近年来, 高熵合金(HEAs) 由于拥有比传统合金更好的机械强度、延展性、硬度和耐磨耐腐蚀性而受到广泛关注[1,2,3]。随着高熵合金的发展, 以控制结构熵来影响固溶体相稳定性的设计理念也随之发展起来。结构熵$\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\Delta {{S}_{\text{config}}}=-R\underset{i=1}{\overset{N}{\mathop \sum }}\,{{x}_{i}}\ln {{x}_{i}}$(式中R表示理想气体常数, xi表示相应元素的摩尔分数)。如果一个系统的结构熵(ΔSconfig)大于1.5R, 则该系统为高熵材料; 当1R≤∆Sconfig<1.5R 为“中熵”; ΔSconfig<1R为“低熵”[4]。目前, 高熵材料已经扩大到非金属化合物领域, 如氧化物[5]、碳化物[6]、硼化物[7]、氮化物[8]以及硫化物[9]。
Rost等[5]首次将高熵材料的研究延伸到氧化物体系, 成功制备出具有单一岩盐型结构(FCC)的(Mg0.2Ni0.2Co0.2Cu0.2Zn0.2O)高熵氧化物, 并证明高结构熵是使含有五种不同阳离子的岩盐型氧化物以单相形式稳定存在的关键。Berardan等[10]研究发现, 与传统二元或掺杂氧化物相比, 这些新型氧化物具有独特的性能优势, 这为高熵氧化物陶瓷领域的发展提供了极大的动力。目前, 已经发展出多种结构高熵氧化物陶瓷, 岩盐型高熵氧化物是最早得到研究的体系, 具有优秀的储锂性能[11]、高介电常数[12]、锂离子超导[13]和反铁磁性[14]等特点, 在催化剂载体上也有很好的应用[15,16]; 萤石结构的高熵氧化物具有高电导率和低热导率等特点[17,18]; 尖晶石型和反尖晶石型高熵陶瓷具有良好的铁磁性、储锂性能和电催化性能[19,20]; 烧绿石结构[21]和石榴石结构[22]的高熵陶瓷大都具有较低的热导率, 可用作热绝缘材料。
钙钛矿(ABO3)氧化物包含一个配位数12的A位阳离子、一个配位数6的B位阳离子和一个氧阴离子。对于钙钛矿氧化物, 可以通过掺杂不同阳离子来调控物理性质, 以满足不同的实际应用要求。近几年, 钙钛矿型高熵氧化物也得到了快速发展, 但研究主要集中在组成成分和制备方法的探索上[23], 对材料的性能研究较少。共沉淀法作为一种优秀的粉体制备方法, 制备的前驱体粉末粒度小、比表面积大, 反应活性强, 因而对材料的合成温度要求较低。但目前为止, 共沉淀法并未在高熵陶瓷领域得到很好的应用。
本研究通过共沉淀法结合煅烧工艺制备了La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3钙钛矿结构高熵陶瓷粉体, 研究了陶瓷粉体的物相转变、形貌和元素分布。并将前驱体粉末压制成块状坯体, 利用可视化形变分析仪分析了坯体在煅烧过程中的体积变化。最后对材料的电学性能进行了测试。
1 实验方法
1.1 试剂
分析纯试剂: 六水合硝酸镧(阿拉丁试剂), 六水合硝酸镍(北京化工厂), 九水合硝酸铬(阿拉丁试剂), 九水合硝酸铁(国药集团), 四水合硝酸锰(阿拉丁试剂), 六水合硝酸钴(阿拉丁试剂), 氢氧化钠(阿拉丁试剂), 碳酸钠(阿拉丁试剂), 无水乙醇(沪试), 氢氧化钾(科密欧试剂);电池级: 乙炔黑(山西力之源), 聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)(科密欧试剂), N-甲基吡咯烷酮(NMP)(科密欧试剂), 泡沫镍(江苏嘉亿盛)。
1.2 制备方法
按表1各元素比例称取对应的硝酸盐, 溶于去离子水。将混合溶液置于磁力搅拌机上搅拌均匀。称取一定量氢氧化钠与碳酸钠, 用去离子水溶解, 置于磁力搅拌机搅拌均匀, 制成沉淀剂。将沉淀剂缓慢滴入混合溶液中, 不断搅拌, 并控制溶液pH=10保持30 min不变, 即可停止滴加。室温下老化10 h后抽滤, 去离子水洗涤3次, 无水乙醇洗涤2次, 并在100 ℃下干燥10 h。对所得前驱体粉末仔细研磨后, 在800~1500 ℃煅烧2 h得到钙钛矿高熵陶瓷粉体, 升温速率均为5 ℃/min。使用DX-2700型X射线衍射仪对样品结构进行分析, CuKα射线, 波长λ为0.154 nm, 扫描速度为20 (°)/min, 扫描范围2θ=10°~80°。使用场发射扫描电子显微镜观察样品形貌, 电压为20 kV, 样品的元素分布用EDS分析。
