无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 96-104.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250077 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20250077
蒋妮玉1( ), 孙浩宸1, 林明梅1, 王定远2, 刘来君1(
), 孙浩宸1, 林明梅1, 王定远2, 刘来君1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-22
修回日期:2025-04-04
出版日期:2026-01-20
网络出版日期:2025-05-09
通讯作者:
刘来君, 教授. E-mail: ljliu2@163.com作者简介:蒋妮玉(2004-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: nyjiang6271@163.com
基金资助:
JIANG Niyu1( ), SUN Haochen1, LIN Mingmei1, WANG Dingyuan2, LIU Laijun1(
), SUN Haochen1, LIN Mingmei1, WANG Dingyuan2, LIU Laijun1( )
)
Received:2025-02-22
Revised:2025-04-04
Published:2026-01-20
Online:2025-05-09
Contact:
LIU Laijun, professor. E-mail: ljliu2@163.comAbout author:JIANG Niyu (2004-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: nyjiang6271@163.com
Supported by:摘要: 电卡效应制冷技术因其高效节能、易小型化及环境友好等优势成为固态制冷领域的研究热点, 然而在低电场下实现大绝热温变(ΔT)和宽工作温区(Tspan)仍面临挑战。本研究通过传统固相反应法制备了不同钛酸铅(PT)含量的(1-x)Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-xPbTiO3(x=0.08, 0.10, 0.12, 0.14)铁电弛豫体陶瓷, 探究了PT含量对材料电卡性能的影响机制。结果表明, 随着PT含量增加, 材料的弛豫体特性逐渐减弱, 介电频率色散程度降低, 铁电行为趋于典型铁电体。其中, 0.88PMN-0.12PT样品在50 kV/cm低电场下表现出优异的电卡性能, ΔT最大值达1.60 K, 且在30~180 ℃宽温区内ΔT均高于0.5 K。压电力显微镜(Piezoresponse force microscopy, PFM)显示该样品具有均匀分布的长程铁电畴结构, 其温度变化源于电场卸载过程中铁电畴从有序态向无序态转变引起的熵变。结合介电、铁电及畴结构分析, 揭示了弛豫铁电体的弥散相变特性与宽温区电卡性能的关联性。本研究为低场驱动、宽温区适用的铅基电卡材料设计提供了理论依据, 并展示了其在固态制冷器件中的潜在应用价值。
中图分类号:
蒋妮玉, 孙浩宸, 林明梅, 王定远, 刘来君. 铌镁酸铅-钛酸铅(PMN-PT)陶瓷的电卡效应[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 96-104.
JIANG Niyu, SUN Haochen, LIN Mingmei, WANG Dingyuan, LIU Laijun. Electrocaloric Effect of Lead Magnesium Niobate-lead Titanate (PMN-PT) Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 96-104.

