无机材料学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (12): 1420-1426.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230167 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20230167
所属专题: 【信息功能】介电、铁电、压电材料(202506); 【信息功能】纪念殷之文先生诞辰105周年虚拟学术专辑
康文烁1,2( ), 郭晓杰1,2, 邹凯1,2, 赵祥永3, 周志勇1, 梁瑞虹1(
), 郭晓杰1,2, 邹凯1,2, 赵祥永3, 周志勇1, 梁瑞虹1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-06
修回日期:2023-05-10
出版日期:2023-09-12
网络出版日期:2023-09-12
通讯作者:
梁瑞虹, 研究员. E-mail: liangruihong@mail.sic.ac.cn作者简介:康文烁(1994-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: kangwenshuo20@mails.ucas.ac.cn
基金资助:
KANG Wenshuo1,2( ), GUO Xiaojie1,2, ZOU Kai1,2, ZHAO Xiangyong3, ZHOU Zhiyong1, LIANG Ruihong1(
), GUO Xiaojie1,2, ZOU Kai1,2, ZHAO Xiangyong3, ZHOU Zhiyong1, LIANG Ruihong1( )
)
Received:2023-04-06
Revised:2023-05-10
Published:2023-09-12
Online:2023-09-12
Contact:
LIANG Ruihong, professor. E-mail: liangruihong@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:KANG Wenshuo (1994-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: kangwenshuo20@mails.ucas.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
BiFeO3-BaTiO3(BF-BT)陶瓷兼具高居里温度和优异的压电性能, 在高温压电传感器和驱动器等部件具有广泛的应用前景。BF-BT陶瓷在高温环境下电阻率较低, 易造成器件高温性能恶化甚至失效。因此, 改善BF-BT陶瓷电阻性能是应用推广必须解决的关键问题。作为一种铁酸盐, 其电阻率很难通过掺杂改性等常规方法进行改善。本研究在BF-BT陶瓷体系中发现一种电阻率异常升高的现象, 并证实这与样品中的第二相Bi25FeO40有关。显微结构分析表明, 该第二相具有一种特殊的层状周期性结构, 其中每三排原子构成一个周期, 而缺陷大多集中在其中一层原子当中。本研究采用传统固相法成功地制备出纯相的Bi25FeO40, 将其作为外添加剂加入到0.70BF-0.30BT组分中, 使基体组分在300 ℃的电阻率从1.03 MΩ·cm提高到4.33 MΩ·cm。此外, COMSOL仿真模拟的结果证实, 通过引入该第二相可以将0.67BF-0.33BT组分电阻率提高一个数量级。根据能量过滤效应, 这种特殊的结构具有高能垒, 可以阻碍载流子迁移, 从而提高BF-BT陶瓷电阻率。本工作为改善BF-BT陶瓷电阻率提供了一种切实可行的方法。
中图分类号:
康文烁, 郭晓杰, 邹凯, 赵祥永, 周志勇, 梁瑞虹. 层状结构第二相增强BiFeO3-BaTiO3陶瓷电阻率研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1420-1426.
KANG Wenshuo, GUO Xiaojie, ZOU Kai, ZHAO Xiangyong, ZHOU Zhiyong, LIANG Ruihong. Enhanced Resistivity Induced by the Second Phase with Layered Structure in BiFeO3-BaTiO3 Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1420-1426.
