|
|
Recent Advances in the High Performance BiOX(X=Cl, Br, I) Based Photo-catalysts
LIU Jia-Qin, WU Yu-Cheng
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1009–1017
 Abstract
Abstract(
1638 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(637KB)(
5196
)
Bismuth-based semiconductor of BiOX(X=Cl, Br, I) has proved to be a new promising photocatalytic material due to its unique layered crystal structure and suitable band gaps, which exhibits superior photocatalytic performance and high stability. In this review, some key scientific topics in terms of photocatalysis of BiOX(X=Cl, Br, I) were firstly addressed, then the effective modification methods were comprehensively summarized, including microstructure adjustment, heterojunction construction, noble-metal deposition, doping, surface sensitization, etc. In addition, the research progress in catalyst immobilization by loading nano-structured BiOX(X=Cl, Br, I) onto appropriate carriers were also reviewed. Generally, this review presents the most recent advances of high performance of the BiOX(X=Cl, Br, I) based photocatalysts in depth and also prospects the research trend of the BiOX(X=Cl, Br, I) catalyst.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Porous g-C3N4 Loaded With Highly Dispersed PANI by Interfacial Polymerization and Its Photocatalytic Performance
LI Xian-Hua, ZHANG Lei-Gang, WANG Xue-Xue, YU Qing-Bo
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1018–1024
 Abstract
Abstract(
966 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(594KB)(
2107
)
Polyaniline (PANI) was successfully loaded on porous graphitic carbon nitride (porous g-C3N4) by interfacial polymerization of aniline monomers. The structure, morphology and properties of the prepared samples were characterized by XRD, FTIR, SEM, TGA, UV-Vis and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscope (EIS). Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue was investigated to determine the photoactivity of the catalyst. The porous g-C3N4 showed good dispersion and interfacial adhesion to PANI, which improved the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and thermal stability. The improved photocatalytic activity could be attributed to the improved visible light utilization, oxidation power and electron transport property.
|
|
|
Preparation of RuO2/ZrO2/TaON Composite Photocatalyst and Its Photocatalytic Properties for Water Splitting Hydrogen Evolution
GUO Dong-Xue, ZHANG Qing-Hong, WANG Hong-Zhi, LI Yao-Gang, CAO Guang-Xiu
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1025–1030
 Abstract
Abstract(
990 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(530KB)(
2061
)
ZrO2/Ta2O5 composite oxide powders in a fine particle size were prepared by the controlled hydrolysis method, and subsequently nitrided in a flowing ammonia at a flow rate of 90 mL/min at 850℃ for 10 h, to form ZrO2/TaON. Then, RuO2 co-catalyst was immobilized on the ZrO2/TaON via an impregnation method. The samples were characterized with XRD, SEM, TEM and UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectroscope. Both ZrO2 and RuO2 were in a crystallite size of ca. 10 nm, while TaON was in a crystallite size of ca. 25 nm, and composite photocatalysts absorbed the visible light at wavelength less than 500 nm. The introducing of ZrO2 reduced the defect density of TaON and increased the specific surface area of TaON. The photocatalytic efficiency of composite photocatalysts was quantitatively evaluated via determining the photo-current density as well as in the water splitting hydrogen evolution reaction. The sample with a RuO2 loading of 2.0wt% showed the photocurrent of 0.6 mA/cm2 at a bias voltage of 0.6 V, and H2 evolution rate as high as 6.0 μmol/h under a Xe lamp irradiation.

|
|
|
Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of La2CoFeO6 Bamboo-like Hollow Nanofibers
BI Jun, WU Yan-Bo, ZHAO Heng-Yan, WEI Bin-Bin
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1031–1036
 Abstract
Abstract(
792 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(443KB)(
1809
)
La2CoFeO6 bamboo-like hollow nanofibers photocatalytic material was successfully prepared by electrostatic spinning. La2CoFeO6 nanofibers, which were connected to each other by rhombic La2CoFeO6 nanoparticles, had stable one-dimensional structure and clear bamboo-like hollow structure. The specific surface area of as-prepared inorganic nanofibers reached 98.7 m2/g. La2CoFeO6 nanofibers had a high utilization for natural light and its band gap was 1.6 eV. When concentration of methyl orange was 10 mg/L with pH of 2 and the dosage of La2CoFeO6 nanofibers was 1.5 g/L, methyl orange was degraded by La2CoFeO6 nanofibers within 2 h under natural light at 96.9%.