表1 六组样品各元素组分摩尔之比
Table 1
| Sample | La | Co | Cr | Fe | Mn | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| La(Cr0.25Fe0.25Mn0.25Ni0.25)O3 La(Co0.25Fe0.25Mn0.25Ni0.25)O3 La(Co0.25Cr0.25Mn0.25Ni0.25)O3 La(Co0.25Cr0.25Fe0.25Ni0.25)O3 La(Co0.25Cr0.25Fe0.25Mn0.25)O3 | 4 4 4 4 4 | No 1 1 1 1 | 1 No 1 1 1 | 1 1 No 1 1 | 1 1 1 No 1 | 1 1 1 1 No |
将La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3前驱体粉末通过冷等静压法压制成ϕ10 mm×2 mm圆盘状坯体, 再将坯体1000 ℃煅烧并保温2 h得到钙钛矿高熵陶瓷, 升温速率均为5 ℃/min。使用天津中环电炉股份有限公司的TA-16A01型可视化高温形变分析仪对坯体在煅烧过程中的体积变化进行检测, 据此分析粉体合成过程中材料的体积变化与煅烧温度和材料相变之间的关系。
以1000 ℃煅烧所得陶瓷粉体为电极材料, 在玛瑙研钵中将其与导电剂(乙炔黑)和粘结剂(PVDF)混合均匀, 研磨成细腻的浆料, 电极材料、导电剂(乙炔黑)、粘结剂(PVDF)的质量比为15:2:3, PVDF的浓度为0.1 g/L(溶剂为N-甲基吡咯烷酮)。将浆料均匀涂覆在泡沫镍(1 cm×1 cm)上面, 然后在60 ℃的电热鼓风干燥箱中干燥2 h以上。将干燥好的电极片在压片机下以10 MPa的压力保压10 s以上制成工作电极。使用上海辰华CHI660D型电化学工作站进行循环伏安(CV)及恒流充放电(GCD)测试。循环伏安(CV)测试的电压窗口为0~0.7 V, 扫描速率为5~100 mV/s;恒流充放电(GCD)测试的电流密度为1~10 A/g。所有测试均采用三电极体系, 参比电极为甘汞电极, 对电极为铂片(2 cm×2 cm), 填充电解液为1 mol/L的KOH溶液。
2 结果与分析
2.1 La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3的物相形貌表征
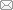
图1是不同温度煅烧所得La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3高熵陶瓷粉体的XRD图谱。结果显示, 当煅烧温度为800 ℃时, 钙钛矿结构已经生成, 但有少量第二相。当煅烧温度为1000 ℃时, 样品结构全部转化为钙钛矿结构, 且结晶性良好。有研究使用喷雾热解法制备的La系高熵钙钛矿氧化物, 需要在1200 ℃煅烧才能减少非晶相[24], 使用高能球磨法制备的Ba系、Sr系钙钛矿高熵氧化物所需煅烧温度达1400 ℃[23]。而本研究仅在1000 ℃就合成了La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3高熵陶瓷粉体。这是由于在共沉淀法制备过程中, 溶液中的各种反应物均以离子状态混合, 各种金属离子通过沉淀形成混合均匀、粒径小的前驱体粉末, 粉末的比表面积大, 具有较高的反应活性[25,26], 从而显著降低了高熵陶瓷粉体的合成温度。从图1还可以看出, 当煅烧温度上升到1300 ℃后, 又会生成第二相。
图1
图1
不同温度煅烧所得La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3陶瓷粉体的XRD图谱
Fig. 1
