无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (10): 1058-1064.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220093 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20220093
甘洪宇1( ), 冯燕1, 杨德鸿1, 田煜彬1, 李阳1, 邢涛2, 李智2,3, 赵学波1, 代鹏程1(
), 冯燕1, 杨德鸿1, 田煜彬1, 李阳1, 邢涛2, 李智2,3, 赵学波1, 代鹏程1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-02-28
修回日期:2022-03-26
出版日期:2022-10-20
网络出版日期:2022-04-07
通讯作者:
代鹏程, 副教授. E-mail: dpcapple@upc.edu.cn作者简介:甘洪宇(1998-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: hongyugan@163.com
基金资助:
GAN Hongyu1( ), FENG Yan1, YANG Dehong1, TIAN Yubin1, LI Yang1, XING Tao2, LI Zhi2,3, ZHAO Xuebo1, DAI Pengcheng1(
), FENG Yan1, YANG Dehong1, TIAN Yubin1, LI Yang1, XING Tao2, LI Zhi2,3, ZHAO Xuebo1, DAI Pengcheng1( )
)
Received:2022-02-28
Revised:2022-03-26
Published:2022-10-20
Online:2022-04-07
Contact:
DAI Pengcheng, associate professor. E-mail: dpcapple@upc.edu.cnAbout author:GAN Hongyu (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: hongyugan@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
碳材料以其低成本、良好的化学稳定性和热稳定性等优异特性被广泛应用于各种催化反应中。本研究利用来源广泛的天然脱脂棉为原材料, 通过原位气相掺杂的方法制备了N掺杂、B掺杂、BN共掺杂的生物质碳材料, 并将其应用在丙烷直接脱氢制丙烯反应中。研究发现, 与未掺杂的生物质碳相比, 杂原子掺杂的生物质碳均表现出更高的丙烷转化率和丙烯选择性, 而且N、B单独掺杂的生物质碳材料催化性能优于BN共掺杂的生物质碳材料, 其中N掺杂的生物质碳具有最优催化性能: 在600 ℃反应温度下, 丙烷转化率达到17.6%, 总烯烃收率达14.8%, 且经过12 h的脱氢反应后, 催化剂性能无明显的衰减。通过对这些碳材料的化学结构和催化性能的对比分析, 发现N掺杂和B掺杂使得碳材料表面的大量C-O基团转变为具有丙烷脱氢活性的C=O基团, 抑制反应过程中的C-C键断裂, 从而提高目标产物丙烯的选择性。生物质碳材料成本低廉且来源广泛, 以其作为催化剂可以极大地推动丙烷脱氢工业的发展。
中图分类号:
甘洪宇, 冯燕, 杨德鸿, 田煜彬, 李阳, 邢涛, 李智, 赵学波, 代鹏程. 杂原子掺杂生物质碳催化丙烷直接脱氢制丙烯[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(10): 1058-1064.
GAN Hongyu, FENG Yan, YANG Dehong, TIAN Yubin, LI Yang, XING Tao, LI Zhi, ZHAO Xuebo, DAI Pengcheng. Heteroatom-doped Biochar for Direct Dehydrogenation of Propane to Propylene[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1058-1064.
| Sample | C/% | N/% | O/% | B/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-BC | 82.6 | - | 16.57 | 0.83 |
| N-BC | 68.38 | 17.2 | 14.42 | - |
| BN-BC | 66.13 | 18.65 | 14.09 | 1.13 |
| BC | 83.76 | - | 16.24 | - |
表1 XPS对样品B-BC、N-BC、BN-BC及BC的组成分析(原子分数)
