无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 1212-1220.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250056 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250056
王宏宾1( ), 王乐莹1(
), 王乐莹1( ), 罗凌虹1(
), 罗凌虹1( ), 程亮2, 徐序1
), 程亮2, 徐序1
收稿日期:2025-02-13
修回日期:2025-04-13
出版日期:2025-11-20
网络出版日期:2025-04-24
通讯作者:
王乐莹, 副教授. E-mail: wly8858@163.com;作者简介:王宏宾(1998-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: wanghongbin612@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Hongbin1( ), WANG Leying1(
), WANG Leying1( ), LUO Linghong1(
), LUO Linghong1( ), CHENG Liang2, XU Xu1
), CHENG Liang2, XU Xu1
Received:2025-02-13
Revised:2025-04-13
Published:2025-11-20
Online:2025-04-24
Contact:
WANG Leying, associate professor. E-mail: wly8858@163.com;About author:WANG Hongbin (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: wanghongbin612@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
界面工程调控是开发具备优异CO2催化活性的固体氧化物电解池燃料极材料的有效策略。本研究采用静电纺丝技术直接制备La0.3Sr0.6Ti1-xNixO3-δ/Ce0.9Gd0.1O2-δ(LSTNx/GDC)复合纤维, 构建由LSTNx电子通道骨架、GDC离子通道嵌入以及原位Ni出溶纳米颗粒修饰构成的纤维基燃料极, 研究不同B位镍掺杂量对纤维基燃料极形貌结构以及CO2催化活性的影响。扫描结果显示在x=0.15、0.20镍掺杂量的作用下, 成功制得直径均匀(100~150 nm)、无明显颗粒团聚及断裂缺口的LSTNx/GDC复合纤维, 所制备的燃料极在还原气氛工况下可原位析出更多的Ni金属纳米颗粒(20~30 nm)。通过弛豫时间分布分析证实, B位镍金属纳米颗粒原位出溶能提供较多的活性位点, 并与复合纤维、浸渍物构成丰富的异质界面, 加快界面电荷转移, 显著增强电极对CO2的吸附催化能力。掺杂量x=0.20的电解池在1.5 V、850 ℃、CO2 : H2=5 : 5(体积比)条件下, 电解电流密度达到0.799 A·cm-2, 极化阻抗仅为0.171 Ω·cm2, 其长期稳定性测试显示该电解池在1.3 V、850 ℃、CO2 : H2=5 : 5(体积比)条件下70 h内可维持电流无明显波动。