|
|
|
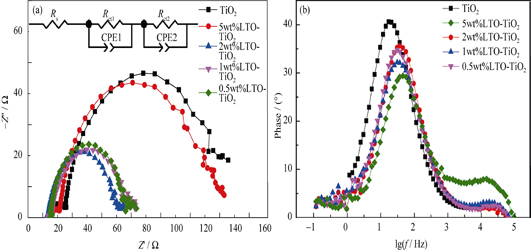
Hybrid Photoanodes Based on Nanoporous Lithium Titanate Nanostructures in Dye-sensitized Solar Cells
HU Xue-Mei, GU Zheng-Ying, LI Xiao-Min, GAO Xiang-Dong, SHI Ying
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1037–1042
 Abstract
Abstract(
687 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(596KB)(
1552
)
Li4Ti5O12 with nanoporous feature and good conductivity was used to enhance the photoelectrochemical performance of traditional nanocrystalline TiO2 photoanodes in Dye-sensitized Solar Cells (DSSC). Using tetrabutyl titanate and lithium hydroxide as raw materials, the spinel Li4Ti5O12 was obtained from common Sol-Gel, solvethermal and annealing processes. The dependence of the crystallinity, morphology and pore structure of the Li4Ti5O12 powders on the annealing temperature were investigated. Li4Ti5O12-TiO2 hybrid photoanodes were prepared by the doctor-blade method using the slurry of TiO2 nanocrystallite which was blended with Li4Ti5O12 powders. The effects of the mass ratio of Li4Ti5O12 to TiO2, the crystallinity and the porous structure of Li4Ti5O12 powders on the performance of DSSC were examined. Results show that with the annealing temperature increasing, the crystallinity of the Li4Ti5O12 powders is enhanced, the crystallite size increased obviously, and the specific surface area decreased dramatically. The Li4Ti5O12-TiO2 hybrid photoanodes exhibit higher dye-loading capacity and lower resistance at TiO2/dye/electrolyte interface than does the pure TiO2 counterpart, accompanied by higher Jsc (Jsc=13.91 mA/cm2) and Voc(Voc =0.8 V) values than by the TiO2 photoanode. The highest conversion efficiency (7.011%) is achieved by 1wt% Li4Ti5O12 hybrid cell, which is 30% higher than by the TiO2 nanocrystallite counterpart (5.384%).
|
|
|
Optimization Rule of Anode Materials for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
CHANG Xi-Wang, CHEN Ning, WANG Li-Jun, BIAN Liu-Zhen, LI Fu-Shen, CHOU Kuo-Chih
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1043–1048
 Abstract
Abstract(
690 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(441KB)(
1803
)
Based on the first principle total energy calculation method, the structural stability, electronic performance as well as mechanical properties of the 3rd-6th period metals and their oxides, potential to be used as anode material for solid oxide fuel cells, were studied. Considering anode working condition (high temperature and reduction atmosphere), transformation of anode structure and its performance were analyzed, and the tendencies of bulk modulus and band gap of metal/oxide were obtained. The results indicated that the metal/oxides stabilized in middle area of the formation tendency diagram would be easy to take part in oxidation/reduction reactions, and therefore suitable for anode working environment. The element which was close to metal region could introduce electronic conduction and improve the catalytic performance, while the ones near the oxides region could enhance the anode stability. These results may benefit for selection of anode materials according to various anode working conditions.

