|
|
Fabrication and Property of rGO/SiC Composite
HUANG Yi-Hua, JIANG Dong-Liang, CHEN Zhong-Ming, LIU Xue-Jian, ZHANG Xian-Feng, LIAO Zhen-Kui, HUANG Zheng-Ren
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1147–1153
 Abstract
Abstract(
1203 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(2037KB)(
1697
)
SiC ceramics have excellent mechanical properties, but its toughness is relatively low. To enhance the fracture toughness of SiC ceramics, graphene is introduced as fillers. In this study, the silicon carbide-reduced graphene oxide (SiC/rGO) composites with different contents of rGO were fabricated by hot press sintering (HP). Near fully-dense SiC/rGO composite was obtained after being hot-pressed under 2050℃, 40 MPa for 1 h. In addition, the influences of graphene reinforcement on the sintering process, microstructure, and mechanical properties (fracture toughness, bending strength, and Vickers hardness) of SiC/rGO composites were discussed. The three-point flexural strength of 4wt% rGO/SiC composite reached 564 MPa, and the fracture toughness reached 4.02 MPa•m1/2, which were 6% and 54% higher than those of hot-pressed SiC ceramics, respectively. The flexural strength of the three points of 6wt% rGO/SiC composite was 420 MPa, which was lower than that of hot-pressed SiC ceramics. While its fracture toughness was up to 4.56 MPa•m1/2, which was 75% higher than that of hot-pressed SiC ceramics. The results of crack propagation show that the toughening mechanism can be ascribed to crack deflection, crack bridging and rGO pullout.
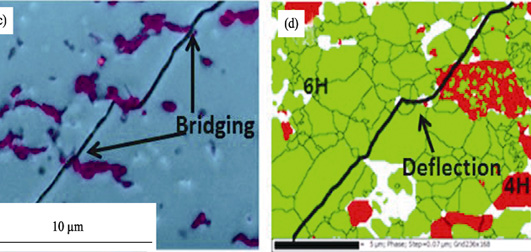
|
|
|
Fabrication of PEG Crosslinked Organosilica Hybrid Membranes for Reverse Osmosis Desalination
XU Rong, JIANG Wan, QI Lv, ZHANG Qi, ZHONG Jing
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1154–1160
 Abstract
Abstract(
1015 )
 HTML
HTML(
16)
 PDF
PDF(2159KB)(
1180
)
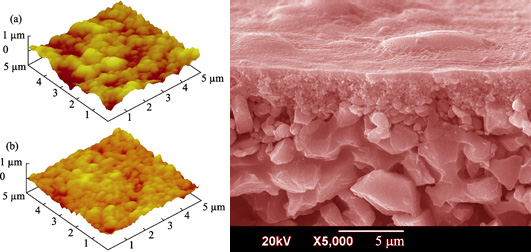
A series of poly(ethylene glycol)(PEG) crosslinked organosilica hybrid membranes were fabricated via co-polymerization with PEG as crosslinker and bis(triethoxylsilyl)ethane(BTESE) as the Si precursor, using porous α-Al2O3 membranes as the support. The membrane structure and physicochemical properties were characterized by atomic force microscopy (AFM), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) and water contact angle measurements (CA). The prepared BTESE/PEG hybrid membranes were applied to desalination by reverse osmosis (RO). The effects of PEG content, operating pressure, feed concentration, and operating temperature on RO performances of the membrane were investigated. Compared with the un-modified BTESE membrane, the BTESE/PEG hybrid membrane with an optimum PEG content of 10wt% exhibited higher water permeability and observed NaCl rejection in RO experiments. In addition, the observed NaCl rejection increased whereas the water permeability remained almost constant with an increase in operating pressure and a decrease in salt concentration. Moreover, the BTESE/PEG-10 membrane exhibited high hydrothermal stability in temperature cycles up to 70℃, always delivering high NaCl rejections of >97% and excellent water permeabilities of up to 1.2×10-12m3/(m2·s·Pa).