中图分类号:
王宏宾, 王乐莹, 罗凌虹, 程亮, 徐序. 固体氧化物电解池La0.3Sr0.6Ti1-xNixO3-δ基纤维燃料极电解CO2性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1212-1220.
WANG Hongbin, WANG Leying, LUO Linghong, CHENG Liang, XU Xu. Electrolytic CO2 Performance of La0.3Sr0.6Ti1-xNixO3-δ-based Fiber Fuel Electrode for Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1212-1220.
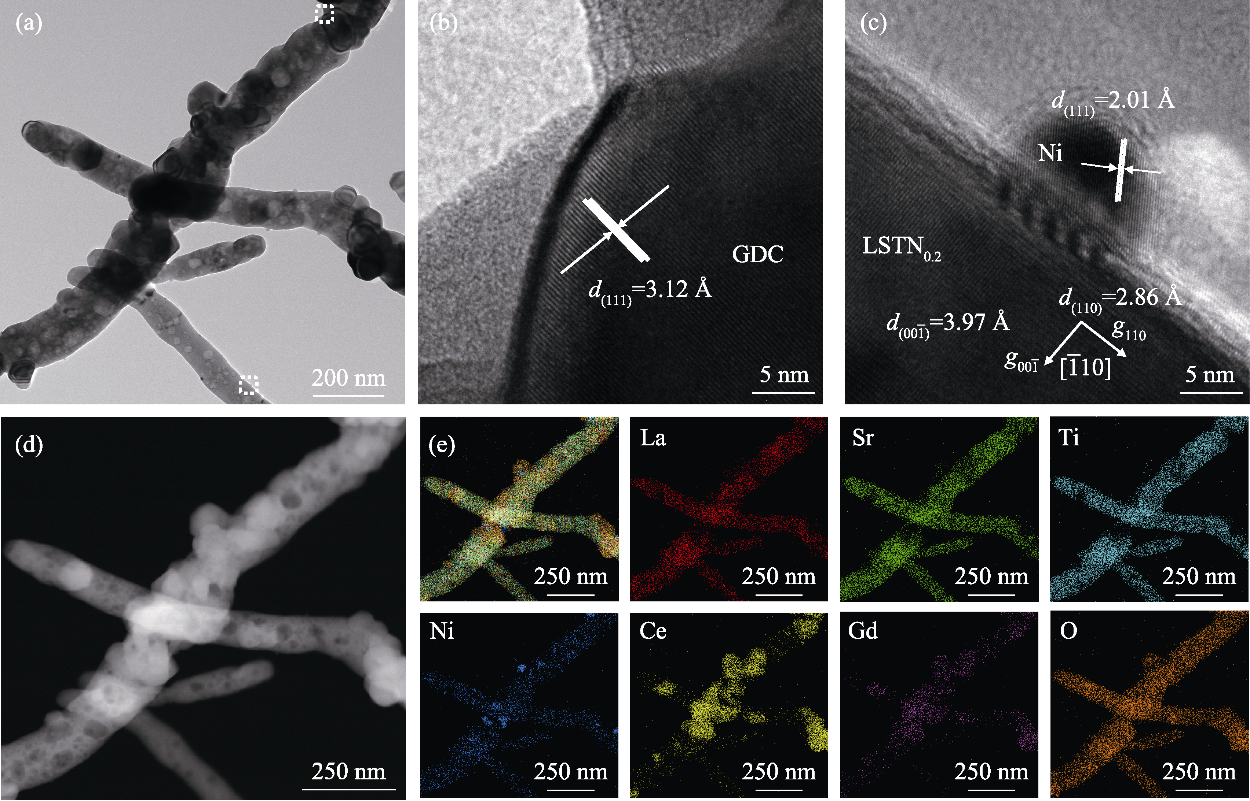
图2 LSTN0.20/GDC复合纤维经800 ℃还原后的TEM照片及EDS元素分布图
Fig. 2 TEM images and EDS elemental mappings of LSTN0.20/GDC composite fiber after reduction at 800 ℃ (a) TEM image; (b, c) HRTEM images; (d) HAADF image; (e) EDS mappings
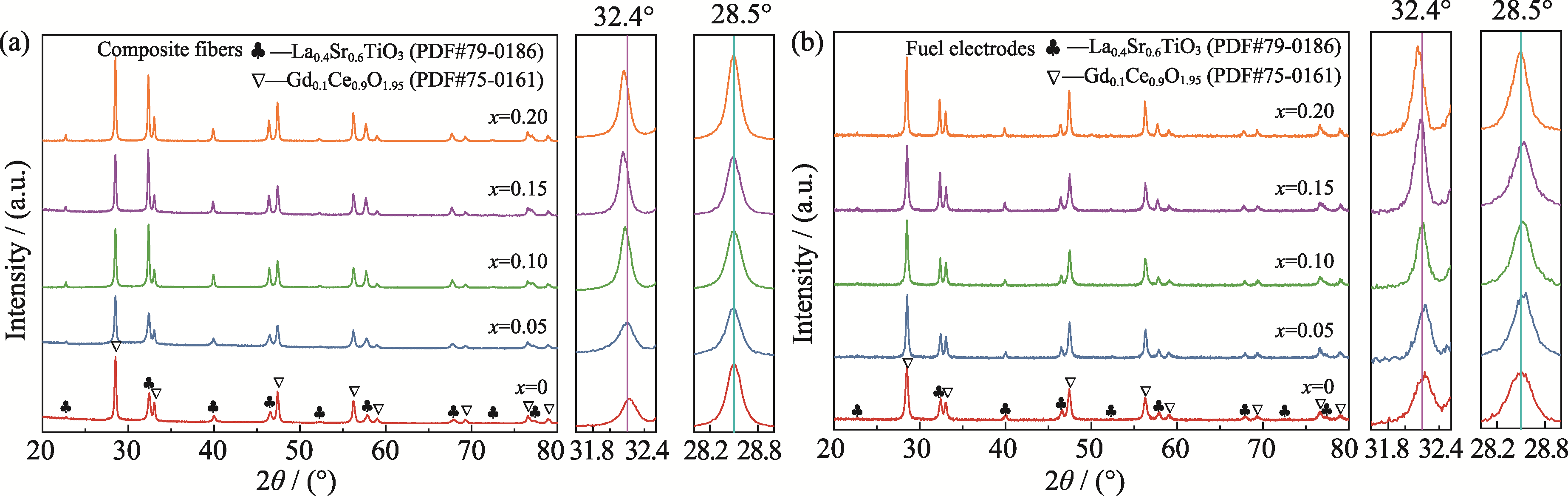
图3 LSTNx/GDC(x=0、0.05、0.10、0.15、0.20)复合纤维(a)和燃料极(测试前)(b)的XRD图谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of (a) LSTNx/GDC (x=0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20) composite fibers and (b) fuel electrodes before testing
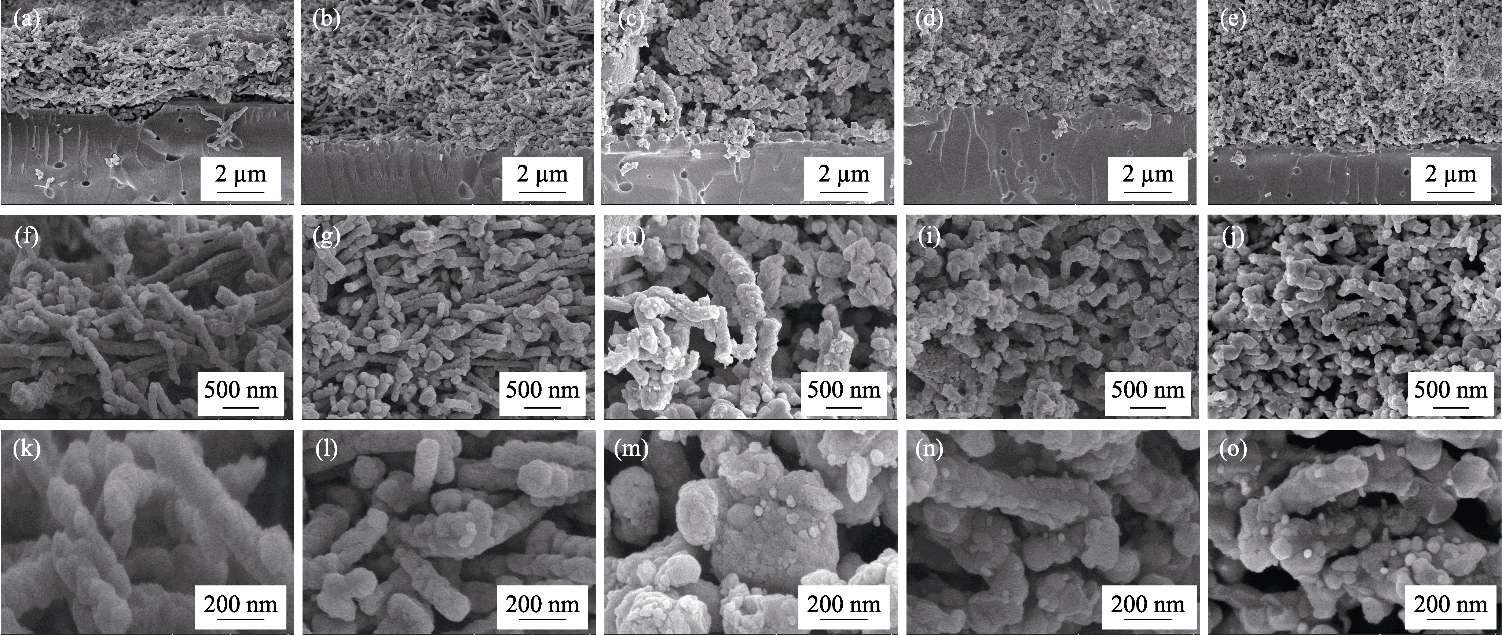

图4 CNO@LSTNx/GDC(x=0、0.05、0.10、0.15、0.20)燃料极测试后的SEM照片
Fig. 4 SEM images of CNO@LSTNx/GDC (x=0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20) fuel electrodes after testing (a, f, k) x=0; (b, g, l) x=0.05; (c, h, m) x=0.10; (d, i, n) x=0.15; (e, j, o) x=0.20
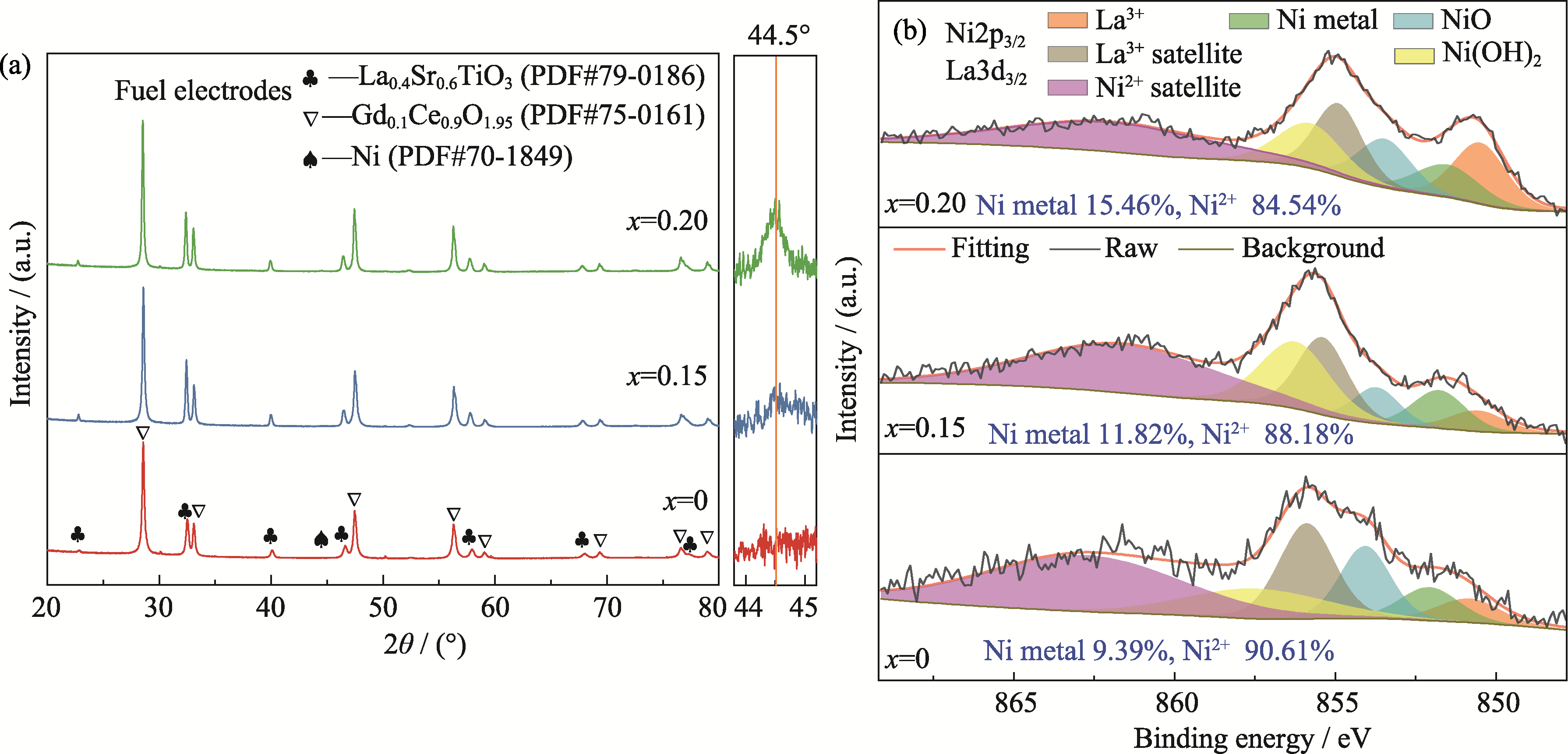
图5 CNO@LSTNx/GDC(x=0、0.15、0.20)燃料极测试后的(a)XRD图谱和(b)XPS谱图
