
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (12): 1250-1256.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170112
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
WEN Ya-Bing1,2, ZHANG Jing-Chao2, YE Xiao-Feng2, WANG Yong1, HAN Jin-Duo2, LUO Wen-Hua3, GU Sui2, MENG Jian-Bo3, WEN Zhao-Yin2
Received:2017-03-13
Revised:2017-04-28
Published:2017-12-20
Online:2017-11-21
CLC Number:
WEN Ya-Bing, ZHANG Jing-Chao, YE Xiao-Feng, WANG Yong, HAN Jin-Duo, LUO Wen-Hua, GU Sui, MENG Jian-Bo, WEN Zhao-Yin. Nickle Electrodes for High-temperature Proton-conducting Electrolytes: Preparation by Electroless Plating and Electrochemical Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(12): 1250-1256.
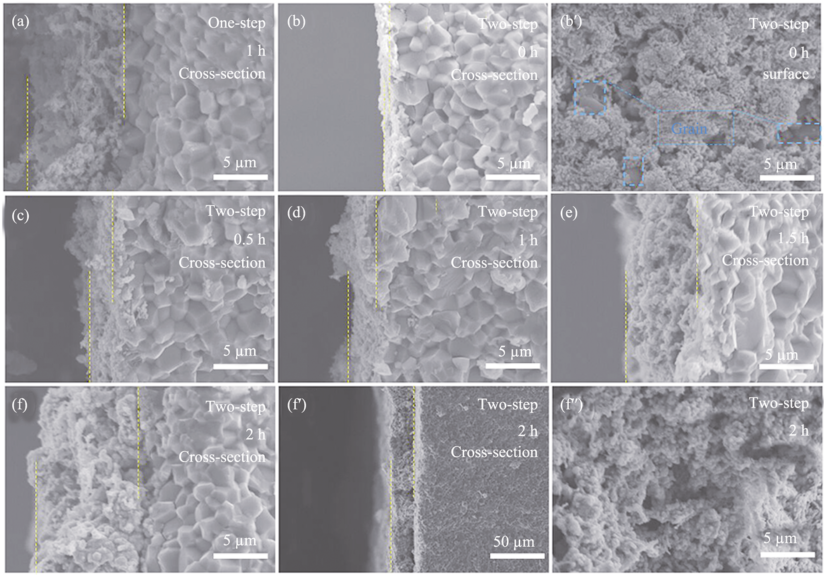
Fig. 4 Cross-section and surface morphology of electrodes after electroless plating for different periods(a) One-step, 1 h; (b) Two-step, 0 h; (c) Two-step, 0.5 h; (d) Two-step, 1 h; (e) Two-step, 1.5 h; (f) Two-step, 2 h
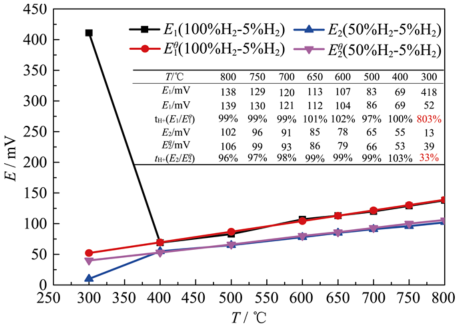
Fig. 8 EMFs, theoretical electromotive force values and proton transport rates of hydrogen concentration cell: H2 (PH2=105 Pa)/ H2+N2 (PH2=5×104 Pa), Ni | CZI |Ni, H2+Ar (PH2=5×103 Pa)
| [1] | SCHOBER T.Applications of oxidic high-temperature proton conductors.Solid State Ionics, 2003, 162(1): 277-281. |
| [2] | NOWICK A S, VAYSLEYB A V.Isotope effect and proton hopping in high-temperature protonic conductors.Solid State Ionics, 1997, 97(1): 17-26. |
| [3] | WEN Z Y, LI J Z.New applications of solid state ionics.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(11): 1163-1164. |
| [4] | MATSUMOTO H, OKUBO M, HAMAJIMA S,et al. Extraction and production of hydrogen using high-temperature proton conductor. Solid State Ionics, 2002, 152(12): 715-720. |
| [5] | COLLINS J P, WAY J D.Preparation and characterization of a composition palladium-ceramic membrane.Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1993, 32(12): 3006-3013. |
| [6] | UCHIDA H, TANAKA S, IWAHARA H.Polarization at Pt electrodes of a fuel cell with a high temperature-type proton conductive solid electrolyte.Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1985, 15(1): 93-97. |
| [7] | NARAYANAN T, BASKARAN I, KRISHNAVENI K,et al. Deposition of electroless Ni-P graded coatings and evaluation of their corrosion resistance. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2006, 200(11): 3438-3445. |
| [8] | ACRES G J K, HARDS G A. Electrocatalysts for fuel cells.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society a-Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1996, 354(1712): 1671-1680. |
| [9] | LEE J H, MOON H, LEE H W,et al. Quantitative analysis of microstructure and its related electrical property of SOFC anode, Ni-YSZ cermet. Solid State Ionics, 2002, 148(1/2): 15-26. |
| [10] | KOIDE H, SOMEYA Y, YOSHIDA T,et al. Properties of Ni/YSZ cermet as anode for SOFC. Solid State Ionics, 2000, 132(3/4): 253-260. |
| [11] | ARUNA S T, MUTHURAMAN M, PATIL K C.Synthesis and properties of Ni-YSZ cermet: anode material for solid oxide fuel cells. Solid State Ionics, 1998, 111(1/2): 45-51. |
| [12] | KIM H, LU C, WORRELL W L, et al. Cu-Ni cermet anodes for direct oxidation of methane in solid-oxide fuel cells. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2002, 149(3): A247-A250. |
| [13] | GRGICAK C M, PAKULSKA M M, O'BRIEN J S,et al. Synergistic effects of Ni1-xCox-YSZ and Ni1-xCux-YSZ alloyed cermet SOFC anodes for oxidation of hydrogen and methane fuels containing H2S. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 183(1): 26-33. |
| [14] | AN W, GATEWOOD D, DUNLAP B,et al. Catalytic activity of bimetallic nickel alloys for solid-oxide fuel cell anode reactions from density-functional theory. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(10): 4724-4728. |
| [15] | KAN H, LEE H.Sn-doped Ni/YSZ anode catalysts with enhanced carbon deposition resistance for an intermediate temperature SOFC.Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2010, 97(1/2): 108-114. |
