
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 1230-1236.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160099
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
KANG Gui-Ying, CHEN Yong, LI Juan-Juan
Received:2016-02-24
Revised:2016-04-19
Published:2016-11-10
Online:2016-10-25
About author:KANG Gui-Ying. E-mail: 18193117856@163.com
CLC Number:
KANG Gui-Ying, CHEN Yong, LI Juan-Juan. Comparison on Structure and Electrochemical Performances of NiAl-LDH, CoAl-LDH and NiCoAl-LDH[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(11): 1230-1236.
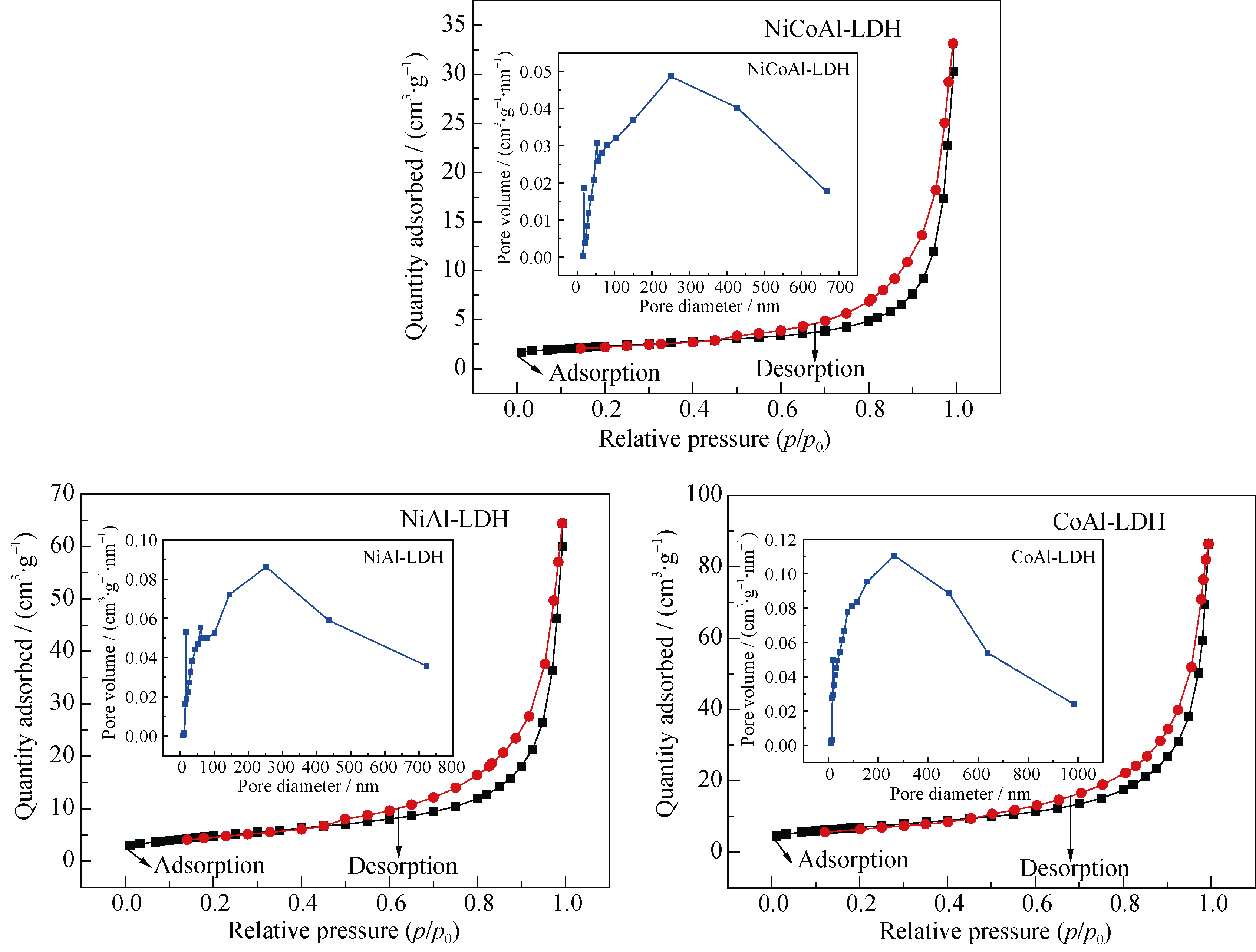
Fig. 3 Nitrogen adsorption desorption isotherms of NiCoAl-LDH (a), NiAl-LDH (b) and CoAl-LDH (c), and their corresponding pore size distribution curve in inset
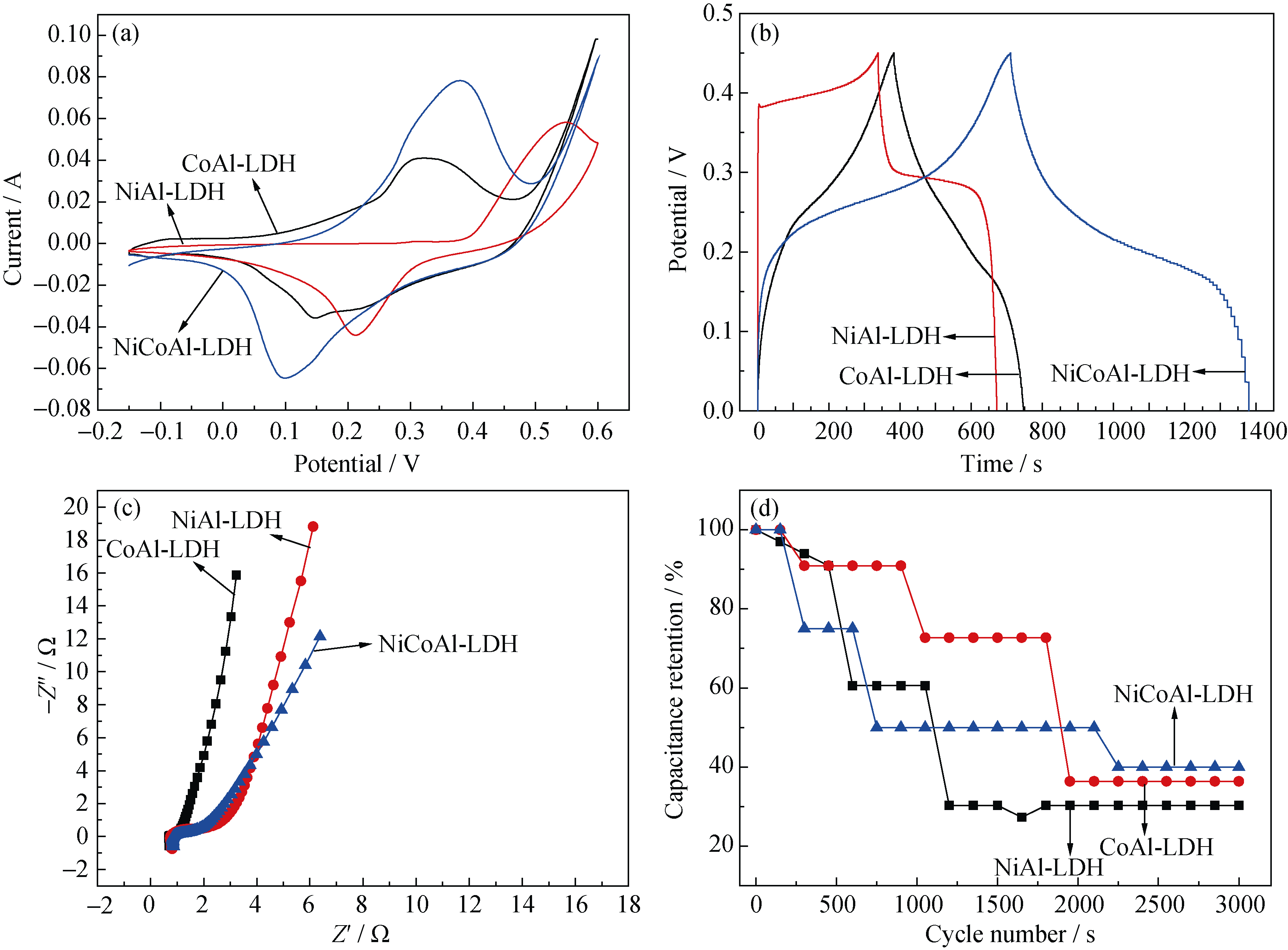
Fig. 5 Electro-chemical properties of the sample(a) CV curves of samples at a scan rate of 5 mV/s; (b) GCD curves of samples at a current density of 0.6 A/g; (c) AC impedance plots of samples at open circuit voltage; (d) Charge-discharge cycling test of samples electrode at the current density of 6 A/g
| NiAl-LDH | CoAl-LDH | NiCoAl-LDH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rs | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| Rp | 0.64 | 0.22 | 0.18 |
Table 1 Simulation data of equivalent circuit
| NiAl-LDH | CoAl-LDH | NiCoAl-LDH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rs | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| Rp | 0.64 | 0.22 | 0.18 |
| [1] | KÖTZ R, CARLEN M. Principles and applications of electrochemical capacitors. Electrochimica Acta, 2000, 45(15/16): 2483-2498. |
| [2] | LIU Y L, JIA X, ZHENG J, et al.Synthesis and electrochemical property of graphene/Co-Ni double hydroxides composites.Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2012, 28(9): 1878-1884. |
| [3] | YAN L, KONG H, LI Z J.Synthesis and supercapacitor property of three-dimensional graphene/Ni-Al layered double hydroxide composite.Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013, 71(5): 822-828. |
| [4] | LIU X M, ZHANG X G.CoAl layered double hydroxide as electrode material for supercapacitor.Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 27(3): 315-317. |
| [5] | LEI L X, ZHANG W F, HU M, et al.Layered double hydroxides: structures, properties and applications.Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2005, 21(4): 451-463. |
