
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 513-520.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200386
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Zhaowu1( ), JI Haipeng1(
), JI Haipeng1( ), WANG Feixiang1, HOU Xinghui1, YI Shasha1, ZHOU Ying1, CHEN Deliang1,2(
), WANG Feixiang1, HOU Xinghui1, YI Shasha1, ZHOU Ying1, CHEN Deliang1,2( )
)
Received:2020-07-09
Revised:2020-08-26
Published:2021-05-20
Online:2021-04-19
Contact:
JI Haipeng, lecturer. E-mail: jihp@zzu.edu.cn; CHEN Deliang, professor. E-mail: dlchen@zzu.edu.cn
About author:WANG Zhaowu(1985-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail:smithen0504@gs.zzu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Zhaowu, JI Haipeng, WANG Feixiang, HOU Xinghui, YI Shasha, ZHOU Ying, CHEN Deliang. Valence State Control of Manganese in MgAl2O4:Mn4+ Phosphor by Varying the Al2O3 Crystal Form[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 513-520.
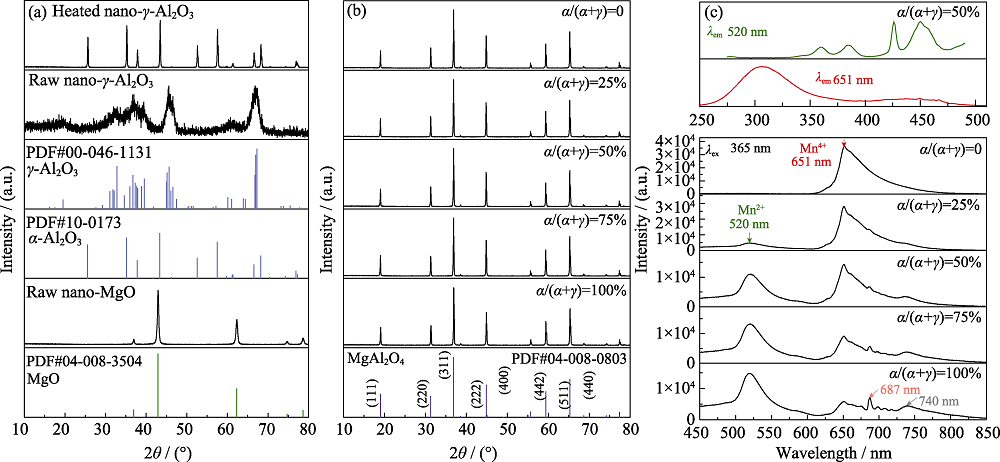
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of the raw and heat-treated (at 1400 ℃ for 5 h) nano-γ-Al2O3 (the standard patterns for γ-Al2O3 and α-Al2O3 are also given) (a), XRD patterns of MgAl2O4:Mn phosphors synthesized using alumina sources with different α/(α+γ) ratios (b), and photoluminescence emission spectra of the MgAl2O4:Mn synthesized using alumina sources with different α/(α+γ) ratios (λex=365 nm) and the excitation spectra monitored for 520 and 651 nm emission of MgAl2O4:Mn with α/(α+γ)=50% (c)

Fig. 2 Digital images (λex=365 nm) of the MgAl2O4:Mn phosphors synthesized using the alumina sources with different α/(α+γ) ratios (a) 100%; (b) 75%; (c) 50%; (d) 25%; (e) 0
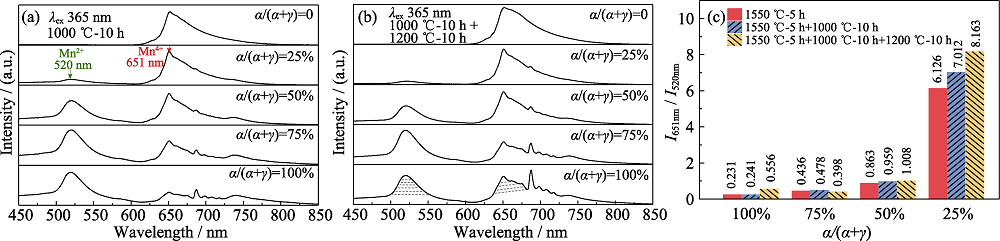
Fig. 5 Photoluminescence emission spectra (λex=365 nm) of the MgAl2O4:Mn phosphors using the Al2O3 with different α/(α+γ) ratios annealed at 1000 ℃ for 10 h (a), annealed at 1000 ℃ for 10 h and at 1200 ℃ for another 10 h (b), I651 nm/I520 nm ratios calculated from the luminescence spectra of the MgAl2O4:Mn phosphors (both as-prepared and post-annealed) (c)
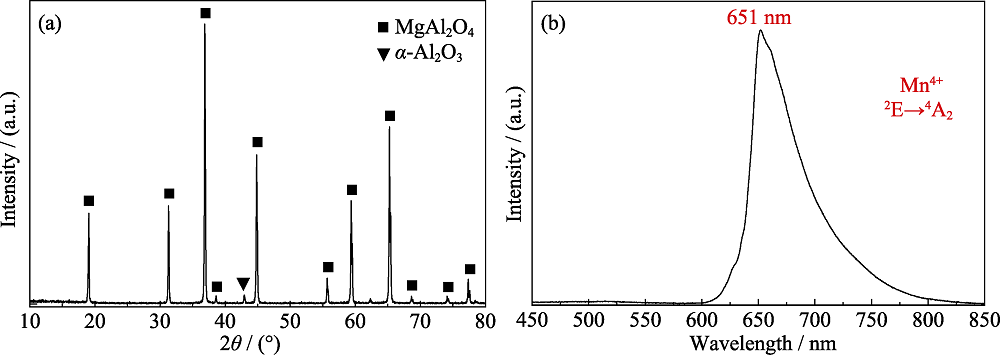
Fig. 6 XRD pattern (a) and photoluminescence spectrum (λex=365 nm) (b) of the phosphor synthesized at 1550 ℃ for 5 h using Al2O3 (AR, γ-phase, micro size) as the alumina source