|
|
|
Structural and Electrochemical Properties of A2B7-type La1-xScxNi2.6Co0.3Mn0.5Al0.1 (x = 0~0.5) Hydrogen Storage Alloys
MEI Xing-Zhi, LUO Yong-Chun, ZHANG Guo-Qing, KANG Long
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1049–1055
 Abstract
Abstract(
838 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(596KB)(
1679
)
A2B7-type La1-xScxNi2.6Co0.3Mn0.5Al0.1(x = 0-0.5) hydrogen storage alloys were prepared by vacuum arc melting method and annealed at 1173 K. XRD and SEM-EDS results showed that the annealed alloys mainly consisted of La2Ni7, LaNi5, LaNi, and ScNi2 phases. The enthalpy of formation calculation analyses showed that the enthalpy of formation of binary alloy of Sc-Ni was more negative than that of La-Ni and Mg-Ni. This was one of the main reasons that the phase rule of Sc-contained alloy was different from Mg-contained alloy, which facilitated forming ScNi2 phase. The electrochemical measurement results showed that the discharge capacity and the cycle stability of the alloys were all firstly increased and then decreased with the x value increasing. The discharge capacity and cyclic stability (S100) of alloy electrodes reached the maximum of 261.1 mAh/g and 80.47%, respectively, when x value was equal to 0.2. The appropriate amount of Sc in alloy could obviously inhibit the hydrogen-induced amorphous, meanwhile the alloy with Sc content also tends to form the non-hydrogen absorbing ScNi2 phase, which is the main reason that the discharge capacity of alloy electrode is not significantly improved.

|
|
|
Influences of CuAl2O4 Doping on the Dielectric Properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 Ceramics
LI Jian-Ying, HOU Lin-Lin, JIA Ran, GAO Lu, WU Kang-Ning, LI Sheng-Tao
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1056–1062
 Abstract
Abstract(
746 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(588KB)(
1378
)
The influences of CuAl2O4 doping on the microstructure and dielectric relaxation of CaCu3Ti4O12 (CCTO) ceramics were investigated. The dielectric properties were measured in the frequency from 10-1 Hz to 107 Hz under the temperature from 153 to 453 K. It was found that reduced CCTO grains as well as improved microstructure were achieved by addition of 30mol%-50mol% CuAl2O4. When sintered at 1100℃ for 4 h, enhanced electric breakdown field of 13 kV/cm was obtained with 50mol% CuAl2O4 addition, while its dielectric loss at low frequency was greatly suppressed. Three energy levels of dielectric relaxation processes were found. It is suggested that energy level 1 eV of ~0.10 eV, corresponding to high frequency relaxation and barely varied with CuAl2O4 addition, is attributed to the intrinsic electronic relaxation. Energy level 2 decreased from 0.50 eV to 0.22 eV with increased additional CuAl2O4, possibly resulted from multi impurities and boundaries. The energy level of conduction process rose from 0.66 eV to 0.86 eV with increased CuAl2O4 addition, which can be attributed to the block effect of more grain boundaries. In addition, the excessive content CuAl2O4 resulted in collapse of grain boundary barrier, leading to the vanish of non-ohmic properties and high dielectric constant.

|
|
|
Horizontal Zone Refining of Indium Iodide (InI) Polycrystal
XU Zhao-Peng, ZHANG Lei, WANG Qian, JI Liang-Liang, LI Ya-Ke
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1063–1068
 Abstract
Abstract(
829 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(449KB)(
1911
)
The indium iodide (InI) polycrystal which was synthesized by two-zone vapor transporting method was purified by using horizontal zone refining method. Preparation process on high quality and single phase InI polycrystal was successfully fixed. The lattice structure, morphology, component and impuritily concentration of InI crystal were investigated by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscope-Energy Dispersive Spectrometer (SEM-EDS) and Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry (ICP-AES). The results indicate that the InI polycrystal after refinement has better lattice structure and higher quality than before. The lattice constants of a, b and c are 0.476 nm, 1.278 nm and 0.491 nm, respectively, which are very close to the theoretical values. The stoichiometric ratio of In to I is effectively modified and close to the theoretical stoichiometric ratio 1:1. The intermediate products and impurities concentrations decrease significantly. An InI single crystal with high resistivity (about 1010 Ω·cm) is grown by Czochralski (CZ) method with the purified InI polycrystal obtained in this work.