| [6] | ZHAO Y, LIANG J, LI F, et al.Kinetic study on the thermal decomposition of layered double hydroxides.Tsinghua Univ.(Sci. & Tech.), 2004, 44(2): 149-152. |
| [7] | XI L J, LIU Y, LV H B.Synthesis and application of layered double hydroxides for removal of anions in wastewater.Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2013, 32(8): 1567-1572. |
| [8] | ZHANG L J.Preparation and Supercapacitive Properties of Graphene/Layered Double Hydroxides Composites. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2012. |
| [9] | WU H P, KONG H, NIU Y L, et al.Synthesis of graphene/nickel- aluminium layered double-hydroxide composites using surfactant as a soft template and its supercapacitor performance.Journal of Jiangnan University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 12(6): 725-731. |
| [10] | MAO M.Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of Graphene and Nickel-iron Layered Double Hydroxide. Changsha: Central South University, 2014. |
| [11] | VIALAT P, LEROUX F, TAVIOT-GUEHO C, et al.Insights into the electrochemistry of (CoxNi(1-x))2Al-NO3 layered double hydroxides.Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 107(3): 599-610. |
| [12] | XUE J Y, REN W Z, WANG M M, et al.Synthesis of nanofiber-composed dandelion-like CoNiAl triple hydroxide as an electrode material for high- performance supercapacitor.Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2014, 16(12): 1-8. |
| [13] | ZHANG F, JIANG J, YUAN C, et al.Glycine-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of nanostructured CoxNi1-x-Al layered triple hydroxides as electrode materials for high-performance supercapacitors.Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2012, 16(5): 1933-1940. |
| [14] | LU Q, GUO Y, XIA S, et al.Electrochemical immunosensor with NiAl-layered double hydroxide/graphene nanocomposites and hollow gold nanospheres double-assisted signal amplification. Bioprocess & Biosystems Engineering, 2015, 38(8): 1-14. |
| [15] | YANG J, YU C, FAN X, et al.Facile fabrication of MWCNT- doped NiCoAl-layered double hydroxide nanosheets with enhanced electrochemical performances.Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(6): 1963-1968. |
| [16] | FU G R, HU Z A, XIE L J, et al.Electrodeposition of nickel hydroxide films on nickel foil and its electrochemical performances for supercapacitor.International Journal of Electrochemical science, 2009, 4(8): 1052-1062. |
