
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 208-216.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250177
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Xiaomin1,2( ), TONG Liangyu1, GAO Hongjie2, CHEN Xu1, YAN Huhu1, GAO Yang1
), TONG Liangyu1, GAO Hongjie2, CHEN Xu1, YAN Huhu1, GAO Yang1
Received:2025-04-26
Revised:2025-06-09
Published:2026-02-20
Online:2025-06-10
About author:ZHANG Xiaomin (1975-), male, professor. E-mail: xmzhang@xauat.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHANG Xiaomin, TONG Liangyu, GAO Hongjie, CHEN Xu, YAN Huhu, GAO Yang. 3D Network-structured Fly Ash Microbeads@Carbon Nanotubes Composites for Electromagnetic Wave Absorption[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 208-216.
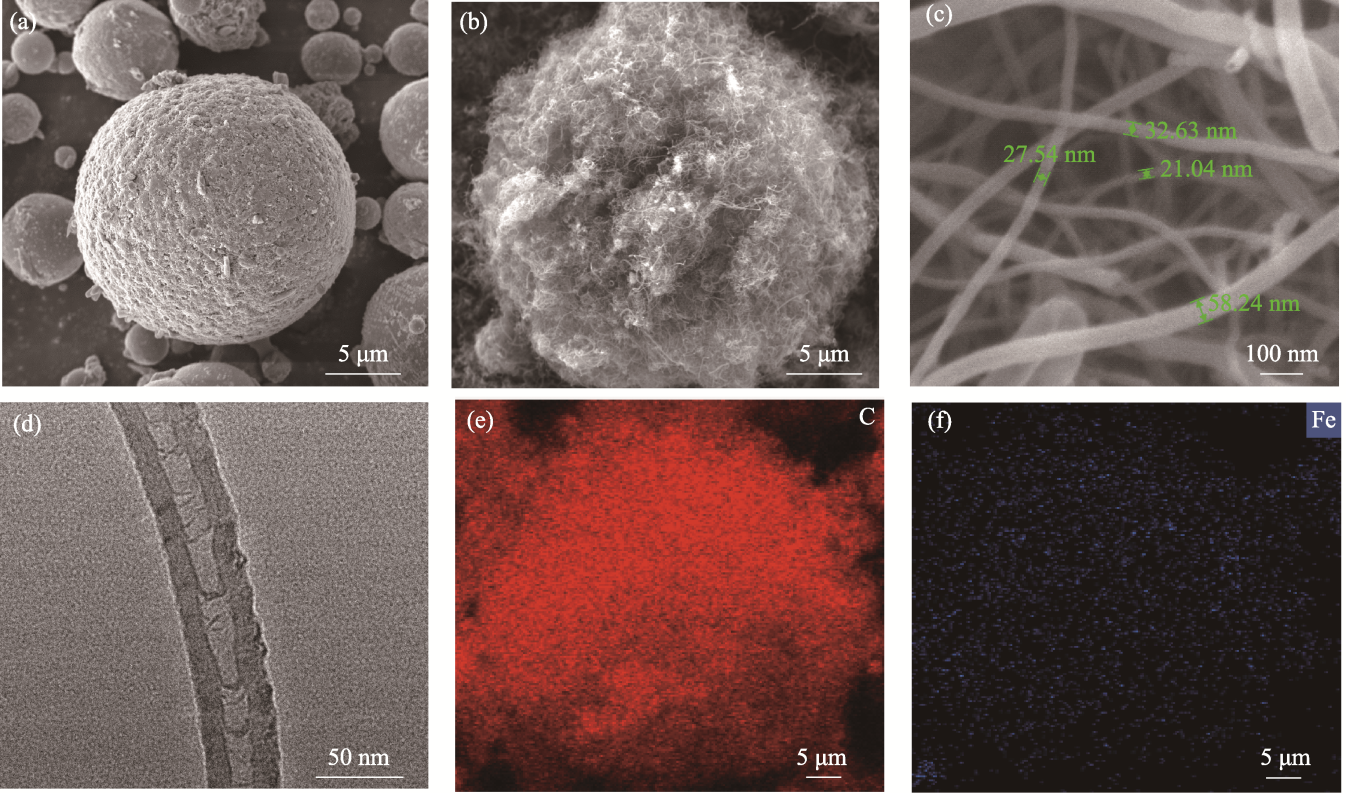