|
|
|
In-situ Transformation of Borate Glass and Its Effect on pH of Soaking-liquid
ZHU Kai-Ping, WANG De-Ping, FAN Hong-Yuan, WANG Hui, YAO Ai-Hua, YE Song
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1069–1074
 Abstract
Abstract(
685 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(508KB)(
1648
)
The Na-Ca-B glass microspheres with composition of 10Na2O-10CaO-80B2O3(wt%) and 19Na2O-17CaO- 64B2O3(wt%) were prepared (denoted by S1 and S2, respectively) by flame spray ball method. The in-situ transformation of the microspheres into hollow hydroxyapatite(HA) and the influence on the pH value of the soaking-liquid were investigated by using pH meter, XRD, SEM, SEM-EDS, FTIR and BET measurements. In addition, the vancomycin was used as model drug to further investigate the sustained-release performance of hollow HA. The results indicate that S1-HA has larger cavity volume and better drug loading performance with 13.5 mg/g and 16.8% for its drug loading amount and efficiency, respectively. S2 microspheres can greatly influence the pH value of the soaking-liquid. Meanwhile, S2-HA present remarkable multilayered structure and better sustained-release performance with the release time of 60 h.
|
|
|
Titanium Modification by Calcium Ion Chelated Polydopamine and Its Cytocompatibility
TAN Guo-Xin, OUYANG Kong-You, ZHOU Lei, LIU Yan, ZHANG Lan, NING Cheng-Yun
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1075–1080
 Abstract
Abstract(
1158 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(1095KB)(
2235
)
Calcium ions chelation platform was successfully obtained on a titanium surface by modification with polydopamine. The chelation mechanism of polydopamine with Ca2+ was studied. The in vitro bioactivity and cytocompatibility of Ca2+ chelation platform was assessed by incubation in simulated body fluids (SBF) and cultural osteoblast cells (MC3T3-E1), respectively. The results showed that the functional groups of polydopamine chelated Ca2+ were changed from phenolic hydroxyl to benzoquinone. The titanium surface modified by Ca2+-chelated polydopamine could induce nucleation and growth of hydroxyapatite in SBF. Meanwhile, Cell attachment and viability assay demonstrated that low concentration of Ca2+ chelation possessed good cytocompatibility.
|
|
|
A Low-cost Preparation of SiO2 Aerogel Monoliths from Silica Sol
ZHAO Jing-Jing, SHEN Jun, ZOU Li-Ping, WANG Wen-Qin, ZU Guo-Qing, ZHANG Zhi-Hua
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1081–1084
 Abstract
Abstract(
983 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(328KB)(
29471
)
Porous monolithic SiO2 materials were prepared via ambient pressure drying process with low cost silica sol as precursor and water as solvent. Cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) was used as the surface modifier to get rid of the cumbersome process of solvent substitution which was necessary in the traditional ambient drying process. The densities, specific surface area and the average pore size of the obtained SiO2 monoliths are in the range of 150-260 mg/cm3, 91-140 m2/g and 15-27 nm, respectively. The thermal conductivity was as low as 0.048 W/(m·K) at room temperature. This method greatly reduced the preparation cost as well as the operation difficulty and risk, which will largely promote the industrial production and application of porous SiO2 materials.
|
|
|
Effect of Water-soluble Epoxy Resin on Microstructure and Properties of Porous Alumina Ceramics by Gel-casting
ZHANG Xiao-Qiang, SUN Yi, SHIMAI Shun-Zo, WANG Shi-Wei
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1085–1088
 Abstract
Abstract(
1065 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(319KB)(
1754
)
Porous alumina ceramics with high porosity were fabricated by gel-casting and mechanical foaming. Here, PIBM, a co-polymer of isobutylene and maleic anhydride, was used as both dispersant and gelling agent, and two kinds of surfactants were selected as the foaming agent. Then, the effect of DE211 (a water-soluble epoxy resin) on the microstructure and properties of porous alumina ceramics were studied systematically. The results showed that porous alumina ceramics with maximum porosity up to 92.4% was achieved by this method. With addition of DE211 epoxy resin from 0 to 0.5wt%, porosity of porous alumina ceramics slightly decreased and mean pore size decreased from 582 μm to 331 μm, but compressive strength increased from 0.5 MPa to 3 MPa. Besides, there is hardly collapse of cell wall in the porous ceramics. These results are ascribed to the reaction between epoxy group of DE211 and anhydride of PIBM that enhanced the gelling rate and stabilized the foam structure.