图3 (1-x)PMN-xPT陶瓷的介电温谱和介电损耗随温度的变化曲线
Fig. 3 Temperature dependence of dielectric spectra and dielectric loss of (1-x)PMN-xPT ceramics (a) x=0.08; (b) x=0.10; (c) x=0.12; (d) x=0.14

图4 10 kHz下(1-x)PMN-xPT陶瓷的Lorentz拟合关系
Fig. 4 Lorentz fitting relationships of (1-x)PMN-xPT ceramics at 10 kHz (a) x=0.08; (b) x=0.10; (c) x=0.12; (d) x=0.14
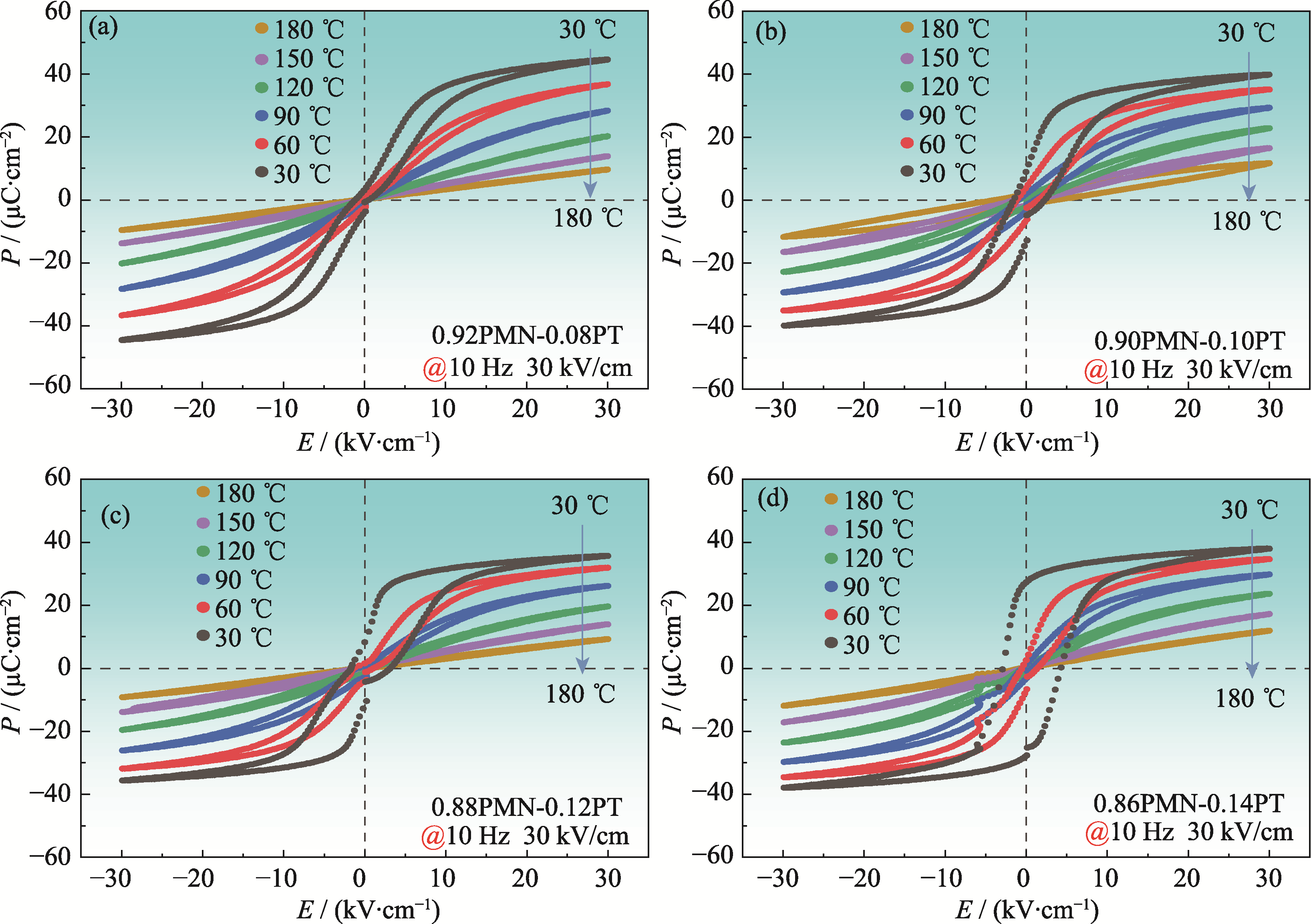
图6 30 kV/cm外加电场下(1-x)PMN-xPT陶瓷在30~180 ℃范围内电滞回线的演变
Fig. 6 Evolution of P-E loops in the range of 30-180 ℃ in an applied electric field of 30 kV/cm for (1-x)PMN-xPT ceramics (a) x=0.08; (b) x=0.10; (c) x=0.12; (d) x=0.14
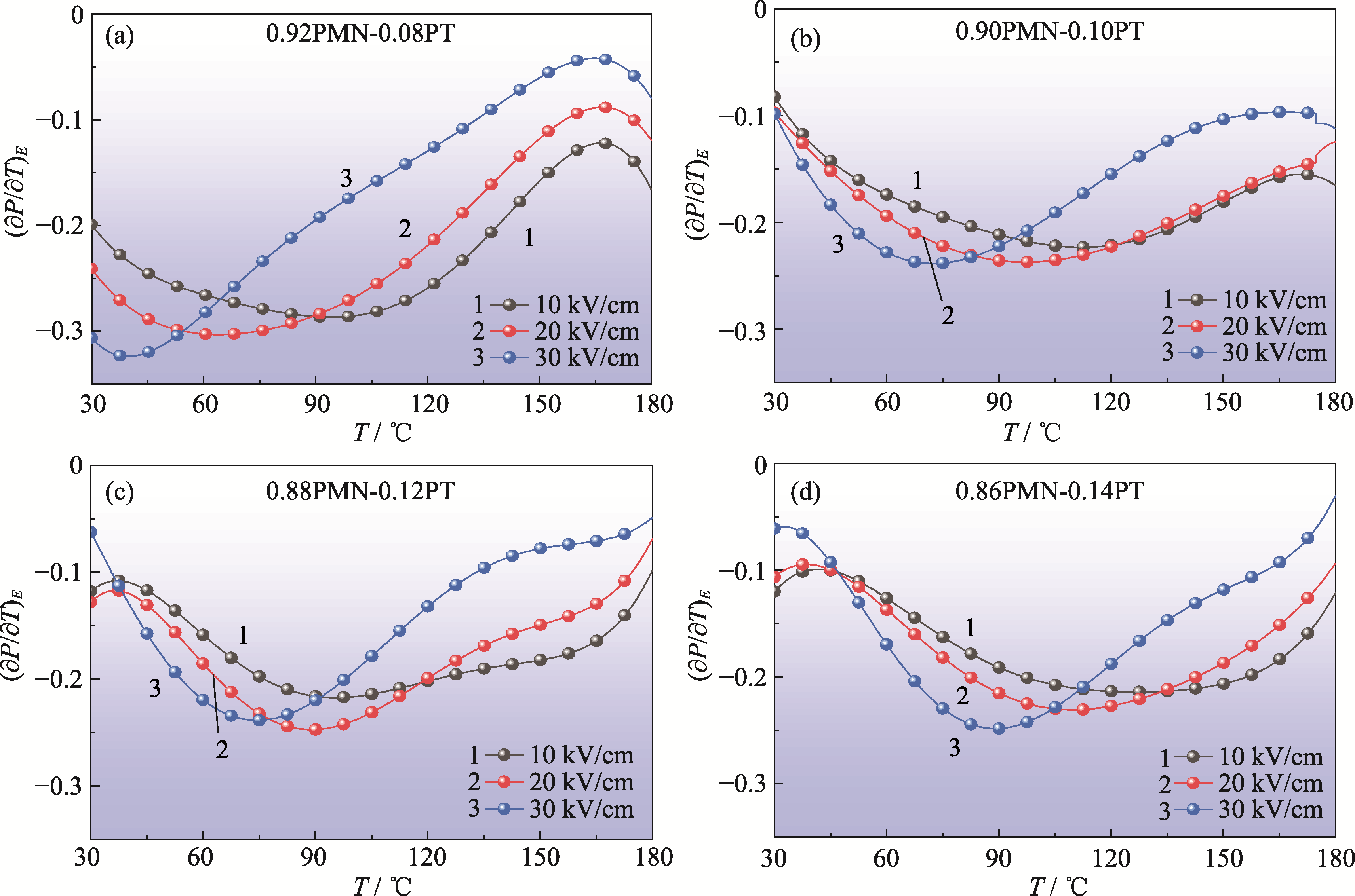
图7 (1-x)PMN-xPT陶瓷在选定的外加电场下热释电系数(∂P/∂T)E与温度的关系
Fig. 7 Temperature dependence of pyroelectric coefficient (∂P/∂T)E in selected electric fields for (1-x)PMN-xPT ceramics (a) x=0.08; (b) x=0.10; (c) x=0.12; (d) x=0.14
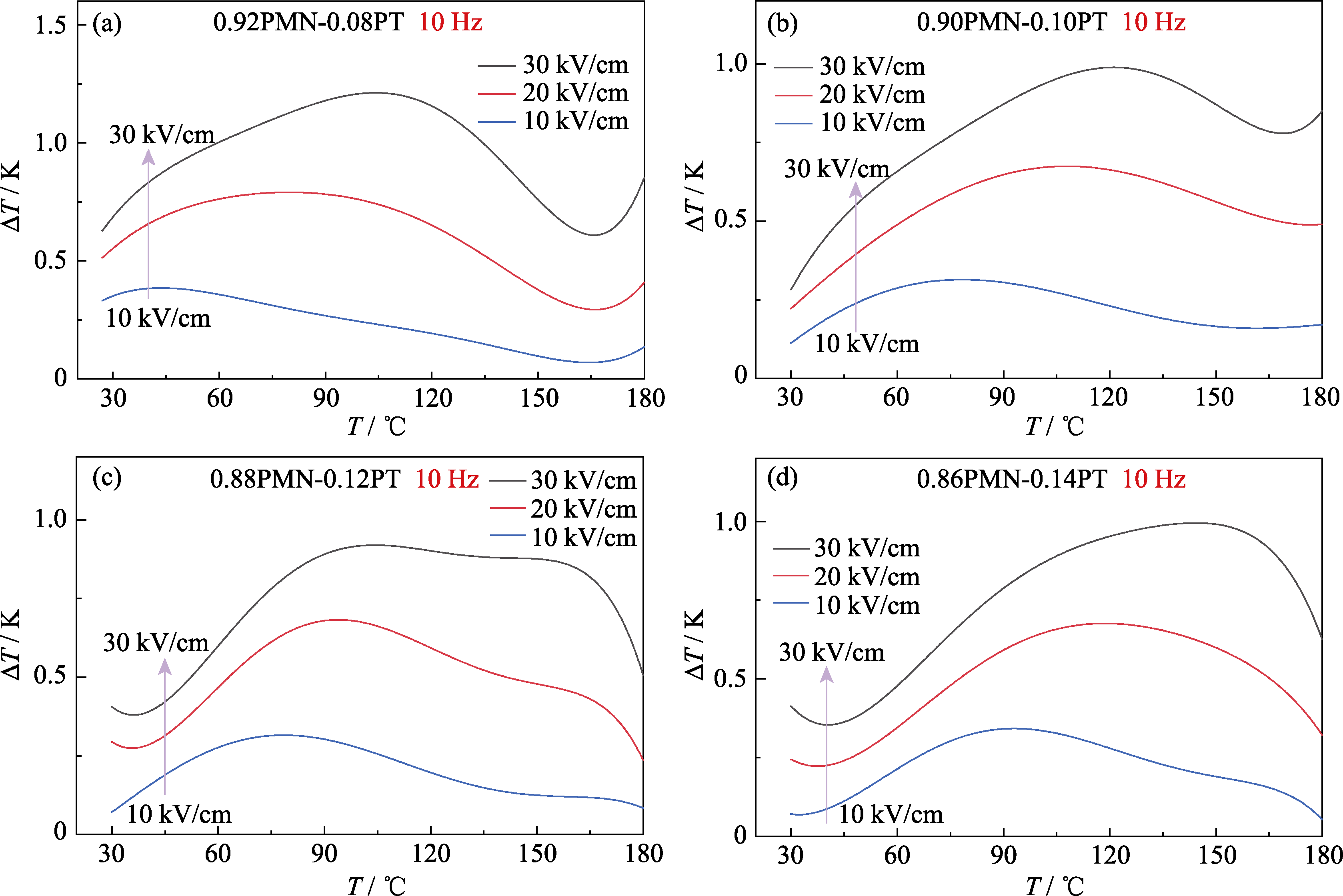
图8 (1-x)PMN-xPT陶瓷在10~30 kV/cm电场下ΔT的温度依赖性
Fig. 8 Temperature dependence of ΔT in the electric field range of 10-30 kV/cm for (1-x)PMN-xPT ceramics (a) x=0.08; (b) x=0.10; (c) x=0.12; (d) x=0.14