Fig. 2 Microscopic morphologic structures of MFA and MFA@CNTs microspheres (a-c) SEM images of (a) MFA, (b) MFA@CNTs and (c) CNTs on the surface of MFA@CNTs; (d) TEM image of CNTs; (e, f) EDS elemental mappings of (e) C and (f) Fe in MFA@CNTs as shown in Fig. (b)
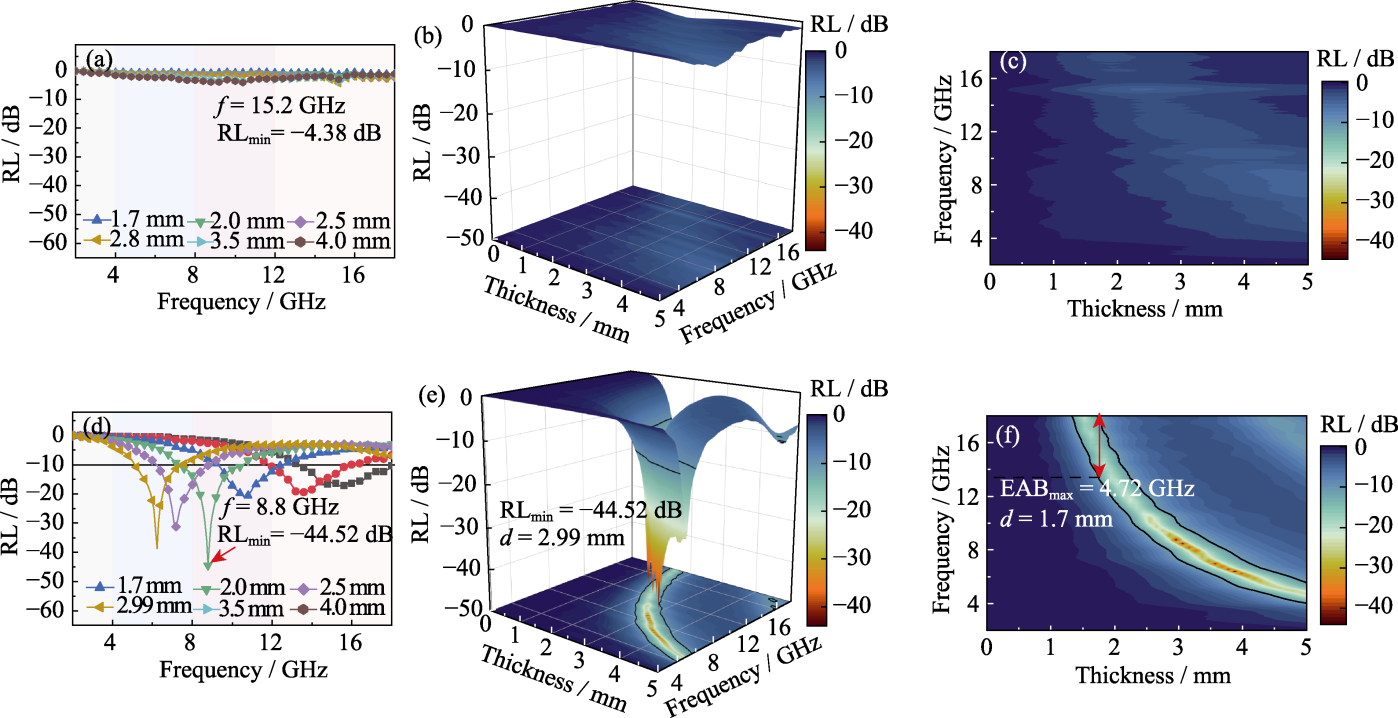
Fig. 5 Reflective loss diagrams of MFA and MFA@CNTs microspheres (a) RL, (b) 3D mapping RL and (c) 2D mapping RL of MFA; (d) RL, (e) 3D mapping RL and (f) 2D mapping RL of MFA@CNTs. Colorful figures are available on website
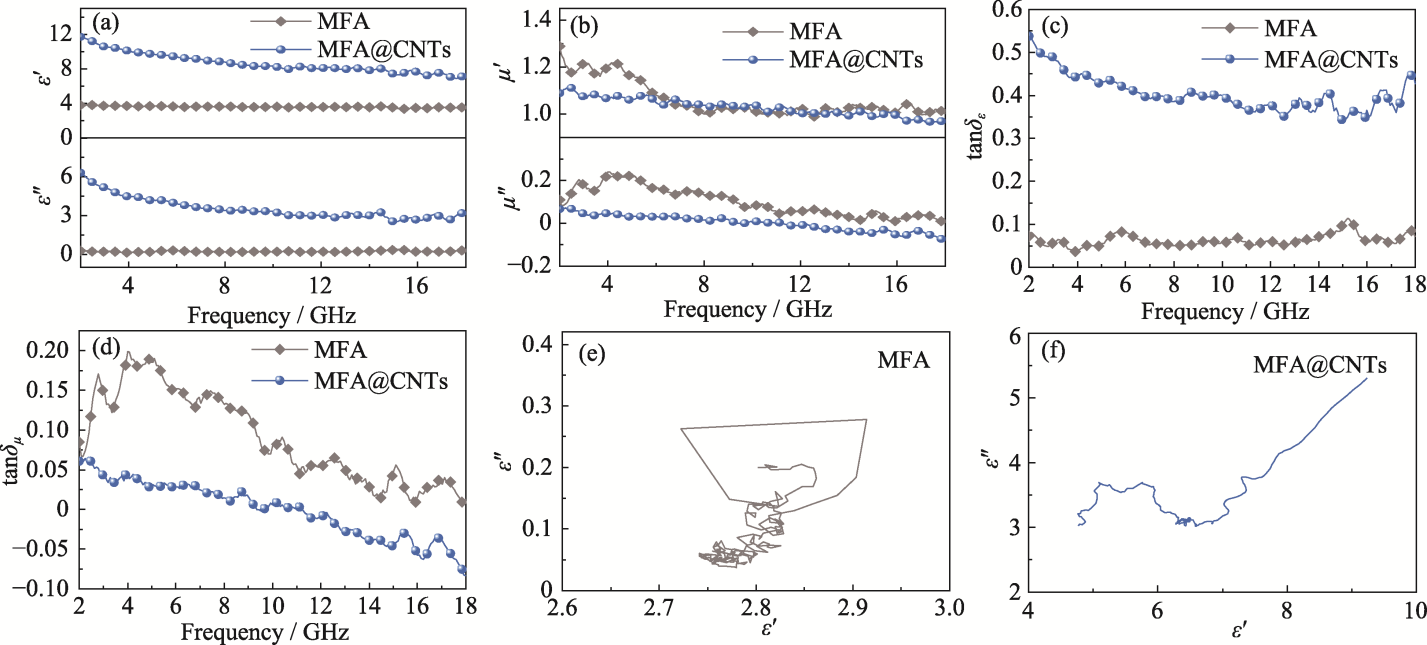
Fig. 6 Electromagnetic parameters of MFA and MFA@CNTs microspheres (a) Real part (ε′) and imaginary part (ε″) of relative permittivity; (b) Real part (μ′) and imaginary part (μ″) of relative permeability; (c) Dielectric loss tangent (tanδε); (d) Magnetic loss tangent (tanδµ); (e, f) Cole-Cole curves of (e) MFA and (f) MFA@CNTs
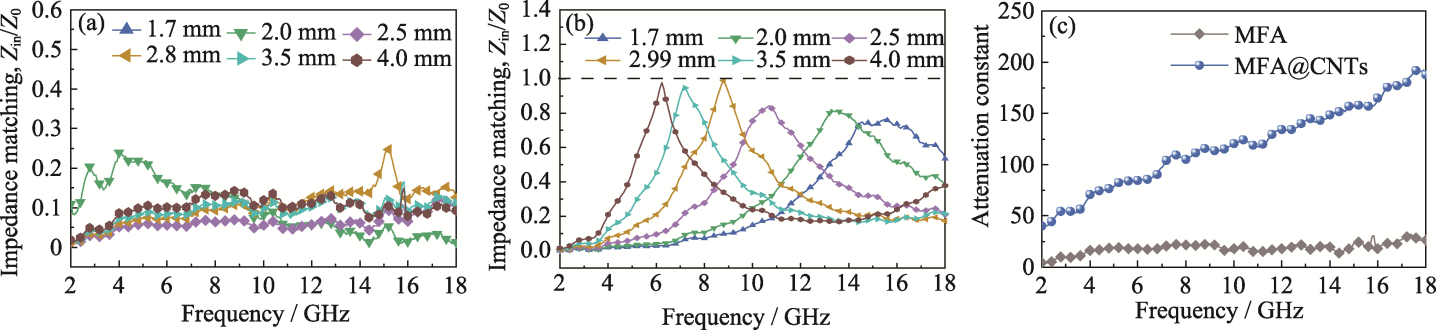
Fig. 7 Impedance matching and attenuation coefficients of MFA and MFA@CNTs microspheres (a, b) Impedance matching of (a) MFA and (b) MFA@CNTs; (c) Attenuation coefficients