|
|
|
TiN and TiSiN Coated Al2O3/TiCN Ceramic Cutting Tools and Their Cutting Performance
ZENG Jun-Jie, LIU Wei, LONG Ying, GU Shang-Xian, LI An-Qiong, WU Shang-Hua
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1089–1093
 Abstract
Abstract(
872 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(367KB)(
3044
)
The TiN, TiSiN coatings were deposited on Al2O3/TiCN matrix by physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique. The microstructure, hardness and adhesion evaluation of the coatings were studied by scanning electron microcope (SEM), micro-hardness tester and scratch test, respectively. Turning tests were carried out on both uncoated and coated tool in gray cast iron turning under dry environment. Cutting performance, wear mechanism and machining quality of the uncoated and coated matrix were investigated. The results show that PVD-TiN and TiSiN coating can distinctly improve the hardness of cutting tool by 25% and 65%, respectively, leading to the tool life being enhanced. The dominant wear mechanism of TiN and TiSiN coated tools after turning tests were abrasion, meanwhile TiN coated tool was accompanied by adhesive wear. Compared with the un-coated tools, the PVD coated tools showed no chipping and significant improvement in surface roughness of the finish parts.
|
|
|
High Resolution X-ray Diffraction Analysis of Defect Density of Gallium Nitride Epitaxial Layer
CUI Ying-Xin, XU Ming-Sheng, XU Xian-Gang, HU Xiao-Bo
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1094–1098
 Abstract
Abstract(
1365 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(380KB)(
5206
)
The measurement of dislocation densities in heteroepitaxial semiconductor GaN film is important for the developement of blue light-emitting diodes, laser diode and high temperature, high-frequency electronic devices. As there is no matching substrate material, GaN thin films prepared by epitaxial growth often contain a large number of defects, most of which are edge dislocations. High resolution X-ray diffraction method and the mosaic model were used to measure and analyze the dislocation density of GaN film fabricated by metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) on a 4H-SiC substrate with an AlGaN buffer layer. The crystal face tilting angle, in-plane twisting angle, grain size and crystal bending radius were investigated by symmetry and oblique symmetry diffraction methods. By eliminating the instrumental broadening width (mainly the incident beam divergence), grain size and wafer curvature influenced on the contribution to the full width at half maximum of rocking curves, Screw dislocation density and edge dislocation density of the GaN film were accurately determined to be 4.62×107 cm-2 and 5.20×109 cm-2, respectively. The total dislocation density was 5.25×109 cm-2. There were less than 1% screw dislocations, and the ratio of mixed to edge dislocation failed to be determined.

|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of CdxTe Thin Films Deposited by Co-evaporation
SHU Qing, WU Li-Li, FENG Liang-Huan, WANG Wen-Wu, CAO Wu-Xing, ZHANG Jing-Quan, LI Wei, LI Bing
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1099–1104
 Abstract
Abstract(
670 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(481KB)(
1611
)
CdxTe thin films with different x values were deposited for the first time through controlling evaporation rates of CdTe and Te powder by vacuum co-evaporation. Then the films were annealed in N2 atmosphere at 185℃. The morphological, structural, optical, and electrical properties of the CdxTe films were investigated by X ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), UV-visible absorption spectrum and temperature dependence of the dark conductivity. UV-visible absorption spectrum demonstrates that energy band gaps (Eg) of different CdxTe films change from 0.99 eV to 1.46 eV. The absorption edges of different CdxTe films move towards longer wavelength and their transmittances reduce dramatically as the x value decreases from 0.8 to 0.2. XRD shows that as-deposited CdxTe thin films are amorphous when value of x is less than 0.6. Otherwise, CdxTe thin films are crystalline whose CdTe phase with preferential in (111) direction while value of x is approaching 1. The result indicates that annealing treatment is helpful for the films shifting from amorphous to polycrystalline. All the films exhibit p-type conductivity and the conductivity increases firstly as temperature rises. But it becomes abnormal while the temperature reaches a certain point. Data from this research suggest that CdxTe thin films can potentially be used for CdTe thin film solar cells to improve the long wavelength response.