图9 50 kV/cm外加电场下0.88PMN-0.12PT陶瓷的电卡性能
Fig. 9 Electrocaloric properties of 0.88PMN-0.12PT ceramics in an applied electric field of 50 kV/cm (a) Evolution of P-E loops from 30 ℃ to 180 ℃; (b) Temperature dependence of pyroelectric coefficient (∂P⁄∂T)E; (c) Temperature dependence of ΔT
| [1] |
MISCHENKO A, ZHANG Q, SCOTT J F, et al. Giant electrocaloric effect in thin-film PbZr0.95Ti0.05O3. Science, 2006, 311(5765): 1270.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LU S G, LI D D, LIN X W, et al. Influence of electric field on the phenomenological coefficient and electrocaloric strength in ferroelectrics. Acta Physica Sinica, 2020, 69(12): 127701.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
GSCHNEIDNER K A, PECHARSKY V K, TSOKOL A O.Recent developments in magnetocaloric materials. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2005, 68(6): 1479.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
SCOTT J F. Applications of modern ferroelectrics. Science, 2007, 315(5814): 954.
PMID |
| [5] |
TANG H, NIU X, YANG Z P, et al. Giant electrocaloric effect enhancement due to the polarization flip and influence of Mn4+ doping on the dielectric, ferroelectric properties in 0.7BiFeO3- 0.3BaTiO3 ceramics. Acta Physica Sinica, 2022, 71(14): 147701.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
MAÑOSA L, PLANES A, ACET M. Advanced materials for solid-state refrigeration. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(16): 4925.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
BARMAN A, KAR-NARAYAN S, MUKHERJEE D. Caloric effects in perovskite oxides. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2019, 6(15): 1900291.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHEN J Y, LEI L P, FANG G. Elastocaloric cooling of shape memory alloys: a review. Materials Today Communications, 2021, 28: 102706.
DOI URL |
| [9] | ZHANG C, CEN F J, XIAO W R, et al. Electrocaloric effect of ferroelectric ceramic and its application. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2022, 50(3): 642. |
| [10] |
HU H L, ZHANG F, LUO S B, et al. Electrocaloric effect in relaxor ferroelectric polymer nanocomposites for solid-state cooling. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(33): 16814.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
MOYA X, KAR-NARAYAN S, MATHUR N D. Caloric materials near ferroic phase transitions. Nature Materials, 2014, 13(5): 439.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
GRÜNEBOHM A, MA Y B, MARATHE M, et al. Origins of the inverse electrocaloric effect. Energy Technology, 2018, 6(8): 1491.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
HU Q Y, TIAN Y, ZHU Q S, et al. Achieve ultrahigh energy storage performance in BaTiO3-Bi(Mg1/2Ti1/2)O3 relaxor ferroelectric ceramics via nano-scale polarization mismatch and reconstruction. Nano Energy, 2020, 67: 104264.
DOI URL |
| [14] | VALASEK J. Piezo-electric and allied phenomena in rochelle salt. Rochelle Salt, 1921, 17(4): 475. |
| [15] |
ZHANG L L, HUANG Y N. Theory of relaxor-ferroelectricity. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 5060.
