|
|
Research Progress on the Transformation, Fracture Mechanism and Properties of Structural Ceramics at Cryogenic Temperatures
XUE Wei-Jiang, XIE Zhi-Peng
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 337–344
 Abstract
Abstract(
1159 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(618KB)(
2320
)
Currently, the rapid development of cryogenic techniques makes them required for a wide range of applications such as aeronautics & astronautics, superconducting fields, nuclear fusion and so on. Structural ceramics are promising cryogenic structural materials which are prior to some kinds of metals and polymer materials in some specific applications. The research history and progress of several classical types of structural ceramics at cryogenic temperatures are reviewed. The contents of the present paper include the transformation mechanism and properties of zirconia-based ceramics, alumina ceramics and basic mechanical properties and fracture mechanisms of Si3N4 and SiC ceramics at cryogenic temperatures.
|
|
|
Research Progress on Growth Rate Controlling of Atomic Layer Deposition
LU Wei-Er, DONG Ya-Bin, LI Chao-Bo, XIA Yang, LI Nan
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 345–351
 Abstract
Abstract(
1078 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(617KB)(
5430
)
Based on the self-limiting nature of sequential surface chemical reaction, atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique could grow films layer by layer. ALD has advantages of low growth temperature, precise thickness controllability, good conformity and uniformity. Therefore, it becomes a primary method for preparing thin films. As a key indicator of ALD technique, the growth rate of film plays an important role not only on the film quality and density, but also on the integrated circuit production efficiency. This paper reviews the recent research results of the ALD growth mechanism and rate, and the factors that affect the growth rate. Finally, this paper provides a summary and some research trends on improving and optimizing the ALD growth rate.
|
|
|
Assembly, Characterization and Ultraviolet Properties of Sulfosalicylic Acid Intercalated Mg/Cu/Zn/Al-LDHs
DU Bao-Zhong, TANG Xiao-Qing, PENG Zhen-Guo, MI Hai-Tao
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 352–356
 Abstract
Abstract(
865 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(504KB)(
1681
)
Sulfosalicylic acid intercalated Mg/Cu/Al-LDHs composite material was prepared by coprecipitation method. The as-prepared material was characterized by XRD, FT-IR and TG-DTA measurements. It was found that the object was intercalated into LDHs layers and the layer distance changed from 0.832 nm to 1.125 nm. Based on these data, a structure model about the LDHs layers was speculated. EDS analysis verified that the element ratio of intercalated LDHs was close to the theoretical value and the LDHs excellent layer structure was maintained after intercalating assembly. Furthermore, the thermal stability of LDHs was improved due to the effects of electrostatic and hydrogen bond between the object and basal planes. Meanwhile, it was indicated by UV-DRS results that the intercalated LDHs composite show both shielding and absorbing effects to UV light.
|
|
|
Synthesis of ZSM-5/EU-1 Composite Zeolite and Its Application in Conversion of Methanol to Xylene
YANG Dong-Hua, WANG Xin-Bo, SHI Bao-Bao, WU Zheng-Huang, Li Xiao-Feng, DOU Tao
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 357–363
 Abstract
Abstract(
856 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(622KB)(
1591
)
Heteroatom-containing ZSM-5/EU-1 composite zeolites with porous structure were synthesized by hydrothermal method using silica sol, aluminum sulfate, sodium hydroxide, TPABr, boric acid and iron nitrate as raw materials, and EU-1 as crystal seed. The synthetic samples were investigated by XRD, SEM, N2 adsorption-desorption and NH3-TPD. Catalyst performance of the composite zeolites for conversion of methanol to xylene was evaluated on a continuous-flow reactor. The results show that the heteroatom-containing ZSM-5/EU-1 composite zeolite with good crystallinity has diffraction peaks for both ZSM-5 and EU-1. Its average pore size has been significantly enlarged and its amount and strength of acid were also increased, which benefited for the aromatization trend of methanol and the priority diffusion of xylene. Selectivity of aromatics in the oil phase can reach 84.70% when using B-ZSM-5/EU-1 as catalyst. It is found that the contents of xylene product are the highest both in B-ZSM-5/EU-1 and in Fe-ZSM-5/EU-1 catalytic products in the range of 41.32%–45.88% and 33.88%–39.16%, respectively. The reason why B-ZSM-5/EU-1 catalytic effect is better than that of Fe-ZSM-5/EU-1 is that the acidity of former is higher and pore diameter smaller (0.8060 nm), both characters favoring xylene formation. However, the selectivity of p-xylene in B-ZSM-5/EU-1 catalytic xylene products is in the range of 29.75%~47.47% which is lower than that of Fe-ZSM-5/ EU-1 with the highest of 53.75%. This result can be attributed to larger particle size of Fe-ZSM-5/EU-1 which provides a longer pore structure for the catalytic reaction so that o-xylene and m-xylene are easier to convert into p-xylene during the diffusion process.