XRD patterns of the La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3 ceramic powders calcined at different temperatures
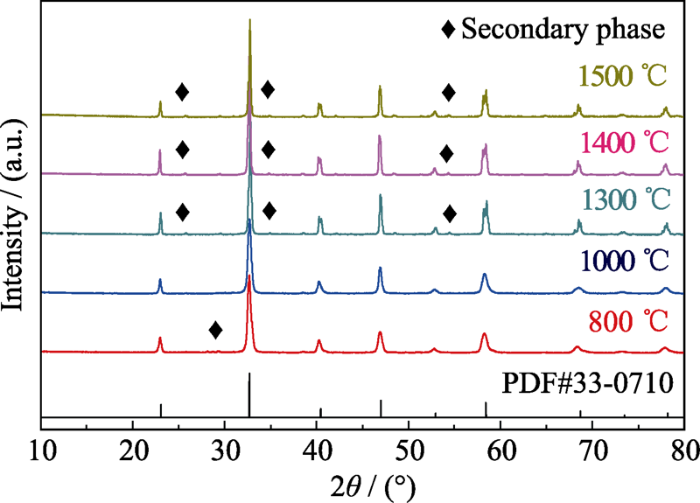
为了进一步分析结构熵对系统稳定性的影响, 在相同制备条件下, 制备了五种四组元粉末材料, 对其进行XRD分析, 结果如图2所示。这五种材料都没有形成单相钙钛矿结构, 出现了大量第二相。根据结构熵的计算公式可以得知, 当体系内组元数减少, 该体系的结构熵也随之下降。对于五组元钙钛矿氧化物而言, 其结构熵为1.61R, 而四组元氧化物的结构熵则下降到1.39R。吉布斯自由能公式如下:
图2
图2
1000 ℃下煅烧所得四元系粉体的XRD图谱
Fig. 2
XRD patterns of the quaternary systems powders calcined at 1000 ℃
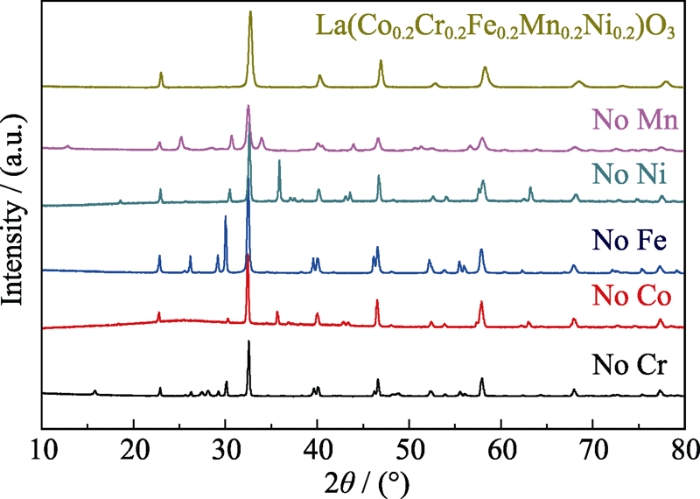
图3是在煅烧过程中坯体体积随温度的变化情况。从图中可以看出, 升温至200 ℃左右, 样品高度和宽度出现小幅度增长, 这是由于样品受热体积膨胀导致的, 属于物理变化;在200~500 ℃升温过程中, 样品高度和宽度大幅度减小, 内部逐渐形成钙钛矿结构, 同时致密化程度不断增强;500 ℃以上升温过程中, 样品高度和宽度只是小幅度缓慢变化, 钙钛矿结构大体形成, 内部不再发生明显致密化;在1000 ℃保温过程中, 样品高度和宽度不再发生变化。
图3
图3
样品高度和宽度随煅烧温度的变化
Fig. 3
Height and width of sample varied with calcination temperature
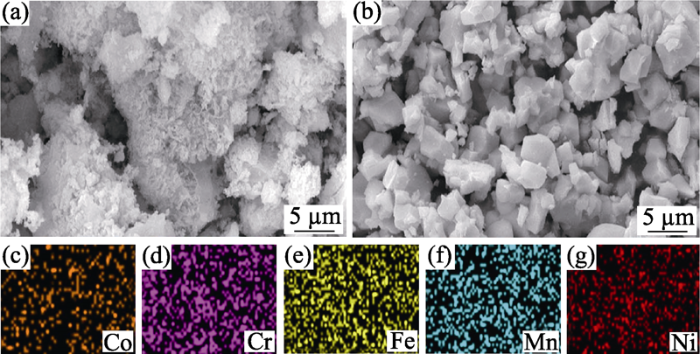
图4
图4
800 ℃煅烧La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3样品的SEM照片(a), 1000 ℃煅烧La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3样品的SEM照片(b)及其元素的EDS分布(c~g)
Fig. 4
SEM image of sample La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3 calcined at 800 ℃ (a), SEM image (b) and corresponding EDS element mapping (c-g) of La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3 calcined at 1000 ℃
2.2 La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3的电学性能表征
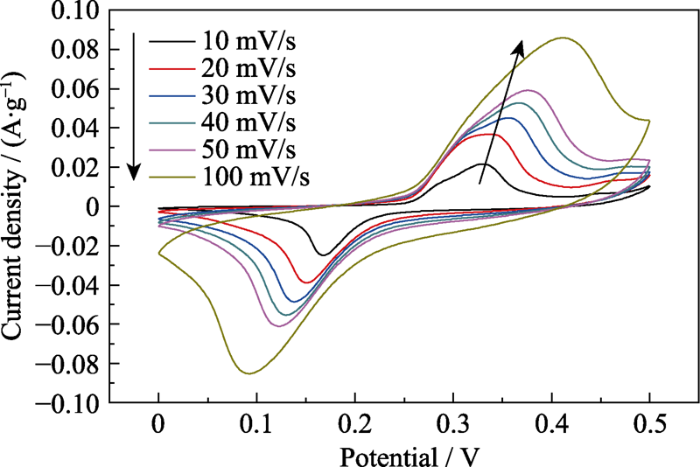
为了分析La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3的电学性能, 对其制成的工作电极进行CV和GCD测试。从图5的CV曲线可以看出, 每一条CV曲线都具有明显且对称的电流峰值, 这表明电极材料中的金属离子之间发生了可逆的氧化还原反应[28,29]。随着扫描速率的增大, 氧化/还原峰面积都不断增加, 且两者面积几乎相同, 说明电极在反应过程中电子离子传递速率较快, 准可逆性良好, 具有典型的法拉第赝电容特性[30]。同时由于发生极化, 氧化峰和还原峰分别向高电位和低电位处移动[31], 即使在100 mV/s的扫描速率下, CV曲线的氧化峰和还原峰依然很明显, 说明该材料具有良好的倍率性能[32,33]。
图5
图5
La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3 电极的CV曲线
Fig. 5