Table 1 Component analyses of samples B-BC, N-BC, BN-BC, and BC (atom fraction)
| Sample | C/% | N/% | O/% | B/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-BC | 82.6 | - | 16.57 | 0.83 |
| N-BC | 68.38 | 17.2 | 14.42 | - |
| BN-BC | 66.13 | 18.65 | 14.09 | 1.13 |
| BC | 83.76 | - | 16.24 | - |
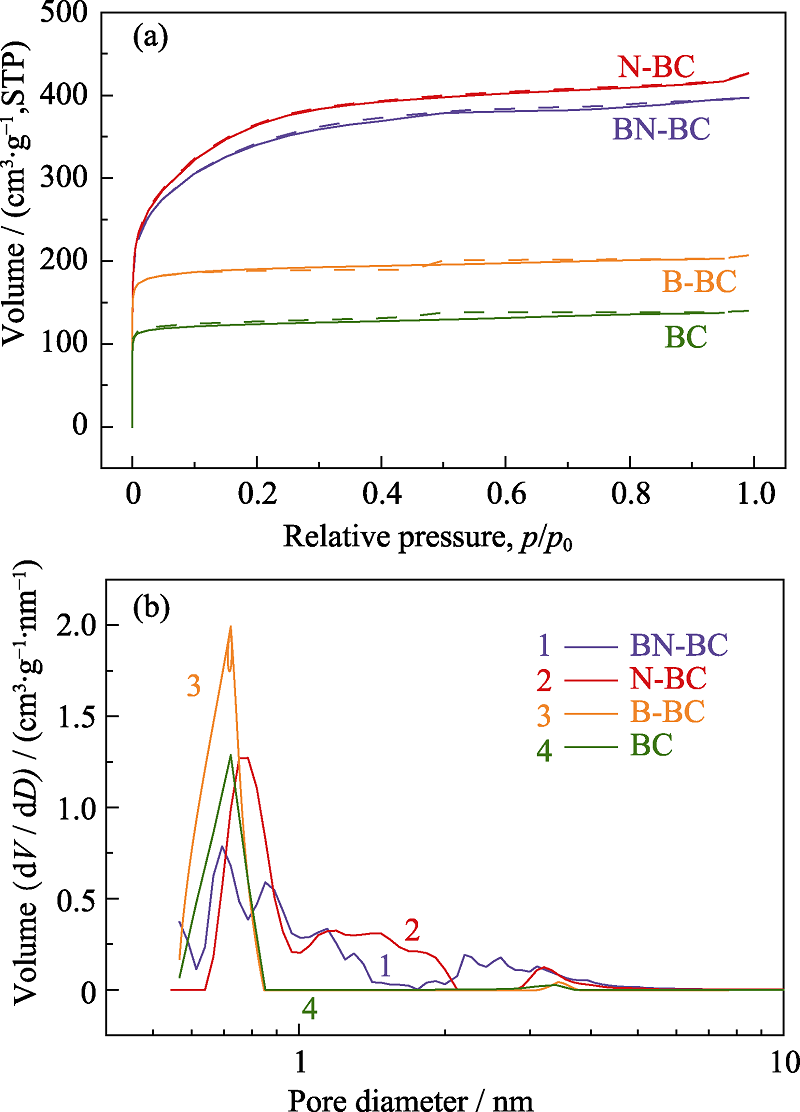
图4 样品B-BC、N-BC、BN-BC及BC的N2吸附-脱附等温线(a)和孔径分布(b)
Fig. 4 N2 absorption/desorption isotherms (a) and DFT pore size distribution (b) of samples B-BC, N-BC, BN-BC, and BC
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Vtotal/(cm3·g-1) | Pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-BC | 1303 | 0.582 | 0.79-2.10 |
| BN-BC | 1226 | 0.535 | 0.62-4.50 |
| B-BC | 765 | 0.281 | 0.73-3.50 |
| BC | 497 | 0.191 | 0.62-0.87 |
表2 样品的比表面积、孔体积及平均孔径
Table 2 Specific surface area, pore volume and average pore size of the samples
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Vtotal/(cm3·g-1) | Pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-BC | 1303 | 0.582 | 0.79-2.10 |
| BN-BC | 1226 | 0.535 | 0.62-4.50 |
| B-BC | 765 | 0.281 | 0.73-3.50 |
| BC | 497 | 0.191 | 0.62-0.87 |
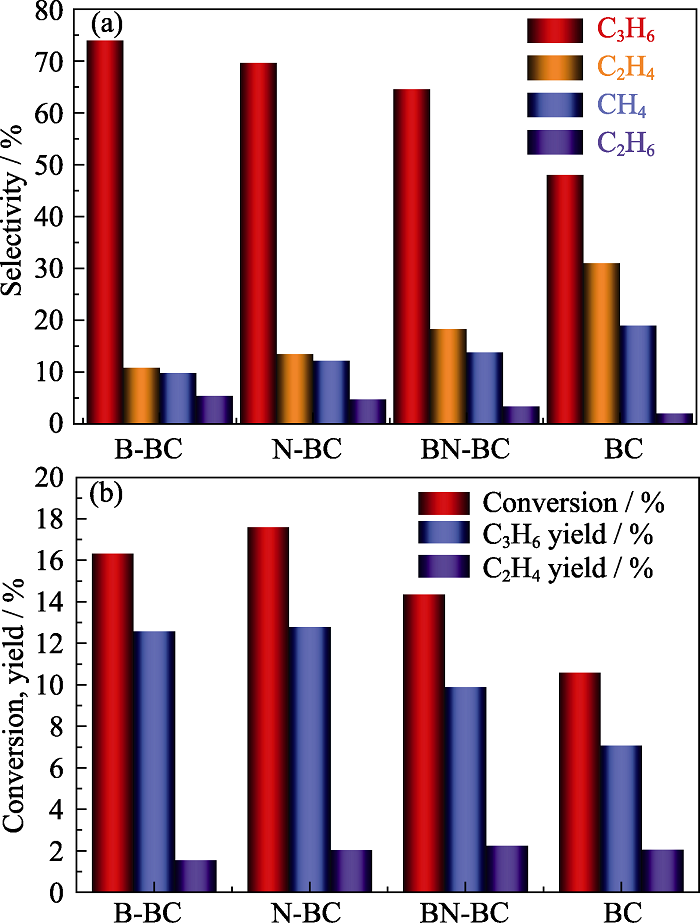
图6 不同催化剂在相同丙烷转化率(20%)下的产物分布(a)和相同温度(600 ℃)下丙烷转化率及烯烃收率(b)
Fig. 6 Product distribution at the same conversion (20%) (a) and conversion and olefins yield of propane (b) over different carbon catalysts at reaction temperatures of 600 ℃ The reaction conditions: 0.5 g catalyst, He-to-propane ratio = 3, GHSV = 3840 mL·g-1·h-1 Colorful figures are available on website
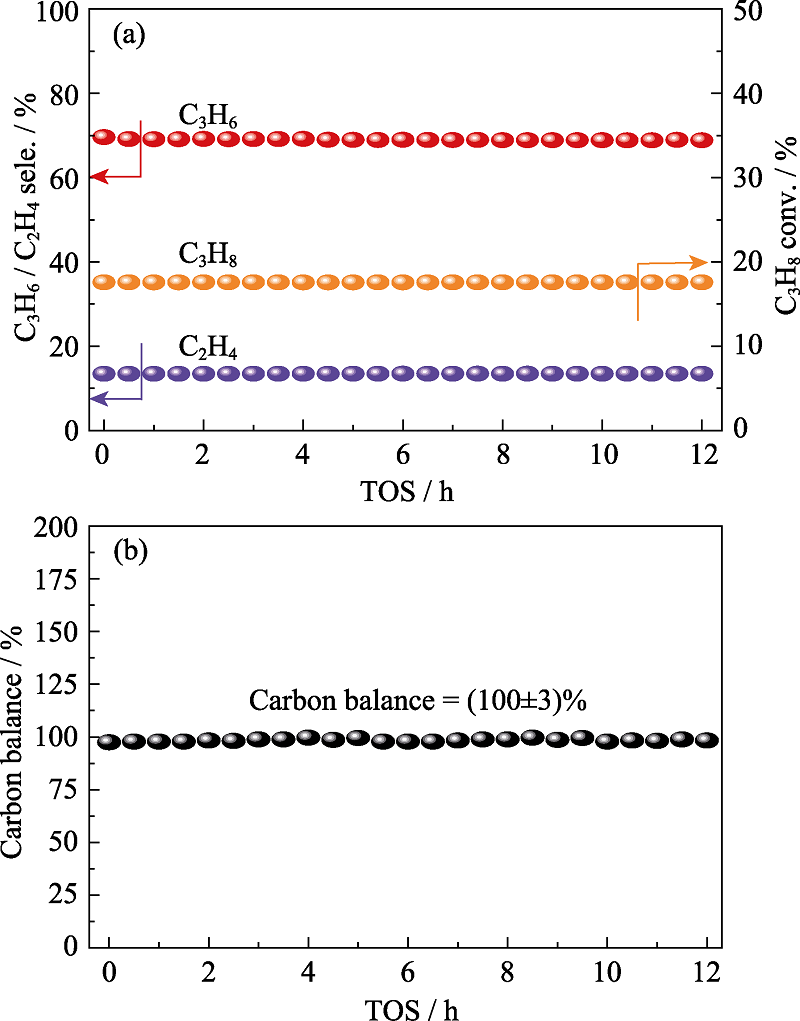
图8 N-BC催化丙烷脱氢稳定性测试(a)和反应12 h内碳平衡数据(b)
Fig. 8 Stability test (a) and carbon balance during the catalytic test (b) of N-BC for direct dehydrogenation (DDH) reaction over 12 h GHSV = 3840 mL·g-1·h-1; TOS: Time on stream
| Catalyst | T/℃ | X% (C3H8) | Y% (Olefins) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-BC | 600 | 17.6 | 14.8 | This work |
| BN-BC | 600 | 14.35 | 12.1 | This work |
| B-BC | 600 | 16.31 | 14.1 | This work |
| BC | 600 | 10.58 | 9.1 | This work |
| 5Cr2O3/SBA-15 | 580 | 18.0 | 14.8 | [ |
| PtSn/HZSM-5 | 590 | 22.9 | 11.2 | [ |
| CNTs | 600 | 9.0 | 7.9 | [ |
| GC | 600 | 6.5 | 6.1 | [ |