| Microwave absorption material* | RL/dB | EAB/GHz | dEAB**/mm | f/ GHz | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNTs/PyCHMs | -56.0 | 4 | 3.0 | 12.2 | [ |
| Fe/C | -21.0 | 6.3 | 2.5 | 12.8 | [ |
| TiC/Fe@NCNHs | -41.62 | 4.85 | 1.4 | 17.66 | [ |
| ZnFe2O4@PHCMS | -51.43 | 3.52 | 4.8 | 7.2 | [ |
| Ni@CNT | -44.4 | 4.3 | 1.5 | 13.5 | [ |
| CoFe2O4@CNTs | -34.6 | 7.1 | 2.5 | 13.4 | [ |
| FeCo/Cu/CNTs | -48.1 | 5.76 | 1.8 | 15.2 | [ |
| MFA@CNTs | -44.52 | 4.72 | 1.7 | 8.8 | This work |
Table 1 Comparison of microwave absorption performance[15,17,22,25,35 -37]
| Microwave absorption material* | RL/dB | EAB/GHz | dEAB**/mm | f/ GHz | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNTs/PyCHMs | -56.0 | 4 | 3.0 | 12.2 | [ |
| Fe/C | -21.0 | 6.3 | 2.5 | 12.8 | [ |
| TiC/Fe@NCNHs | -41.62 | 4.85 | 1.4 | 17.66 | [ |
| ZnFe2O4@PHCMS | -51.43 | 3.52 | 4.8 | 7.2 | [ |
| Ni@CNT | -44.4 | 4.3 | 1.5 | 13.5 | [ |
| CoFe2O4@CNTs | -34.6 | 7.1 | 2.5 | 13.4 | [ |
| FeCo/Cu/CNTs | -48.1 | 5.76 | 1.8 | 15.2 | [ |
| MFA@CNTs | -44.52 | 4.72 | 1.7 | 8.8 | This work |
| [1] |
GAO C Q, GOU D M, HUANG G, et al. Spiderweb-structured aerogels with high-efficiency microwave absorption and multifunctionality. Nano Energy, 2025, 138(1): 110863.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DU L F, ZHANG J S, ZHOU Q, et al. Hierarchical CNTs/PyC/SiBCN foam with tunable microwave absorption properties conspired by melamine-derived pyrolyzed carbon and carbon nanotubes. Carbon, 2025, 234(5): 120030.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
SONG L M, FAN B B, CHEN Y Q, et al. Ultralight and hyperelastic SiC nanofiber aerogel spring for personal thermal energy regulation. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11: 1235.