DOI |
| [16] |
MOYA X, STERN-TAULATS E, CROSSLEY S, et al. Giant electrocaloric strength in single-crystal BaTiO3. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(9): 1360.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHANG Y, ZHANG J, ZHANG N, et al. Hierarchical compositional ordering in lead-based perovskite relaxors. Physical Review B, 2023, 107(5): 054101.
DOI URL |
| [18] | JAFFE B, COOK W R, JAFFE H. Piezoelectric ceramics. New York and London: Academic Press, 1971: ix+317. |
| [19] |
CHOI S W, SHROUT R T R, JANG S J, et al. Dielectric and pyroelectric properties in the Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 system. Ferroelectrics, 1989, 100: 29.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WU H H, COHEN R E. Electric-field-induced phase transition and electrocaloric effect in PMN-PT. Physical Review B, 2017, 96(5): 054116.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
VRABELJ M, URŠIČ H, KUTNJAK Z, et al. Large electrocaloric effect in grain-size-engineered 0.9Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.1PbTiO3. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(1): 75.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
BRADEŠKO A, VRABELJ M, FULANOVIĆ L, et al. Implications of acceptor doping in the polarization and electrocaloric response of 0.9Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.1PbTiO3 relaxor ferroelectric ceramics. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2021, 9(9): 3204.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
SUN E W, CAO W W. Relaxor-based ferroelectric single crystals: growth, domain engineering, characterization and applications. Progress in Materials Science, 2014, 65: 124.
PMID |
| [24] |
HO J C, LIU K S, LIN I N. Study of ferroelectricity in the PMN-PT system near the morphotropic phase boundary. Journal of Materials Science, 1993, 28(16): 4497.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SUH D H, LEE D H, KIM N K. Phase developments and dielectric/ferroelectric responses in the PMN-PT system. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2002, 22(2): 219.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SHVARTSMAN V V, LUPASCU D C. Lead-free relaxor ferroelectrics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(1): 1.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
VIEHLAND D, JANG S J, CROSS L E, et al. Deviation from Curie-Weiss behavior in relaxor ferroelectrics. Physical Review B, 1992, 46(13): 8003.
PMID |
| [28] |
BOKOV A A, YE Z G. Phenomenological description of dielectric permittivity peak in relaxor ferroelectrics. Solid State Communications, 2000, 116(2): 105.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
MACKEVICIUTE R, GRIGALAITIS R, BANYS J, et al. Electrical properties of PMN-33PT thin film at MPB. Ferroelectrics, 2017, 512(1): 1.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
HAN F X, QIN Y L, ZHANG Y C, et al. Domain configuration and domain switching in Dy-doped 0.72PMN-0.28PT piezoceramics with high d33 coefficient. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(16): 23061.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
LIU G, YU W Z, WANG Y, et al. Electrocaloric effect of (Ba1-xSrx)(HfxTi1-x)O3 lead-free ferroelectric ceramics with phase structure regulation. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(22): 34387.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
SMIRNOVA E, SOTNIKOVA G, SOTNIKOV A, et al. Peculiarities of the electrocaloric effect in relaxors. Journal of Materiomics, 2023, 9(1): 223.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LI J J, YIN R W, LI J T, et al. Correlation between multi-factor phase diagrams and complex electrocaloric behaviors in PNZST antiferroelectric ceramic system. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2023, 12(3): 463.
DOI URL |
| [34] | CHENG L Q, YAN Y K, LI X T, et al. Electrocaloric performance of multilayer ceramic chips: effect of geometric structure induced internal stress. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(32): 38508. |
| [35] |
GE P Z, JIAN X D, LIN X G, et al. Composition dependence of giant electrocaloric effect in PbxSr1-xTiO3 ceramics for energy- related applications. Journal of Materiomics, 2019, 5(1): 118.