Fig. 5 (a) XRD patterns and (b) XPS spectra of CNO@LSTNx/GDC (x=0, 0.15, 0.20) based fuel electrode after testing Colorful figures are available on website
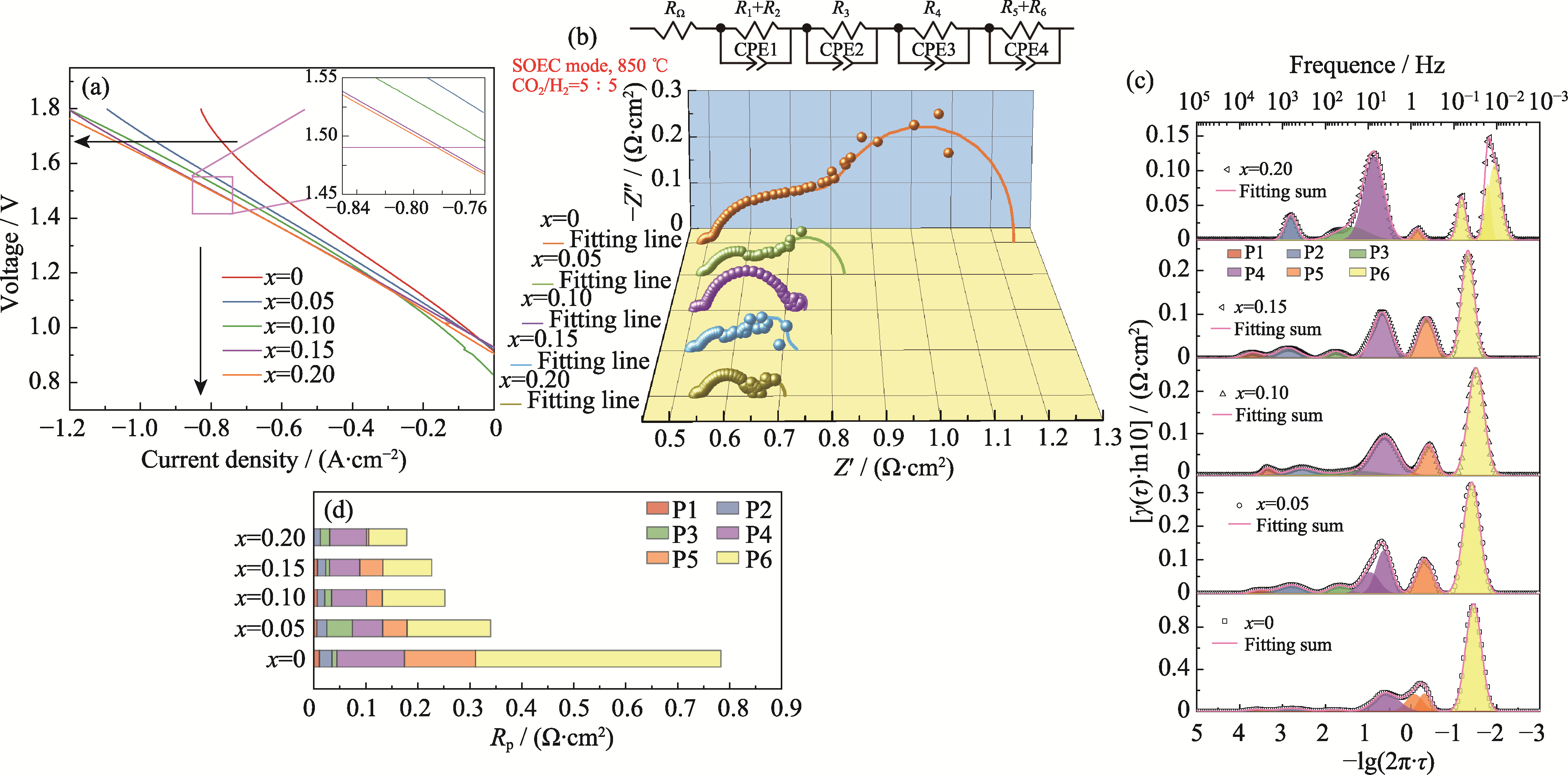
图6 电解池在850 ℃、CO2 : H2=5 : 5(体积比)条件下的电解性能
Fig. 6 Electrolytic performance of single cells at 850 ℃ under CO2 : H2 at 5 : 5 (in volume) (a) I-V curves; (b) EIS spectra, fitting lines and equivalent circuit under 1.5 V; (c) DRT fitting spectra; (d) Histograms of polarization resistance for each peak in (c). Colorful figures are available on website
| Sample | HF(P1+P2) | IF(P3+P4) | LF(P5+P6) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x=0 | 0.035 | 0.139 | 0.609 | 0.783 |
| x=0.05 | 0.025 | 0.107 | 0.208 | 0.340 |
| x=0.10 | 0.021 | 0.080 | 0.151 | 0.252 |
| x=0.15 | 0.023 | 0.066 | 0.138 | 0.227 |
| x=0.20 | 0.013 | 0.089 | 0.077 | 0.179 |
表1 电解池在1.5 V、850 ℃、CO2 : H2=5 : 5(体积比)下DRT分峰的Rp/(Ω·cm2)
Table 1 Rp/(Ω·cm2) associated with each DRT peak for single cells at 1.5 V, 850 ℃ and CO2 : H2=5 : 5 (in volume)
| Sample | HF(P1+P2) | IF(P3+P4) | LF(P5+P6) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x=0 | 0.035 | 0.139 | 0.609 | 0.783 |
| x=0.05 | 0.025 | 0.107 | 0.208 | 0.340 |
| x=0.10 | 0.021 | 0.080 | 0.151 | 0.252 |
| x=0.15 | 0.023 | 0.066 | 0.138 | 0.227 |
| x=0.20 | 0.013 | 0.089 | 0.077 | 0.179 |
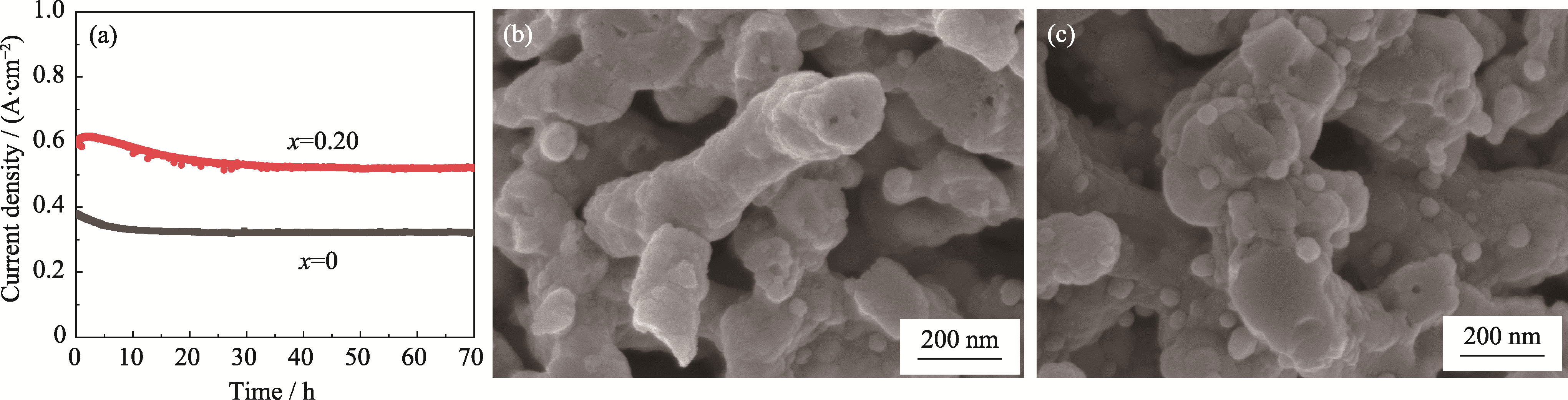

图7 CNO@LSTNx/GDC(x=0、0.20)电解池在1.3 V、850 ℃、CO2 : H2=5 : 5(体积比)条件下的长期稳定性