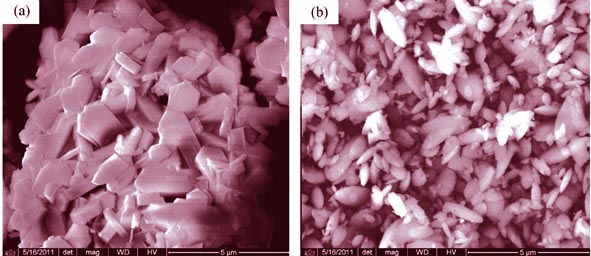
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Amphiphilic w/o-SiO2-void-TiO2 Core-shell Microspheres
MA Zhan-Ying, YAO Bing-Hua, ZHANG Ping
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 364–370
 Abstract
Abstract(
790 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(542KB)(
1608
)
SiO2-void-TiO2 core-shell microspheres were successfully prepared via double-coating with polyfurfuryldehyde and silica, and then removing the mid-layer to create a nanovoid layer between TiO2 core and silica shell. The surfaces of SiO2-void-TiO2 were modified by partial alkylsilylation of n-octadecyltrimethoxysilane to render the surface with amphiphilicity to prepare w/o-SiO2-void-TiO2. Both the SiO2-void-TiO2 and the w/o-SiO2-void-TiO2 were characterized using XRD, TEM, BET, FT-IR and UV-Vis DRS techniques. Results demonstrated that the as-prepared SiO2-void-TiO2 and w/o-SiO2-void-TiO2 showed core(TiO2)-hollow-shell(silica) microspherical structure. The w/o-SiO2-void-TiO2 sample was amphiphilic core-shell microspheres and it could be easily located at the boundary of the dual-phase mixture. Under UV light irradiation for 180 min, the methylene blue degradation rate of SiO2-void-TiO2 and w/o-SiO2-void-TiO2 photocatalysis reached 89.4% and 83.8%, respectively. Based on these results, possible mechanisms of SiO2-void-TiO2 core-hollow-shell microspheres formation and partial modification were discussed.
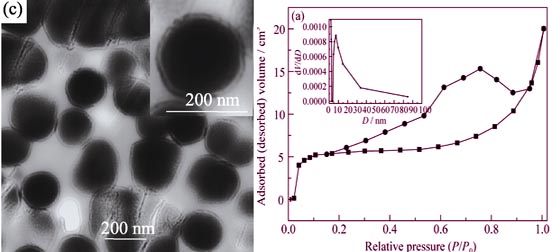
|
|
|
Preparation of 1-3 Dimensional PZT-NFO Nanocomposite Films by Off-axis Magnetron Sputtering
ZHANG Hui, MA Yong-Jun, WANG Yi-Cheng, WEN Dan-Dan, YE Fei, BAI Fei-Ming
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 371–376
 Abstract
Abstract(
836 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(539KB)(
1521
)
Self-assembled nanocomposite Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3-NiFe2O4 films were prepared on the (001)-oriented MgAl2O4 substrates by a 90° off-axis magnetron sputtering method. The influences of substrate temperature, argon over oxygen ratio and sputtering power on the structure and properties of PZT-NFO nanocomposite films were studied. The optimal growth conditions are substrate temperature of 800 ℃, argon over oxygen ratio of 1:1 and sputtering power of 160 W. XRD studies reveal that the PZT-NFO film is epitaxial along both the in-plane and out-of-plane directions, and the vertical lattice mismatch between the PZT phase and the NFO phase is very small. AFM and SEM analysis show that the PZT-NFO films have clear 1-3 dimensional nanocomposite structure, and the diameter of NFO nanorods is 80-150 nm. Further decreasing argon over oxygen ratio is beneficial for the formation of NFO. However, increasing RF power causes a transition from an 1-3 dimensional nanocomposite to a 0-3 dimensional chaotic structure. Magnetic measurement shows that the saturation magnetization of NFO phase is 120-160 kA/m, lower than that of bulk NFO phase, possibly due to the interfacial diffusion between the NFO and the PZT phases.