DOI |
| [4] |
SONG L M, FAN B B, CHEN Y Q, et al. Multifunctional SiC aerogel reinforced with nanofibers and nanowires for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 467(1): 143518.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
YIN L J, YAN J Z, QIU R Q, et al. Preparation and performance of ultra-wideband high-temperature resistant calcium aluminate cement-based electromagnetic wave absorption cone structural composites. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(21): 40911.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZHAO Z B, KANG B, XU J, et al. N-doped carbon hollow spheres supported N-doped carbon nanotubes for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon, 2023, 209: 117995.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZHANG F, JIA Z R, ZHOU J X, et al. Metal-organic framework- derived carbon nanotubes for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 138205.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LIU C, HAN M R, LIN J P, et al. Wood biomass-derived carbon for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing and shielding. Carbon, 2023, 208: 255.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
YANG W, LI L, HOU Y Z, et al. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of SiOC/porous carbon composites. Materials, 2022, 15(24): 8864.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WAN Z L, SHU R W, ZHANG J B, et al. Synthesis of three-dimensional porous nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide/ multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite aerogel as lightweight and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. Diamond and Related Materials, 2021, 112: 108245.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WANG Z, YANG K X, WANG H, et al. CNTs decorated Fe3O4/Co-Ni polyhedrons with heterogeneous interface for promoting microwave absorption. Composites Communications, 2024, 49: 101976.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MENG R, ZHANG T L, LIU X, et al. Graphene oxide-assisted Co-sintering synthesis of carbon nanotubes with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Carbon, 2021, 185(15): 186.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MA Y Z, CHENG Y, DENG Z E, et al. The tune of shell numbers of multi-shell hollow mesoporous carbon microspheres for enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon, 2024, 227(30): 119267.
DOI URL |
| [14] | QIAO J, ZHANG X, LIU C, et al. Non-magnetic bimetallic MOF-derived porous carbon-wrapped TiO2/ZrTiO4 composites for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Letter, 2021, 13: 75. |
| [15] |
KONG L, LUO S, ZHANG G Q, et al. Interfacial polarization dominant CNTs/PyC hollow microspheres as a lightweight electromagnetic wave absorbing material. Carbon, 2022, 193(30): 216.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MAO F Z, FAN X K, LONG L, et al. Constructing 3D hierarchical CNTs/VO2 composite microspheres with superior electromagnetic absorption performance. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(11): 16924.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
CHEN Y, QIANG R, SHAO Y L, et al. Biomass-derived Fe/C composites for broadband electromagnetic wave response. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 968(15): 171952.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG B J, WU H, HOU W X, et al. Optimizing dielectric polarization for electromagnetic wave attenuation via an enhanced Maxwell-Wagner-Sillars effect in hollow carbon microspheres. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11: 23498.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZHANG R N, LI B, YANG Y F, et al. Ultralight aerogel sphere composed of nanocellulose-derived carbon nanofiber and graphene for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano Research, 2023, 16: 7931.
DOI |
| [20] |
FENG K Y, JIANG J, REN L G, et al. Magnetic porous carbon composites for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2023, 25(8): 2201353.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
JIA Z R, ZHANG X Y, GU Z, et al. MOF-derived Ni-Co bimetal/porous carbon composites as electromagnetic wave absorber. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2023, 6: 28.
DOI |
| [22] | 许莉, 朱启程, 张育斌, 等. TiC/Fe@氮掺杂碳纳米角复合材料的电磁吸波性能. 复合材料学报, 2025, 42(1): 336. |
| [23] |
ZHANG H X, JIA Z R, WANG B B, et al. Construction of remarkable electromagnetic wave absorber from heterogeneous structure of Co-CoFe2O4@mesoporous hollow carbon spheres. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 421: 129960.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
MA T T, DAI Z, SHEN X R, et al. Three-dimensional porous MnCo2S4 microrugby balls supported on carbon cloth for efficient oxygen evolution reaction. ChemElectroChem, 2022, 9(13): e202200552.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
CHAI L, WANG Y Q, ZHOU N F, et al. In-situ growth of core-shell ZnFe2O4@porous hollow carbon microspheres as an efficient microwave absorber. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 581: 475.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
MENG X W, QIAO J, YANG Y F, et al. Three-dimensional porous manganese oxide/nickel/carbon microspheres as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers with superb photothermal property. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 629: 884.
