-110. |
| [5] | 武向权, 滕家琛, 季祥旭, 郝禹博, 张忠明, 徐春杰. 织构化多孔Al2O3-SiO2复合陶瓷片-球混合浆料特性及光强分布仿真[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 769-778. |
| [6] | 程博, 安晓航, 李定华, 杨荣杰. ATH/ADP配比对EVA阻燃性能及机理转变的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 509-516. |
| [7] | 沈斌, 张旭, 熊怀, 李海元, 谢兴龙. 溶胶-凝胶SiO2减反膜的制备与光学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 525-530. |
| [8] | 赵雅文, 屈发进, 汪岩屹, 王智文, 陈初升. 基于硅酸铝纤维的柔性氧敏感元件的制备和性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1084-1090. |
| [9] | 戴乐, 刘洋, 高轩, 王书豪, 宋雅婷, 唐明猛, 刘丽莎, 汪尧进. 浓度梯度掺杂实现BiFeO3薄膜自极化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 99-106. |
| [10] | 刘文龙, 赵瑾, 刘娟, 毛小建, 章健, 王士维. 微波干燥自发凝固成型氧化铝湿坯[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 461-468. |
| [11] | 贾玉娜, 曹旭, 焦秀玲, 陈代荣. 无机酸铝体系氧化铝连续纤维的制备技术研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1257-1264. |
| [12] | 王士维. 基于疏水作用的陶瓷浆料自发凝固成型研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 809-820. |
| [13] | 王新刚, 杨青青, 林根连, 高巍, 秦福林, 李荣臻, 康庄, 王小飞, 蒋丹宇, 闫继娜. 国产550级连续氧化铝陶瓷纤维的高温拉伸性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 629-635. |
| [14] | 孙铭, 邵溥真, 孙凯, 黄建华, 张强, 修子扬, 肖海英, 武高辉. RGO/Al复合材料界面性质第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 651-659. |
| [15] | 周港怀, 刘耀, 石原, 刘绍军. 活性氧化铝催化剂载体的光固化浆料制备与成型[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 297-302. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||