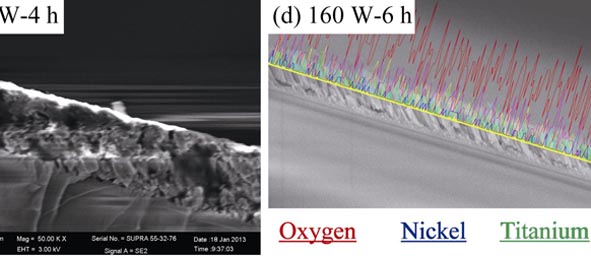
|
|
|
Deposition of Functional Modified Inorganic Particles on A Macroporous Tube for Synthesis ZIF-7 Membrane by Counter Diffusion Method
YIN Hui-Min, YANG Jian-Hua, XIE Zhong, WANG Jin-Qu, LU Jing-Ming, ZHANG Yan
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 377–381
 Abstract
Abstract(
847 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(533KB)(
1402
)
A ‘‘two-in-one’’ approach, namely, through deposition of APTES-functionalized Al2O3 particles onto a coarse macroporous support, was applied to synthesize zeolitic imidazolate tramework-7 (ZIF-7) membranes. The effect of molar ratio of APTES and Al2O3 particles on the formation of ZIF-7 membranes were investigated in detail.
When nAPTES:nAl2O3=1:3, the obtained continuous and thin ZIF-7 membrane with thickness ranging from 2 to 3 μm exhibited H2 permeance at 4.70×10-7 mol/(m2·s·Pa). Its ideal molecular sieving selectivity of H2/CO2 and H2/N2 was at 5.87 and 4.59, respectively.
|
|
|
Effect of Calcination Temperature on Crystal Structure and Photocatalytic Property of TiO2/Diatomite Nanoparticles
WANG Bin, ZHANG Guang-Xin, ZHENG Shui-Lin, LIU Ze-Yu
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 382–386
 Abstract
Abstract(
897 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(467KB)(
1749
)
TiO2/diatomite photocatalysts were synthesized by a facile Sol-Gel method using diatomite as supporter and tetrabutyl titanate (TBOT) as precursor. The crystalline and morphological properties of catalysts with different calcination temperatures were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and UV-Vis spectroscopy. Results reveal that the crystallite size becomes larger and the anatase phase transforms to the rutile phase at elevated temperature. Compared with unimmobilized TiO2, the diatomite supporter impedes the transformation and prevents nano-TiO2 particles from aggregation. The effect of calcination temperature on photocatalytic reactivities of these catalysts was investigated by UV-assisted degradation of 10 mg/L Rhodamine B (RhB). The sample calcined at 750℃ exhibits significantly enhanced reactivity with the removal rate of RhB up to about 100% after irradiation for 120 min, equivalent to that of Degussa P25 under similar conditions. The highest photocatalytic activity is observed in TiO2/diatomite calcined under 750℃ which can be attributed to the presence of anatase and rutile phases in an appropriate ratio at 9:1.