Fig. 7 Long-term stability of CNO@LSTNx/GDC (x=0, 0.20) single cells at 1.3 V, 850 ℃ under CO2 : H2 at 5 : 5 (in volume) (a) Long-term stability testing; (b, c) Cross-sectional SEM images of fuel electrodes with x at (b) 0 and (c) 0.2 after long-term stability testing
| [1] |
QIAO J L, LIU Y Y, HONG F, et al. A review of catalysts for the electroreduction of carbon dioxide to produce low-carbon fuels. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(2): 631.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
XU R J, LIU S, YANG M T, et al. Advancements and prospects of perovskite-based fuel electrodes in solid oxide cells for CO2 electrolysis to CO. Chemical Science, 2024, 15(29): 11166.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
EBBESEN S D, MOGENSEN M. Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in solid oxide electrolysis cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 193(1): 349.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DU Y Q, LING H, ZHAO L Y, et al. The development of solid oxide electrolysis cells: critical materials, technologies and prospects. Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 607: 234608.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
KEANE M, FAN H, HAN M F, et al. Role of initial microstructure on nickel-YSZ cathode degradation in solid oxide electrolysis cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(33): 18718.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
PECHO O, MAI A, MUNCH B, et al. 3D microstructure effects in Ni-YSZ anodes: influence of TPB lengths on the electrochemical performance. Materials, 2015, 8(10): 7129.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
HAUNCH A, KUNGAS R, BLENNOW P, et al. Recent advances in solid oxide cell technology for electrolysis. Science, 2020, 370(6513): eaba6118.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
FU C J, MA Q, GAO L M, et al. Recent advances in perovskite oxides electrocatalysts: ordered perovskites, cations segregation and exsolution. ChemCatChem, 2023, 15(11): e202300389.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LEI Y R, WANG Z, BAO A, et al. Recent advances on electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to resources: target products, reaction pathways and typical catalysts. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 453: 139663.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
MA Q L, TIETZ F. Comparison of Y and La-substituted SrTiO3 as the anode materials for SOFCs. Solid State Ionics, 2012, 225: 108.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 卢恺振, 王乐莹, 罗凌虹, 等. 可逆固体氧化物电池SrTiO3基燃料极材料的研究进展. 陶瓷学报, 2023, 44(6): 1066. |
| [12] |
