无机材料学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 1141-1146.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170012 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20170012
左亚卓, 李红, 王少雷, 杨敏, 任慕苏, 孙晋良
收稿日期:2017-01-06
修回日期:2017-03-21
出版日期:2017-11-20
网络出版日期:2017-10-20
作者简介:左亚卓(1991-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: zuoyazhuo@163.com
基金资助:ZUO Ya-Zhuo, LI Hong, WANG Shao-Lei, YANG Min, REN Mu-Su, SUN Jin-Liang
Received:2017-01-06
Revised:2017-03-21
Published:2017-11-20
Online:2017-10-20
摘要:
将SiC纤维毡与C纤维毡交替层叠, 通过针刺工艺制备(C-SiC)f/C预制体, 采用化学气相渗透与前驱体浸渍裂解复合工艺(CVI+PIP)制备(C-SiC)f/C复合材料, 研究(C-SiC)f/C复合材料H2-O2焰烧蚀性能。利用SEM、EDS和XRD对烧蚀前后材料的微观结构和物相组成进行分析, 探讨材料抗烧蚀机理。结果表明: (C-SiC)f/C复合材料表现出更优异的耐烧蚀性能。烧蚀750 s后, (C-SiC)f/C复合材料的线烧蚀率为1.88 μm/s, 质量烧蚀率为2.16 mg/s。与C/C复合材料相比, 其线烧蚀率降低了64.5%, 质量烧蚀率降低了73.5%; SiC纤维毡在烧蚀中心区表面形成的网络状保护膜可以有效抵御高温热流对材料的破坏; 在烧蚀过渡区和烧蚀边缘区形成的熔融SiO2能够弥合材料的裂纹、孔洞等缺陷, 阻挡氧化性气氛进入材料内部, 使材料表现出优异的抗烧蚀性能。
中图分类号:
左亚卓, 李红, 王少雷, 杨敏, 任慕苏, 孙晋良. (C-SiC)f/C复合材料的烧蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(11): 1141-1146.
ZUO Ya-Zhuo, LI Hong, WANG Shao-Lei, YANG Min, REN Mu-Su, SUN Jin-Liang. Ablation Behavior of (C-SiC)f/C Composites[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(11): 1141-1146.
| Sample | Structure | Density/ (g•cm-3) | Open porosity | Mass fraction of SiC/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (C-SiC)f/C | CF felt/ SiCF felt | 1.80 | 8.0% | 5%-6% |
| C/C | CF felt | 1.80 | 5.1% | 0 |
表1 (C-SiC)f/C复合材料与C/C复合材料基本参数
Table 1 Basic parameters of (C-SiC)f/C and C/C composites
| Sample | Structure | Density/ (g•cm-3) | Open porosity | Mass fraction of SiC/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (C-SiC)f/C | CF felt/ SiCF felt | 1.80 | 8.0% | 5%-6% |
| C/C | CF felt | 1.80 | 5.1% | 0 |
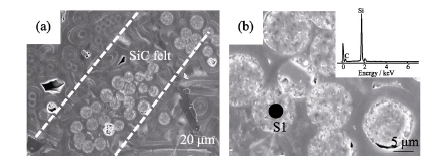
图4 (C-SiC)f/C复合材料截面形貌照片和EDS谱图(插图)
Fig. 4 Cross-sectional morphologies and EDS spectrum (insert) of (C-SiC)f/C composites (a) Low magnification; (b) High magnification
| Samples | Ablation time/s | Linear ablation rate/(μm·s-1) | Mass ablation rate/(mg·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (C-SiC)f/C | 750 | 1.88 | 2.16 |
| C/C | 750 | 5.29 | 8.14 |
表2 (C-SiC)f/C与C/C复合材料的线烧蚀率与质量烧蚀率
Table 2 Linear and mass ablation rates of (C-SiC)f/C and C/C
| Samples | Ablation time/s | Linear ablation rate/(μm·s-1) | Mass ablation rate/(mg·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (C-SiC)f/C | 750 | 1.88 | 2.16 |
| C/C | 750 | 5.29 | 8.14 |
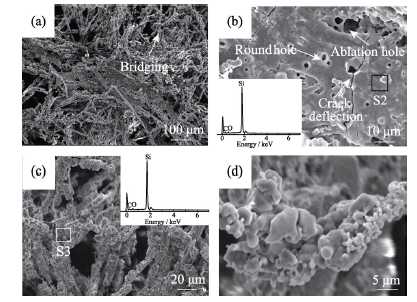
图6 (C-SiC)f/C复合材料烧蚀中心区SEM照片和EDS谱图(插图)
Fig. 6 SEM images and EDS spectrum (insert) of the ablation center zone in (C-SiC)f/C composites (a) Low magnification; (b,d) High magnification

图8 (C-SiC)f/C复合材料烧蚀边缘区不同位置SEM照片和EDS谱图(插图)
Fig. 8 SEM images and EDS spectrum (insert) of ablation marginal zone at different places in (C-SiC)f/C composites (a) Near the transitional zone; (b) Edge of the marginal zone
| No. | Reaction |
|---|---|
| 1 | SiC(s) → SiC(l) |
| 2 | 2/3SiC(s) + O2(g) → 2/3SiO2(s) + 2/3CO(g) 2/3SiC(s) + O2(g) → 2/3SiO2(l) + 2/3CO(g) 2/3SiC(l) + O2(g) → 2/3SiO2(g) + 2/3CO(g) |
| 3 | 1/2SiC(s) + O2(g) → 1/2SiO2(s) + 1/2CO2(g) 1/2SiC(s) + O2(g) → 1/2SiO2(l) + 1/2CO2(g) 1/2SiC(l) + O2(g) → 1/2SiO2(g) + 1/2CO2(g) |
| 4 | SiC(s) + O2(g) → SiO(g) + CO(g) |
| 5 | 2/3SiC(s) + O2(g) → 2/3SiO(g) + 2/3CO2(g) |