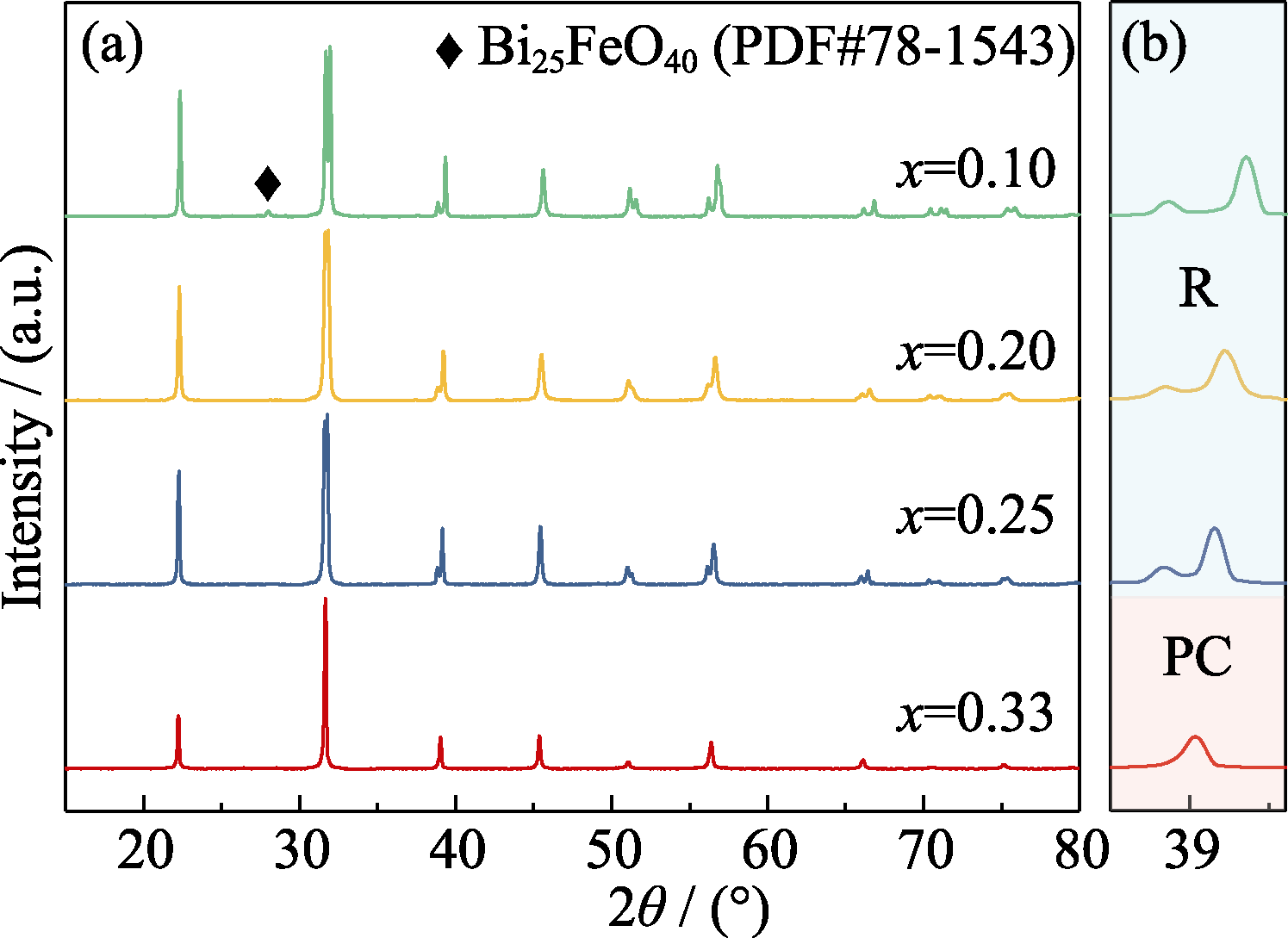
图1 (1−x)BF-xBT陶瓷烧结后的样品在2θ=15°~80°范围的XRD图谱(a)以及2θ=39°附近衍射峰的放大图(b)
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of sintered (1−x)BF-xBT samples in the range of 2θ=15°-80° (a) and the magnified image at 2θ=39° (b)

图2 (1−x)BF-xBT陶瓷样品自然断面的背散射形貌(a~d)和x=0.10组分抛光的表面形貌(e)以及面扫能谱(f, g)
Fig. 2 Backscattered electron images of the cross-section for (1−x)BF-xBT ceramics (a-d), polished surface image for x=0.10 composition (e), and EDS mapping of Bi (f) and Fe (g)

图3 (1−x)BF-xBT陶瓷的直流电阻率(a)、复阻抗数据(b)以及x=0.10组分两段圆弧的拟合结果(c)
Fig. 3 DC resistivity versus temperature of (1−x)BF-xBT ceramics (a), Nyquist plots at 300 ℃ (b), and grain boundary resistivity obtained from fitting Cole-Cole plots of x=0.10 composition (c)

图4 x=0.10组分在不同温度的模量频谱图(a)以及从中提取的电容值随温度的变化关系(b)
Fig. 4 Modulus plots versus temperature for x=0.10 composition (a), and capacitance values extracted from modulus peaks at different temperatures (b)

图5 第二相[111]取向的TEM图像(a)、选区电子衍射(b)、高分辨TEM图像(c)以及高角环形暗场像(d,e),(e)中插图为绿色框中的原子柱强度
Fig. 5 TEM image (a), selected-area electron diffraction (b) and high-resolution TEM image (c) at [111] of second phase, and high-angle annular dark-field images in [111] zone axis (d, e) with illustration in (e) showing intensity plot of atoms in green box

图6 对含有第二相的BF-BT陶瓷电阻性能的仿真模拟(a)、第二相提高电阻率的作用机理(b)和Schottky能垒模型(c)
Fig. 6 Resistivity simulation of the BF-BT composite ceramic at 300 ℃ (a), schematic diagram describing carrier migration (b), and Schottky barrier model (c)
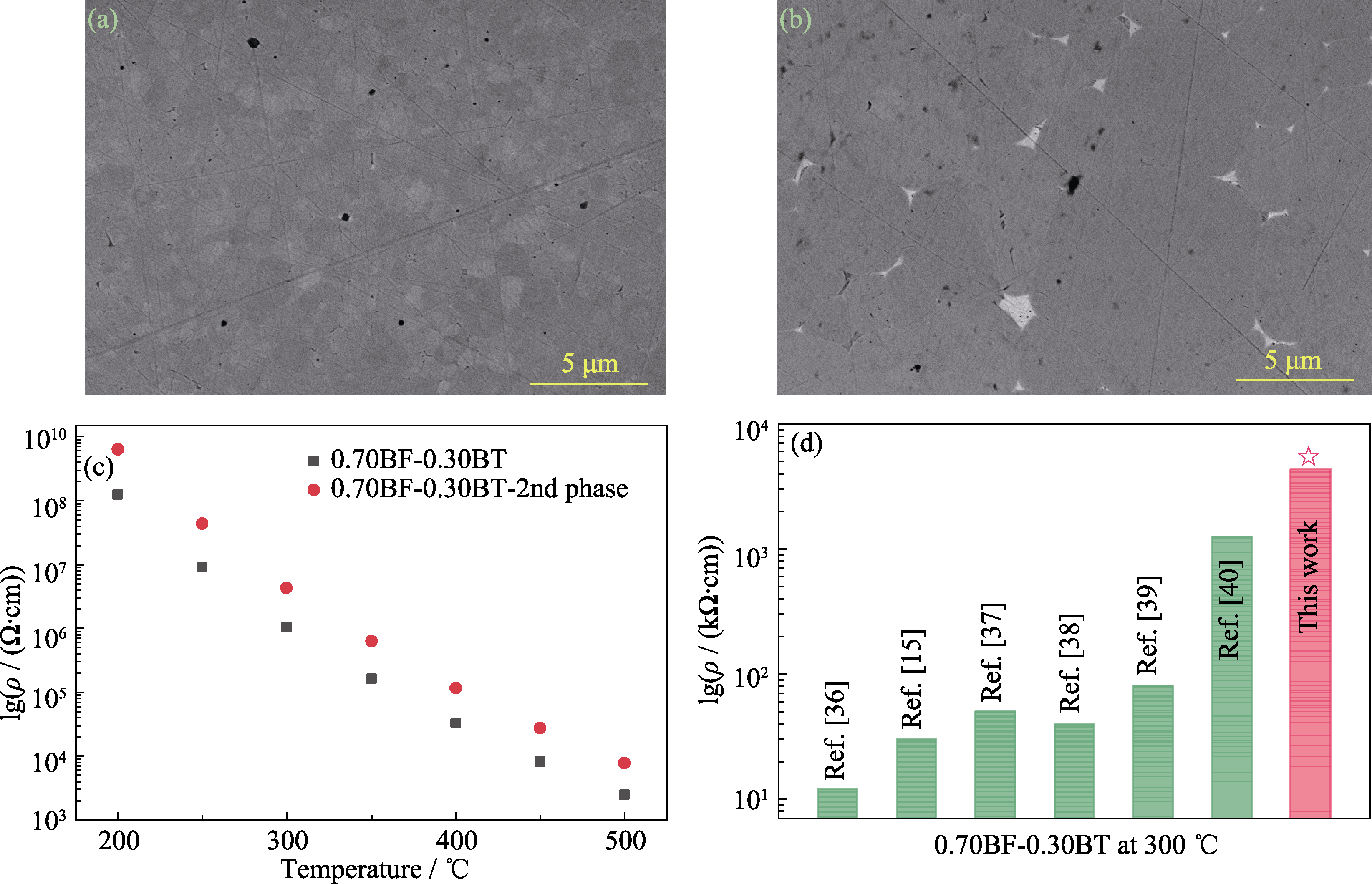
图7 0.70BF-0.30BT纯组分样品加入Bi25FeO40前(a)后(b)的背散射形貌、电阻率随温度的变化关系(c)以及文献报道的0.70BF-0.30BT在300 ℃的电阻率