|
|
|
Preparation and Flexural Property of In-situ Vapor Grown Carbon Fibers Reinforced C/C Composites
YAN Ming-Yang, YANG Min, LI Hong, REN Mu-Su, YU Ming-Ming, SUN Jin-Liang
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1161–1166
 Abstract
Abstract(
792 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(3608KB)(
1113
)
The in-situ vapor grown carbon fibers (VGCFs) were synthesized by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on carbon felt and C/C composites of different densities, using propylene as carbon resources and FeCl3·6H2O as catalyst. And VGCFs-C/C composites were prepared on carbon felt and C/C composites of different densities with in-situ VGCFs. The effects of pressure in the reactor and density of the substrate on growth of VGCFs were investigated, and the morphology of in-situ VGCFs and the change of morphology of pyrolytic carbon on the substrate with in-situ VGCFs were observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and optical microscope. In addition, the flexural properties of C/C composites and VGCFs-C/C composites were investigated. Results show that low density of substrate is beneficial to the in-situ growth of VGCFs when the pressure in the reactor is 3700 Pa. In-situ VGCFs change the morphology of pyrolytic carbon, and induce the formation of the spherical structure, which can enhance the interface bonding force like nails doing. Therefore, the flexural strength of sample with high content of VGCFs is improved.
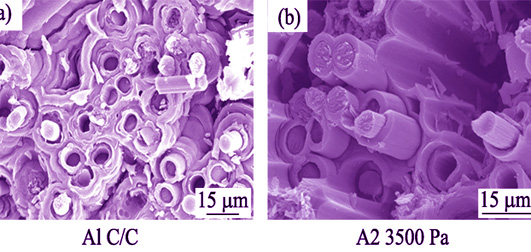
|
|
|
Grain Composition on Solid-state-sintered SiC Ceramics
XING Yuan-Yuan, WU Hai-Bo, LIU Xue-Jian, HUANG Zheng-Ren
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1167–1172
 Abstract
Abstract(
1200 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(9964KB)(
1585
)
Strengthening and toughening of dense solid-state-sintered SiC (S-SiC) ceramics was achieved by grain composition of coarse and fine SiC powder, whose median particle sizes were ~4.6 μm and ~0.5 μm, respectively. The fraction effects of coarse SiC powder on densification, microstructures, and mechanical properties of S-SiC ceramics were systematically investigated. High relative densities (higher than 98.3%) were successfully acquired for the S-SiC samples with the fraction of coarse powder less than 75wt%. The linear sintering shrinkage of SiC samples sharply decreased with increasing fraction of coarse powder, with the minimum fraction as low as 14.5%. Moreover, the coarse SiC powder significantly suppressed abnormal grain growth in S-SiC ceramics by Zener pining of grain boundaries. As a result, SiC grains became smaller and equiaxial, which was beneficial for obtaining high flexural strength for S-SiC ceramic. Meanwhile, the introduction of coarse SiC powder induced fracture mode transfer S-SiC ceramic from transgranular type to transgranular-intergranular mixture type, resulting in improved fracture toughness. The S-SiC ceramic added with 65wt% coarse powder achieved an increase of 14.0% in flexural strength ((440±35) MPa) and 17.1% in fracture toughness ((4.92±0.24) MPa·m1/2).