| 6 | SiO2(l) → SiO2(g) |
| 7 | SiO2(l) + CO(g) → SiO(g) + CO2(g) |
| 8 | SiO2(l) + C(s) → SiO(g) + CO(g) |
| 9 | 1/3SiO2(l) + C → 1/3SiC(s) + 2/3CO(g) 1/3SiO2(g) + C → 1/3SiC(s) + 2/3CO(g) 1/3SiO2(g) + C → 1/3SiC(l) + 2/3CO(g) |
| 10 | 1/2SiO2(l) + C → 1/2SiC(s) + 1/2CO2(g) 1/2SiO2(g) + C → 1/2SiC(s) + 1/2CO2(g) 1/2SiO2(g) + C → 1/2SiC(l) + 1/2CO2(g) |
| 11 | SiC(s) + 2SiO2(l) → 3SiO(g) + CO SiC(l) + 2SiO2(g) → 3SiO(g) + CO |
| 12 | C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) |
| 13 | 2C(s) + O2(g) → 2CO(g) |
| 14 | C(s) + H2O(g) → CO(g) + H2(g) |
表3 C和SiC在烧蚀过程中主要发生的反应
Table 3 Main reactions occured in thermo-chemical ablation process
| No. | Reaction |
|---|---|
| 1 | SiC(s) → SiC(l) |
| 2 | 2/3SiC(s) + O2(g) → 2/3SiO2(s) + 2/3CO(g) 2/3SiC(s) + O2(g) → 2/3SiO2(l) + 2/3CO(g) 2/3SiC(l) + O2(g) → 2/3SiO2(g) + 2/3CO(g) |
| 3 | 1/2SiC(s) + O2(g) → 1/2SiO2(s) + 1/2CO2(g) 1/2SiC(s) + O2(g) → 1/2SiO2(l) + 1/2CO2(g) 1/2SiC(l) + O2(g) → 1/2SiO2(g) + 1/2CO2(g) |
| 4 | SiC(s) + O2(g) → SiO(g) + CO(g) |
| 5 | 2/3SiC(s) + O2(g) → 2/3SiO(g) + 2/3CO2(g) |
| 6 | SiO2(l) → SiO2(g) |
| 7 | SiO2(l) + CO(g) → SiO(g) + CO2(g) |
| 8 | SiO2(l) + C(s) → SiO(g) + CO(g) |
| 9 | 1/3SiO2(l) + C → 1/3SiC(s) + 2/3CO(g) 1/3SiO2(g) + C → 1/3SiC(s) + 2/3CO(g) 1/3SiO2(g) + C → 1/3SiC(l) + 2/3CO(g) |
| 10 | 1/2SiO2(l) + C → 1/2SiC(s) + 1/2CO2(g) 1/2SiO2(g) + C → 1/2SiC(s) + 1/2CO2(g) 1/2SiO2(g) + C → 1/2SiC(l) + 1/2CO2(g) |
| 11 | SiC(s) + 2SiO2(l) → 3SiO(g) + CO SiC(l) + 2SiO2(g) → 3SiO(g) + CO |
| 12 | C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) |
| 13 | 2C(s) + O2(g) → 2CO(g) |
| 14 | C(s) + H2O(g) → CO(g) + H2(g) |
| [1] | LI H J.C/C composites.New Carbon Materials, 2001, 16(2): 79-80. |
| [2] | WINDHORSE T, DLOUNT G. C/C composites: a summary of recent developments and application. Materials and Design#/magtechI#, 1997, 18(1): 11-15. |
| [3] | WANG Y, CHEN Z F, YU S J, et al. Ablation behavior . Ablation behavior and mechanism analysis of C/SiC composites. Journal of Materials Research and Technology#/magtechI#, 2016, 5(2): 170-182. |
| [4] | WANG Y, XU Y D, WANG Y G,et al. Effects of TaC addition on the ablation resistance of C/SiC. Materials Letters, 2010, 64(19): 2068-2071. |
| [5] | XUE L, SU Z A, YANG X, et al. Microstructure. Microstructure and ablation behavior of C/C-HfC composites prepared by precursor infiltration and pyrolysis.Corrosion Science, 2015, 94(5): 165-170. |
| [6] | LI K Z, XIE J, LI H J, et al. Ablative. Ablative and mechanical properties of C/C-ZrC composites prepared by precursor infiltration and pyrolysis process. Journal of Materials Science & Technology#/magtechI#, 2015, 31(1): 77-82. |
| [7] | LIU L, LI H J, HAO K, et al. Effect of SiC location on the ablation of C/C-SiC composites in two heat fluxes. Journal of Materials Science & Technology#/magtechI #. Effect of SiC location on the ablation of C/C-SiC composites in two heat fluxes. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2015, 31(4): 345-354. |
| [8] | CUI Y Y, LI A J, LI B, et al. Microstructure. Microstructure and ablation mechanism of C/C-SiC composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society#/magtechI#, 2014, 34(2): 171-177. |
| [9] | WEI L F, LI K Z, WU F, et al. Preparation. Preparation and ablation properties of SiC modified C/C Composites. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society#/magtechI#, 2011, 39(2): 251-255. |