Fig. 7 Backscatter morphologies of the polished 0.70BF-0.30BT pure component sample (a) and the sample modified with the second phase (b), resistivities of two samples versus temperature (c), and summary results of the resistivities of 0.70BF-0.30BT at 300 ℃ reported in the literatures (d)
| [1] |
YAO Z H, XU C B, LIU H X, et al. Greatly reduced leakage current and defect mechanism in atmosphere sintered BiFeO3- BaTiO3 high temperature piezoceramics. J. Mater. Sci-Mater. El., 2014, 25(11): 4975.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LEONTSEV S O, EITEL R E. Dielectric and piezoelectric properties in Mn-modified (1-x)BiFeO3-xBaTiO3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2009, 92(12): 2957.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
WAN Y, LI Y, LI Q, et al. Microstructure, ferroelectric, piezoelectric, and ferromagnetic properties of Sc-modified BiFeO3- BaTiO3 multiferroic ceramics with MnO2 addition. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2014, 97(6): 1809.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LEE M H, KIM D J, PARK J S, et al. High-performance lead- free piezoceramics with high curie temperatures. Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(43): 6976.
DOI URL |
| [5] | ICHIRO FUJII S W. Structural and electrical characteristics of potential candidate lead-free BiFeO3-BaTiO3piezoelectric ceramics. J. Appl. Phys., 2017, 122: 164105. |
| [6] |
ZHANG S, YU F. Piezoelectric materials for high temperature sensors. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2011, 94(10): 3153.
DOI URL |