CV curves of La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3 electrode
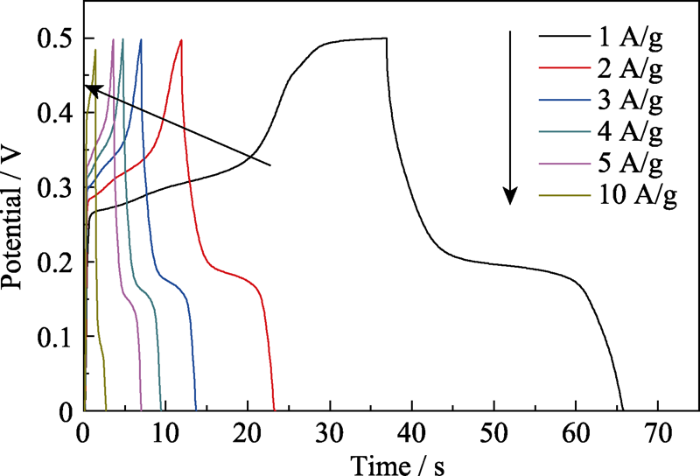
图6
图6
La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3电极的GCD曲线
Fig. 6
GCD curves of La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3 electrode
式中, im表示电流密度, V1和V0表示最高电位和最低电位。经过计算, 该电极材料在1 A/g的电流密度下的比容量为154.8 F/g (负载量为7 mg/cm2); 当电流密度增大到10 A/g时, 该电极材料仍然能保持初始比容量的47%(73 F/g)。这也说明La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3具有较好的倍率性能。
3 结论
研究通过共沉淀法结合煅烧工艺制备出La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3钙钛矿结构高熵陶瓷粉体, 并得出以下结论:
1) 通过XRD、SEM和EDS分析表明, 当煅烧温度为1000 ℃时, 制备的高熵陶瓷粉体具有单相钙钛矿结构, 无第二相生成, 并且颗粒分布均匀, 尺寸较小。同时也证明高结构熵是使多组元钙钛矿氧化物以单相结构稳定存在的关键。
2) 以La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3为电极材料制作的工作电极具有较好的倍率性能, 在1 A/g的电流密度下获得了154.8 F/g的比容量, 当电流密度增大到10 A/g时, 仍然能保持初始比容量的47%(73 F/g), 表明该材料在超级电容器方面具有一定的应用潜力。
参考文献
High-entropy alloys: a critical review
A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts
Microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNiZrx eutectic high-entropy alloys
High entropy oxides: fundamental aspects and electrochemical properties
Entropy-stabilized oxides
Processing and properties of high-entropy ultra-high temperature carbides
Bulk equiatomic (Hf-Ta-Zr-Ti)C and (Hf-Ta-Zr-Nb)C high entropy Ultra-High Temperature Ceramic (UHTC) carbide compositions were fabricated by ball milling and Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS). It was found that the lattice parameter mismatch of the component monocarbides is a key factor for predicting single phase solid solution formation. The processing route was further optimised for the (Hf-Ta-Zr-Nb)C composition to produce a high purity, single phase, homogeneous, bulk high entropy material (99% density); revealing a vast