| [10] | YANG X, HU H F, ZHANG Y D, et al. Thermal shock properties of 3D-C/SiC composites prepared via polymer infiltration pyrolysis. Thermal shock properties of 3D-C/SiC composites prepared via polymer infiltration pyrolysis (PIP). Ceramics International , 2014, 40(7): 9087-9094. |
| [11] | ZHANG Z, HAO Z B, YAN L S. Preparation methods and application of C/C-SiC composites. Carbon#/magtechI#, 2008, 2: 29-35. |
| [12] | WEN S Q, LI K Z, SONG Q, et al. Enhancement of the oxidation resistance of C/C composites by depositing SiC nanowires onto carbon fibers by electrophoretic deposition. Journal of Alloys. Enhancement of the oxidation resistance of C/C composites by depositing SiC nanowires onto carbon fibers by electrophoretic deposition. Journal of Alloys and Compounds#/magtechI#, 2015, 618(1): 336-342. |
| [13] | YANG X, HUANG Q Z, SU Z A, et al. Ablative property. Ablative property and mechanism of C/C-ZrB2-ZrC-SiC composites reinforced by SiC networks under plasma flame. Corrosion Science#/magtechI#, 2016, 107(6): 9-20. |
| [14] | TOSHIHIRO I, HIROSHI O. Defect control of SiC polycrystalline fiber synthesized from poly-aluminocarbosilane. Journal of the European Ceramic Society#/magtechI#, 2016, 36(15): 3657-3662. |
| [15] | FONG C X, XUE J G, SONG Y C. The progress of research on silicon carbide fiber.Hi-Tech Fiber & Application#/magtechI#, 2003, 28(1): 15-19. |
| [16] | 实用化学手册编写组. 实用化学手册. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001. |
| [1] | 苟燕子, 康伟峰, 王堋人. 烧结条件对制备高结晶近化学计量比SiC纤维的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 405-414. |
| [2] | 李伟, 许志明, 苟燕子, 尹森虎, 余艺平, 王松. SiC纤维烧结陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 177-183. |
| [3] | 苟燕子, 康伟峰, 张庆雨. 由聚钛碳硅烷制备高结晶近化学计量比SiC(Ti)纤维[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1377-1383. |
| [4] | 吴爽, 苟燕子, 王永寿, 宋曲之, 张庆雨, 王应德. 高温热处理对国产KD-SA型SiC纤维组成结构与力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 569-576. |
| [5] | 王袁杰, 裴学良, 李好义, 徐鑫, 何流, 黄政仁, 黄庆. 自由基引发活性聚碳硅烷交联及其在制备SiC纤维中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 967-973. |
| [6] | 王西,王克杰,柏辉,宋卓林,王波,张程煜. 化学气相渗透2D-SiCf/SiC复合材料的蠕变性能及损伤机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(7): 817-821. |
| [7] | 王堋人, 苟燕子, 王浩. 第三代SiC纤维及其在核能领域的应用现状[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(5): 525-531. |
| [8] | 余汉青, 董志军, 袁观明, 丛野, 李轩科, 罗永明. B-C掺杂SiC纤维的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(5): 493-501. |
| [9] | 王国栋, 宋永才. 熔融纺丝过程优化制备细直径碳化硅纤维及其对力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(7): 721-727. |
| [10] | 穆阳, 邓佳欣, 李皓, 周万城. 两种连续SiC纤维的高温介电及吸波性能对比[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(4): 427-433. |
| [11] | 曹适意, 王 军, 王 浩, 王小宙. 自由碳的脱除对SiC纤维微观结构和性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(5): 529-534. |
| [12] | 袁 钦, 宋永才. 连续SiC纤维和SiCf/SiC复合材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(11): 1157-1165. |
| [13] | 袁文玉, 成来飞, 武 恒, 刘永胜. 硅源对植物纤维制备SiC纤维的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(2): 159-164. |
| [14] | 王得印, 宋永才, 简 科. 组成和结构对连续SiC纤维电阻率的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(2): 162-168. |
| [15] | 张荣军, 杨延清, 沈文涛. 三级化学气相沉积法制备SiC纤维及拉伸性能测试[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(8): 840-844. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||