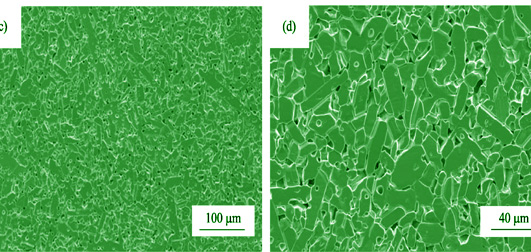
|
|
|
Characterization of Tetrahedral Amorphous Carbon Film with Various Thickness by High Through-put Method
WEI Jing, LI Han-Chao, KE Pei-Ling, WANG Ai-Ying
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1173–1178
 Abstract
Abstract(
847 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(2314KB)(
973
)
Materials Genome Initiative (MGI), which greatly accelerates the research and development progress of new materials with reduced cost, has received widespread attention in recent years. In this report, high-quality ta-C films with different thicknesses, ranging from 4.7 nm to 183 nm, were high through-put deposited by a home-built double 45° bent filtered cathodic vacuum arc system, which was realized by the control of carbon plasma beam and substrate position. Meanwhile, the effects of film thickness on surface roughness, microstructure, and carbon atomic bond were investigated by atomic force microscope, spectroscopic ellipsometry, Raman spectra and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Results show that the high through-put method by regulation of carbon plasma beam and selective placement of substrate enables to prepare ta-C films with various thicknesses. Particularly, the prepared ta-C films show almost constant smooth surface (Ra=(0.38±0.02) nm) and the value of Disp(G) regardless of the thickness changes, revealing the unchanged size of sp2 cluster and sp3 content with different thicknesses. Furthermore XPS results confirm that sp3 relative content is kept at (55±5)%. In addition, the optical band gaps of ta-C films with different thicknesses remain at (1.02±0.08) eV. These results could provide new insight into design and fabricate the controlled microstructure and optical property of ta-C film with different thicknesses.
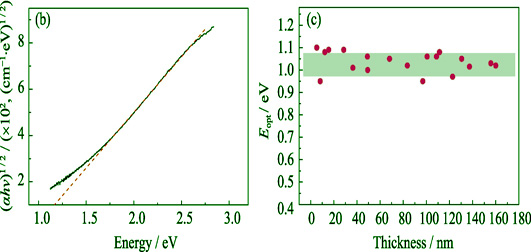
|
|
|
Preparation of Boron Nitride Coating from BCl3-NH3-H2-N2 Precursor by Chemical Vapor Deposition
WANG Meng-Qian, JIA Lin-Tao, LI Ai-Jun, PENG Yu-Qing, ZHANG Fang-Zhou
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1179–1185
 Abstract
Abstract(
1244 )
 HTML
HTML(
20)
 PDF
PDF(781KB)(
1822
)
Boron nitride (BN) coatings were prepared using BCl3-NH3-H2-N2 precursor system by chemical vapor deposition process in a vertically-placed hot wall reactor. The effect of processing parameters on the deposition rates was analyzed. The morphology and microstructure of the BN coating on the surface of the silicon carbide fiber were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) . The dominant gas-surface reactions and crucial gas-phase components during BN deposition process were established. The results show that the deposition rates of BN increase gradually with the elevating deposition temperature from 600℃ to 850℃. And at a defined temperature, the deposition rates of BN gradually decrease along the gases flow direction in the deposition area, indicating that the gas-phase components are gradually consumed along the gases flow direction. The deposition rates of BN increase firstly and then decrease with the increase of system pressures, which suggests that the deposition process change from surface reactions control to mass transfer control. The BN deposition rates increase at 1-3 cm away from gases inlet, but decrease after increase firstly at 4-5 cm away from gases inlet as the residence time getting longer. SEM results show that BN coating on the surface of silicon carbide fiber is relatively smooth and dense. The chemical compositions of coating determined by XPS are BN and B2O3. XRD results indicate that the deposited BN at 650℃is amorphous. After heat-treatment at 1200℃ for 2 h, it transformed into the hexagonal BN(h-BN). The deposition of BN is achieved by the intermediate gas-phase species composed of Cl2BNH2, ClB(NH2)2 and B(NH2)3 which were generated by the reaction of BCl3 and NH3.