| No. | Methods | Results |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Control of atmosphere | Reducing atmosphere generating green-emitting MgAl2O4:Mn2+ phosphor [ |
| 2 | Control of charge compensator | Deficient MgO generating green-emitting MgAl2O4:Mn2+ phosphor in the raw materials while excessive MgO generating red-emitting MgAl2O4:Mn4+ phosphor[ |
| 3 | Control of heating temperature | Heating at low temperatures generating red-emitting MgAl2O4:Mn4+ phosphors while heating at higher temperature with longer duration period generating green-emitting MgAl2O4:Mn2+ phosphor[ |
| 4 | Control of Al3+- bearing source | Highly reactive γ-Al2O3 as the Al3+-bearing source preferentially producing red-emitting MgAl2O4:Mn4+ phosphor |
Table 1 Methods to regulate the valence state of manganese ion in the MgAl2O4:Mn phosphor
| No. | Methods | Results |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Control of atmosphere | Reducing atmosphere generating green-emitting MgAl2O4:Mn2+ phosphor [ |
| 2 | Control of charge compensator | Deficient MgO generating green-emitting MgAl2O4:Mn2+ phosphor in the raw materials while excessive MgO generating red-emitting MgAl2O4:Mn4+ phosphor[ |
| 3 | Control of heating temperature | Heating at low temperatures generating red-emitting MgAl2O4:Mn4+ phosphors while heating at higher temperature with longer duration period generating green-emitting MgAl2O4:Mn2+ phosphor[ |
| 4 | Control of Al3+- bearing source | Highly reactive γ-Al2O3 as the Al3+-bearing source preferentially producing red-emitting MgAl2O4:Mn4+ phosphor |
| [1] |
WANG L, XIE R J, SUEHIRO T, et al. Down-conversion nitride materials for solid state lighting: recent advances and perspectives. Chemical Reviews, 2018,118(4):1951-2009.
URL PMID |
| [2] |
ZHAO M, LIAO H X, NING L X, et al. Next-generation narrow-band green-emitting RbLi(Li3SiO4)2:Eu2+ phosphor for backlight display application. Advanced Materials, 2018,30:1802489.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
QIAO J W, ZHOU G J, ZHOU Y Y, et al. Divalent europium- doped near-infrared-emitting phosphor for light-emitting diodes. Nature Communications, 2019,10:5267.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] |
ZHAO M, LIAO H, MOLOKEEV M S, et al. Emerging ultra- narrow-band cyan-emitting phosphor for white LEDs with enhanced color rendition. Light-Science & Application, 2019,8:38.