DOI URL |
| [27] | WANG B, WU Q, FU Y, et al. A review on carbon/magnetic metal composites for microwave absorption. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 86: 91. |
| [28] |
LU J B, FENG Y R, LIU J, et al. Improved electromagnetic wave absorbing performance of PDCs-SiCN(Ni) fibers with different nickel content. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(16): 23578.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 朱培, 张晓民, 俞洁, 等. 粉煤灰磁珠Fe含量和研磨粒径对Fe3C@C-CNTs复合材料结构和吸波性能的影响. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(1): 342. |
| [30] |
YIN L J, LV H L, ZENG M Y, et al. Extending the modified steel slag cement into the hydrophobic and anti-icing application. Materials Today Communications, 2023, 38(299): 107843.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
WU Z Y, LI L Y, ZHU R, et al. Boosting the electromagnetic wave absorption performance of glass fiber by in-situ modification with carbon nanotubes using a coordination solution method. Composites Communications, 2025, 56: 102365.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
WEN B, YANG G R, ZHOU X Y, et al. Intelligent diffusion regulation induced in-situ growth of cobalt nanoclusters on carbon nanotubes for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 634: 74.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LV H L, YANG Z H, LIU B, et al. A flexible electromagnetic wave-electricity harvester. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 834.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
DONG Y Y, ZHU X J, PAN F, et al. Implanting NiCo2O4 equalizer with designable nanostructures in agaric aerogel-derived composites for efficient multiband electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon, 2022, 190: 68.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
WENG J, LIU Y A, HUANG X X. Synthesis of in situ grown CNTs on MOF-derived Ni@CNT with tailorable microstructures toward regulation of electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Carbon, 2025, 231: 119678.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
LIU G J, WANG L, ZHANG H, et al. Cage-structured CoFe2O4@CNTs from Fe-Co-MOF confined growth in CNTs for high electromagnetic wave absorption performances. Composites Communications, 2021, 27: 100910.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
LIU X W, YU L H, ZHU G Z, et al. Hollow porous FeCo/Cu/ CNTs composite microspheres with excellent microwave absorption performance. Nano Research, 2024, 17: 9857.
DOI |
| [38] |
SONG L M, WANG L A, CHEN Y Q, et al. Engineered core-shell SiC@SiO2 nanofibers for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Small, 2024, 20(52): 2407563.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
SONG L M, ZHANG F, CHEN Y Q, et al. Multifunctional SiC@SiO2 nanofiber aerogel with ultrabroadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14: 152.
DOI |
| [40] |
SONG L M, FAN B B, CHEN Y Q, et al. Multifunctional SiC nanofiber aerogel with superior electromagnetic wave absorption. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(17): 25140.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
SONG L M, CHEN YQ, GAO Q C, et al. Low weight, low thermal conductivity, and highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption of three-dimensional graphene/SiC-nanosheets aerogel. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2022, 158: 106980.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
NING Y, ZENG X J, HUANG J, et al. Multifunctional electromagnetic responsive porous materials synthesized by freeze casting: principles, progress, and prospects. Advanced Functional Materials, 2025, 35(6): 2414838.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
ZENG X J, JIANG X, NING Y, et al. Constructing built-in electric fields with semiconductor junctions and Schottky junctions based on Mo-MXene/Mo-metal sulfides for electromagnetic response. Nano-Micro Letters, 2024, 16: 213.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | XIANG Chang-Shu,YANG Jiong,ZHU Yong,PAN Yu-Bai,GUO Jing-Kun. Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties of Carbon Nanotube-Fused Silica Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(1): 101-105. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||