SUN X F, WANG S R, WANG Z R, et al. Anode performance of LST-xCeO2 for solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 183(1): 114.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MOGENSEN M, LINDEGAARD T, HANSEN U R, et al. Physical properties of mixed conductor solid oxide fuel cell anodes of doped CeO2. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1994, 141(8): 2122.
DOI |
| [14] |
XU J, ZHOU X L, CHENG J H, et al. Electrochemical performance of highly active ceramic symmetrical electrode La0.3Sr0.7Ti0.3Fe0.7O3-δ- CeO2 for reversible solid oxide cells. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 257: 64.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHANG X M, SONG Y F, GUAN F, et al. Enhancing electrocatalytic CO2 reduction in solid oxide electrolysis cell with Ce0.9Mn0.1O2-δ nanoparticles-modified LSCM-GDC cathode. Journal of Catalysis, 2018, 359: 8.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
PAN J L, MA G J, SONG L M, et al. Non-precious high stability/ catalytic activity co-based perovskite as SOFC anode: in-situ preparation by fuel reducing method metals. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 911.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LV H F, LIN L, ZHANG X M, et al. In situ investigation of reversible exsolution/dissolution of CoFe alloy nanoparticles in a co-doped Sr2Fe1.5Mo0.5O6-δ cathode for CO2 electrolysis. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(6): 1906193.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