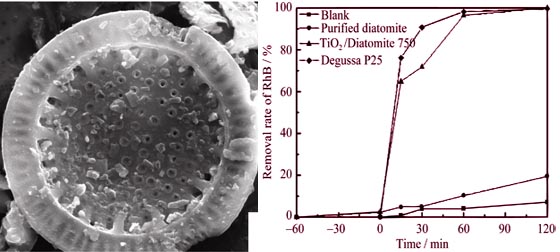
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Hydrophobic Platinum Catalyst for Hydrogen Isotope Exchange between Hydrogen and Liquid Water
YE Lin-Sen, LUO De-Li, YANG Wan, GUO Wen-Sheng, XU Qin-Yin, LUO Li-Zhu
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 387–392
 Abstract
Abstract(
855 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(541KB)(
2195
)
The carbon-supported Pt catalyst was synthesized via the impregnation-liquid-reduction method. Polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE) was used to bind the carbon-supported Pt catalyst and the inert carrier and waterproof the catalyst, where porous ceramic spheres (5.5 mm in diameter) were used as the inert carrier for hydrophobic catalysts (0.8% Pt-C-PTFE). The physical properties of the catalyst were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and scanning electron microscope (SEM), and the separation of deuterium from liquid water was carried out by liquid phase catalytic exchange (LPCE) reactions. As a result, the mean particle size of Pt particles in Pt/C catalyst is about 2.4 nm when the Pt loading is less than 20%. The Pt0, Pt2+ and Pt4+ are co-existed in the catalyst, with Pt0 content of about 60%. It is also found that the content of loaded-Pt, catalyst packed ratio and catalytic exchange temperature are the main factors in determining the overall mass transfer coefficient of hydrogen-water diffusion and exchange, which occur on Pt and its oxides active sites.
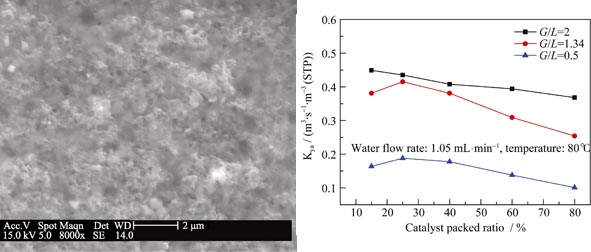
|
|
|
Sol-Gel Derived Al3+,Yb3+ Co-doped Silica Fiber Core
LOU Feng-Guang, WANG Shi-Kai, WANG-Meng, Feng Su-Ya, YU Chun-Lei, HU Li-Li
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 393–398
 Abstract
Abstract(
872 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(464KB)(
1680
)
Using TEOS, YbCl3, AlCl3 as precursors, Al3+, Yb3+ co-doped silica fiber core glass was fabricated by Sol-Gel method. ICP-AES tests showed that the compositions of the gel derived from base catalyzed sol were not uniform. The composition inhomogeneity of the gel was eliminated by acid catalyzed sol. The Al3+, Yb3+ co-doped silica core glass with 2.5 mm in diameter and 50 mm in length was obtained after heat-treatment, melting and polishing. The absorption, infrared transmission and fluorescence spectra were measured with glass slice at 2 mm thickness. The fluorescent lifetime centered at 1020 nm was 896 μs, and the Hydroxyl radical (-OH) content was 0.4×10-6. The glass structures from acid and base catalyzed sols were analyzed by micro Raman spectroscope. Fiber preform was fabricated by rod-in-tube technique with the obtained core glass. The Al3+, Yb3+ co-doped single cladding silica fiber was drawn at 2000℃. Its optical homogeneity was evaluated by the refractive index profiler. Refractive index difference (Δn) in fiber core area was less than 2×10-4. This work can supply homogeneous and large size core glass for large mode PCF and large mode cladding fiber. And it can provide reference for preparation of homogeneous multi-component optical material by the Sol-Gel method.
|
|
|
Phase Transitions in PLZT Ceramics Observed by In-situ Raman Spectroscopy
ZHANG Sa, LIU Ying, LIU Yi-Xuan, CHENG Xuan, ZHANG Ying
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 399–404
 Abstract
Abstract(
693 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(533KB)(
2126
)
The PLZT ceramics (atomic ratio Zr/Ti≈52/48, doped with small amounts of La) were prepared by conventional solid state reaction technique and identified to be pure perovskite phase by XRD. To observe the phase transition in the PLZT ceramics, the in-situ Raman spectra were measured at different temperatures. Accordingly, the variations of characteristic Raman shifts and intensities of the modes with temperatures were obtained. It is confirmed that two types of phase transitions near morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) occurred at 0℃ from rhombohedral to tetragonal and at 350℃ from tetragonal to cubic, in the temperature range from -200℃ to 600℃. What’s more, the phase transitions for rhombohedral from low. to high-temperature phases and mixed phases may take place near -150℃ and 250℃, respectively.