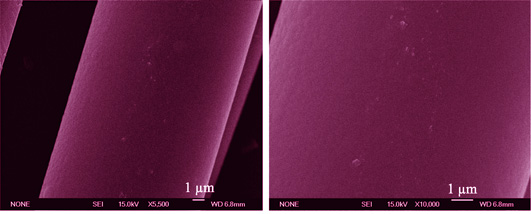
|
|
|
High-surface-area Magnesium Fluoride: Preparation by Template Method and Catalytic Activity for the Dehydrofluorination of HFC-152a
DING Shan-Shan, CHEN Xin-Xin, LI Yu-Zhen, HAN Wen-Feng, LV De-Yi, LI Ying, TANG Hao-Dong
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1186–1192
 Abstract
Abstract(
1103 )
 HTML
HTML(
16)
 PDF
PDF(2035KB)(
1287
)
Magnesium-based solid acid catalysts exhibit satisfactory catalytic performance for the preparation of fluorocarbons. In the present study, magnesium fluoride with high surface area was obtained by template method. The influences of SiO2 template doping amount on phase structure, porosity, and surface acidity of MgF2 were investigated. Physical and chemical properties of the as-prepared MgF2 were characterized by N2 physical adsorption-desorption iso-therms, X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), NH3-temperature programmed desorption (NH3-TPD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS). The catalytic performance was evaluated for the dehydrofluorination of 1,1-difluoroethane (HFC-152a, CH3CHF2) to vinyl fluoride (VF, CH2=CHF). Results show that the doping amount of SiO2 template plays a major role in the specific surface area, crystal size and acidity of MgF2. With the presence of 14 mol% SiO2 template in the Mg(CH3COO)2 and NH4F solution, the derived MgF2 possesses a specific surface area as high as 304 m2/g, which is almost 2.5 times higher than that of MgF2 prepared without SiO2 template. In addition, with suitable doping amounts of SiO2 template, smaller crystal sizes and under-coordinated sites (five-fold and four-fold coordination Mg species) are derived. Consequently, with enhanced amounts of under-coordinated sites, acidic sites (Lewis acid) of MgF2 are improved significantly. As the dehydrofluorination of 1,1-difluoroethane catalyzed by Lewis acid, as a result, the conversion of 1,1-difluoroethane is increased dramatically. In summary, it is confirmed that template method with SiO2 as the template is an effective route for the fabrication of MgF2 catalyst.
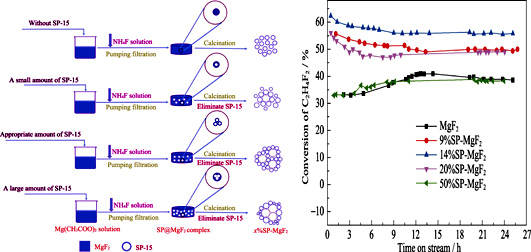
|
|
|
Hierarchical ZSM-5 Zeolite: Preparation by Sequential Desilication-dealumination and Catalytic Performance in Methanol to Gasoline Reaction
WANG You-He, WANG Xiao-Dong, XU Jing-Wei, SUN Hong-Man, WU Cheng-Cheng, YAN Zi-Feng, JI Sheng-Fu
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1193–1200
 Abstract
Abstract(
959 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(3219KB)(
1383
)
Hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites were prepared by desilication and sequential desilication-dealumination using commercial ZSM-5 zeolite as raw material. The samples were characterized with XRD, FT-IR, SEM, TEM, and N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms. The catalytic performance was investigated in methanol to gasoline (MTG) reaction. The results indicated that the hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite catalysts with abundant intracrystalline meso- and macropores could be prepared by desilication or sequential desilication-dealumination treatment. Compared with commercial ZSM-5 zeolite, the hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites had higher mesopore surface area, larger mesopore volume and higher accessibility index, but with less acid amount and lower acid strength. The results of catalytic performance evaluation showed that the gasoline yield and lifetime of hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite catalysts were significantly enhanced after modification. Simultaneously, the yield of aromatic hydrocarbon was reduced. Compared with the sample prepared by the desilication treatment, physicochemical properties and catalytic performance of the hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite prepared by sequential desilication-dealumination treatment were improved.