| [7] | SHI Y, DONG X, ZHAO K, et al. Potential high-temperature piezoelectric ceramics with remarkable performances enhanced by the second-order Jahn-Teller effect. ACS Appl. Mater. & Interf., 2021, 13(12): 14385. |
| [8] |
KE Q, LOU X, WANG Y, et al. Oxygen-vacancy-related relaxation and scaling behaviors of Bi0.9La0.1Fe0.98Mg0.02O3ferroelectric thin films. Phys. Rev. B, 2010, 82(2): 024102.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
VERWEIJ H. Thermodynamics and transport of ionic and electric defects in crystalline oxides. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1997, 80(9): 2175.
DOI URL |
| [10] | ZHENG T, WU J, XIAO D, et al. Recent development in lead-free perovskite piezoelectric bulk materials. Prog. in Mater. Sci., 2018, 98: 552. |
| [11] | WANG T, JIN L, TIAN Y, et al. Microstructure and ferroelectric properties of Nb2O5-modified BiFeO3-BaTiO3 lead-free ceramics for energy storage. Mater. Lett., 2014, 137: 79. |
| [12] |
QI X D, DHO J, TOMOV R, et al. Greatly reduced leakage current and conduction mechanism in aliovalent-ion-doped BiFeO3. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2005, 86(6): 062903.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
WEFRING E T, EINARSRUD M A, GRANDE T. Electrical conductivity and thermopower of (1-x)BiFeO3-xBi0.5K0.5TiO3(x = 0.1, 0.2) ceramics near the ferroelectric to paraelectric phase transition. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.: PCCP, 2015, 17(14): 9420.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZHU L F, SONG A, ZHANG B P, et al. Boosting energy storage performance of BiFeO3-based multilayer capacitors via enhancing ionic bonding and relaxor behavior. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10(13): 7382..