KIM Y H, JEONG H, WON B, et al. Exsolution modeling and control to improve the catalytic activity of nanostructured electrodes. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(16): 2208984.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
XU M, CAO R, QIN H, et al. Exsolved materials for CO2 reduction in high-temperature electrolysis cells. Materials Reports: Energy, 2023, 3(2): 100198.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
NECHACHE A, HODY S. Alternative and innovative solid oxide electrolysis cell materials: a short review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 149: 111322.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
GAN L Z, YE L T, TAO S W, et al. Titanate cathodes with enhanced electrical properties achieved via growing surface Ni particles toward efficient carbon dioxide electrolysis. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 18(4): 3137.
DOI URL |
| [22] | YANG X X, SUN W, MA M J, et al. Achieving highly efficient carbon dioxide electrolysis by in situ construction of the heterostructure. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(17): 20060. |
| [23] |
HE S, ZOU Y F, CHEN K F, et al. A critical review of the nano- structured electrodes of solid oxide cells. Chemical Communications, 2022, 58(76): 10619.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 陈静, 冯宇, 赵祯祥, 等. 静电纺丝技术在固体氧化物燃料电池中的应用. 硅酸盐学报, 2021, 49(9): 1861. |
| [25] |
张志鹏, 蒋耀, 周星宇, 等. 静电纺丝技术在固体氧化物燃料电池电极材料的应用. 功能材料, 2023, 54(9): 9038.