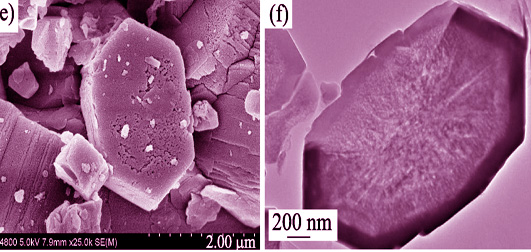
|
|
|
Adsorption of Enzyme for Sulfur Mustard Decontamination by Mesocellular Foam
ZHENG He, ZHONG Jin-Yi, LIU Jing-Quan, ZHANG Zhe, CUI Yan, ZHENG Yong-Chao
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1201–1207
 Abstract
Abstract(
946 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(1012KB)(
1551
)
With polyoxyethylene-polyoxypropylene-polyoxyethylene (P123) as template, 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (TMB) as swelling agent and tetramethoxysilane (TEOS) as silica source, mesocellular foam (MCF) with three dimensional (3D) cage-like mesopores linked by windows was successfully synthesized by hydrothermal method. N2 isothermal adsorption characterization indicated that the largest pore size was 17.3 nm, and the other structural parameters as window size, specific surface area and pore volume were 8.2 nm, 770.3 m2/g, 2.3 cm3/g, respectively. MCF was employed as carrier for adsorption of DhaA which is an enzyme for sulfur mustard decontamination. The effect of pH to saturated adsorption capacity of DhaA in MCF was studied and the results showed that the largest loading amount of DhaA was achieved at pH 6.5. The adsorption kinetics followed Elovich kinetic model very well, and rate-determining step of this adsorption process was intraparticle diffusion. Adsorption isotherm curve of DhaA matched Sips model. The catalytic activity and conformation of DhaA changed obviously after being adsorbed in MCF. The residual activity of DhaA was 12.4% after being adsorbed, and the intrinsic fluorescence spectrum was found red shift. From the experimental results it can be observed that the big pore size, large specific surface area, and 3D cage-like structure of MCF facilitated the adsorption of DhaA, The electrostatic repulsion between DhaA and MCF influenced the adsorption process, and the conformation change of DhaA was the major factor of the decreased catalytic activity.
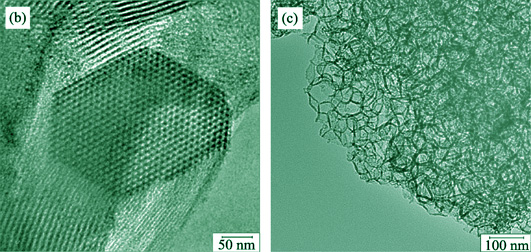
|
|
|
Electrochemical Performance of Bi2WO6/CNOs Nanocomposites Synthesized via a Hydrothermal Method
WANG Jia-Wei, YANG Yan-Qing, GAO Ze-Yu, LIANG Ying, DENG Chuan, ZHANG Wei-Ke
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1208–1212
 Abstract
Abstract(
774 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(723KB)(
1891
)
In order to enhance the performance of supercapacitor and reduce environmental pollution as far as possible, electrode materials especially low-cost and eco-friendly electrode materials with high energy density have attracted a great deal of attention. In this paper, Bi2WO6/CNOs (CNOs, Carbon Nano Onions) and Bi2WO6 nanocomposites have been synthesized via a hydrothermal method. And the structures and morphologies of samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The electrochemical performances of the as-prepared samples were investigated by cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge - discharge measurements and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. At a current density of 2 mA·cm-2, the specific capacitance of the Bi2WO6/CNOs and Bi2WO6 was 328 F·g-1 and 218 F·g-1 with 1 mol·L-1 KOH served as electrolyte, respectively. After 300 charge-discharge cycles at a current density of 5 mA·cm-2, the specific capacitance of the Bi2WO6/CNOs improved 34.37% compared with pure Bi2WO6. Thus, CNOs can enhance the electrochemical performance of Bi2WO6 obvously.