DOI URL |
| [5] | ZHOU Y Y, WANG L Y, DENG T T, et al. Recent advances in Mn4+-doped fluoride narrow-band red-emitting phosphors. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2017,47(11):1111-1125. |
| [6] |
JI H P, ZHANG Z T, XU J, et al. Advance in red-emitting Mn4+-activated oxyfluoride phosphors. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020,35(8):847-856.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
JI H P, HOU X H, MOLOKEEV M, et al. Ultrabroadband red luminescence of Mn4+ in MgAl2O4 peaking at 651 nm. Dalton Transactions, 2020,49(17):5711-5721.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] |
XU Y D, WANG D, WANG L, et al. Preparation and luminescent properties of a new red phosphor (Sr4Al14O25:Mn4+) for white LEDs. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013,550:226-230.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
PENG M Y, YIN X W, TANNER P A, et al. Orderly-layered tetravalent manganese-doped strontium aluminate Sr4Al14O25:Mn4+: an efficient red phosphor for warm white light emitting diodes. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2013,96(9):2870-2876.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
SASAKI T, FUKUSHIMA J, HAYASHI Y, et al. Synthesis and photoluminescence properties of a novel Sr2Al6O11:Mn4+ red phosphor prepared with a B2O3 flux. Journal of Luminescence, 2018,194:446-451.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WANG X, LI P F, BRIK M G, et al. Thermal quenching of Mn4+ luminescence in SrAl12O19:Mn4+. Journal of Luminescence, 2019,206:84-90.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WANG B, LIN H, XU J, et al. CaMg2Al16O27:Mn4+-based red phosphor: a potential color converter for high-powered warm W-LED. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014,6(24):22905-22913.
URL PMID |
| [13] |
TAO S, HUANG W F, LIU Y S, et al. Three-dimensional hollow spheres of the tetragonal-spinel MgMn2O4 cathode for high-performance magnesium ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018,6(18):8210-8214.
DOI URL |
| [14] | ZHONG R X, ZHANG J H, WEI H Z, et al. The different luminescent characteristics of MgAl2O4:Mn2+ between phosphor powder and nanoparticles. Chemical Physics Letters, 2011,508(4/5/6):207-209. |
| [15] | SONG E H, ZHOU Y Y, WEI Y, et al. A thermally stable narrow- band green-emitting phosphor MgAl2O4:Mn2+ for wide color gamut backlight display application. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019,7(27):8192-8198. |
| [16] | WAKUI Y, SHAN Y J, TEZUKA K, et al. Crystal-site engineering approach for preparation of MgB2O4:Mn2+,Mn4+(B=Al,Ga) phosphors: control of green/red luminescence properties. Materials Research Bulletin, 2017,90:51-58. |
| [17] | ZHANG Y L, LIU Y L, YANG L, et al. Preparation and luminescence properties of thermally stable Mn4+ doped spinel red-emitting ceramic phosphors. Journal of Luminescence, 2020,220:117016. |
| [18] | CHI N T K, QUANG N V, TUAN N T, et al. Deep red emitting MgAl2O4:Cr3+ phosphor for solid state lighting. Journal of Electronic Materials. 2019,48(9):5891-5899. |
| [19] | ZHANG Y L, HU S, LIU Y L, et al. Red-emitting Lu3Al5O12:Mn transparent ceramic phosphors: valence state evolution studies of Mn ions. Ceramics International, 2018,44(18):23259-23262. |
| [20] | DUAN C J, DELSING A C A, HINTZEN H T. Photoluminescence properties of novel red-emitting Mn2+-activated MZnOS (M= Ca, Ba) phosphors. Chemistry of Materials, 2009,21(6):1010-1016. |
| [21] | KÜCK S, HARTUNG S, HURLING S, et al. Optical transitions in Mn3+-doped garnets. Physical Review B, 1998,57(4):2203-2216. |
| [22] | ZHANG Y L, HU S, LIU Y L, et al. Influences of thermal post-treatment on the Mn valence states and luminescence properties of red-emitting Lu3Al5O12:Mn4+ transparent ceramic phosphors. Optical Materials , 2020,101:109705. |
| [23] | CHEN L, XUE S, CHEN X, et al. The site occupation and valence of Mn ions in the crystal lattice of Sr4Al14O25 and its deep red emission for high color-rendering white light-emitting diodes. Materials Research Bulletin, 2014,60:604-611. |
| [24] | XU H, WANG L, MA X, et al. A novel Mn(II)-based green phosphor and its self-reduction mechanism. Journal of Luminescence, 2018,194:303-310. |
| [1] | QU Mujing, ZHANG Shulan, ZHU Mengmeng, DING Haojie, DUAN Jiaxin, DAI Henglong, ZHOU Guohong, LI Huili. CsPbBr3@MIL-53 Nanocomposite Phosphors: Synthesis, Properties and Applications in White LEDs [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1035-1043. |
| [2] | JI Haipeng, ZHANG Zongtao, XU Jian, TANABE Setsuhisa, CHEN Deliang, XIE Rongjun. Advance in Red-emitting Mn4+-activated Oxyfluoride Phosphors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 847-856. |
| [3] | ZHANG Rui, Wang Bo-Yang, WANG Hai. Advances in Phosphor-in-Glass for White LED [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(4): 337-345. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||