new compositional space for the exploration of new UHTCs. One sample was observed to chemically decompose; indicating the presence of a miscibility gap. While this suggests the system is not thermodynamically stable to room temperature, it does reveal further potential for the development of new in situ formed UHTC nanocomposites. The optimised material was subjected to nanoindentation testing and directly compared to the constituent mono/binary carbides, revealing a significantly enhanced hardness (36.1 +/- 1.6 GPa,) compared to the hardest monocarbide (HfC, 31.5 +/- 1.3 GPa) and the binary (Hf-Ta)C (32.9 +/- 1.8 GPa).
High-entropy metal diborides: a new class of high-entropy materials and a new type of ultrahigh temperature ceramics
The structure and properties of high-entropy alloys and nitride coatings based on them
Data-driven design of ecofriendly thermoelectric high-entropy sulfides
High-entropy compounds with compositional complexity can be designed as new thermoelectric materials. Here a data-driven model was developed, which chose suitable elements to reduce the enthalpy of formation and hence to increase the chance of single phase formation. Using this model, two high-entropy sulfides were designed, metallic Cu5SnMgGeZnS9 and semiconducting Cu3SnMgInZnS7. They were then successfully fabricated as single-phase dense ceramics with homogeneously distributed cations, and their phase stability and atomic local structures were investigated using density functional theory calculations. Finally, a zT value of 0.58 at 773 K was obtained for Cu5Sn1.2MgGeZnS9, where additional Sn was used to tune the carrier concentration. This work provides a simple approach to find new high-entropy functional materials in the largely unexplored multielement chemical space.