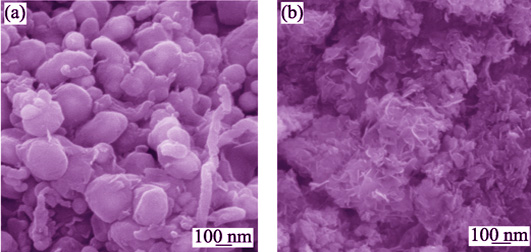
|
|
|
Synthesis and Photoelectrocatalytic Performance of Sb2S3 Nanorods from Natural Stibnite
JIA Si-Qi, JIANG Zheng, CHI Li-Na, YE Ying, HU Shuang-Shuang
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1213–1218
 Abstract
Abstract(
925 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(4625KB)(
2121
)
Antimony trisulfide (Sb2S3) nanorods were successfully synthesized via hydrothermal method with the assistance of polyethylene glycol (PEG) and N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), using natural stibnite as precursor. The effects of experimental parameters on the morphology and the properties of the obtained Sb2S3 were systematically studied, and the possible formation mechanism of Sb2S3 nanorods in the preparation process was also discussed. Phase, compositions, morphology and photoelectric properties of the products were investigated by a series of characterization methods. The photocatalytic activity of nano Sb2S3 on the degradation of methyl orange were investigated under the visible light irradiation. The results showed that the Sb2S3 nanoflakes formed after hydrothermal synthesis at 160℃ for 12 h, and the nanoflakes would transform into nanorods eventually after N2-annealing at 400℃ for 1 h. The obtained Sb2S3 nanorods with a single crystal structure are typically 2~3 μm in length, 100~200 nm in width, which are direct semiconductor with band gap of 1.66 eV. Photocatalytic degradation rate of the obtained Sb2S3 nanorods on methyl orange under visible light irradiation is higher than that of commercial Sb2S3, which is up to 87.6% after 60 min degradation, exhibiting obvious visible-light activity.
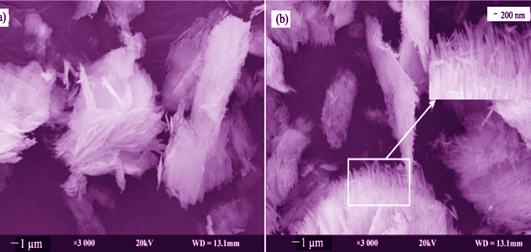
|
|
|
Environmental Stable SiO2 Antireflective Coating Modified via NH3/HTMS Vapor Phase Treatment
ZHAO Hui-Yue, WANG Xiao-Dong, FENG Jian-Bin, LIU Yuan, HUANG Ji-Chen, SHEN Jun
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1219–1224
 Abstract
Abstract(
905 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(2247KB)(
1150
)
Sol-Gel derived silica antireflective coatings have been widely used in high power laser system because of their ultra-low refractive index and high laser damage threshold. However, water vapor and volatile organic compounds in the laser system contaminate these coatings and reduce their antireflective efficiency and laser damage resistance. In this work, environmental stable SiO2 antireflective coating was prepared by vapor phase treatment of ammonia and HTMS. Monodisperse colloidal silica sol was synthesized by Sol-Gel method using tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) as precursor, ammonia as catalyst, and ethanol as solvent. The silica coatings were then deposited on the BK7 glass using dip-coating method. Ammonia vapor phase treatment and HTMS vapor phase treatment were combined to improve the environmental stability of the antireflective coating. The peak transmittance of the BK7 glass coated with the modified coating decreased only 0.03% after being exposed in the humid environment for 2 m. Meanwhile, the transmittance curve of the BK7 glass coated with modified coating had almost no change after being placed under low vacuum condition with oil pollutants for 2 m, indicating that the coating modified via combined vapor phase treatment of ammonia and HTMS possessed an excellent environmental stable performance. Therefore, the combination of ammonia and HTMS vapor phase treatment is effective to improve the working life of SiO2 antireflective coating in high power laser system.