| [16] | FUKUI T, MURATA K, OHARA S,et al. Morphology control of Ni-YSZ cermet anode for lower temperature operation of SOFCs. Journal of Power Sources, 2004, 125(1): 17-21. |
| [17] | HWANG C, YU C H.Formation of nanostructured YSZ/Ni anode with pore channels by plasma spraying.Surface & Coatings Technology, 2007, 201(12): 5954-5959. |
| [18] | WANG C, DAIMON H, ONODERA T,et al. A general approach to the size- and shape-controlled synthesis of platinum nanoparticles and their catalytic reduction of oxygen. Angewandte Chemie- International Edition, 2008, 47(19): 3588-3591. |
| [19] | VIDAL-IGLESIAS F J, SOLLA-GULLON J, RODRIGUEZ P,et al. Shape-dependent electrocatalysis: ammonia oxidation on platinum nanoparticles with preferential (100) surfaces. Electrochemistry Communications, 2004, 6(10): 1080-1084. |
| [20] | SHAO Y, YIN G, WANG Z,et al. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell from low temperature to high temperature: material challenges. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 167(2): 235-242. |
| [21] | ATTARD G S, BARTLETT P N, COLEMAN N R B,et al. Mesoporous platinum films from lyotropic liquid crystalline phases. Science, 1997, 278(5339): 838-840. |
| [22] | NIESEN T P, DE GUIRE M R. Review: deposition of ceramic thin films at low temperatures from aqueous solutions.Journal of Electroceramics, 2001, 6(3): 169-207. |
| [23] | TANG Y, LIU Y, SAMPATHKUMARAN U,et al. Particle growth and particle-surface interactions during low-temperature deposition of ceramic thin films. Solid State Ionics, 2002, 151(1/4): 69-78. |
| [24] | HAN J, WEN Z, ZHANG J,et al. Fabrication of dense CaZr0.90In0.10O3-delta ceramics from the fine powders prepared by an optimized solid-state reaction method. Solid State Ionics, 2008, 179(21-26): 1108-1111. |
| [25] | NATIVIDAD E, LATASTE E, LAHAYE M,et al. Chemical and morphological study of the sensitisation, activation and Cu electroless plating of Al2O3 polycrystalline substrate. Surface Science, 2004, 557(1/2/3): 129-143. |
| [26] | BASKARAN I, NARAYANAN T S N S, STEPHEN A. Effect of accelerators and stabilizers on the formation and characteristics of electroless Ni-P deposits.Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2006, 99(1): 117-126. |
| [27] | CHEONG W J, LUAN B L, SHOESMITH D W.The effects of stabilizers on the bath stability of electroless Ni deposition and the deposit.Applied Surface Science, 2004, 229(1-4): 282-300. |
| [28] | EL MAHALLAWY N, BAKKAR A, SHOEIB M, et al. Electroless Ni-P coating of different magnesium alloys. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2008, 202(21): 5151-5157. |
| [29] | KURITA N, FUKATSU N, ITO K,et al Protonic conduction domain of indium-doped calcium zirconate.Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1995, 142(5): 1552-1559. |
| [1] | JIANG Jin-Long,TAO Hui-Qing,ZENG Chang-Feng,ZHANG Li-Xiong,XU Nan-Ping. Preparation of Magnetic ZSM-5/Ni Hollow Fibers Using Poly (vinylidene fluoride) Hollow Fiber Microfiltration Membranes as Templates [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(3): 475-480. |
| [2] | ZOU Gui-Zhen,CAO Mao-Sheng,ZHANG Liang,JIN Hai-Bo,XU Hui,WANG Zheng-Ping. Preparation and Dielectric Enhancement of Nickel-coated β-SiC Nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2006, 21(4): 797-802. |
| [3] | YU Shi-Jun,SONG Li-Xin,HUANG Yin-Song,ZHAO Rong-Gen,HU Xing-Fang. Electroless Ni-P-SiC Composite Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2004, 19(3): 647-652. |
| [4] | SHAO Zhong-Cai,ZHAI Yu-Cun,TIAN,Yan-Wen,LI Bac-Shan. Kinetics of Preparation of Ni Electroless Plating on ZrO2 Uultrafinepowders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1999, 14(3): 397-402. |
| [5] | CHEN Wangping,LI Longtu,GUI Zhilun,QI Jianquan,WANG Dejun. Fundamental Study of the Influence of Electroless Nickel Plating on PTC Effect in BaTiO3-based Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1997, 12(4): 620-622. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||