Room temperature lithium superionic conductivity in high entropy oxides
Tunable pseudocapacitive contribution by dimension control in nanocrystalline-constructed (Mg0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Cu0.2Zn0.2)O solid solutions to achieve superior lithium-storage properties
Colossal dielectric constant in high entropy oxides
Long-range antiferromagnetic order in a rocksalt high entropy oxide
Entropy-stabilized metal oxide solid solutions as CO oxidation catalysts with high-temperature stability
Mechanochemical synthesis of high entropy oxide materials under ambient conditions: dispersion of catalysts via entropy maximization
Multicomponent equiatomic rare earth oxides with narrow band gap and associated praseodymium multivalency
High-entropy fluorite oxides
Spinel-structured high entropy oxide (FeCoNiCrMn)3O4 as anode towards superior lithium storage performance
Facile synthesis and ferrimagnetic property of spinel (CoCrFeMnNi)3O4 high-entropy oxide nanocrystalline powder
Spinel to rock-salt transformation in high entropy oxides with Li incorporation
High-entropy pyrochlores with low thermal conductivity for thermal barrier coating materials
High entropy (Y0.2Yb0.2Lu0.2Eu0.2Er0.2)3Al5O12: a novel high temperature stable thermal barrier material
A new class of high-entropy perovskite oxides
Rare earth and transition metal based entropy stabilised perovskite type oxides
Synthesis of Mn1-xZnxFe2O4 ferrite powder by co-precipitation method
Preparation of Li1.5Al0.5Ti1.5(PO4)3 solid electrolyte via a co-precipitation method
The co-precipitation method can make the materials react uniformly at molecular level and has the advantages of lower polycrystalline synthesized temperature and shorter sintering time. Therefore, it is expected that the mass production of Li1.5Al0.5Ti1.5(PO4)(3) (LATP) solid electrolyte would be possible by application of the co-precipitation method for LATP preparation. In this study, an application of the co-precipitation method for a preparation of LATP solid electrolyte is attempted. Crystallized LATP powder is obtained by heating precipitant containing Li, Al, Ti, and PO4 at 800 A degrees C for 30 min. The LATP bulk sintered pellet is successfully prepared using the crystallized LATP powder by calcinating at 1,050 A degrees C. The cross-sectional SEM images show that many crystal grains exist, and the grains are in good contact with each other, i.e., there is no void space. All diffraction peaks of the pellet are attributed to LATP in XRD pattern. The sintered pellet is obtained by calcinating at 1,050 A degrees C, which is more than 150 A degrees C lower than that of conventional method. The LATP solid electrolyte shows a good conductivity which is 1.4 x 10(-3) S cm(-1) for bulk and 1.5 x 10(-4) S cm(-1) for total conductivities, respectively.