|
|
|
Effect of pH on the Infrared Radiation Property of CoFe2O4 Powders Synthesized by Sol-Gel Method
WU Xiao-Yan, YU Hong-Bing, DONG Heng, YANG Lei, GENG Li-Juan
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 405–410
 Abstract
Abstract(
747 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(474KB)(
1670
)
Cobalt ferrite powders with excellent infrared radiation property were synthesized via the Sol-Gel method, where iron nitrate and cobalt nitrate were used as the original materials and citric acid as the chelating reagent. The effects of pH of the starting solution (pH=1, 3, 5 and 7) on the infrared radiation property of CoFe2O4 powders were examined according to the normal direction emissivity. The structure and morphology of the powders were characterized basing on FTIR, TG/DSC, XRD, SEM and BET measurements. It was found that the dried gels obtained from the starting solutions possessed the self-propagating combustion behavior. The pure spinel CoFe2O4 powders were obtained by the further treatment of sintered at 600℃ for 2 h. It was foumd that the optimum pH of the starting solution was 5. Under this condition, the highest infrared emissivity (0.92) of the sample was achieved in the 8-14 μm waveband, and the primary mesoporous structure was formed with the largest specific surface area of 65.44 m2/g.
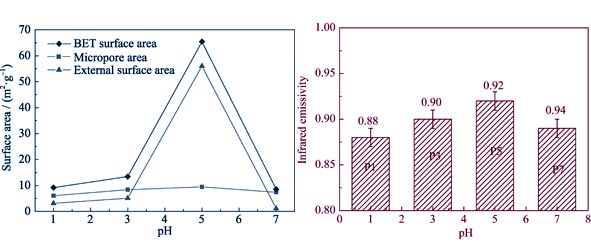
|
|
|
Effect of Magnetic Annealing on IrMn Based Spin Valve Materials with SAF Structure
Li Jian-Ping, QIAN Zheng-Hong, SUN Yu-Cheng, BAI Ru, LIU Jian-Lin, ZHU Jian-Guo
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 411–416
 Abstract
Abstract(
764 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(473KB)(
1559
)
IrMn based spin valve materials with SAF (CoFe/Ru/CoFe) structure were deposited by magnetron sputtering system. HRTEM, AFM and XPS techniques were utilized to characterize the microstructures and composition of the spin valve materials. First, the deposited materials were annealed at 200℃, 245℃, 255℃ and 265℃ for 4 h in vacuum (<10-5 Pa). It was found that obvious interlayer diffusion was happened after being annealed at 265℃, which resulted in the decrease of magneto-resistance (MR) ratio. Set field annealing temperature at 245℃, the spin valve materials were annealed at fields of 80, 160, 240, 400 and 560 kA/m along the pinning direction for 4 h in vacuum, respectively. It was found that the MR ratio of the materials declined to 5.87% and 6.31% from 8.80% after 80 kA/m and 160 kA/m annealing, respectively. After 240 kA/m annealing, the MR ratio became 7.91%. After 400 kA/m annealing, the MR ratio increased to 9.89%. After 560 kA/m annealing, the MR ratio reached 10.79%, which was increased by 22.6% as compared with the material before annealing.