DOI |
| [26] | ZHANG X X, ZHENG Y P, DING Z F, et al. Nanoscale intertwined biphase nanofiber as active and durable air electrode for solid oxide electrochemical cells. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2023, 11(23): 8592. |
| [27] |
XU C M, ZHANG L H, SUN W, et al. Building efficient and durable 3D nanotubes electrode for solid oxide electrolytic cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 556: 232479.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
HU Q J, FAN L Q, WANG Y W, et al. Nanofiber-based LaxSr1-xTiO3-GdyCe1-yO2-δ composite anode for solid oxide fuel cells. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(15): 12145.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ZHANG D, ZHOU J, LUO Y, et al. Robust cobalt-free perovskite type electrospun nanofiber cathode for efficient electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction reaction. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 587: 233705.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
CIUCCI F, CHEN C. Analysis of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy data using the distribution of relaxation times: a bayesian and hierarchical bayesian approach. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 167: 439.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
EFFAT M B, CIUCCI F. Bayesian and hierarchical bayesian based regularization for deconvolving the distribution of relaxation times from electrochemical impedance spectroscopy data. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 247: 1117.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
CHOI Y, CHO H J, KIM J, et al. Nanofiber composites as highly active and robust anodes for direct-hydrocarbon solid oxide fuel cells. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(9): 14517.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
ZHOU Z L, CUI J J, LIU Z R, et al. Exsolved medium-entropy alloy fecocuni in titanate fibers enables solid oxide cells with superb electrochemical performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2025, 13: 7563.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 卢恺振, 王乐莹, 罗凌虹, 等. 可逆固体氧化物电池La0.2Sr0.8TiO3-δ基纤维燃料极的浸渍改性. 硅酸盐学报, 2024, 52(5): 1676. |
| [35] |
CHAO Y, KE W X, ZHOU W Y, et al. Constructing LaNiO3/NiO heterostructure via selective dissolution of A-site cations from La1-xSrxNiO3 for promoting oxygen evolution reaction. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 941: 168908.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
WANG T P, SUN N, WANG R Z, et al. In-situ dual-exsolved nanometal anchoring on heterogeneous composite nanofiber using as SOEC cathode for direct and highly efficient CO2 electrolysis. Journal of Power Sources, 2025, 626: 235821.
DOI URL |
| [37] | YANG CC, TIAN Y F, PU J, et al. Anion fluorine-doped La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Ni0.2O3-δ perovskite cathodes with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for solid oxide electrolysis cell direct CO2 electrolysis. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2022, 10(2): 1047. |
| [38] |
JIANG Y, CHEN F L, XIA C R. A review on cathode processes and materials for electro-reduction of carbon dioxide in solid oxide electrolysis cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 493: 229713.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
WILLIAMS N J, OSBORNE C, SEYMOUR I D, et al. Application of finite Gaussian process distribution of relaxation times on SOFC electrodes. Electrochemistry Communications, 2023, 149: 107458.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
LU C Y, XU C M, SUN W, et al. Enhancing catalytic activity of CO2 electrolysis by building efficient and durable heterostructure for solid oxide electrolysis cell cathode. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 574: 233134.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 李跃军, 曹铁平, 孙大伟. S型异质结Bi4O5Br2/CeO2的制备及其光催化CO2还原性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 963-970. |
| [2] | 张晓山, 王兵, 吴楠, 韩成, 吴纯治, 王应德. 高温隔热用微纳陶瓷纤维研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 245-256. |
| [3] | 王玥, 崔常松, 王士维, 占忠亮. LaxSr2-xFe1.5Ni0.1Mo0.4O6-δ对称电池电解CO2研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1323-1329. |
| [4] | 王 雪, 张文强, 于 波, 陈 靖. 基于DRT和ADIS的SOFC/SOEC电堆电化学阻抗谱研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(12): 1279-1288. |
| [5] | 杨 琪, 胡文彬. 无定形SnO2-C复合纤维及其电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(8): 861-866. |
| [6] | 汤营茂, 缪清清, 肖荔人, 钱庆荣, 陈庆华. 静电纺丝制备磁性碳纳米复合纤维及其表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(8): 827-834. |
| [7] | 李跃军, 曹铁平, 邵长路, 王长华. γ-Bi2O3/TiO2复合纤维的制备及光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(7): 687-692. |
| [8] | 于 波, 张文强, 梁明德, 张 平, 徐景明. PMMA造孔剂对固体氧化物电解池制氢性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(8): 807-812. |
| [9] | 孔江榕, 周 涛, 刘 鹏, 张 勇, 徐景明. La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ基固体氧化物电解池复合阳极的制备及性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(10): 1049-1052. |
| [10] | 孙良奎,程海峰,楚增勇,周永江,孙国亮. C/SiO2同轴复合纤维的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(2): 310-314. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||