DOI URL |
| [36] | KRUPSKA-KLIMCZAK M, FATHABAD S M, KAJEWSKI D, et al. Dielectric, piezoelectric, ferroelectric, and electrocaloric properties of Ba, Sr-doped PZT. Ceramics International, 2025, 54(14): 19649. |
| [37] |
MENSUR-ALKOY E, OKATAN M B, AYDIN E, et al. Effect of texture on the electrical and electrocaloric properties of 0.90Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.10PbTiO3 relaxor ceramics. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 128(8): 084102.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
URŠIČ H, PRAH U, ROJAC T, et al. High radiation tolerance of electrocaloric (1-x)Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-xPbTiO3. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(13): 5575.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
SARKAR A, ŠADL M, JAZBEC A, et al. Influence of neutron and gamma irradiation on the electrocaloric properties of Mn-doped 0.9Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.1PbTiO3 ceramics. Journal of Physics: Energy, 2023, 5(4): 045006.
DOI |
| [40] |
CHENG L Q, MA Z H, LU J T, et al. Grain-orientation-engineered PMN-10PT ceramics for electrocaloric applications. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 106(2): 1194.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
LI J H, LIN J X, LI F, et al. Temperature-insensitive large electrocaloric effect near room temperature in La3+-doped lead magnesium niobate-lead titanate ceramics. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(6): 8391.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 董晨雨, 郑维杰, 马一帆, 郑春艳, 温峥. 压电力显微镜表征Pb(Mg,Nb)O3-PbTiO3超薄膜弛豫特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 675-682. |
| [2] | 吴明, 肖娅男, 李华强, 刘泳斌, 高景晖, 钟力生, 娄晓杰. 反铁电材料中负电卡效应的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 376-386. |
| [3] | 喻瑛, 杜红亮, 杨泽田, 靳立, 屈绍波. 无铅块体陶瓷的电卡效应: 现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 633-646. |
| [4] | 韩刘洋, 郭少波, 闫世光, RÉMIENSDenis, 王根水, 董显林. Pb0.3CaxSr0.7-xTiO3陶瓷的室温电卡效应[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 1011-1014. |
| [5] | 刘 颖, 龙西法. 新型铁电晶体铌镥酸铅-钛酸铅的生长与性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(1): 47-51. |
| [6] | 鲁圣国, 唐新桂, 伍尚华, ZHANG Qi-Ming. 铁电材料中的大电卡效应[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(1): 6-12. |
| [7] | 徐 琴, 丁士华, 宋天秀, 彭 勇, 吴小亮. 复合掺杂BCZT陶瓷的介电弛豫行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(4): 441-446. |
| [8] | 黎辉东,冯楚德,向平华. 掺La3+对0.94(Na1/2Bi1/2)TiO3-0.06BaTiO3陶瓷介电行为和压电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(3): 579-585. |
| [9] | 王歆,庄志强,齐雪君. PMN-PT弛豫铁电粉体的溶胶-凝胶法制备及其性质[J]. 无机材料学报, 2002, 17(2): 306-310. |
| [10] | 邸利锋,丁爱丽,何夕云,罗维根. 溶胶-凝胶法中热处理对PMNT薄膜结构的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2002, 17(2): 299-305. |
| [11] | 李东林,王评初,罗豪甦,殷之文. 67 Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-33PbTiO_3单晶90°铁电畴光学研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2000, 15(4): 678-684. |
| [12] | 赵常雷,冯楚德. 铋掺杂铌镁酸铅陶瓷的制备及其有序现象研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2000, 15(1): 103-108. |
| [13] | 李新元,冯楚德,李承恩,庄志诚. 退火处理对PMN弛豫铁电体B位有序性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 1999, 14(4): 699-704. |
| [14] | 李新元,冯楚德,李承恩,鲍军. PMN铁电陶瓷B位有序与介电弛豫特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 1998, 13(6): 823-829. |
| [15] | 岳振星,王晓莉,张良莹,姚熹. 低温烧结Ph(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3基复相陶瓷中的两相共存与介电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 1998, 13(2): 189-194. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||