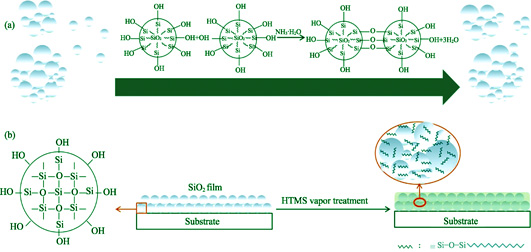
|
|
|
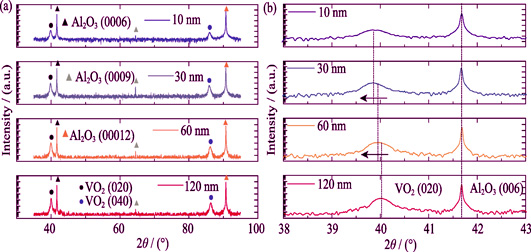
Stress Induced Modulation of the Structure and Photoelectric Property of Vanadium Oxide Films on Sapphire Substrate
ZHANG Cong, KANG Chao-Yang, ZONG Hai-Tao, LI Ming, LIANG Shan-Shan, CAO Guo-Hua
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1225–1231
 Abstract
Abstract(
889 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(1081KB)(
1981
)
VO2 thin films with different thicknesses were deposited on sapphire substrates by pulsed laser deposition. Structure, surface morphologies and photoelectric properties of the films were characterized. The results indicated that the Monoclinic-VO2 thin films deposited on the sapphire substrates were high quality poly-crystalline stoichiometric with no detectable impurities, and the sheet resistance changed up to 3-4 orders of magnitude and the transmittance at 2500 nm up to 56% across metal-insulator transition (MIT). The optimized integral luminous transmittance (Tlum) and solar regulation rate (∆Tsol) were 43.2% and 8.7%, respectively. The stress on the interface had important influence on the VO2 thin film, and the photoelectric properties of VO2 thin films could be regulated by adjusting the film thickness. When the VO2 film was thinner, the film was subjected to tensile stress, which could significantly reduce the phase-change temperature, and the increase of the carrier concentration as well as carrier mobility accounted for the decrease of electrical resistance across the MIT. While the VO2 film was thicker, the film was subjected to compressive stress and the phase transition temperature of VO2 film was close to that of body VO2. The increase of the carrier concentration accounted almost entirely for the decrease of electrical resistance and the change in mobility had little contribution to the MIT.
|
|
|
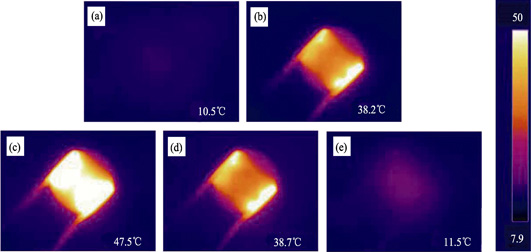
Preparation and Performance of Reduced Graphene Oxide Functionalized Flexible and Multicolor Electrothermal Chromatic Films
ZHANG Bin, HOU Cheng-Yi, WANG Hao-Peng, WANG Zhi-Qiang, BAI Yu-Miao, LI Qiang, ZHANG Qing-Hong, LI Yao-Gang, WANG Hong-Zhi
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1232–1236
 Abstract
Abstract(
712 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(2538KB)(
1173
)
By using a chemical oxidation-reduction method, reduced graphene oxide (RGO) nanomaterials were synthesized. The powder materials were further dispersed in water and filtered to form a RGO film, which was used as a conductive layer. On the other side of the filter paper, a color changing layer was prepared through screen printing. A multicolor (red-blue-white and orange-yellow-white, etc.) and flexible electrothermal chromatic film was then obtained through combining conductive and color changing layers with protecting substrates. The structural properties of the film (red-blue-white) were analyzed by using SEM, XRD and Raman, etc. Their thermal and color-changing properties were studied by using infrared thermal imaging and absorption spectrum. The results show that when surface temperature of the film reaches 38℃ (within 3.4 s under Joule heat treatment at ambient conditions), it turns blue. Further heating to 45℃ (within 6.3 s under Joule heat treatment), it turns white. The multi-color changes are achieved at low working voltage (6 V). After switching off the voltage, the film restores its original color within 9.2 s. The electrothermal chromatic films have good flexibility too, therefore, they might be applied in wearable displays.