|
|
|
Growth and Characterization of Hybrid Organolead Halide CH3NH3PbI3 Thin Films Prepared by Single Source Thermal Evaporation
FAN Ping, GU Di, LIANG Guang-Xing, LUO Jing-Ting, ZHANG Dong-Ping, CHEN Ju-Long
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1105–1109
 Abstract
Abstract(
1087 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(443KB)(
2158
)
Hybrid organolead halide CH3NH3PbI3 thin films were prepared by thermal evaporation with single source. The microstructure, composition, surface morphology and optical properties of the thin films were characterized by X-ray diffractometry (XRD), X-ray dispersive spectroscope (EDS), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and spectrophotometer technique, respectively. The comparison on properties for the films prepared by different methods (thermal evaporation and spin coating) was illustrated. Compared to the film prepared by spin coating, uniform, the nonporous and complete surface coverage perovskite thin film with high level of phase purity and good crystallization is formed by single source thermal evaporation. A direct bandgap of 1.57 eV for CH3NH3PbI3 thin films is obtained which makes this material to be a good light absorber.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Optical Absorption of Eu-doped CeB6 Nanocrystalline
BAO Li-Hong, MING Ming, O.Tegus
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1110–1114
 Abstract
Abstract(
767 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(316KB)(
1339
)
The Eu-doped CeB6 nanocrystalline was successfully synthesized by a solid-state reaction and their optical properties were investigated. The XRD and EDS analyses fully confirm that the Eu element has been successfully doped into the lattice of CeB6. The optical absorption results show that maximum absorption red-shifted from 938 nm to 1718 nm. Meanwhile, it is interestingly found that the maximum transmission also red-shifts from visible region of 798 nm to near-infrared region of 1138 nm, which is for the first time to be obtained tunable optical characteristic CeB6 by Eu doping. Thus, these interesting findings on CeB6 nanocrystalline can extend its optical application.
|
|
|
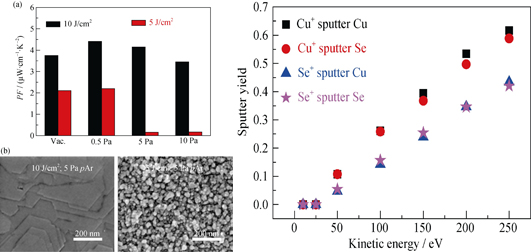
Congruent Growth of Cu2Se Thermoelectric Thin Films Enabled by Using High Ablation Fluence During Pulsed Laser Deposition
LV Yan-Hong, CHEN Ji-Kun, DOBELI Max, LI Yu-Long, SHI Xun, CHEN Li-Dong
2015 Vol. 30 (10): 1115–1120
 Abstract
Abstract(
932 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(388KB)(
1530
)
The importance of the laser ablation fluence in congruent growth of Cu2Se thermoelectric thin films during pulsed laser deposition was shown in this work. By using a larger laser ablation fluence, a more consistent composition between as-grown thin films and the target material has been realized in the pulsed laser deposition of Cu2Se films. This is associated with the enhanced plasma shielding effect, which weakens direct laser-solid interaction when increasing laser fluence. Reducing the ablation fluence can obviously increase the amount of the copper deficiencies, due to more effective laser ablation of Se (higher vapor pressure) than that of Cu when the laser direct lasser-solid interaction becomes more efficient. Apart from tuning the ablation fluence, thermoelectric performances of as-grown Cu2Se thin films are further optimized as a function of the used argon background gas pressures. The maximum thermoelectric performance of the Cu2Se thin film can be obtained when using the highest ablation fluence (~10 J/cm2) and a low argon background pressure(~10-1 Pa).
|
|