表S1 部分催化剂用于丙烷直接脱氢制丙烯的反应活性
Table S1 Catalytic performance of some catalysts for direct dehydrogenation of propane
| Catalyst | T/℃ | X% (C3H8) | Y% (Olefins) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-BC | 600 | 17.6 | 14.8 | This work |
| BN-BC | 600 | 14.35 | 12.1 | This work |
| B-BC | 600 | 16.31 | 14.1 | This work |
| BC | 600 | 10.58 | 9.1 | This work |
| 5Cr2O3/SBA-15 | 580 | 18.0 | 14.8 | [ |
| PtSn/HZSM-5 | 590 | 22.9 | 11.2 | [ |
| CNTs | 600 | 9.0 | 7.9 | [ |
| GC | 600 | 6.5 | 6.1 | [ |
| [1] |
SATTLER J J H B, JAVIER RM, ELDVARDO S J, et al. Catalytic Dehydrogenation of light alkanes on Metals and metal oxides. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(20): 10613-10653.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
CAVANI F, BALLARINI N, CERICOLA A. Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane and propane: how far from commercial implementation? Catalysis Today, 2007, 127(1): 113-131.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ZHAO Z, GE G, LI W, et al. Modulating the microstructure and surface chemistry of carbocatalysts for oxidative and direct dehydrogenation: a review. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 37(5): 644-670.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
WECKHUYSEN B M, SCHOONHEYDT R A. Alkane dehydrogenation over supported chromium oxide catalysts. Catalysis Today, 1999, 51(2): 223-232.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
PHAM H N, SATTLER J J H B, WECKHUYSEN B M, et al. Role of Sn in the regeneration of Pt/γ-Al2O3 light alkane dehydrogenation catalysts. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(4): 2257-2264.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
MOTAGAMWALA A H, ALMALLAHI R, WORTMAN J, et al. Stable and selective catalysts for propane dehydrogenation operating at thermodynamic limit. Science, 2021, 373(6551): 217-222.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | HU Z P, ZHANG L F, WANG Z, et al. Bean dregs-derived hierarchical porous carbons as metal-free catalysts for efficient dehydrogenation of propane to propylene. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2018, 93(12): 3410-3417. |