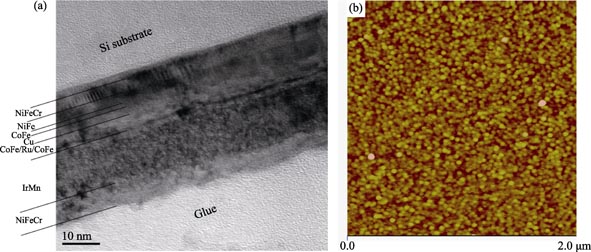
|
|
|
Preparation, Mechanical Properties and Thermal Properties of Elastic Aerogels
ZU Guo-Qing, SHEN Jun, ZOU Li-Ping, WANG Wen-Qin, LIAN Ya, ZHANG Zhi-Hua
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 417–422
 Abstract
Abstract(
929 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(476KB)(
1497
)
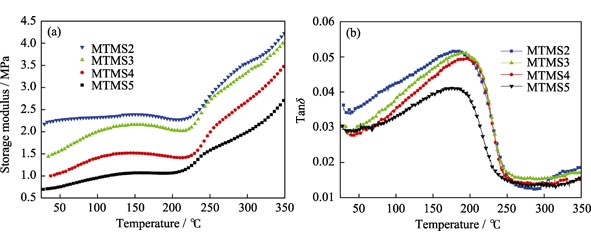
Transparent and monolithic aerogels were prepared via acid-base two step Sol-Gel process with Methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS), water, acetic acid and ammonia as precursor, solvent, acid and base accelerators, respectively, followed by drying under a supercritical condition using alcohol as drying medium. Scan electron microscope, N2 adsorption analyzer, dynamic mechanical analyzer, hotdisk thermal analyzer were used to characterize the morphology, pore structure, mechanical properties and thermal properties of the aerogels. The obtained aerogels showed good elastic properties. They could shrink up to 60% in linear scale and rebound to 78% of their original size when unloaded, and finally spring back to 94% of their original size after heat treatment at about 100℃. The aerogels also had good thermal insulation properties. The thermal conductivity was about 0.028 W/(m?K) at room temperature. The contact angle was up to 154°, showing good hydrophobicity. The heat-resistance temperature of the aerogels was about 440℃, above which would result in oxidation of methyl groups in the aerogels. The aerogels have good mechanical and thermal insulation properties, showing prospect in the application of thermal insulation.
|
|
|
TiB2-B4C-Fe3(C, B) Composite Synthesized by Plasma Heating
CUI Hong-Zhi, ZHANG Shan-Shan, WANG Xiao-Bin, HE Qing-Kun, SONG Qiang
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 423–428
 Abstract
Abstract(
841 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(714KB)(
1561
)
TiB2-B4C-Fe3(C, B) composites were prepared by plasma heating synthesis with Ti, B4C and Fe powders as raw materials. Effects of plasma current on phase composition, microstructure and hardness of the final composites were studied. The results show that the final composites are composed of TiB2, B4C and Fe3(C, B). Because of fast heating and cooling during the plasma heating synthesis and directional heat releasing, plate-like TiB2 grains grow along the fastest heat releasing direction. TiB2 plates and white Fe3(C, B) are alternating distribution while the unreacted B4C grains are packed into gaps. Plasma current affects the heat which inputted into the sample in unit time. Hence, increasing current is conducive to the growth of TiB2, but decrease the hardness of the composites.
|
|
|
Effect of Carbon Nanoparticle Content on Machinability and Wettability of Carbon/Silicon Carbide Ceramics
LU You-Jun, WANG Yan-Min, PAN Zhi-Dong, HUANG Zhen-Kun, WU Lan-Er
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 429–432
 Abstract
Abstract(
681 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(424KB)(
1112
)
Nanoparticle(nano-Cp)/silicon carbide(SiC) ceramics (Cp/SiC) were prepared via pressureless sintering. Effect of nano-Cp content on machinability and wettability of the Cp/SiC ceramics as a glass clamp was investigated. Phase composition and morphology of the ceramics were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM), respectively. Results show that the machinability of the ceramics increases with the increase of the nano-Cp content. According to the evaluation of the machinability index(M) for ceramic materials, M15 = 0.921(for 15wt%Cp/SiC composite)>M25=0.547(for 25wt%Cp/SiC composite)>M5=0.056(for 5wt%Cp/SiC composite)>M0=0.021(for SiC ceramic). The pretreatment by oxidation of Cp in the ceramics could depress the formation of SiO2 film on the surface of SiC, thus preventing the wettability between the ceramics and glass smelt and hindering the splice of the fixture material with glass smelt.