Microstructure and dielectric properties of high entropy Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.2Sn0.2Hf0.2Me0.2)O3 perovskite oxides
Green preparation and supercapacitive performance of NiCo2S4@ACF heterogeneous electrode materials
2S4 vulcanization process requires high-temperature and high energy supply, and has disadvantage of low conductivity. In this study, an environmental friendly vulanization method was utilized to prepare unique NiCo2S4@ACF core-shell heterstructure materials with activated carbon fiber (ACF) as skeleton at room temperature. NiCo2S4@ACF composite electrode material owns layered structures, which can effectively expand contact area with electrolyte, improve electron transmission path, and better create electrochemical performance. Specific capacitance of NiCo2S4@ACF composite electrode materials reached 1541.6 F/g (678 μF/cm2) at the current density of 1 A/g. In addition, the asymmetric supercapacitors (ASC) device fabricated with NiCo2S4@ACF as positive electrode and ACF as negative electrode exhibited energy density as high as 49.38 Wh/kg at the power density of 800 W/kg, and preeminent cycle stability up to 90.28% after 2000 cycles. All these data demonstrated that NiCo2S4@ACF is a promising potential application in the field of high-performance supercapacitors in the future.]]>
Facile and low-cost combustion-synthesized amorphous mesoporous NiO/carbon as high mass-loading pseudocapacitor materials
Design and synthesis of 3D Co3O4@MMoO4 (M=Ni, Co) nanocomposites as high-performance supercapacitor electrodes
Recent attentions have been focused on the synthesis and application of nanocomposites for supercapacitors, which can have superior electrochemical performance than single-structured materials. Here we designed and synthesized three-dimensional (3D) Co3O4@MMoO4 (M = Ni, Co) nanocomposites on Ni foam, which combined separately the advantages of the good rate capability of Co3O4 and the high specific capacitances of MMoO4 (M = Ni, Co), and the materials have shown surprising specific capacitances (2041 Fg(-1) of Co3O4@NiMoO4 and 857 Fg(-1) of Co3O4@CoMoO4 at a current density of 0.5 A g(-1)) and excellent cycling stability (72% capacitance retention of Co3O4@NiMoO4 and 100% capacitance retention of Co3O4@CoMoO4 after 3000 cycles). To enhance energy density, the asymmetric supercapacitors were assembled where Co3O4@MMoO4 (M = Ni, Co) and activated carbon (AC) acted as the positive and negative electrodes, respectively. The maximum specific capacitance (128 Fg(-1) of AC//Co3O4@NiMoO4 and 105 Fg(-1) of AC//Co3O4@CoMoO4) and the specific energy 41.9 Wh kg(-1) of AC//Co3O4@ NiMoO4 and 38 Wh kg(-1) of AC//Co3O4@CoMoO4) are demonstrated for a cell voltage between 0 to 1.6V, exhibiting a high energy density and stable power characteristics. (C) 2014 Elsevier Ltd.
Hierarchical MoS2-coated three-dimensional graphene network for enhanced supercapacitor performances
3D Ni3S2 nanosheet arrays supported on Ni foam for high-performance supercapacitor and non-enzymatic glucose detection
3D Ni3S2 nanosheet arrays grown on Ni foam were successfully synthesized through a facile one-step hydrothermal approach and then directly applied as the electrode for a high-performance supercapacitor and non-enzymatic glucose sensor. The structure and morphology of the prepared Ni3S2 were characterized by X-ray power diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electronic microscopy (FESEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The subsequent electrochemical measurements showed that the Ni3S2 nanosheet array electrode possessed a superior specific capacitance of 1370.4 F g(-1) at a current density of 2 A g(-1). Remarkably, a specific capacitance of 952.0 F g(-1) could be still achieved at a high current density of 20 A g(-1), indicating its excellent rate capability. And 91.4% of the specific capacitance was retained after 1000 cycles at a current density of 6 A g(-1). Besides, to demonstrate its practical application, an asymmetric supercapacitor based on the Ni3S2 nanosheet array electrode as the positive electrode and activated carbon as the negative electrode was assembled. It delivered high energy density and good long-term stability. Additionally, serving as a non-enzymatic sensor, the 3D Ni3S2 nanosheet array electrode exhibited remarkable electrocatalytic activity towards glucose oxidation with a high sensitivity of 6148.0 mu A mM(-1) cm(-2). All these impressive performances suggest that the Ni3S2 nanosheet array is a promising electrode material for supercapacitors and non-enzymatic glucose sensors.
The synthesis of NiO and NiCo2O4 nanosheets by a new method and their excellent capacitive performance for asymmetric supercapacitor
Surfactant dependence of nanostructured NiCo2S4 films on Ni foam for superior electrochemical performance