| [8] | PARAKNOWITSCH J P, THOMAS A. Doping carbons beyond nitrogen: an overview of advanced heteroatom doped carbons with boron, sulphur and phosphorus for energy applications. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(10): 2839-2855. |
| [9] |
SHENG J, YAN B, LU W D, et al. Oxidative dehydrogenation of light alkanes to olefins on metal-free catalysts. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(2): 1438-1468.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
FRANK B, ZHANG J, BLUME R, et al. Heteroatoms increase the selectivity in oxidative dehydrogenation reactions on nanocarbons. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(37): 6913-6917.
DOI URL |
| [11] | LIU L, DENG Q F, AGULA B, et al. Ordered mesoporous carbon catalyst for dehydrogenation of propane to propylene. Chemicial Communications, 2011, 47(29): 8334-8336. |
| [12] |
SONG Y, LIU G, YUAN Z Y. N-, P- and B-doped mesoporous carbons for direct dehydrogenation of propane. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(97): 94636-94642.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SÁNCHEZ-MONEDERO M A, SÁNCHEZ-GARCíA M, ALBURQUERQUE J A, et al. Biochar reduces volatile organic compounds generated during chicken manure composting. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 288: 121584.
DOI URL |
| [14] | LIU W J, JIANG H, YU H Q. Emerging applications of biochar- based materials for energy storage and conversion. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(6): 1751-1779. |
| [15] |
DE JESÚS DÍAZ VELÁSQUEZ J, SUÁREZ L M C, FIGUEIREDO J L. Oxidative dehydrogenation of isobutane overactivated carbon catalysts. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2006, 311: 51-57.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LI L, ZHONG Q, KIM N D, et al. Nitrogen-doped carbonized cotton for highly flexible supercapacitors. Carbon, 2016, 105: 260-267.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
KIM N D, KIM S J, KIM G P, et al. NH3-activated polyaniline for use as a high performance electrode material in supercapacitors. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 78: 340-346.