| [17] | HE F, HU Z, LIU K, et al.Facile fabrication of GNS/NiCoAl-LDH composite as an advanced electrode material for high-performance supercapacitors.Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2015, 19(2): 607-617. |
| [18] | HUANG X L, ZHAO X, WANG Z L, et al.Facile and controllable one-pot synthesis of an ordered nanostructure of Co(OH)2 nanosheets and their modification by oxidation for high-performance lithium- ion batteries.J. mater. Chem, 2012, 22(9): 3764-3769. |
| [19] | GUPTA V, GUPTA S, MIURA N, et al.Statically deposited nanostructured CoxNi1-x layered double hydroxides as electrode materials for redox-supercapacitors.Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 175(1): 680-685. |
| [20] | TANG Y F, LIU Y Y, GUO W C, et al.Floss-like Ni-Co binary hydroxides assembled by whisker-like nanowires for high-performance supercapacitor.Ionics, 2015, 21(6): 1655-1663. |
| [21] | NIEDZIOLKA J, OPALLO M.Electrochemical redox reaction at silicate based electrode-silicate based electrolyte interface.Electrochemistry Communications, 2003, 5(11): 924-928. |
| [22] | SI W J, WU X Z, ZHOU J, et al.Reduced graphene oxide aerogel with high-rate supercapacitive performance in aqueous electrolytes.Nanoscale Research Letters, 2013, 8(1): 1-8. |
| [23] | STOLLER MD, PARK S, ZHU Y, et al.Graphene-based ultracapacitors.Nano Letter, 2008, 8(10): 3498-3502. |
| [1] | JIANG Zongyu, HUANG Honghua, QING Jiang, WANG Hongning, YAO Chao, CHEN Ruoyu. Aluminum Ion Doped MIL-101(Cr): Preparation and VOCs Adsorption Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 747-753. |
| [2] | SUN Jing, LI Xiang, MAO Xiaojian, ZHANG Jian, WANG Shiwei. Effect of Lauric Acid Modifier on the Hydrolysis Resistance of Aluminum Nitride Powders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 826-832. |
| [3] | XIONG Siyu, MO Chen, ZHU Xiaowei, ZHU Guobin, CHEN Deqin, LIU Laijun, SHI Xiaodong, LI Chunchun. Low-temperature Sintering of LiBxAl1-xSi2O6 Microwave Dielectric Ceramics with Ultra-low Permittivity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 536-544. |
| [4] | LIAN Minli, SU Jiaxin, HUANG Hongyang, JI Yuyin, DENG Haifan, ZHANG Tong, CHEN Chongqi, LI Dalin. Supported Ni Catalysts from Ni-Mg-Al Hydrotalcite-like Compounds:Preparation and Catalytic Performance for Ammonia Decomposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 53-60. |
| [5] | FENG Guanzheng, YANG Jian, ZHOU Du, CHEN Qiming, XU Wentao, ZHOU Youfu. Mechanism for Hydrothermal-carbothermal Synthesis of AlN Nanopowders [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 104-110. |