DOI URL |
| [15] | ZENG F, FAN G, HAO M, et al. Conductive property of BiFeO3- BaTiO3 ferroelectric ceramics with high Curie temperature. J. Alloys and Compd., 2020, 831: 154853. |
| [16] |
VALANT M. Peculiarities of a solid-state synthesis of multiferroic polycrystalline BiFeO3. Chem. Mater., 2007, 19(22): 5431.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SOSNOWSKA I, NEUMAIER T P, STEICHELE E. Spiral magnetic ordering in bismuth ferrite. J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys., 1982, 15(23): 4835.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
PALAI R, KATIYAR R S, SCHMID H, et al. β phase and γ-β metal-insulator transition in multiferroic BiFeO3. Phys. Rev. B, 2008, 77(1): 014110.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
GHEORGHIU F P, IANCULESCU A, POSTOLACHE P, et al. Preparation and properties of (1-x)BiFeO3-xBaTiO3multiferroic ceramics. J.. Alloys and Compd., 2010, 506(2): 862.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WANG G, LI J, ZHANG X, et al. Ultrahigh energy storage density lead-free multilayers by controlled electrical homogeneity. Energ. Environ. Sci., 2019, 12(2): 582.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
MORRISON F D, SINCLAIR D C, WEST A R. Characterization of lanthanum-doped barium titanate ceramics using impedance spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2001, 84(3): 531.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
SUNDARAKANNAN B, KAKIMOTO K, OHSATO H. Frequency and temperature dependent dielectric and conductivity behavior of KNbO3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys., 2003, 94(8): 5182.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
IRVINE J T S. Electroceramics characterization by impedance spectroscopy. Adv. Mater., 1990, 2(3): 132.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
JEBARI H, TAHIRI N, BOUJNAH M, et al. Structural, optical, dielectric, and magnetic properties of iron-sillenite Bi25FeO40. Appl. Phys. A, 2022, 128(9): 842.
DOI |
| [25] | JIANG T, WANG Y, GUO Z, et al. Bi25FeO40/Bi2O2CO3 piezoelectric catalyst with built-in electric fields that was prepared via photochemical self-etching of Bi25FeO40for 4-chlorophenol degradation. J. Cleaner Prod., 2022, 341: 130908. |
| [26] |
SEI K K, MASARU M, HIROAKI Y. Electrical anisotropy and plausible explanation for dielectric anomaly of Bi4Ti3O12 single crystal. Mater. Res. Bull., 1996, 31(1): 121.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
AUCIELLO O, KRAUSS A R, IM J, et al. Studies of film growth processes and surface structural characterization of ferroelectric memory-compatible SrBi2Ta2O9 layered perovskites via in situ, real-time ion-beam analysis. Appl. Phys. Lett., 1996, 69(18): 2671.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WASER R. Grain boundaries in dielectric and mixed-conducting ceramics. Acta Mater., 2000, 48(4): 797.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
YOON S H, RANDALL C A, HUR K H. Influence of grain size on impedance spectra and resistance degradation behavior in acceptor (Mg)-doped BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2009, 92(12): 2944.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
REISS G, VANCEA J, HOFFMANN H. Grain-boundary resistance in polycrystalline metals. Phys. Rev. Lett., 1986, 56(19): 2100.
PMID |
| [31] |
HAILE S M, WEST D L, CAMPBELL J. The role of microstructure and processing on the proton conducting properties of gadolinium- doped barium cerate. J. Mater. Res., 1998, 13(6): 1576.