DOI URL |
| [18] | DAI P, XUE Y, ZHANG S, et al. Paper-derived flexible 3D interconnected carbon microfiber networks with controllable pore sizes for supercapacitors. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(43): 37046-37056. |
| [19] | CHHETRI M, MAITRA S, CHAKRABORTY H, et al. Superior performance of borocarbonitrides, BxCyNz, as stable, low-cost metal-free electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Energy & Environmental Science, 2016, 9(1): 95-101. |
| [20] |
LI Y T, Pi Y T, LU L M, et al. Hierarchical porous active carbon from fallen leaves by synergy of K2CO3 and their supercapacitor performance. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 299: 519-528.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
MACHAKA R, ERASMUS R M, DERRY T E. Formation of c-BN nanocrystals by He+ implantation into hBN. Diamond and Related Materials, 2010, 19(10): 1131-1134.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
CHEN D, HOLMEN A, SUI Z, et al. Carbon mediated catalysis: a review on oxidative dehydrogenation. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 35(6): 824-841.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHAO Y, YANG L, CHEN S, et al. Can boron and nitrogen co-doping improve oxygen reduction reaction activity of carbon nanotubes? Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(4): 1201-1204.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
SANTHOSH KUMAR M, HAMMER N, RØNNING M, et al. The nature of active chromium species in Cr-catalysts for dehydrogenation of propane: New insights by a comprehensive spectroscopic study. Journal of Catalysis, 2009, 261(1): 116-128.
DOI URL |
| [25] | LI H, ZHOU S, ZHOU Y, et al. Effect of strontium addition to Plat inum catalyst for propane dehydrogenation. China Petroleum Processing & Petrochemical Technology, 2012, 14(3): 75-82. |
| [1] | 郝策, 刘自若, 刘炜, 史彦涛. 用于氧还原反应的碳基负载金属单原子催化剂研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 820-834. |
| [2] | 徐国皓, 余金鹏, 徐华胜, 李春成, 黄金花, 王鹏飞. CH3COONa处理HZSM-5分子筛及其催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(5): 546-552. |
| [3] | 曹磊, 代鹏程, 刘丹丹, 顾鑫, 李良军, 赵学波. 羰基化石墨片催化丙烷氧化脱氢制丙烯[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(11): 1187-1192. |
| [4] | 鲍 艳, 康巧玲. 中空TiO2微球的制备及其对聚丙烯酸酯薄膜保温性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(6): 581-586. |
| [5] | 李晓玉, 张 莉, 唐新峰, 张清杰. γ-NaxCoO2粉体的聚丙烯酸钠凝胶法制备及其表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(6): 603-608. |
| [6] | 郭 宇, 李东昕, 吴红梅, 金玉家, 周立岱, 陈强强. 负载型TS-1沸石膜催化剂的制备、表征及其催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(6): 631-636. |
| [7] | 秦显忠, 杨 改, 高 剑, 蔡飞鹏, 谭春晖. 聚丙烯酰胺改性LiFePO4/C正极材料的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(5): 517-522. |
| [8] | 秦兆鲁, 李定华, 杨荣杰. 氢氧化铝包覆改性聚磷酸铵及其在阻燃聚丙烯中的应用研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(12): 1267-1272. |
| [9] | 王素卿, 张学军, 田艳红, 张 丽, 李雅东. 锂离子电池负极材料PAN-ACF/SnO2的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(8): 836-840. |
| [10] | 王志勇, 彭超群, 王日初, 王小锋, 刘 兵. 煅烧工艺对氧化锌铝(AZO)粉体光学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(2): 171-176. |
| [11] | 李海晏, 谭业强, 张 路, 陈 涛, 宋义虎, 叶 瑛, 夏枚生. 生物填料的制备及其对聚丙烯复合材料性能影响的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(9): 977-983. |
| [12] | 于晓琳, 肖春霞, 郭露村. D-山梨醇对聚丙烯酸-水基氧化铝悬浮液流变性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(5): 545-549. |
| [13] | 王玉东, 张豪杰, 何丹农. Pd-ZrO2/Al2O3 催化剂对丙烯选择性催化还原 NO 的催化活性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(3): 311-316. |
| [14] | 汤 潇, 索红莉, 叶 帅, 刘 敏, 吴紫平, 周美玲. 低氟TFA-MOD工艺快速制备YBCO超导厚膜的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(9): 971-974. |
| [15] | 县 涛,杨 华,沈 希,冯有才,张海民,冯旺军. 聚丙烯酰胺凝胶法合成BiFeO3纳米颗粒[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(3): 251-254. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||