|
|
|
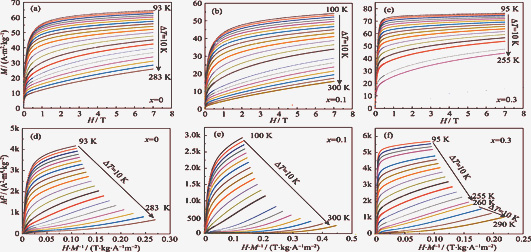
Electromagnetic Property of Co-doped La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 Perovskite Manganese Oxides
LIU Jiao, WANG Wen-Qing, WU Hong-Ye, TIAN Ye, CAO Feng-Ze, ZHAO Jian-Jun
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1237–1247
 Abstract
Abstract(
796 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(1843KB)(
1493
)
La0.8Sr0.2Mn1-xCoxO3 (x = 0, 0.1, 0.3) samples were prepared via the conventional high-temperature solid-state reaction method. The effects of Co doping on Griffiths phase, magnetic entropy change, critical behavior, and electrical transport properties of La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 (LSMO) polycrystalline samples were systematically investigated. Results show that the prepared polycrystalline samples all have rhombohedral symmetry structures with Griffiths phase above the low temperature magnetic transition temperature (TC2). When magnetic field is applied to the La0.8Sr0.2Mn1-xCoxO3 (x = 0, 0.1, 0.3) samples, the maximum magnetic entropy change ΔSmax for 7 T is -2.88, -2.05, and -2.75 J/(kg·K), respectively. Doping of Co element makes ΔSmax decrease first and then increase. The critical behavior of the parent phase fits best with the mean field model, and that of the sample after doping fits best with the 3D Heisenberg model. The mother phase is a semiconductor material, and the metal insulator transition appears near the low temperature magnetic transition temperature (TC2) when the Co element doping amount reaches 0.1. The conductivity of the three samples in high temperature region satisfies the small polaron model.
|
|
|
Effect of Excessive Nb2O5 on the Sintering and Electrical Property of Lead Metaniobate Piezoelectric Ceramics
XIA Biao-Jun, ZHOU Zhi-Yong, DONG Xian-Lin
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1248–1252
 Abstract
Abstract(
907 )
 HTML
HTML(
16)
 PDF
PDF(1850KB)(
1426
)
PbNb2O6-xmol%Nb2O5 (PN-x=0, 5, 10, 15, 20) Piezoelectric ceramics were prepared by solid-state reaction method. The effects of excess Nb2O5 on the sintering and electrical properties of PbNb2O6 ceramics were investigated. The sintering and electrical properties were evidently improved after the addition of Nb2O5 into PN in the condition set for a high Tc and high coupling anisotropy. The improvement may originate from NbO6 octahedral distortion by excess Nb2O5, which prevents phase transition from rhombohedral to tetragonal during the sintering process. With excess addition of Nb2O5, the piezoelectric coefficient (d33) and relative density of PN ceramics increased and reached up to 69 pC/N and 93.1%, respectively, at 5mol% addition of Nb2O5.
|
|
|
Growth and Characterization of All-inorganic Perovskite CsPbBr3 Crystal by a Traveling Zone Melting Method
XU Jia-Yue, LIANG Xiao-Xiao, JIN Min, ZENG Hai-Bo, KIMURA Hideo, HU Hao-Yang, SHAO He-Zhu, SHEN Hui, TIAN Tian, LI Hai-Xia
2018 Vol. 33 (11): 1253–1258
 Abstract
Abstract(
2075 )
 HTML
HTML(
45)
 PDF
PDF(1202KB)(
2093
)
A self-designed traveling zone melting method was employed to fabricate perovskite CsPbBr3 crystals, which is helpful for impurities removing and moisture excluding. A large-size CsPbBr3 crystal with a dimension of ϕ 25 mm× 60 mm is successfully obtained. The as-grown crystal shows orange color and displays an excellent transmittance of 78.6% in the range of 600 nm - 2000 nm wavelength. It is revealed by DSC analysis that there is phase transition at 88.1℃ and 131.25℃, respectively. The band gap Eg of the crystal is calculated to be 2.25 eV. The above results prove that the traveling zone melting method is indeed a potential approach for large size and high quality CsPbBr3 crystal preparation.
|
|