DOI URL |
| [32] | LUO T. Maxwell-Wagner Polarization Characteristics in BaTiO3 PVDF Nanocomposites. High Voltage Engineering, 2019. |
| [33] |
ZHANG C, CHEN Y, LI X, et al. Effect of LiF addition on sintering behavior and dielectric breakdown mechanism of MgO-based microwave dielectric ceramics. J. Materiomics, 2021, 7(3): 478.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ABRANTES J C C. Applicability of the brick layer model to describe the grain boundary properties of strontium titanate ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2000, 20(10): 1603.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
BENNETT N S, BYRNE D, COWLEY A. Enhanced Seebeck coefficient in silicon nanowires containing dislocations. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2015, 107(1): 013903.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
SINGH H, KUMAR A, YADAV K L. Structural, dielectric, magnetic, magnetodielectric and impedance spectroscopic studies of multiferroic BiFeO3-BaTiO3ceramics. Mater. Sci. and Engin.: B, 2011, 176(7): 540.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
LI Q, WEI J, TU T, et al. Remarkable piezoelectricity and stable high-temperature dielectric properties of quenched BiFeO3-BaTiO3ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2017, 100(12): 5573.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
WANG L, LIANG R, ZHOU Z, et al. Electrical conduction mechanisms and effect of atmosphere annealing on the electrical properties of BiFeO3-BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 39(15): 4727.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
MURAKAMI S, AHMED N T A F, WANG D, et al. Optimising dopants and properties in BiMeO3 (Me = Al, Ga, Sc, Y, Mg2/3Nb1/3, Zn2/3Nb1/3, Zn1/2Ti1/2) lead-free BaTiO3-BiFeO3 based ceramics for actuator applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2018, 38(12): 4220.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
MURAKAMI S, WANG D, MOSTAED A, et al. High strain (0.4%) Bi(Mg2/3Nb1/3)O3-BaTiO3-BiFeO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics and multilayers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2018, 101(12): 5428.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 胡忠良, 傅赟天, 蒋蒙, 王连军, 江莞. Nb/Mg3SbBi界面层热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 931-937. |
| [2] | 苏茂心, 李昕宸, 熊开南, 王升, 陈云琳, 涂小牛, 施尔畏. LGT晶体高温电阻率与全矩阵材料系数表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1364-1370. |
| [3] | 杨艳国, 任海深, 何代华, 林慧兴. 阳离子场强对BaO-SiO2-Ln2O3微晶玻璃结构及高温性能影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1207-1215. |
| [4] | 王旭, 顾明, 廖锦城, 宋庆峰, 史迅, 柏胜强, 陈立东. Fe/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3热电元件高温稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 197-202. |
| [5] | 赵占奎, 李涛, 鲁书含, 王明罡, 张京京, 程道文, 吴臣, 迟悦, 王虹力. SPS界面反应增强机制调控的软磁复合材料磁性能和电阻率[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(11): 1223-1226. |
| [6] | 张骐昊, 廖锦城, 唐云山, 顾明, 刘睿恒, 柏胜强, 陈立东. 方钴矿热电材料/Ti88Al12界面稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(8): 889-894. |
| [7] | 彭 旭, 朱德贵, 李杨绪, 周加敏, 吕 振, 郭鹏超. AlN-BN复相陶瓷的热等静压制备与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(5): 535-541. |
| [8] | 唐云山, 柏胜强,任都迪,廖锦城,张澜庭, 陈立东. Yb0.3Co4Sb12/Mo-Cu热电元件的界面结构与界面电阻[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(3): 256-260. |
| [9] | 熊小庆, 袁观明, 李轩科, 董志军, 张中伟, 王俊山. 不同晶体取向中间相沥青基带状炭纤维的制备与表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(11): 1186-1192. |
| [10] | 李 勇, 徐协文, 杨现锋, 谢志鹏. Fe高温浸渗法制备防静电3Y-TZP陶瓷及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(10): 1099-1104. |
| [11] | 王得印, 宋永才, 简 科. 组成和结构对连续SiC纤维电阻率的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(2): 162-168. |
| [12] | 杜玉成, 颜 晶, 孟 琪, 李 扬, 戴洪兴. Sb-SnO2包覆硅藻土多孔导电材料制备及表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(10): 1031-1036. |
| [13] | 蒋晓娜,兰中文,余 忠,庄亚明,刘培元. Mn3O4对LiZn铁氧体磁性能、微结构和电阻率的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(1): 77-82. |
| [14] | 王得印,毛仙鹤,宋永才,王应德. 一种具有稳定富碳表层的SiC纤维的制备与性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(6): 1209-1213. |
| [15] | 张东炎,张惠敏,靳先静,常爱民. Co0.8Mn0.8Ni0.9Fe0.5O4 纳米粉体的制备及热敏特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(5): 1008-1012. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||