| [6] | CHENG Bo, AN Xiaohang, LI Dinghua, YANG Rongjie. Flame-retardant Properties and Transformation of Flame-retardant Mechanisms of EVA: Effect of ATH/ADP Ratio [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 509-516. |
| [7] | JING Xinxin, CHEN Biqing, ZHAI Jiaxin, YUAN Meiling. Ni-Co-B-RE (Sm, Dy, Tb) Composite Electrodes: Preparation by Chemical Deposition Method and Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 467-476. |
| [8] | YANG Bo, LÜ Gongxuan, MA Jiantai. Electrocatalytic Water Splitting over Nickel Iron Hydroxide-cobalt Phosphide Composite Electrode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 374-382. |
| [9] | ZHAO Yawen, QU Fajin, WANG Yanyi, WANG Zhiwen, CHEN Chusheng. Preparation and Properties of Aluminum Silicate Fiber Supported PtTFPP-PDMS Flexible Oxygen Sensing Components [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1084-1090. |
| [10] | SUN Qiangqiang, CHEN Zixuan, YANG Ziyue, WANG Yimeng, CAO Baoyue. Amorphous Vanadium Oxide Loaded by Metallic Nickel-copper towards High-efficiency Electrocatalyzing Hydrogen Production [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 647-655. |
| [11] | JIA Yuna, CAO Xu, JIAO Xiuling, CHEN Dairong. Preparation of Alumina Ceramic Continuous Fibers with Inorganic Acidic Aluminum Sol as Precursor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1257-1264. |
| [12] | ZHU Hezhen, WANG Xuanpeng, HAN Kang, YANG Chen, WAN Ruizhe, WU Liming, MAI Liqiang. Enhanced Lithium Storage Stability Mechanism of Ultra-high Nickel LiNi0.91Co0.06Al0.03O2@Ca3(PO4)2 Cathode Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 1030-1036. |
| [13] | SUN Ming, SHAO Puzhen, SUN Kai, HUANG Jianhua, ZHANG Qiang, XIU Ziyang, XIAO Haiying, WU Gaohui. First-principles Study on Interface of Reduced Graphene Oxide Reinforced Aluminum Matrix Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 651-659. |
| [14] | SHU Chaoqin, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Cobalt-incorporated Chlorapatite: Preparation by Molten Salt Method, Anti-oxidation and Cytocompatibility [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(11): 1225-1235. |
| [15] | LI Bangxin, ZHANG Qian, XIAO Jie, XIAO Wenyan, ZHOU Ying. Iron-doping Enhanced Basic Nickel Carbonate for Moisture Resistance and Catalytic Performance of Ozone Decomposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 45-50. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||