|
|
|
Buffering of the Sintering Stress for Fabrication of Microporous Al2O3/Stainless-steel Membranes
WEI Lei, YU Jian, HU Xiao-Juan, HUANG Yan
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 433–437
 Abstract
Abstract(
714 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(611KB)(
1592
)
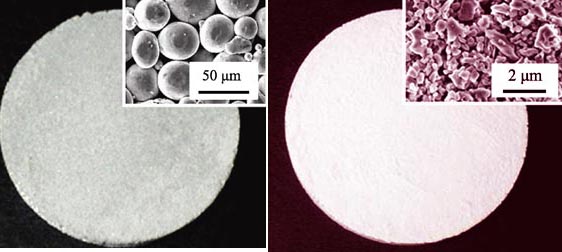
Based on porous stainless-steel disks, three methods were used to fabricate microporous Al2O3/stainless-steel membranes by coating Al2O3 powder with a mean particle diameter size of 0.5 μm. The surface and cross-sectional morphologies were characterized by scanning electron microscople (SEM) and metallographic microscople, respectively. Pore size distribution of the Al2O3/stainless-steel membranes was measured by capillary flow method. The membrane adhesion was tested by means of ultrasonic shocking treatment. It is found that the problem of membrane peeling can be solved by introducing an intermediate layer of stainless-steel fine powder between the substrate and the alumina layer and then performing a co-sintering treatment. The microporous Al2O3/stainless-steel membranes with a thickness of 40-50 μm were successfully achieved. Such an intermediate layer not only helps to modify the substrate surface but also buffers the thermal expansion and sintering shrinkage stresses in the Al2O3 layer during the heat-treatment. Moreover, it can also bond the Al2O3 layer onto the substrate and therefore enhances the membrane adhesion. The co-sintering approach introduced in this study simplifies fabrication process and saves energy. During co-sintering period the sintering, temperature plays a key role in membrane adhesion and pore size distribution. After being co-sintered at 1100, 1150, 1200 and 1250℃, the mean pore sizes of the Al2O3/stainless-steel membranes are 0.2, 0.3, 0.5 and 3.9 μm, respectively, and the pure water fluxes of the membranes are 3.8, 4.1, 6.9 and 20.5 m3/(m2·h·bar), respectively.
|
|
|
Surface Cracks of Solid-phase-sintered Silicon Carbide Ceramics and Their Influeces on Material Strength
YANG Xiao, LIU Xue-Jian, HUANG Zheng-Ren
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 438–442
 Abstract
Abstract(
854 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(361KB)(
1210
)
The effects of surface cracks on bending strength of Solid-phase-sintered Silicon Carbide Ceramic (SSiC) were systematically investigated in aspects of crack size and inclined angle. The relation between the surface cracks and material strength revealed that the Vickers crack size is about 10 μm after 0.5 N indentation load that begins to dominant the fracture of SSiC test bars. Vickers cracks no larger than 3 μm are safe and do not harm to the general bending strength. It is found that inclined Knoop crack after 5 N or above is easier to deflect from the original direction and dominates the sample fracture process. And the relationship between the flexure strength σ and inclined angle θ is found to correspond with σ∝(sinθ)-1/2. When the indentation load is smaller than 1–2 N, Knoop crack plays a similar effect as intrinsic defect that they randomly dominate the sample fracture process; and this randomness makes the impact of inclined angle on the flexure strength irregularly.
|
|
|
Preparation of LiMn0.4Fe0.6PO4/C Composite by A New Route Combining Solid-state Reaction with Hydrothermal Synthesis
LI Jian, YAO Shu-Heng, ZHOU Hong-Ming, GENG Wen-Jun
2014 Vol. 29 (4): 443–448
 Abstract
Abstract(
1294 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(466KB)(
2010
)
The olivine type LiMn0.4Fe0.6PO4 was synthesized via a new route that combining solid-state reaction with hydrothermal synthesis from Li2CO3, FeC2O4·2H2O, MnCO3 and NH4H2PO4 (molar ratio of 5:6:4:10). The structure, particle size and surface morphology of these cathode active materials were investigated by XRD, SEM and TEM techniques. The electrochemical properties of LiMn0.4Fe0.6PO4/C as cathode in lithium-ion cells were tested via cyclic voltammetry and galvanostatic charge-discharge measurements. Phase-pure particles of size ~120 nm are prepared with a conductive, thin web of carbon surrounding them. Cyclic voltammetry shows the active voltage range of the material which consists of two pairs of redox peaks: 3.5 V corresponding to Fe3+/Fe2+ reaction and 4.0 V corresponding to Mn3+/Mn2+ reaction. An initial discharge capacity of 160 mAh/g at 0.1C, 143 mAh/g and a stable cycling property at 0.5C are obtained for the LiMn0.4Fe0.6PO4/C composite.
|
|